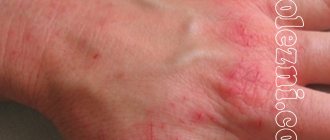
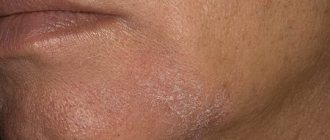
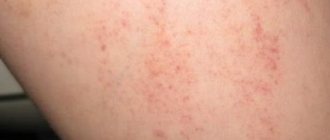
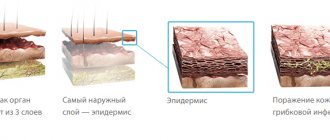
Medical practice shows that today the number of people experiencing allergic skin lesions is increasing. Various types of eczema account for 40% of cases.
The most common types of eczema:
- True. The acute stage is accompanied by the appearance of bubbles with liquid, pinpoint erosions and redness. The patient experiences itching, the intensity of which varies in each case. With a chronic course, the swelling intensifies, and the affected skin becomes covered with cracks.
- Microbial. This type of eczema appears after infection of the skin around cracks, fistulas and ulcers. The rash, covered with crusts and scales, is pink in color. After removing the scales, bloody dew appears. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease will turn into eczema.
- Professional. In its manifestations it resembles the real one, but appears after prolonged contact of hands with the allergen. In the early stages, development can be easily stopped, and the skin morphology will be completely restored. The first exacerbations resemble contact dermatitis. If the impact of the irritating factor does not stop, the inflammatory process becomes persistent and recurrent.
- Seborrheic. This type of dermatitis affects the scalp. The rash appears on the forehead, on the skin of the back, chest and limbs. The affected area of skin becomes covered with scales and becomes moist due to the secreted fluid.
- Children's room. This type of eczema appears in children in infancy and goes away by the age of 3. Rashes appear on the face. As the disease progresses, there is damage to the body, accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes.
The first signs of eczema
Eczema on the hands in the initial stage develops rapidly. Each subsequent stage is characterized by the development of complications and severe skin lesions.
First signs:
- redness of the skin on the hands, between the fingers and on the back of the hands;
- itching in inflamed areas, increasing every day;
- vesicles filled with serous contents appear in the affected areas;
- a burning sensation occurs, the itching intensifies, the affected areas become hot to the touch;
- the area of erosion increases, a dense crust appears, and wet areas appear;
- the risk of infection through inflamed skin increases.
Stages
At the initial stage of the disease, as can be clearly seen in the attached photo, red spots and slight swelling appear on the affected skin of the chest, elbows, ankles, face and neck. They are accompanied by itching and do not have clear outlines: the photo of the initial stage below clearly demonstrates this.
At the same time, polymorphic rashes begin to appear, and the primary stage enters the active phase.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eczema on the hands in the initial stage (see photo) will vary depending on what type of disease affects the person.
Symptoms of idiopathic eczema on the hands:
- The rash may appear as erythema, papules, or blisters. They are localized on open areas of the body, including the legs and arms, and are most often symmetrical.
- The beginning of an exacerbation of the disease is characterized by the appearance of bubbles, which subsequently merge and, after destruction, form erosions.
- The entire process of inflammation is accompanied by severe skin itching, which may precede the onset of the disease.
- When the process becomes chronic, lichenification of the skin occurs.
Symptoms of occupational eczema on the hands:
- Inflammation appears only in those areas of the skin that come into contact with the irritant. It is the hands and fingers that are most susceptible to the appearance of occupational eczema.
- As the disease progresses, eczema spreads to other areas of the body.
- The inflammation process occurs like idiopathic eczema.
Symptoms of atopic eczema on the hands:
- The skin swells and turns red, covered with small blisters.
- The bubbles resolve, leaving behind areas of weeping.
- As the disease progresses, the skin becomes covered with crusts and scales, becomes dry, and begins to peel.
- Itching can plague the patient both during remission and during exacerbation of eczema. However, when the process enters the acute phase, the itching becomes extremely pronounced.
Symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema:
- A rash appears that looks like small blisters filled with liquid.
- The rash initially appears on the sides of the fingers and then spreads to the palms.
- The skin becomes swollen and red.
- After the vesicles open, erosions appear on the inflamed areas and become profusely wet. At the same time, the skin begins to peel off.
- The disease is accompanied by severe itching.
- Often a secondary infection occurs, which provokes the appearance of pain, cracks, and lichenification.
Symptoms of microbial eczema:
- Microbial eczema is located around existing wounds, burns, fistulas with purulent inflammation.
- Eczema initially affects only that part of the skin where there is a pustular disease. The stratum corneum peels off, peeling begins, or exudate separates.
- Subsequently, the exudate dries and forms crusts.
- Eczema is not treated, then it begins to affect symmetrically located skin areas.
- As a rule, itching does not bother the patient much.
How to avoid worsening dermatitis in winter
In winter, exacerbation of dermatitis is common. Even healthy skin can have a hard time coping with temperature changes and dry indoor air. The following will help you get rid of the symptoms of the disease even in the frosty months:
- cold compresses,
- warm baths with oatmeal or baking soda,
- creams or ointments for the body with a high concentration of oils in the composition (apply the cream immediately after a bath or shower).
In winter, it is especially important to try not to irritate the skin, do not rub it with a towel, avoid scratches, and do not use cosmetics with fragrances (Fig. 4). When cleaning, be sure to wear gloves and goggles when using aerosol cleaners. In clothing, preference should be given to soft, natural fabrics, such as cotton. Thus, during the cold season, the daily routine should be even more gentle than usual.
Figure 4. How to care for skin with eczema in winter. Illustration: MedPortal
Diagnostics
Before treating eczema on your hands, you need to visit a dermatologist who can determine the cause of the disease.
Basically, doctors make a diagnosis based on an external examination of the skin and a conversation with the patient, but in rare cases additional examination is required - a general blood test, a smear to determine the infectious agent. If a specialist suspects the presence of another disease with a similar course (scabies, psoriasis), he may prescribe a skin biopsy.
It should be said that treatment with traditional medicine or the use of antihistamine creams should not be started without first consulting a doctor, as they can cause complications. The only thing a patient with suspected eczematous rash can do is go on a diet, removing “harmful” foods from their diet.
What kind of disease is this?
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that has a chronic course, accompanied by itching, pain, and frequent relapses.
It is non-infectious in nature; its occurrence and course are influenced by a combination of various factors.
The so-called microbial eczema deserves special mention. This is an infectious disease that affects damaged skin. Microbial and mycotic eczema are caused by the saprophytic flora of humans, therefore, despite their infectious nature, cases of infection from patients are quite rare.
The most common form is true eczema. This pathology has quite characteristic symptoms (eczematous wells, crusts, severe itching).
Types of rashes on the arms, legs, face (photo)
There are other types: professional, children's, seborrheic . Their features are mainly related to the conditions of their occurrence. Occupational eczema is a disease associated with exposure to occupational hazards, seborrheic eczema affects areas of oily skin, etc.
What does eczema on the hands look like: photo
Since at home it is quite problematic to determine the type of eczema of the hands by the characteristic features of its course, if the listed symptoms are detected, the patient is recommended to seek the advice of a qualified dermatologist.
Causes
Several factors play a role in the occurrence of eczema. In particular:
- Hereditary predisposition. However, a burdened hereditary history does not necessarily mean the development of the disease.
- External conditions - deficiency of B vitamins, gastrointestinal diseases, immune pathologies, allergic diseases.
Typically, the disease occurs due to a combination of several causes. For example, when treating various forms of eczema in adults, it often turns out that there is a history of untreated childhood eczema, allergic diseases, and other pathologies of the immune system.
Endocrine diseases also have an impact - diabetes, hyperthyroidism, disorders of the production of sex hormones.
General drug therapy
Pathogenetic therapy is the main type of treatment, without which it is impossible to cure eczema on the hands. This type of therapy is aimed at leveling or weakening the negative influence of the external environment or altered functions of internal organs.
When eczema on the fingers is diagnosed, treatment often includes nonspecific desensitizing therapy: autohemotherapy, blood transfusions, hirudotherapy, lactotherapy.
In case of severe eczema, hemosorption, enterosorption and plasmapheresis are performed.
Biostimulants are prescribed: course injections of aloe or placenta extract, 1.0–1.5 ml.
For severe neurotic disorders, the following is prescribed:
- the doctor may prescribe sodium bromide orally 5-15 ml 3 times a day
- Bromocamphor also three times a day for 2 weeks
- only as prescribed by a doctor, tranquilizers in small doses - Nozepam, Phenozepam, Chlozepid for no more than 10 days
- sedative herbal remedies - Novopassit, Persen, Valerian, Peony tincture, Sedasen
Enterosorbents and drugs to reduce intoxication:
- Among the energy sorbents we can highlight Polyphepan, Multisorb, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Atoxil, Filtrum STI (instructions) also for a short course of no more than 10 days
- Intravenous injections of sodium thiosulfate 10-20 infusions of 10 ml. or calcium chloride
- For mycotic eczema, hexamethylenetetramine solution
- Calcium gluconate intramuscularly 10-20 injections
Hormone therapy
Persistent eczema of the fingers and between the fingers is treated with hormonal drugs, which are used only as prescribed by a doctor, for a short course, with gradual withdrawal of the drug and only in cases of extreme necessity. Taking corticosteroids has serious side effects and a number of contraindications; it can contribute to the development of infectious processes and exacerbation of chronic diseases, since it reduces immunity (see hormonal ointments for psoriasis).
Their prolonged or frequent uncontrolled use is especially dangerous. If eczema is localized only on the hands and fingers, you can limit yourself to using only local hormonal agents, but in the case of generalization of the inflammatory process, oral hormonal therapy can also be prescribed; it lasts no more than 10–15 days in moderate, controlled doses:
- corticotropin 40 units daily (800–1000 units per course)
- prednisolone 20-40 mg daily
- triamcinolone 10 mg daily
- dexamethasone 2.5 tablets daily
Vitamin therapy
Vitamin therapy is indicated for the treatment of any type of eczema on the hands. However, taking into account the latest research by scientists, preparations containing synthetic vitamins should be treated very carefully (see the dangers of synthetic vitamins):
- Vitamin E (oil solution)
- Ascorbic and nicotinic acid
- B vitamins in injections
- Folic acid
Antihistamines are indicated for any type of eczema on the hands:
- In acute cases, parenteral administration of diphenhydramine, chloropyramine, promethazine is indicated.
- For moderate severity, 1 tablet orally for 2 weeks 3 times a day
- Then you can use 2nd and 3rd generation drugs, such as ebastine (Kestin 300 rub. 10 pcs.), cetirizine (Cetrin 150 rub. Zirtec, Zodak, Parlazin), Loratadine (Clarisens, Claritin, Lomilan, Loragexal, Loratin), fexofenadine (Telfast , Fexadine) desloratadine (Erius, Lordestin, Dezal) see full list of allergy medications.
- It is also possible to use Ketotifen - stabilizers of mast cell membranes
Immunomodulators
After an acute process, when inflammatory manifestations subside, persons with immunodeficiency conditions only under the supervision of an immunologist and an immunogram are shown the following immunomodulators, the use of which should also be treated with caution (see drugs to enhance immunity):
- Stimulators of phagocytosis, these include Polyoxidonium, Lykopid, Prodigiosan
- Timomimetics are Thymogen, Timalin, Immunofan
- According to indications, it is possible to use - Vitreous body, humisol solution, Plazmol, placenta extract; they can be used to treat eczema on the hands and body only in case of a chronic process.
For dysbacteriosis, indigestion
When eczema is combined with pancreatitis, other gastrointestinal diseases, gastroduodenitis, bile salts, enzyme preparations, pepsin are prescribed - these are Pancreatin, Ermital, Creon, Festal, Solizim, Enzistal, Panzinorm forte, Micrazim, Pangrol, Gastenorm, Pepfiz, Biozym. If eczema on the hands is accompanied by a violation of the intestinal microflora (see treatment of intestinal dysbiosis), courses of probiotics are used, such as Hilak Forte, Lactobacterin, Bifiform, Rio flora immuno (see list of dietary supplements and probiotics, Linex analogues).
For microbial eczema
In the presence of a purulent process in microbial eczema, antibacterial agents are used. To maximize the effectiveness of the treatment, it is better to pre-seed the flora and determine the resistance and sensitivity of the eczema pathogen to specific antibiotics. Macrolides, 2nd generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides are usually used.
When a fungal infection occurs, antifungal drugs in tablets or local treatment with antifungals - ointments, creams - are indicated.
Sources
- National Center for Health Statistics, National Health Interview Survey, 2014.
- National Eczema Association website. Eczema causes and triggers.
- Thomas N. Helm and all. What is the role of neomycin in the etiology of allergic contact dermatitis? Medscape. -2020
- Susana Vilaça and all. Simultaneous contact allergy to neomycin, bacitracin, polymyxin, and dexamethasone: An often unrecognized cause of allergic contact dermatitis in patients using topical antibiotics. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. -2012, -V. 6, -I. 4, -S. 1, -P. AB74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.316
- A. C. de Groot, A. Herxheimer. Isothiazolinone preservative: cause of a continuing epidemic of cosmetic dermatitis. Lancet. -1989. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91318-4
- Atopic Dermatitis 101 for Adults. National eczema association. -2017
- JI Silverberg and all. Symptoms and diagnosis of anxiety and depression in atopic dermatitis in US adults. British Journal of Dermatology. -2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.17683
- A. Wollenberg and all. Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: part IJ Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. -2018. DOI: 10.1111/jdv.14891
- John Elflein. Global use of prescription topical treatments and phototherapy for eczema 2021. -2020
- C. Fookes. Topical Steroids. Drugs.com. -2018
- A. Roeder and all. Safety and efficacy of fluticasone propionate in the topical treatment of skin diseases. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. -2005. DOI: 10.1159/000081680
- NHS. Topical corticosteroids
- Give Topical Steroids the Fingertip. National eczema association
- Instructions for the medical use of the drugs FeniVate cream RU P N012556/01 dated 07/15/2009 and FeniVate ointment RU P N012556/02 dated 07/16/2009.
- New, sales start in June 2021
- Katsambas A.D., Lotti T.M. European treatment guidelines in dermatology. 2014, MEDpress-inform LLC, 3rd ed., trans. from English, 736 p.
- Ellie Choi and all. Efficacy of targeted education in reducing topical steroid phobia: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. -2020. -V. 83, -I. 6. -P. 1681-1687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.079
- NIAID. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) Treatment
Local drug therapy
If a patient is diagnosed with microbial eczema, then he needs to lubricate the crust on his hands with the following creams and ointments:
- Brilliant green, Methyl violet solution, Gentian violet solution.
- Creams and aerosols: Panthenol, Polcortolon, Levovinisol.
- If the disease is chronic, lotions with a solution of Resorcinol or Ethacridine Lactate are recommended.
Lotion can have an anti-inflammatory effect and reduce itching with the application of the following compositions:
- Goulard;
- Burov's fluid;
- Resorcinol in solution up to 1%;
- Copper sulfate, zinc sulfate in solution 0.1%;
- Silver nitrate in solution 0.15%;
- Phenol in solution up to 5%;
- Citric acid in solution 1%;
- Metol solution up to 1.0%;
- Podophylline ointment;
- Diphenhydramine paste.
Effective means for relieving acute inflammation are powders with white clay, zinc oxide, and wheat starch. When the disease subsides somewhat, you can use zinc oil, as well as neutral ointments that do not contain active ingredients.
A solution of boric acid, a solution of tannin, and a solution of galascorbine helps eliminate swelling of the skin, reduce weeping, and remove redness.
To speed up the healing process at the stage of extinction of inflammation, you can use Lassara paste, zinc ointment with the addition of Naftalan paste, Ichthyol paste, Boron-zinc and Boron-naphthalan paste, Dermatol and Methyluracil paste.
As for corticosteroid ointments, to get rid of eczema on the hands, doctors often prescribe Elokom, Advantan, Skin-cap, Flucinar, Celestoderm. If the patient has microbial eczema, then it is best to use Trimistin, Lorinden S, Celestoderm with Garamycin, Travocort, Kremgen.
Indications and contraindications
Ointments and creams of any kind are recommended for eczema with the following symptoms:
- Dry tissue, which causes peeling, sores and redness.
- Itching.
- Rash in the form of blisters with liquid contents.
- Weeping wounds that do not heal.
Eczema most often appears on the face, arms and legs. Different medications are used for each area, but only after consulting a doctor. Main contraindications of local drugs:
- Hormonal ointments are not used in the presence of secondary fungal infection. Ointments are not applied to open wounds, acne or rosacea.
- Hormonal creams are not recommended for children under 2 years of age or pregnant women.
- The combination of an antibiotic and a hormone in one composition is prohibited for use on children.
- Medicines containing zinc are not applied to purulent inflammations.
- Ointment with sulfur should not be used by children under 3 years of age.
- Naftalan is prohibited for kidney disease, liver disease, anemia and cancer.
Any ointment can cause side effects, which are often expressed as allergies. In this case, the symptoms of eczema worsen and the general condition worsens. More often, the consequences develop when applying hormonal ointment or cream:
- Severe allergies.
- Development of the vascular network.
- Skin atrophy.
- Increase in pressure.
- Hormonal imbalance causing growth retardation.
The occurrence of negative consequences from treatment should be discussed with a dermatologist. Medicines need to be changed or their dosage reduced.
Useful: Vodka with pepper for colds - recipe
Diet and nutrition for eczema
Any food allergen can trigger the development of eczema in some cases, and what is extremely undesirable for one person is completely tolerated by others. For this reason, the diet should be selected strictly individually, excluding those foods that provoke an exacerbation of eczema in a particular patient.
The usual frequency of meals for eczema is from 4 to 6 times in small portions.
In order to identify foods that cause aggravation, it is necessary to keep a food diary for some time, where you write down not only everything that is eaten and drunk during the day, but also the body’s reaction over the next 2 days. After analyzing the relevant records, “calculating” the guilty product of work is not difficult. Such products should be excluded from the diet completely and not used even in combination with others, for example, when preparing salads or as one of the components of baked goods. The duration of such a strict diet is about 1 year, after which the body usually “forgets” the allergen and does not react with inflammation to its presence in food.
The most common allergens in animal products are:
- bird,
- seafood,
- caviar,
- fish,
- eggs,
- milk (including goat milk).
Plant products containing allergens:
- Cereals: corn, barley, rye, wheat.
- Nuts.
- Legumes: peas, soybeans, beans, lentils.
- Vegetables, fruits of red, yellow or orange color: citrus fruits, melon, persimmon, apricot, peach, watermelon, carrots, beets, strawberries, strawberries, raspberries, currants, pomegranates, grapes, tomatoes.
- Chocolate: candies, cocoa.
- Other products: kiwi, garlic, avocado, radish, horseradish, mushrooms, eggplant, radish, chestnut, spices, ketchup, mayonnaise, smoked meats, caramel, pickles, pastry, honey, coffee, mustard, vinegar, cheeses, kvass, etc. P.
When creating a hypoallergenic diet, it is necessary to remember that there is a so-called cross-allergy, when eating one product causes an allergic reaction when eating others:
- milk - beef - digestive enzymes,
- pollen - fruits - berries.
- Mold (for example, in cheese) - kefir - various cheeses - products made from yeast baked goods - last year's fruits.
In this case, if an allergy is detected, say, to pollen, then it is necessary to exclude or sharply limit berries and fruits.
In the event of eczema, you must fully comply with all recommendations, since one episode of eczema can be associated with one allergen, then a subsequent exacerbation of the disease can be triggered by completely different allergens.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
They contribute to the resolution of inflammatory elements and are an important component of treatment. Applicable:
- 2-4 chamber baths
- dry radon baths, mineral water baths
- aerotherapy, electrosleep
- diphenhydramine inhalations
- general galvanization
- diadynamic therapy
- segmental ultrasound exposure
- ultraviolet irradiation
- ultraphonophoresis of external medicinal products
- mud therapy, ozokerite therapy
- laser therapy, ozone therapy
- low frequency magnetic field
- acupuncture
- paraffin applications
Spa treatment
For patients with eczema, a dry maritime climate (for example, the southern coast of Crimea) is recommended in autumn or spring.
How to live with dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in adults can become chronic, and then you will have to fight it all your life. There is no cure for eczema, but the good news is that the disease can be controlled by keeping symptoms to a minimum. To do this you need 18:
- know and exclude contacts with triggers that provoke inflammation,
- take good care of your skin,
- use medications prescribed by a specialist.
It is very important to individually select the type and form of the drug so that the therapy is effective and comfortable for the patient. This also applies to topical steroids. In addition, you need to constantly monitor the development of the disease and be under the supervision of a specialist. Long-term remission may be a reason to gradually discontinue medications or switch to small doses of the drug. If symptoms increase, the specialist will help adjust the treatment plan by selecting a new therapy.
Unfortunately, sometimes eczema is unpredictable. It can flare up suddenly, and sometimes it can be difficult to understand why it has returned. The cause of its manifestation may be stress, anxiety, climate change or the quality of tap water. Living with eczema, you always need to be on guard. But even if the disease makes itself felt at the most inopportune moment, you should not perceive it as a disaster. Since our emotional state is closely related to the manifestations of eczema, we can overcome the disease only by accepting our skin as it is. There is no need to hide dermatitis, it needs to be treated, and then the skin will definitely reciprocate the love shown.
Folk remedies for the treatment of eczema
The home medical book contains many recipes and tips that will help you fight eczema.
- Vinegar, egg and water. In a glass you need to beat one egg with the addition of 50 ml of vinegar and the same amount of water. Lubricate the weeping eczema before going to bed and cover with a clean cloth. In the morning, there is no need to wash off the dried film; cover it with another layer of the mixture prepared the day before. A few days of such treatments and the eczema will stop getting wet.
- Calendula, chamomile, sage. Pour one tablespoon of each plant into a quart jar. Pour boiling water over the collection, cover with a lid and let it brew for a couple of hours. When the broth has cooled to a warm state, dip your hands into it. Chamomile perfectly relieves inflammation and soothes the skin, sage eliminates itching and burning, calendula disinfects the surface of the wound. Such baths can be done several times a day.
- Salt baths. Hot salt baths are very effective for dry eczema. They disinfect the surface, relieve inflammation and itching. Pour a couple of tablespoons of salt into a liter of hot water and dissolve it. Place your hands in the bath and keep them there for at least half an hour.
- Aloe and Kalanchoe juice. These plants have powerful bactericidal properties. The leaves can be crushed in a blender and then squeezed out through cheesecloth. You need to lubricate the eczema with freshly prepared juice 2-3 times a day to speed up wound healing.
- Strawberries. Strawberries will help relieve inflammation and burning. Fresh berries should be mashed and applied to affected areas of the skin.
- Oil and vinegar. Any vegetable oil contains a huge amount of vitamin E, which is involved in collagen synthesis and promotes skin regeneration. Vinegar disinfects the wound and helps relieve inflammation. Mix the two components in equal proportions, soak a clean piece of gauze in the liquid, and then apply the lotion to the eczema for 10 minutes. Two procedures a day will be enough for the wound to begin to heal within 3-4 days.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Sea buckthorn oil is excellent for softening tissues during dry erosion. The oil must be preheated and applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- Cabbage and milk. Cabbage leaves should be carefully removed from the head, pour milk over them and put on medium heat. When the milk boils, reduce the heat and simmer the leaves until they become soft. Milk cabbage leaves should be applied to the affected skin of the hands twice a day.
These recipes are quite effective, but can only be used in combination with conservative treatment.
Side effects of eczema medications
The list of side effects depends on the drug chosen. For example, hormonal medications are stronger, but their list of side effects is much longer. So, in addition to being addictive to the components in the composition, they can cause even the slightest overdose, they can cause skin pigmentation, rash, itching, numbness of the skin, acne, skin atrophy, body hair, acne, adrenal cortex insufficiency, increased intraocular pressure, lens opacities, mental disorders, decreased metabolism.
Ordinary natural ointments rarely cause side effects, which include only an allergic reaction due to individual intolerance to the components in the composition. They are allowed for pregnant women, children, the elderly, and people with diseases of internal organs (with the exception of some drugs).
Eczema on the hands during pregnancy - features
Pregnancy itself is a serious test for the female body. The properties of the immune system are aimed at the successful gestation and development of the child. If before pregnancy a woman suffered from any allergic skin diseases, it is highly likely that dermatitis will make itself felt again.
In addition, after the implantation of the fertilized egg inside the uterus, serious hormonal changes occur in the body of the expectant mother; prostaglandins are intensively produced, which are necessary for relaxing smooth muscles. These factors can become provocateurs in the development of the inflammatory process of the skin.
Expectant mothers note that during pregnancy, the skin becomes drier and sensitivity increases. Using conventional shower gels, soaps and creams can cause the development of eczema.
To prevent such troubles, cosmetics and hygiene products should be replaced with hypoallergenic ones, and also, starting from the 4th month of pregnancy, the skin should be nourished with baby oil or special milk for expectant mothers - this will eliminate such unpleasant symptoms as tightness, dryness and flaking.
Every pregnant woman, faced with eczema, worries: will the disease affect the development of her baby? Experts say that dermatitis itself does not pose any threat to the intrauterine development of the fetus, but itching of the skin, irritability of the woman and insomnia against the background of unpleasant sensations can lead to negative consequences.
Features of treatment in children and pregnant women
Treatment for eczema on the fingers during pregnancy is slightly different from the standard regimen, since the immune system of the expectant mother is weakened. The same can be said about young children, whose immunity has not yet fully developed. First of all, it is necessary to make some adjustments to the diet of the child and the expectant mother, limiting or completely eliminating fermented milk products, green vegetables and fruits. Also, children are not recommended to consume spicy, smoked and fatty foods, flour products and carbonated drinks.
Treatment of eczema during pregnancy is prescribed by a specialist
To strengthen the immune system of pregnant women, doctors prescribe special vitamin complexes. During the period of therapy, if possible, it is recommended to completely eliminate all possible contacts with household chemicals. During pregnancy, dermatotropic and antihistamine drugs are used, for example, Sudocrem or Bepanten.
For eczema in children, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- lotions using “Boric acid” or “Furacilin”;
- the use of calcium-containing drugs (with eczema in a child’s body, the level of this microelement decreases);
- use of external agents containing antibiotics (Lorinden is most often prescribed);
- To eliminate itching or reduce its activity, antihistamines (Zyrtec, Fenistil and others) are used.
Eczema on the fingers in children
Treatment of eczema in childhood or pregnancy does not only involve the use of prescribed medications. During the therapy period, it is also necessary to maintain optimal sanitary condition of the apartment and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Prevention
To prevent relapses of the disease, it is recommended to protect yourself from all possible allergens: dusty furniture and carpets, pet hair, fish food, household chemicals. Sleep should be complete. Stress and insomnia reduce the body's resistance to the disease, and it can recur. It is not recommended to take water procedures for longer than 5-10 minutes. It is also necessary to constantly use hypoallergenic nourishing hand creams.
Particular attention should be paid to diet, eliminating all possible allergens and harmful foods from the diet. It is recommended to engage in aerobic sports and often walk in the fresh air.