- Conservative therapy
A brain abscess is a local formation of an infectious nature, which is an accumulation of pus isolated from healthy brain tissue by a hard connective tissue capsule. It makes up no more than 1-2% of all intracranial formations. It can occur at any age, but most often occurs in people over 40. Men are more often affected.
Brain abscess is of inflammatory or post-traumatic origin
Stages of disease development
The pathogenesis of a brain abscess involves four stages of its development:
- Early brain inflammation (1-3 days). The patient develops encephalitis, a limited inflammation of brain tissue. The important thing is that at this stage it is still quite possible to reverse the disease. The inflammatory process can end spontaneously or upon completion of antibacterial therapy.
- Late stage (4-9 days). This stage occurs when the protective functions of the patient’s body are weakened or due to incorrectly chosen treatment tactics. Therefore, the inflammation begins to progress - the cavity filled with pus begins to increase in size.
- Early encapsulation (10-13 days). This stage of inflammation is characterized by necrosis of the central part of the brain, as well as the formation of a capsule that limits the further spread of pus.
- Late encapsulation (starting from day 14). Starting from the second week after activation of the inflammatory process, the patient is diagnosed with a clear collagen capsule filled with pus and surrounded by a zone of gliosis. The further development of inflammation depends on the reactivity of the patient’s body, the virulence of the flora, and proper treatment. Often at this stage there is an increase in the volume of purulent content and the formation of new foci of inflammation.
Possible complications
When purulent inflammation of brain tissue is detected, a person must immediately seek medical help, since lack of treatment can lead to:
- abscess breakthrough and secondary infection;
- osteomyelitis of the skull bones;
- epilepsy;
- loss of vision;
- disorders of the central nervous system;
- paralysis
General cerebral symptoms
General cerebral symptoms arise due to sudden jumps in intracranial pressure. The most common symptom of the pathology is headache accompanied by vomiting. The patient may experience problems with vision: often, against the background of an abscess, optic neuritis develops, and congestive discs appear in the fundus. The clinical picture of the disease also includes mental disorders, inhibition of thought processes, lethargy, weakness, and apathy. In the case of intracranial hypertension, epileptic seizures may occur. Most patients also experience persistent drowsiness, and in the most severe cases, coma may occur.
General information
A brain abscess is a condition in which pus accumulates locally in the brain matter. As the brain abscess progresses, it provokes headaches, fever , lethargy, as well as focal neurological symptoms. An abscess, as well as swelling that forms around it, can lead to increased intracranial pressure .
This disease is most often diagnosed in people aged 35-45 years, but it also occurs in children and adolescents. This disease is rare in children under two years of age. Men develop brain abscess more often than women.
Why such brain damage develops, how it manifests itself, and what treatment methods are most effective will be discussed in this article.
Course of a brain abscess
As for the course of the disease, it often has a very violent and acute onset, which is characterized by focal and hypertensive manifestations. The inflammatory process almost always develops against a background of elevated temperature. In rare cases, the onset of the disease may be less pronounced and resemble the clinical picture of meningitis. However, with minimal symptoms and normal temperature, the first stage of the disease is extremely rare.
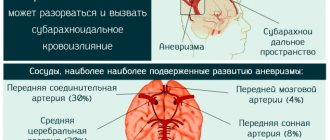
After 5-30 days, the disease passes into the next, latent, stage, which is characterized by either a complete absence of any symptoms, or minimally expressed signs of the disease. The patient may complain of severe and regular headaches, mental retardation and vomiting. The duration of this stage varies: in some patients it lasts a couple of days, while in others it lasts several years. Then, due to the influence of some factor (for example, infection), this stage ends and the patient’s symptoms begin to actively progress. The most severe and life-threatening consequence of a brain abscess is its rupture, which usually leads to death.
What pathogenetic stages does the disease have?
The most common brain infection is streptococcal infection. If a person has an open head injury, then staphylococcal damage occurs more often. People with immunodeficiency conditions - HIV, the period after radiation, chemotherapy or organ transplantation - are more susceptible to an abscess claim. In twenty-five percent of cases, the contents of the purulent lesion are sterile, so doctors cannot determine which bacterium has become the infectious agent.
When the disease occurs, it goes through several stages:
- In the first three days, the disease only begins to develop, but qualified doctors can already make a diagnosis. If therapy is started at this stage, then in most cases it is possible to prevent further development of the pathological process.
- From the fourth to the ninth day, inflammation increases; a cavity begins to form in the brain, in which purulent exudate accumulates.
- From the tenth to the thirteenth day, a dense capsule is formed around the accumulation of pus, preventing further spread of the inflammatory process.
- After two weeks of the disease, the capsule gradually thickens and a zone of gliosis forms around it. If therapy is not started at this stage, new purulent foci will form.
Important! Early diagnosis and initiation of therapy provide a good chance for a quick cure and prevent complications.
In most cases, the disease begins acutely, hypertensive and focal signs are pronounced. If the disease begins less violently, then the symptoms may resemble a general infection or meningitis. Occasionally, the onset of the disease may be with slight hyperthermia and a minimal clinical picture. Ensuction (the appearance of a capsule around pus) can begin at any point from five days to a month from the onset of the disease. At this stage, symptoms decrease or disappear altogether. The encystation stage can last several days or several days.
Under the influence of certain factors or without them, a rapid progression of cerebral and focal symptoms begins, which can lead to very serious complications - a breakthrough of the capsule of a purulent formation into the ventricular system or into the subarachnoid space. This complication can occur at any stage of pathology development and almost always causes death.
Diagnosis of brain abscess
Timely comprehensive diagnosis of brain abscess is important in its further treatment. To make a diagnosis, a neurologist uses medical history and examination results of the patient, as well as information obtained during instrumental and laboratory tests. The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- General blood analysis. The disease is usually indicated by test results such as an increase in ESR and pronounced leukocytosis. At the stage of capsule formation around the abscess, a normal or slightly increased number of leukocytes is observed in the patient’s blood.
- CT scan. The accuracy of detecting an abscess using this technique depends on the stage of the pathology. In the early stages, an abscess is very difficult to detect. At the stage of encephalitis, CT may reveal an area of reduced density that has an uneven shape. At this stage, the contrast agent accumulates unevenly - often only in the peripheral areas. It is much more accurate to diagnose the disease at a late stage in the development of encephalitis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This is a more accurate and effective method of diagnosing an abscess, which allows it to be detected at an early stage. Since the technique is considered the most informative, treatment can be prescribed based on its results even without bacteriological tests.
- Echoencephaloscopy. This diagnostic method is usually prescribed if for some reason MRI and CT cannot be performed. Using this study, it is possible to detect displacement of brain structures, which indicates compression of its tissues by an abscess.
- Bacteriological research. This technique involves taking a puncture of pus from the abscess for examination. A detailed examination of the pus helps to identify the causative agent of inflammation, which then makes it possible to select the most appropriate tactics of drug therapy.
- X-ray of the skull. This technique is used to detect the source of infection that caused the abscess.
- Craniography. Prescribed to detect symptoms of intracranial hypertension.
Tests and diagnostics
In the diagnostic process, the doctor takes into account the medical history of the disease, the presence of characteristic manifestations, and the progressive course.
If a person consults a doctor and the specialist suspects that he is developing a brain abscess, first of all, an MRI or CT scan of the brain with contrast enhancement is performed.
Sometimes there is a need to perform CT-guided aspiration when the material is taken for bacteriological examination.
If it is not possible to conduct such studies, echoencephaloscopy , which makes it possible to detect a possible displacement of the midline structures of the brain. During craniography, intracranial hypertension .
Laboratory blood tests are also carried out, the pathogen is determined through bacteriological examination.
Differential diagnosis of brain abscess
Since the majority of symptoms of brain abscess are not specific, differential diagnosis plays an important role. If the doctor has doubts during diagnosis, he may prescribe MR spectroscopy. This technique is carried out in order to differentiate a brain abscess from tumors of the cerebral hemispheres. It is based on different contents of lactate and amino acids in tumors and purulent accumulations.
As for other diagnostic methods, they are considered less informative. For example, signs such as an increase in C-reactive protein in the blood, chills, an increase in ESR, and leukocytosis may indicate a variety of inflammatory processes. Blood cultures from an abscess are often sterile.
Treatment of brain abscess
Treatment for a brain abscess usually involves both drug therapy and surgery. Doctors select the most optimal treatment tactics based on the results of diagnosing the disease, as well as the general health of the patient. The stage of the disease is also taken into account. For example, in the early stages of abscess formation, conservative treatment can be used. If an abscess has already formed, and a dense capsule has formed around it, neurosurgical intervention cannot be avoided.
- Drug treatment
- Surgery
Drug treatment of brain abscess involves the prescription of antibiotics, decongestants and anticonvulsants. Since the inflammatory process is provoked by bacteria, treatment of the disease necessarily involves their destruction. The combination of penicillin and chloramphenicol has been considered the most standard and commonly used treatment regimen for brain abscess for decades.
Penicillin was prescribed to treat the disease because it can kill streptococci and most other bacteria that can cause brain abscess. Chloramphenicol was used because of its ability to easily dissolve in adipose tissue and destroy anaerobic bacteria.
Today doctors are slightly adjusting this scheme. For example, cefotaxime is prescribed instead of penicillin, and metronidazole is prescribed instead of chloramphenicol. Typically, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy several weeks before surgery. The duration of taking antibiotics can be about 6-8 weeks.
Patients whose brain abscess occurs due to immunodeficiency are also prescribed amphoreticin. If the abscess has resolved, the patient will need to take a course of fluconazole for ten weeks. Drugs such as sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine are commonly included in the treatment regimen of patients with HIV.
Of great importance in the treatment of the disease is the correct identification of the causative agent of infection using an antibiogram. However, there are cases when the culture turns out to be completely sterile. Therefore, in such situations, empirical antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
In addition to antibiotics, medications are also prescribed to help reduce swelling. For example, glucocorticoids are used for this purpose. However, the prescription of these drugs is indicated only in case of a positive result from antibacterial therapy. They can reduce the severity of a brain abscess and reverse the development of the capsule around it. However, the opposite effect is also possible, when glucocorticoids activate the spread of inflammation beyond the boundaries of the lesion. To eliminate convulsive manifestations, phenytoin is usually prescribed.
If a brain abscess is diagnosed in the late stages, and a dense capsule has already formed around it, it is impossible to do without surgery. To treat the disease, puncture aspiration and removal of the abscess are most often used.
As for puncture aspiration, it is advisable to prescribe it in the early stages of the pathology. In this case, antibacterial therapy should be carried out simultaneously. Indications for this procedure may also include multiple abscesses, a deep location of the abscess, the stage of cerebritis and a stable neurological condition of the patient. To ensure that the procedure is performed as accurately as possible, the doctor resorts to stereotactic biopsy and intraoperative ultrasound.
Needle aspiration has one important drawback - in most cases, a repeat procedure may be required after it is performed. In difficult cases, complete removal of the abscess is prescribed. This technique is also prescribed if they want to avoid a possible relapse of the disease. It is advisable to remove an abscess for the following indications: if antibacterial therapy or puncture aspiration are not effective, with a superficial abscess and a well-formed capsule around it.
If multiple abscesses were discovered in a patient during diagnosis, then first you need to drain the inflammation to prevent pus from breaking into the ventricular system of the brain. If neurological disorders increase or there is no positive dynamics on MRI and CT, a repeat operation may be prescribed.
Prognosis for brain abscess
The outcome of the disease depends on whether the doctor was able to identify the causative agent of the abscess from culture. It is extremely important to do this, since then it will be possible to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics and select the most appropriate treatment regimen. The prognosis for the health of a patient with a brain abscess also depends on the number of purulent accumulations, the patient’s health status, and the correct treatment tactics.
The risk of various complications with a brain abscess is very high. Namely, about 10% of all cases of the disease end in death, and 50% result in disability. In addition, most patients may develop epileptic syndrome after treatment, a condition characterized by the occurrence of epileptic seizures.
Doctors give less favorable prognoses to patients who have been diagnosed with subdural empyema. In this case, the patient does not have a clear boundary of the purulent focus due to the high activity of the infectious agent or the body’s insufficient resistance to it. Lethal cases with subdural empyema reach 50%.
The most dangerous form of brain abscess is considered to be fungal empyema, which is accompanied by immunodeficiency. This disease has practically no cure, and the number of deaths with it is about 95%. In turn, epidural empyemas have a more favorable prognosis and are almost never accompanied by complications.
Prevention of brain abscess
There are no effective methods for preventing brain abscess. However, with the help of several preventive measures, the risk of the disease can be significantly reduced. In particular, in the case of traumatic brain injury, the patient must receive adequate surgical care.
The disease can also be prevented by timely elimination of foci of infection (pneumonia, boils), treatment of purulent processes in the inner and middle ear, as well as the paranasal sinuses. Good nutrition also plays a great role in the prevention of brain abscess.
Consequences
With timely treatment, the pathology has a minimum of consequences, but taking into account the fact that the brain substance is involved, it does not go away completely without a trace.
Possible consequences:
- Development of zones of increased excitability in the brain with the formation of epileptic seizures (in severe cases - status).
- Irreversible impairment of certain functions depending on the location of the abscess (impaired speech, writing, attention, vision). Complete or partial loss of any type of sensitivity and persistent disturbances in the motor sphere are possible.
- Development of sepsis with untimely treatment.
- Fatal outcome due to massive purulent process (relatively rare).
The development of possible complications is associated not only with the abscess itself, but also with the risks of its surgical treatment (thrombosis, for example).