A nevus (mole, birthmark) is a benign tumor-like neoplasm consisting of melanocytes (pigment cells). It is brightly colored - brown, black, red or purple - and may be flat or raised above the skin. Nevi can be congenital or acquired. Both occur in more than 90% of people. On average, a person has about 20 nevi on the body, but this number can range from 3 to 100.
Nevus disease or not? Moles themselves are not dangerous and do not cause any harm to health. They should be removed only if they cause aesthetic or physical discomfort or are located in places where they can be easily damaged by mechanical stress (for example, friction against clothing). However, nevi can degenerate into melanoma (skin cancer) - a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, if you have “suspicious” moles, it is recommended to regularly see a dermatologist, and if there are signs of their degeneration into melanoma, immediately consult a doctor.
Causes
Pigment spots can form due to congenital or acquired reasons.
Congenital nevi are a defect of embryonic development. Their occurrence is caused by a disruption in the process of movement of melanocyte precursor cells (melanoblasts) from the neuroectodermal tube into the skin. The accumulation of these cells in the skin causes the appearance of pigment spots.
Acquired age spots are formed under the influence of the following factors:
- significant changes in hormonal levels (puberty, pregnancy);
- skin infections;
- excessive skin exposure.
“before” and “after” photos of laser treatment
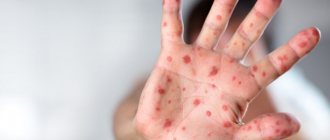
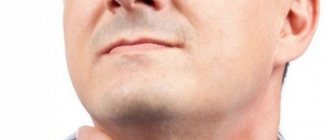
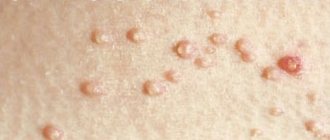
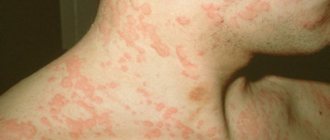
Papular nevi (moles) in the chin area
Papular nevus (nevus) in the area of the nasolabial fold
Papular nevus (mole) in the area of the nasolabial fold after removal after 21 days
Warty pigmented nevi in the navel area
Nevus of the auricle
Nevus (mole) in the nasolabial fold area
Classification
Depending on their size, nevi are divided into several types:
- small – diameter no more than 1.5 cm;
- medium - from 1.6 to 10 cm;
- large – over 10 cm.
If a birthmark occupies a large part of the anatomical area, then it is called giant. Giant forms of the tumor are often localized on the face or back.
Based on their location in the thickness of the skin, the following types of nevi are distinguished:
- borderline or mixed - an accumulation of melanocytes is located on the border of the dermis and epidermis;
- epidermal - a cluster of melanocytes are located in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis);
- intradermal - an accumulation of melanocytes is localized deep in the dermis.
Nevi on the body: causes of the disease
A child can develop moles in the womb, but it is not always possible to see a nevus on a newborn’s body. You can also identify the second type of nevi - acquired. However, dermatologists are of the opinion that a mole itself cannot appear on the body; it is congenital, and simply does not appear immediately. Often their manifestation is provoked by some factor - sunlight, hormonal disorders, etc.
Reasons for the formation of moles in the prenatal period:
- Heredity;
- Pathologies during pregnancy - threat of miscarriage, toxicosis, other diseases;
- Influence of toxic-allergenic factors;
- Reaction to radiation exposure;
- Maternal alcohol abuse before conception or during pregnancy;
- Taking strong hormonal drugs (for example, contraceptives before pregnancy);
- Diseases of the mother's urinary system.
Heredity
According to statistics, out of 100 children born, 99 do not have a nevus at birth, but this does not mean that there are no moles. During adolescence, when puberty begins, moles may appear on the body. Babies can have pigmented and non-pigmented nevi on their bodies.
Depending on how moles are located on the body, they can be divided into intradermal nevi, epidermal and borderline nevi.
Intradermal and epidermal nevi have the appearance of a pea, borderline nevi are flat, like a birthmark.
So, what reasons can trigger the appearance of benign nevi?
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or lactation;
- Allergic or infectious skin diseases;
- Active influence of sun rays on the skin;
- Taking hormonal contraceptive pills;
- Mechanical damage to the skin.
Nevi on the body, regardless of the reason for their appearance, differ from each other in appearance (benign moles in the photo), and to make sure that the mole is not malignant, you need to show it to the doctor.
Types of nevi and their symptoms
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture, age spots are divided into several types, presented in the table:
| View | Symptoms |
| Light blue (blue, Jadassohn–Tiche) | It received its name for the characteristic dark blue color of the surface. Usually it is single, but sometimes multiple pigment spots can be observed. It is a benign tumor, but under the influence of unfavorable factors it can undergo malignancy and turn into melanoma. |
| Border | It looks like a small spot of black, gray or brown color, with a diameter from 2-3 mm to 4-6 cm, but often no more than 1 cm. The surface of the formation is dry and smooth, slightly uneven. She doesn't even have vellus hair. It can appear on absolutely any part of the human body. There is a risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor. |
| Nevus Ota | It looks like a single spot or a group of merging dark blue spots of irregular shape. Located in the upper jaw, cheek, paraorbital region. Pigmentation often spreads to the mucous membranes of the oral and nasal cavities, pharynx, and sclera of the eyes. The disease is unilateral. It poses a certain danger in terms of malignancy. |
| Complex pigment | A brown pigment formation associated with the accumulation of melanin in both the dermis and epidermis. It looks like a round wart or papule with a diameter of no more than 1 cm. There is a high probability of its transformation into melanoma. |
| Verrucous | It is a warty, dark-colored growth that rises above the surface of the skin. The surface is lumpy, reminiscent of cauliflower. Refers to melanoma-neutral forms of the disease. |
| Papillomatous | It has the appearance of a bumpy, papilloma-like mole protruding above the surface of the skin. Most often localized in the scalp area. |
| Nevus of Setton (halonevus) | The pigment spot is surrounded on the periphery by a small area of skin devoid of melanin. Formations can be single or multiple. It is prone to self-regression, but in some cases it is complicated by the development of melanoma. |
| Dysplastic | It looks like a small mole with jagged borders. The surface is colored unevenly brown or black. Can be located on any part of the body and head. Very often exposed to malignancy. |
| Giant pigment | The spot is significant in size (over 20 cm in diameter) and often occupies entire anatomical areas. Subject to degeneration into a malignant tumor. |
| Fibroepithelial | A melanoma-like benign neoplasm on a pedicle, reaching a diameter of 1.5 cm. It has a soft consistency. Color ranges from flesh to dark brown. |
| Nevus of the sebaceous glands | The tumor is formed by altered hair follicles and hyperplastic sebaceous glands. A typical location is the head. It looks like a yellowish-pink plaque with an oval, linear or irregular shape and a warty surface. |
You can see what one or another type of age spots looks like in photos in special atlases of dermatological diseases.
Dangerous nevi: when to sound the alarm
Any mole on the body needs control, even the smallest one. Moles that change in size or color can become cancerous.
The number of moles is not an indicator of the risk of skin cancer or other malignant pathology; sometimes even one single nevus on the skin can be “bad”. It is important to know what signs to look out for and when to contact a specialist.
Signs of a dangerous mole:
- Change in color, especially if the nevus has darkened. Black nevus is considered a rather dangerous formation.
- Intensive growth. The larger the mole in diameter, the easier it is to injure, which can lead to serious problems. Also, a mole that is increasing in size may be a sign of the beginning of the process of malignancy of the nevus.
- The appearance of ulcers and other irregularities on the top of the birthmark or mole, which may bleed from time to time.
- The appearance of unpleasant or painful sensations when touched.
- Hair loss (if any) means poor circulation in that area.
Dangerous moles can develop into a malignant skin tumor, and even lead to the worst thing - melanoma.
According to statistics, more than 75% of cases of the disease are fatal.
Diagnostics
Patients with suspicious pigment spots should be monitored by a dermatologist. During the initial visit, the doctor examines the tumor, specifying its shape, color, size and other visible characteristics. In addition, he conducts a survey of the patient, finding out the following points:
- when did the age spot appear?
- whether its shape, color and/or size has changed recently;
- what caused the changes (attempted removal, scratching, burn, skin infection, injury).
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the benignity or malignancy of the neoplasm, special diagnostic methods are required.
It is strictly unacceptable to perform partial removal of a pigment spot (biopsy) for histological examination, since its traumatization can cause degeneration into melanoma.
Currently, the following are used in the diagnosis of age spots:
- Cytological examination. If there are cracks or bleeding areas on the surface of the lesion, the doctor may take a smear and examine it under a microscope. The result is usually ready the next day.
- Histological examination. Performed in an oncology clinic. Under local anesthesia, complete removal of the formation is carried out with mandatory excision of the healthy tissue surrounding it by approximately 5-6 mm. The wound is sutured with subcutaneous or regular skin sutures. The resulting tissue is sent for histological examination. If malignant cells are detected in it, the patient is prescribed radiation and/or chemotherapy.
- Epiluminescence microscopy. Intravital examination of tissues using a special optical device - a dermatoscope.
- Computer diagnostics. A high-resolution digital camera is used to take a photo of the pigment spot. The resulting image is then processed by a computer program.
How to diagnose nevus
The appearance of new formations on the body is not always a bad sign. It is much worse if existing moles begin to change. At the first changes, you should not surf the Internet looking for information about nevi with a detailed description of the disease and a photo attached to the article. Self-diagnosis is often wrong!
If any formations appear on the body that may interfere or cause discomfort, you should consult a dermatologist. Based on the patient’s complaints and a thorough visual examination, the doctor will determine whether the nevus is dangerous. During the examination, he can clarify how long ago the mole appeared, whether it is growing, or changing color. If there have been injuries - scratching a mole, bruise or burn - you must tell your doctor about this.
Sometimes a visual examination may not be enough to diagnose the type of disease, so additional studies using a special device may be necessary. It should be noted that a piece of a mole is not taken for histological examination!
Any traumatic intervention can lead to serious complications, including the degeneration of a mole into a malignant form. Removing nevi with electric current (electrocoagulation), freezing moles and getting rid of them using chemicals is unacceptable.
How is nevus histology performed? The material for examination is taken from the surface of the mole: a small smear if small cracks or bleeding are observed. Examination of nevus tissue is carried out under a microscope, and the result can be found out the next day.
There is also a diagnostic method that can also be considered therapeutic - a total excisional biopsy, according to which the mole is removed with a small area of unaffected skin and sent for examination. The resulting diagnosis is the most accurate, since the entire tumor is examined, and not just its surface.
It is worth noting that this type of study is only suitable for superficial moles. If the test for a malignant tumor is positive, the location of the mole should be excised more deeply: it is necessary to make sure that the bad cells have not spread to healthy tissue.
Similar “experiments” are carried out in oncology hospitals under the direction of a dermatologist. Material can only be taken by a specialist wearing gloves and using a sterilized instrument.
Inspection of a mole can also be carried out using a dermatoscope - a special device with lighting. The principle of examining a nevus is to examine the formation under a microscope.
Dermatoscope
A few drops of vegetable oil are applied to the pigmented nevus of the skin so that an epiluminescent medium is formed between the object of study and the microscope lens. By leaning the device against the formation on the skin, you can carefully examine it without damaging the surface. In addition, this research method is considered very accurate.
Among the methods for studying pigmented nevus, computer diagnostics can also be distinguished. The formation on the skin is recorded using a digital device with a high degree of accuracy. The resulting photo is processed in a program where it is compared with many photos from the database. Based on the processing, a final diagnosis is issued.
If the nevus is malignant, treatment and surgery are prescribed.
Treatment
Melanomic pigment spots can be removed in one of the following ways:
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser radiation;
- radio knife
If there is a high risk of degeneration of a pigment spot into melanoma, only surgical removal is indicated, with mandatory excision of surrounding healthy tissue.
In some cases, only a specialist can distinguish a melanoma-dangerous mole from a non-dangerous one.
Zolotov Sergey Alexandrovich
- Candidate of Medical Sciences, surgeon, specialist in laser surgery.
- From 2003 to 2009 completed training at the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Russian National Research Medical University" named after. N.I.Pirogov Ministry of Health of Russia.
- From 2009 to 2011, he completed his residency at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution, Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology, specializing in Pediatric Surgery.
- In 2011, he completed training under the program of additional professional education of doctors in laser medicine at the State Scientific Center for Laser Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. From 2011 to 2014, he studied full-time graduate school at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology.
He has extensive experience in removing various benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue using laser surgical methods.
More than 5 years of experience in surgery.
Prevention of melanoma formation
In all countries of the world, there is currently a steady increase in skin melanoma. This malignant tumor is characterized by rapid growth and metastasis to the brain, liver, and lungs. Mortality with it reaches 50%.
According to statistics, the development of melanoma in most cases is preceded by certain types of nevus. Therefore, patients with such skin lesions should observe the following preventive measures:
- try not to be in the open sun during the daytime (for central Russia from 11 to 17 hours), when the intensity of solar radiation is maximum;
- use sunscreen;
- refuse to visit the solarium;
- carefully monitor existing and newly appearing pigment spots.
Patients should be informed that if new pigmented skin formations appear, as well as changes in the characteristics of existing ones (shape, size, color), they need to consult a dermatologist or oncologist as soon as possible.
Signs of nevus degeneration into melanoma
Symptoms of nevus malignancy are:
- Change in color (decrease or increase in pigmentation).
- Mole compaction.
- Growth of the neoplasm – in diameter or height.
- Redness.
- The presence of ulcers on the mole.
- Bleeding from a nevus.
- The appearance of black dots around a mole or birthmark.
- Hair loss from nevus.
- Feeling of warmth, itching or burning in the area of the tumor.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
If such signs are present, you should immediately contact a dermatologist and oncologist.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine has many recipes and remedies for self-removal of nevi.
Before using them, you should definitely consult with a dermatologist or oncologist in order to exclude possible malignancy of the tumor.
- Celandine juice is one of the most famous folk remedies with a pronounced cauterizing and disinfecting effect. The juice should be applied 2-3 times a day to the surface of the mole.
- Lapis - the lapis pencil fights bacteria, disinfects the skin, and reduces inflammation. They are recommended to lubricate nevi in the morning and evening. If after 1-2 weeks of regular use they have not begun to decrease in size, you should discard the lapis pencil.
- Vinegar is an effective remedy for cauterizing moles. It should be applied to skin formations once a day, then wrap the area with several layers of bandage. The course of treatment should not exceed 7 days. Freshly squeezed lemon juice has a similar effect, but it must be used 4-5 times a day.
Danger to life
Moles themselves do not pose any danger to their owners. These are completely harmless benign neoplasms. Removal of such moles is carried out in the presence of physical or aesthetic discomfort .
Possible complications
The main danger to life is the degeneration of a mole into melanoma (malignancy). This process is not typical for all nevi. It occurs only when exposed to provoking factors:
- mechanical impact;
- excess ultraviolet radiation;
- infectious diseases;
- dermatitis;
- chronic diseases of various organs and systems.
Note! The tendency to develop melanoma is inherited. Therefore, patients with a family history of skin cancer are advised to regularly see a dermatologist and conduct self-examination of moles.
Origin of nevi
Discussing the question of the origin of all types of moles, doctors were divided into two camps. Some are confident that the phenomenon in the photo is a congenital malformation that simply appears later. Others are convinced that nevi are acquired. Along with this, a number of factors are identified that can participate in the formation of nevocytes.
Possible complications
The main danger of formation is degeneration into melanoma, that is, a malignant tumor. An important role is played by the location of the mole, which is one of the main risk factors for the development of complications - it can rub against clothing, which will lead to injury.
The first sign of damage is bleeding, itching and burning in the area of the nevus.
Changes in shape and other symptoms should cause concern:
- location of the skin formation in a place of constant rubbing with clothing;
- large moles;
- the appearance of too many formations on the skin - more than 50-60;
- frequent emergence of new formations.
Regardless of the parameters and number of moles, they need to be carefully monitored. If the spot rapidly increases in size (more than 2 times in 2-3 weeks), its contours have become uneven, the color has changed, the skin in the area of the mole is bleeding, peeling or constantly getting wet - this is a reason for an urgent visit to the oncologist.