Why do adults get chickenpox? Until recently, chickenpox was considered an exclusively childhood disease, and in adolescents and adults this disease was extremely rare.
However, in the modern unfavorable environmental situation, an abundance of electromagnetic and radioactive radiation, a mass of chemical harmful substances in food, air, water, an abundance of stress, an increased negative information load on an adult ultimately leads to a decrease in the body’s defenses and disruption of the functioning of the immune system . Therefore, in our time, the occurrence of childhood diseases in adults is possible, and their increase is increasing every year. Chickenpox now accounts for approximately 10% of all cases of this disease in adults.
The causative agent of chickenpox is herpes virus type 3 - Varicella Zoster. If a child is infected with it while still in preschool age, the child receives lifelong immunity and will never get sick with this type of virus again.
There is an opinion that all children are infected with chickenpox and a child can become infected, but not get sick, that is, there will be no symptoms of the disease, this happens in children with a sufficiently strong immune system, or if the amount of virus that entered the body was negligible.
After infection and suffering from an acute form of chickenpox, the pathogen remains in the body in an inactive form, located in the nerve ganglia. If an adult already had chickenpox as a child, this does not mean that the virus cannot be activated.
You should not hope for lifelong immunity; when favorable conditions arise, such as treatment with corticosteroids, treatment of cancer, powerful radiation, severe prolonged hypothermia, serious stress, severe infectious diseases, severe injuries and other unfavorable factors give impetus to the virus emerging from its dormant state, in this case, herpes zoster (shingles) develops.
Those adults who did not have chickenpox in childhood can tolerate it in the same way as children, only it is much more severe.
How can you get infected?
In order to become infected with chickenpox, sometimes it is enough just to be in a room where a sick person was present some time ago. The virus is so small and light that it can be carried by air currents over significant distances. That is why the disease was called chickenpox. The only fact that can restrain the rapid spread of the infection is that the pathogen, once outside the body, dies in about 10 minutes.
The patient begins to release the pathogen into the environment several days before the visual debut of chickenpox, that is, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of infection if the person does not have immunity to the chickenpox virus or is not vaccinated.
If one child in a children's group gets chickenpox, the entire group or class is quarantined.
If someone in the family gets chickenpox: what are the preventive measures?
Most non-severe patients are treated at home.
- It is enough to isolate the patient in a separate room where ventilation is carried out regularly.
- The family member caring for the patient must follow normal sanitary and hygienic rules. Of course, he must have immunity, that is, he must have previously had chickenpox.
- There is no need to disinfect the room and objects used by the patient, since the virus is volatile, but not tenacious outside the body.
- When all the blisters have crusted over, approximately on the 6th day after the appearance of the last blister, the patient is no longer contagious.
Features of the course in adults
In adults, chickenpox is much more severe than in children. A child up to a certain age is protected not only by his own, but also by his mother’s immunity. That is why in childhood the disease is usually quite mild and goes away in a short time. In a person after 15-18 years of age, his own immune system does not cope well with the attacks of Varicella Zoster, as a result of which chickenpox can lead to the development of various complications or exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
In some cases, chickenpox develops again. This is possible if the patient has an extremely suppressed immune system. There are a number of factors that contribute to the occurrence of pathology:
- severe psychological experiences, neuroses;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- autoimmune diseases, HIV or AIDS, hepatitis;
- carcinomatosis;
- past infections;
- therapy with antibacterial agents, cytostatics or steroids;
- extensive abdominal surgery, organ or tissue transplantation;
- hard physical labor.
general information
The danger of contracting chickenpox in adulthood is its severe course, the possible transition of the rash into a hemorrhagic or bullous form (when ulcers appear on internal organs).
In addition, an adult may experience serious complications in the form of encephalitis, disruption of the cardiovascular system, pyoderma or lymphadenitis.
Fun fact: “wind parties” were popular in the early 20th century. Parents deliberately brought their children to those who were already infected with chickenpox so that the child could easily transfer the disease.
Incubation period and degrees of chickenpox
The incubation period for chickenpox in adults ranges from 10 to 21 days (most often 14-17). During this time, the virus manages to take root in the body, begins to multiply on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and spread throughout the body through the lymphatic system.
There are three degrees (forms) of the disease:
- Easy. If you are lucky, the rash will stop after 2-3 days, the temperature should not rise above 38 degrees. This type of chickenpox in adults usually occurs with repeated infection or in people with very strong immunity;
- Moderate severity is the most common form. Intoxication lasts 4-6 days, body temperature rises to 38.5-39, a profuse rash on the body, isolated rashes on the mucous membranes are possible;
- Heavy. The temperature rises above 39 and lasts up to 10 days. Convulsions, nausea and vomiting, and severe headaches are possible. Rashes cover the entire skin, mucous membranes, and can even occur on the eyeballs.
If you have previously received prophylactic immunoglobulin injections, it is likely that you will have an atypical course of chickenpox with mild clinical symptoms. The temperature will not rise above 37.4, rare rashes will be painless, and mild malaise can be attributed to fatigue or a cold.
What diagnostic methods can a doctor prescribe for chickenpox?
With any infectious process, changes are noted in the general blood test, and with chickenpox too, but there are no manifestations specific only to this disease. In most cases, there is an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate - ESR.
To identify the pathogen, they take the contents of a vesicle or a scraping print from the erosion; after special silvering, microscopy determines clusters of viruses or giant cells with many nuclei. In the atypical form, manifested by catarrhal changes in the throat, these reactions are also performed.
Using test systems, molecular biological methods are used to detect antibodies to the virus in the blood, this is called a serological test. As a rule, diagnosis is performed in severe cases, however, the severity of the changes does not correlate with the severity of the disease.
The infectious disease specialist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, having a broad clinical horizon, has at his disposal the most modern diagnostic methods and equipment with the ability to perform complex tests, which affects a favorable prognosis for the patient.
Symptoms in adults
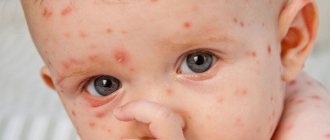
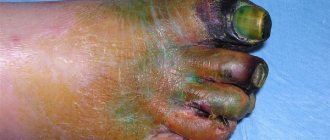
Chickenpox in adults (see photo) manifests itself with characteristic symptoms that are difficult to confuse with manifestations of other diseases. In adults, the course of infection has its own characteristics:
- At the end of the incubation period, headaches, discomfort and aches throughout the body appear, a feeling of weakness, fatigue, and general malaise occurs.
- Soon the disease manifests itself with a sharp rise in temperature to high values (39-40°C), itching throughout the body and the appearance of small reddish blisters with serous contents. Such nodules, slightly rising above the surface of the skin, soon take over the entire body - starting from the head and ending with the limbs. In this case, the skin looks inflamed, hyperemic and swollen. In adults, rashes often spread not only to the skin, but also to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, mouth and genitals.
- The acute period in adults is accompanied by severe fever, high fever, which can lead to damage to the unequal system and symptoms such as photophobia, nausea, vomiting, poor coordination of movements, and convulsions.
- A high temperature in adults is difficult to bring down with antipyretic drugs; it can last for 5 days (in especially severe cases, 7-10 days), after which the body’s thermoregulation gradually returns to normal.
- After about 3-4 days from the onset of the disease, the blisters begin to burst and dry out, becoming covered with a dry crust (scab). At the same time, new rashes may appear, since the picture of the disease is polymorphic. That is, both fresh rashes of the second wave and dried vesicles covered with a dense crust that appeared at the initial stage of the disease may be present on the patient’s body. The wave-like appearance of rashes is a characteristic feature of chickenpox. On average, new watery blisters form on the skin within 10 days.
In adults, the formation of rashes is often accompanied by the addition of a pyogenic infection. In this case, the nodules do not open for a long time, and after resolution they heal poorly, become wet and leave behind unsightly scars on the skin.
During the illness, the patient’s condition deteriorates significantly, experiencing constant malaise, severe weakness, headaches and muscle pain. The course of the disease is accompanied by a lack of appetite, sleep disturbances, and a constant feverish state, the peak of which, characterized by a sharp rise in temperature, occurs on the first day of the development of the infection.
Atypical forms
- Hemorrhagic. It is accompanied by the appearance of blisters filled with bloody contents, small hemorrhages under the skin, the appearance of hematomas, bleeding gums, and blood in the vomit, urine and feces. This form of the disease has the most unfavorable prognosis, leading to death.
- Visceral. It manifests itself as high fever, multiple rashes on the skin, mucous membranes, genitals, and severe intoxication of the body.
- In the bullous form, large flabby blisters—bulae—filled with serous contents appear on the patient’s skin simultaneously with the characteristic rashes. After their resolution, long-lasting ulcers remain on the skin.
- The gangrenous form of chickenpox is rare, mainly in severely malnourished patients with poor care. In this case, the papules become infected with the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. A border consisting of necrotic tissue forms around the papules; the patient’s condition is complicated by high fever and general intoxication of the body.
Chickenpox in adults: photo
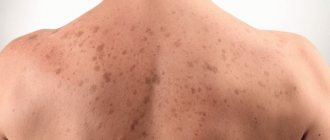
The appearance of the rash is constantly changing, in accordance with the phase of development of the infection. The pathological process goes through several stages. Skin infection with the varicella zoster virus is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic red spots associated with dilation of the capillaries. The spots have a round shape and can be from 3 mm to 1 cm in size. Two to three hours after the spots appear, papules—serous, cavityless nodules—form in the places where they are localized.
During the pathological process, the epidermis is detached and after 12-20 hours, vesicles are formed from the papules - hemispherical vesicles with a pink rim, filled with organic liquid. As they ripen, the vesicles burst and a crust forms in their place. From this moment, the rash element stops developing and ceases to be contagious. The itching stops. From the day the red spots appear until the crust forms, it usually takes five to seven days. During this same period, new bedding forms every two days. Their number depends on the complexity of the form of the disease.
Why do spots and blisters form on the skin?
The main manifestation of chickenpox is a characteristic skin lesion. The chickenpox agent has a tropism for the skin; first of all, it rushes there, penetrates into cells and multiplies. While the particle is in the cell, the body reacts to the disorder by forming an inflammatory wave: nearby vessels expand, through which immune cells are actively arriving, filled with biologically active substances that dissolve all foreign substances. In general, inflammatory edema develops.
The breeding enemy agent and immune defenders together cause cell death. In place of the dead cell, a cavity is formed, which is filled with the surrounding inflammatory fluid, exfoliating the surface layer of the skin. This is how a bubble is formed from the speck.
Is it possible to get sick a second time?
Re-activation of the varicella-zoster virus and chickenpox is possible only against the background of a significant decrease in the body's defenses.
Is it possible:
- in the presence of HIV infection;
- after organ transplantation;
- due to acclimatization or severe stress;
- after a course of chemotherapy;
- after taking corticosteroids, antibiotics or immunosuppressants.
Due to the ability of the virus to mutate, re-infection from an external source is possible. This happens if the body of a person who has previously had chickenpox has not formed enough antibodies against the virus. In this case, varicella-zoster no longer manifests itself in the form of a chickenpox rash, but as another independent disease - herpes zoster, in which the rash takes the form of stripes.
Most often, recurrent infection occurs in people over 40 years of age.
Do you always need to get tested for chickenpox?
Diagnosis is simple, and tests are often not required to identify the causative agent of the infection. Chicken pox has very characteristic clinical manifestations, so diagnosis is carried out by an infectious disease doctor based on symptoms.
The high degree of transmission also speaks in favor of the infection; in most cases, it is possible to trace where the infection came from. Diagnosis of the pathogen may be required in the atypical course of the disease, when the manifestations are either less or more pronounced and do not resemble chickenpox.
Complications
Chickenpox in adults is dangerous to health both in itself and due to the appearance of serious complications. The resulting scars at the site of the blisters are a noticeable cosmetic defect of the skin. Chickenpox can cause complications in people at risk. This category includes:
- pregnant women,
- smoking people,
- patients with weak immunity,
- suffering from chronic lung diseases, except asthmatics.
The older a person is, the more difficult chickenpox can be. Chickenpox in adults is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since chickenpox suffered during the first months of pregnancy can lead to severe pathology or fetal death, and in the last trimester of pregnancy it can contribute to premature birth or the development of congenital chickenpox in the child.
List of possible complications:
- arthritis;
- encephalitis;
- heart disease;
- kidney dysfunction;
- hepatitis;
- abscess;
- serious suppuration;
- pneumonia;
- damage to the lymphatic system;
- skin diseases;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
To avoid consequences from the skin, it is important to ensure careful personal hygiene, to prevent scratching and the entry of pyogenic microorganisms into the nodules.
The consequences of chickenpox
Chickenpox during pregnancy
If a woman does not have immunity to the chickenpox pathogen at the time of conscious planning of pregnancy, she will be recommended to undergo appropriate vaccination. Infection during pregnancy is dangerous for the fetus until about 20 weeks. At this stage, the virus causes intrauterine death of the fetus, which ends in miscarriage or stillbirth. It is also possible to develop severe defects that lead to disability of the born child.
At later stages, the effect of the virus on the body of both mother and fetus weakens, reaching a second peak immediately before childbirth. Infection with chickenpox in the later stages is fraught with the development of pneumonia, which can also lead to the death of the child. In such cases, special therapy with immunoglobulins and specific antibodies is carried out.
Lack of immunity to chickenpox in general is not an indication for termination of pregnancy.
How to treat chickenpox in adults?
The main goals of chickenpox treatment are to relieve symptoms and create an antibacterial space around the patient.
Depending on the form, the doctor prescribes medications that provide rapid treatment and prevent complications in various organs.
It is important to start taking antiviral medications from the very first symptoms of chickenpox. Pockmarks spread not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes and various internal organs.
Below is a table showing the symptoms and how to treat to achieve the desired result:
| Symptom | Treatment | Target |
| Body aches | Taking anti-inflammatory drugs | Reducing pain in the lumbar, shoulder and other areas |
| Fever (above 38.5 degrees Celsius) | Antipyretics, excluding aspirin. Drink plenty of fortified drinks. | Normalization of body temperature |
| Itching at the site of the rash | Antiallergic drugs, lotions with soda solution for 5 minutes on the most itchy areas of the skin, weak cool shower | Stop itching |
| Pain and itching in the affected mucous membrane | Rinsing, washing with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial decoctions, solutions. | Relieving pain |
| Spread of the virus in the body | Taking antiviral drugs according to a special regimen | Elimination of complications, reduction of the toxic effects of viruses on the body |
| Weakening of the immune system | Taking multivitamins | Boosting immunity |
The brilliant green solution, used in the treatment of chickenpox, has disinfectant properties, as it contains 70% alcohol, but the main property, in fact, is the identification of the rash. It is very difficult to determine the last rash without brilliant green. Alcohol can irritate inflamed skin and this makes the itching worse. Antiviral ointment Oxolin is suitable for treating vesicles.
What to do if there is no immunity to the infection, but there was contact with the patient?
Immunity after illness is lifelong. The quarantine period for chickenpox is 21 days, this time is enough for the virus to incubate.
In the first four days after contact with a patient, those who have not previously been ill and have not been vaccinated are vaccinated with the varicella-zoster vaccine.
If vaccination is contraindicated, ZIG or ZIP immunoglobulin can be used intramuscularly within 4 days.
All this will require time and effort; the specialists of the Medicine 24/7 clinic always take into account not only the individual characteristics of the disease, but the capabilities and interests of each patient, so that the treatment is as comfortable as possible and improves the quality of life. Call a specialist from the Center for Infectious Diseases 24/7 +7 (495) 230-00-01
The material was prepared by an infectious disease specialist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences Margarita Vasilievna Nagibina.
Drug treatment
Medications for oral administration or injection are prescribed by a doctor as needed. These may be medications with the following effects:
- Antiviral medications. Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir. The duration of use and dosage are determined by the doctor.
- Antihistamines. Necessary to eliminate symptoms of itching and other manifestations of hypersensitivity. Suprastin, Cetirizine, Loratadine and other drugs are prescribed.
- Antipyretic drugs. Ibuprofen, Panadol.
- Antibiotic drugs. Necessary for correction of complications. Oxacillin, Cefazolin.
- Solutions for intravenous infusion. Necessary for reducing the concentration of toxins in the blood, removing them, and improving circulation. 5% glucose solution, Reopoliglucin.
- Specific antibodies against Varicella Zoster.
All medications are prescribed by a doctor; self-medication can lead to the development of serious complications.
What to do at home?
To prevent bacterial infection, it is recommended:
- Maintain bed rest. The supine position improves blood circulation, which eases the load on the heart and minimizes the risk of complications.
- Avoid overheating. Increased sweating increases itching and the risk of ulcer formation.
- Change underwear and bed linen daily.
- Drink plenty of water up to 2.5 liters per day, unless there are contraindications from the heart and kidneys. Drinking regime helps eliminate toxins.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and trim your nails short to prevent scratching.
- Make cold compresses with 1 tsp soda solution. per glass of water. To reduce itching, it is enough to hold the compress for 10-15 minutes.
- Take a bath with soda added.
- Rinse your mouth after eating: with a soda solution (1 tsp per glass of water);
- furatsilin solution (2 tablets per glass of water);
- decoctions of herbs chamomile, calendula, sage (2 tsp per glass of boiling water).
General patient care
During periods of rising temperature, it is not advisable to take water procedures, but it is still necessary to keep the body clean in order to reduce the risk of infection of the rash.
- You can take a cool shower with low pressure, without opening or damaging the bubbles. Gently wet the skin with a towel. It is necessary to change bed and underwear daily and keep the patient's room clean.
- Avoid contact of bacteria with areas of skin affected by the rash. Treat each vesicle with a disinfectant solution. Choose a drug that will dry out your rash so that it disappears as quickly as possible.
- Possible rashes on the genitals require special care; after each trip to the toilet, it is necessary to wash, preferably with some kind of disinfectant solution.
- Acyclovir ointment is well suited for treating rashes in intimate places . For comfort and to reduce chafing on painful areas of the body, you can avoid wearing underwear during periods of particularly painful sensations, but make sure the area around you is clean.
- Do not apply alcohol-containing preparations to mucous membranes - this will cause even greater discomfort: itching and burning. To reduce itching, lotions with a cool solution of soda or a pink solution of potassium permanganate can help. It is enough to keep the lotion for up to 5 minutes.
- The oral cavity, if it is affected by a rash, must be rinsed with a disinfectant, anti-inflammatory solution. A decoction of anti-inflammatory herbs or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate will do.
As for medications, the doctor can prescribe you antiviral, antihistamine, and sedative medications that will sufficiently reduce your discomfort. Maintain strict bed rest, do not overexert yourself, do not worry, increase the amount of fluid you drink per day, especially if you are taking antiviral drugs, in order to avoid possible complications aimed at your kidneys.
Important! Eliminate fatty, spicy and allergy-causing foods from your diet - this will reduce the risk of new rashes and speed up recovery.
If you suddenly get chickenpox in the bustle, don’t worry! Yes, you may not feel very well in the first few days, but if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, take care of your skin, and take all necessary measures to prevent complications, I assure you, everything will go better than you think.
What can you eat?
Chickenpox is accompanied by high fever and poisoning by viral toxins. In patients, energy expenditure and protein breakdown increase, the function of the digestive glands and gastrointestinal tract organs is inhibited. The chickenpox diet takes these changes into account and ensures a sufficient supply of energy substances, water and vitamins.
The diet of patients should be varied in composition. Food is given in pureed and semi-liquid form, especially if the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx is affected.
For chickenpox it is recommended:
- weak meat and fish broths;
- steamed cutlets and meatballs;
- slimy pureed soups;
- vegetable puree or caviar;
- kefir, yogurt and other fermented milk products;
- cottage cheese with sour cream, curd soufflé;
- beaten egg or steamed omelette;
- not hard berries and fruits, mousses, purees and juices from them;
- juices with pulp, weak tea with lemon or milk, rosehip decoction.
After the oral mucosa is restored and the temperature normalizes, you can return to your normal diet. Until recovery, it is necessary to maintain a drinking regime, especially for patients taking acyclovir and other antiviral drugs. Water can be drunk in its pure form or in the form of dried fruit compotes and tea.
Consequences
The most dangerous consequences of chickenpox include:
- Weakening of the immune system and, as a consequence, loss of its ability to resist more serious viruses;
- Loss of ability to work due to problems with internal organs;
- Lethal outcome is possible if the patient develops chickenpox pneumonia, encephalitis, high fever and hepatitis.
The described consequences can be avoided if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations.
It is not recommended to treat chickenpox on your own, as has already been mentioned several times above. Under unfavorable circumstances, chickenpox may become only the first milestone in a series of health problems.
Folk remedies
With the help of traditional methods of treatment, you can increase the body's defenses and help it quickly get rid of chickenpox intoxication. Herbal drinks are taken orally. Below are some remedies for chickenpox:
- Vitamin drink made from celery and orange juice. Squeeze out the juice from 1 root and 1 citrus fruit, mix and take it all at once before eating.
- A glass of blueberries eaten during the day will support the patient’s immunity.
- For rashes on the mucous membranes, you should rinse your mouth with sage infusion or soda water (1 teaspoon of baking soda per glass of boiled water). The same product can be used to wash the genitals.
- Collection of medicinal herbs No. 1. Mix equal amounts of chamomile flowers, calendula, and string grass. Pour 5 tablespoons of the mixture into 1 liter of water, bring to a boil, remove from heat and let stand for 1 hour. Take half a glass 4 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Collection of medicinal plants No. 2. Finely chop dry raspberry leaves, linden flowers, willow bark and mix in equal proportions. Pour 4 tablespoons of the collection into 1 liter of boiling water and let it brew for 40 minutes. Take half a glass 3-4 times a day before meals.
- Drink with mumiyo. 1 teaspoon of this medicinal raw material is diluted in half a glass of lukewarm water and drunk in the morning before breakfast. This drink perfectly strengthens the immune system and speeds up the healing of wounds.
- Honey drink with lemon. Dilute juice from 1 fruit and a teaspoon of honey in 1 liter of water. Drink several times a day.
The same drink can be prepared with milk and without lemon juice.
Can you swim or not if you have chickenpox?
The question of whether it is possible to wash your hair and body if you have chickenpox rashes is the subject of heated debate. Naturally, any person feels better when he is clean, and not washing for 2-3 weeks (the average duration of the disease) is very problematic.
Today, most doctors have come to the conclusion that swimming during chickenpox is not only possible, but also necessary, under one condition: the acute stage of the disease, characterized by high fever, chills and symptoms of general intoxication, must be left behind.
Water procedures have a positive effect on the skin, cleansing and soothing it. You can take both a shower and a bath. However, there are a number of rules for swimming during chickenpox that must be strictly followed:
- Under no circumstances should you wash with hot water. The water temperature should be comfortable (35–40 degrees).
- It is not recommended to use regular soap - both solid and liquid. It is better to lather your body with a neutral shower gel. A gentle gel-cream for bathing infants is most suitable for chickenpox.
- You cannot use a washcloth or scrubs so as not to disrupt the integrity of the vesicles. You can wash inflamed skin only with your palm.
- You can wash your hair with mild baby shampoo, gently massaging the scalp with your fingers without using nails.
- After bathing, you should not rub your body with a towel, especially a hard one. Ripping off blisters and crusts can lead to wound infection and the development of purulent complications. You just need to blot your skin with a soft flannel diaper. Long hair should be wrung out and allowed to dry on its own. Do not use a hot hairdryer for drying!