Consultation with an ENT (otolaryngologist) – 1,750 rubles.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Nosebleeds are bleeding from the nose that occurs when the vascular wall is damaged. In this case, the blood is scarlet in color and flows out in drops or streams. Excessive bleeding can be life-threatening.
Depending on the location of the damage, there are:
- bleeding from the anterior sections - this affects the small blood vessels of the nasal cavity. Such bleeding is not dangerous and tends to stop on its own;
- bleeding from the posterior sections - large vessels located in the deeper parts of the nose are injured. The blood flows out massively and cannot stop on its own.
Causes of nosebleeds
There are many reasons for bleeding. Weak nasal vessels are one of the most common. For some people, blowing their nose sharply or simply rubbing their nose is enough to cause their nose to bleed. This is not a rare occurrence for people with high blood pressure. Nosebleeds can also occur in a completely healthy person due to sudden changes in atmospheric pressure. Another common cause of bleeding is trauma to the nose.
Nosebleeds can be caused by local or systemic factors
Local factors:
- nasal injury;
- foreign body in the nose;
- inflammatory processes of ARVI, chronic sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, etc.);
- developmental anomalies of the vascular system of the nasal cavity;
- snorting drugs (especially cocaine);
- tumors of the nasal cavity;
- low relative humidity of inhaled air;
- use of a nasal oxygen catheter (dries out the nasal mucosa);
- use of certain nasal sprays;
- surgical intervention in the nasal cavity, etc.
1
Help with nosebleeds in MedicCity
2 Help with nosebleeds in MedicCity
3 Help with nosebleeds in MedicCity
System factors:
- allergy;
- arterial hypertension;
- physical activity, sunstroke, overheating;
- colds;
- side effects of medications;
- alcohol consumption (causes vasodilation);
- blood diseases;
- liver diseases;
- heart failure;
- increased vascular permeability during severe infections (measles, influenza), hypovitaminosis C, hereditary diseases, etc.;
- professional activities associated with sudden changes in barometric pressure (pilot, diver, climber, etc.);
- hormonal disorders (for example, during pregnancy), etc.
When is a nosebleed a reason to make an appointment with an ENT doctor?
From dry mucous membranes due to insufficient air humidity to cancer, from taking aspirin to liver diseases... Why does nosebleed? Just listing the reasons will take a lot of time.
Start to panic when it occurs or treat it as a minor incident? And finally, what to do if it happens?
With questions about the problem of nosebleeds, we came to an appointment with our permanent expert, otolaryngologist at Clinic Expert Kursk LLC, Alexandra Nikolaevna Emelyanova.
- Alexandra Nikolaevna, how common is the problem of nosebleeds in your patients?
Doctors encounter this pathology quite often. According to public information from domestic and foreign researchers, nosebleeds have occurred at least once in 60% of people’s lives. 6% of them visited doctors, about 1.6 out of 10,000 required inpatient treatment. According to other sources, approximately 5-10% of people have an annual episode of nosebleeds. Less than 10% of them go to the doctor, and only 1% of these 10 require hospitalization.
- Is nosebleeds somehow reflected in ICD-10?
Yes, its code is R04.0
-What are the reasons for nosebleeds? When can nosebleeds occur at night?
Most often, this is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of some other pathology or impact.
What can cause nosebleeds? The causes can be divided into two groups: local and general (systemic).
The first includes trauma to the nasal mucosa (including digital), foreign bodies, operations, infectious diseases of the airways, allergic processes, nasal polyps, low air humidity, neoplasms (in particular, juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, nasal hemangioma, papilloma, esthesioneuroblastoma ), inhalation of irritating substances (including cocaine).
The second group includes increased blood pressure, disorders of blood coagulation processes (including those associated with liver diseases, chemotherapy and anticoagulant therapy), acquired disorders of platelet function (for example, after using acetylsalicylic acid and other similar drugs), uremia, vascular pathology , hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, pathological changes in collagen, vasculitis, systemic infections (for example, typhoid fever, nasal diphtheria, congenital syphilis, tuberculosis and others).
Thus, nosebleeds can be a sign of serious pathological conditions and therefore require mandatory clarification of the cause that caused it.
There are no specific reasons for nocturnal nosebleeds.
- Are the causes of nosebleeds the same in children, adolescents and adults? Or are they different?
In principle they are the same. However, there are some features, such as juvenile angiofibroma or bleeding, associated with changes in hormonal status during adolescence. In addition, compared to adults, bleeding is more common in childhood due to trauma to the nasal mucosa (for example, digital), infectious pathologies, and leukemia (leukemia).
- Alexandra Nikolaevna, do you need to see a doctor for every nosebleed?
If it is minor, occurred once, and was successfully stopped at home, then there is no reason to immediately consult a doctor to stop the bleeding.
But even here, finding out the cause of bleeding is mandatory, not to mention all other cases (insignificant in volume, but often repeated, or simultaneous heavy bleeding). Why? Because without this it is impossible to be completely sure how dangerous the cause that caused it is. Therefore, in any case, a person cannot do without a trip to the doctor.
- What research methods are used to clarify the cause of nosebleeds?
These are various laboratory and instrumental methods.
Laboratory methods are aimed, in particular, at searching for disorders of the blood coagulation system (studying its plasma and platelet components).
Instrumental include examination of the nasal cavity (rhinoscopy), including using endoscopic technology, magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
Of course, a rational algorithm for diagnostic search and necessary research should be selected by the doctor depending on the specific clinical situation.
- How can you stop nosebleeds at home?
First aid for nosebleeds involves pinching the nose (pressing the wings of the nose against the nasal septum) for 5-20 minutes. If you have nasal vasoconstrictor drops, you can first put a little cotton wool or, preferably, gauze soaked in 3-4 drops of this drug into the nasal cavity, and then pinch your nose.
It must be remembered that vasoconstrictor drops can increase blood pressure (therefore, be sure to check the instructions for specific drops), and therefore may be contraindicated for hypertension. Therefore, if you are bleeding from the nose and have high blood pressure at the same time, these drops should not be used.
-What should you not do if you have a nosebleed?
When your nose is bleeding, you should not throw your head back. This is one of the most common mistakes. Why shouldn't this be done? This can lead to blood entering the esophagus and then the stomach, causing bloody vomiting, or into the respiratory tract, followed by suffocation. For the same reason, you can't lie down.
During bleeding and for some time after, you should not drink hot drinks or food.
It is necessary to exclude the influence of the factor that allegedly caused the nosebleed: for example, go into the shade if it happened in the sun, stop working, especially if it was physical activity.
- How to properly prevent nosebleeds?
It is necessary to ensure proper hygiene at home and in the workplace. First of all, it is cleanliness and normal air humidity. If there are occupational hazards in the form of polluted air, use personal protective equipment. It is mandatory to undergo scheduled medical examinations and preventive examinations. If an episode of bleeding occurs, you should see an ENT doctor to find out the cause of the bleeding and follow his recommendations.
For reference:
Emelyanova Alexandra Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, otolaryngologist at Clinic Expert Kursk LLC.
Graduate of Kursk State Medical University. She completed her primary specialization in residency in the specialty “otorhinolaryngology”. She completed her full-time postgraduate studies at the same educational institution.
Other interviews with Emelyanova A.N.:
How to treat sinusitis at home?
Why can't my ear hear?
Your nose is stuffy, but you don’t have any drops on hand?
Types of nosebleeds
It is customary to distinguish between 2 types of nosebleeds - “anterior ” and “posterior” .
“Anterior” bleeding is not intense, can stop on its own (or as a result of taking the simplest measures) and does not pose a threat to human life.
With “posterior” nosebleeds, which occur as a result of damage to fairly large vascular trunks localized in the walls of the deep parts of the nasal cavity, a large amount of blood loss is possible. Such bleeding is intense, does not stop on its own, and therefore often requires professional medical attention.
There are also minor, mild, moderate, severe or massive degrees of blood loss during nosebleeds.
If the bleeding doesn't stop
We continue to look at why nosebleeds occur. This disease should be treated by a doctor. If the bleeding does not go away for a long time, it can be caused by an injury to the Kisselbach plexus, which is located on the wall of the nasopharynx. If the patient has pathologies of the hematopoietic system or liver, then the loss can be observed for a long time. It will be quite difficult to stop the bleeding on your own in such a situation, so if such a sign of illness appears, you must call emergency help.
Nosebleeds in children
In the anterior section of the nasal septum there is a rather delicate area where many capillaries are located. It is from this part of the nose that nosebleeds in children occur in 90% of cases. These nosebleeds are not dangerous and can be stopped fairly quickly.
Sometimes the child may bleed from the large vessels of the nose. In such cases, quite strong and intense bleeding occurs. Therefore, it is urgent to call a doctor to help with nosebleeds.
It happens that a child has bleeding from the nose, but the source of bleeding is other organs - the trachea, bronchi, lungs, esophagus or stomach. This is why it is so important to understand the cause of nosebleeds in children. When you bleed from the nose, the blood is a normal color and flows down the back of the throat. Very dark blood, the color of coffee grounds, may indicate bleeding from the stomach.
Rapid and large blood loss is dangerous for the health and life of the child. With significant blood loss, the child may experience general weakness, dizziness, pale skin, noise and ringing in the ears; lines before the eyes, thirst and rapid heartbeat.
Then blood pressure decreases, the child may lose consciousness.
When bleeding from the back of the nose, the child may swallow blood, and only by vomiting with blood clots can one understand that he has a nosebleed.
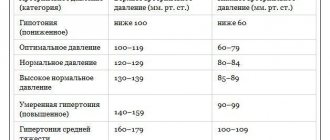
At what pressure?
Blood can come out of the nose at absolutely any pressure level. With hypertension, its flow to the head will occur under pressure, and the walls of the mucous vessels burst as a result of such pathological effects.
In the case of low pressure, the capillaries gradually shrink and the integument of the body turns pale. After some time, bleeding begins. Sudden changes in pressure levels are especially dangerous, as they contribute to rapid wear and tear of blood vessels.
Causes of nosebleeds in children
Damage to the vessels of the nasal mucosa can occur in a child in a variety of cases. Among the main causes of nosebleeds in childhood are the following:
- nasal injuries (fracture, bruise, damage to the nose by a foreign object stuck into it);
- medical operations performed on the nose;
- tumors, polyps, ulcers in the nose;
- rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis;
- deviated nasal septum;
- sun and heatstroke;
- sudden surges in pressure;
- physical activity that is intense for the child’s body;
- lack of calcium, potassium and vitamin C;
- low blood clotting;
- hormonal changes in adolescence;
- hepatitis, liver diseases, etc.
Among women
In addition to the general reasons that can provoke bleeding, in the fair sex, under certain conditions, additional circumstances arise that can lead to such a pathological condition. These include:
- Following various illiterate diets that cause a deficiency of fats, proteins and vitamins in the body.
- Diseases characterized by hormonal imbalances.
- The use of medications for the treatment of thrombophlebitis with varicose veins, which contribute to blood thinning.
Diagnosis of nosebleeds
Diagnosis of nosebleeds in adults and children is carried out using an external examination, examination of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and pharynx. Sometimes it is necessary to differentiate nosebleeds in adults and children from bleeding, the source of which is other organs - the lungs, esophagus or stomach. In such cases, blood enters the nasal cavity and then flows out of the nostrils. It is necessary to undergo examination by other specialists and identify the cause.
MedicCity welcomes specialists from more than 30 specialties. You can make an appointment with them at any time convenient for you.
1 Diagnosis of nosebleeds in MedicCity
2 Diagnosis of nosebleeds in MedicCity
3 Diagnosis of nosebleeds in MedicCity
Medical assistance
Adults and children with severe bleeding and significant blood loss are hospitalized in the ENT department. If you managed to quickly stop it at home, then the child should still be shown to an otolaryngologist and the adult should also consult a doctor. For frequent nosebleeds in children and adults, when no obvious cause can be found, you should be examined by a hematologist, endocrinologist, or neurologist.
Most often, blood flows from the Kisselbach area, to prevent new cases, this place is cauterized. The ENT doctor may do the following:
- remove polyps, foreign body
- posterior or anterior tamponade soaked in a 1% solution of feracryl, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, preserved amnion
- insert a tampon with vagotil or trichloroacetic acid to cauterize the vessel
- coagulation using one of the modern methods: electric current, laser, ultrasound, silver nitrate, liquid nitrogen, chromic acid or endoscopic cryodestruction
- it is possible to administer an oil solution of vitamin A, sclerosing drugs
- use a hemostatic sponge
- in case of severe blood loss, the use of fresh frozen plasma, donor blood transfusion, intravenous administration of hemodez, rheopolyglucin and aminocaproic acid are indicated
- if the above methods do not have an effect, surgical intervention is possible - embolization of large vessels (ligation) in the problem area of the nasal cavity
- prescribing drugs that increase blood clotting - vitamin C, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, Vikasol.
After a nosebleed, it is not advisable to consume hot foods and drinks; you should not exercise for several days, as this promotes a rush of blood to the head and can provoke a recurrence.
Treatment of nosebleeds
If you have a nosebleed, you need to stop the bleeding as quickly as possible to prevent blood loss. Next, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that caused the bleeding - for example, normalize blood pressure. It is necessary to prevent the possible consequences of acute blood loss (decrease in circulating blood volume, for example), to carry out hemostatic therapy.
First aid for nosebleeds
Stopping nosebleeds can be done in the following ways:
In case of “front” nosebleeds, it is necessary to sit the victim down or lie him down, slightly raising his head. It is not recommended to tilt the patient's head back too much: this could cause blood to enter the respiratory tract. A cotton or gauze swab moistened with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide must be inserted into the bleeding nostril, then, pressing the wing of the nose from the outside to the nasal septum with your fingers, hold it in this position for 10-15 minutes - this way the damaged vessel will thrombose. Vasoconstrictor drops (Nazivin, etc.) can also provide a good hemostatic effect. In this case, the drops are not instilled into the nose, but are moistened with a tampon. Cold should be applied to the bridge of the nose.
If your efforts are unsuccessful, and you do not know how to stop a nosebleed on your own, you need to call an ambulance. You should also seek emergency medical help if blood flows from the nose in a stream, without clots.
Prevention
To avoid nosebleeds, humidify the air in the room using a steam generator, you can also put wet towels on the radiator, spray the room with a spray bottle, and have a lot of indoor plants in the house.
If crusts often form in your nose, you should not pick them out; it is better to periodically instill 2-3 drops of sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil into your nose.
To prevent nosebleeds, a course of ascorutin (1 month) is recommended, which strengthens the walls of the capillaries.
Why does my child often bleed from the nose?
More details
How to stop epistaxis? First aid for bleeding
If an adult or elderly person has a nosebleed, follow these steps:
- First aid is to stop the bleeding. First you need to calm down, sit the victim on a chair, tilt his head forward a little.
- In order for air to freely penetrate into the victim’s lungs, you should unbutton his belt, the top buttons of his shirt, untie his tie (if epistaxis occurs in men), unfasten his bra, and remove jewelry (if nosebleeds occur in women).
- You need to place a cold compress (ice from the freezer, wrapped in a napkin) on the bridge of your nose. You need to keep the compress for 10 minutes.
- If blood has dropped into the nasopharynx, it needs to be spat out.
- If the bleeding is mild, you can pinch the nostrils at the wings of the nose with your fingers for 5-7 minutes. If there is an assistant who will pinch the victim's nostrils, the patient can stretch two arms up if epistaxis is observed from two nostrils, or one corresponding to the bleeding nasal passage. Thus, the blood flow in the organ slows down, and the resulting blood clot clogs the vessel.
- If there is significant bleeding, 3% peroxide or any drug with a vasoconstrictor effect can be instilled into the nostrils.
- If the blood continues to flow, then peroxide is applied to a cotton swab and inserted into the nasal passage, gently pressing it against the central wall of the nose.
- If blood flows through the nose unexpectedly due to overheating, the victim must be taken to a cool place and an ice compress applied to the nose. The victim will need hospitalization.
- If the patient is unconscious, you should lay him on his back and move his head to the side. Then call an ambulance.
- If first aid does not give positive results within 15-20 minutes, you need to go to the clinic.
If measures to stop nasal hemorrhage are successful and the victim feels well, he should be given sweet tea and taken out into the fresh air.
What can and cannot be done when bleeding?
What is prohibited?
- Throw your head back - blood can go down the esophagus, causing a gag reflex; cause suffocation.
- Do not blow blood from your nose: the consequence of rash actions is severe bleeding.
- Do not remove the tampon from the nostril with a sharp movement - it should first be soaked with peroxide.
- You should not lean forward too much - this will worsen hemorrhage.
- It is not recommended to lie horizontally and hold your head straight - it is better to turn it to the side.
- If the reason why blood is pouring from the nose is a foreign object, there is no need to try to get it out yourself.
In pregnant women
When carrying a baby, many problems with a woman’s body manifest themselves in the form of this symptom. If a few drops appear, this is not a cause for concern, but the observing specialist should still be told about it.
Constant bleeding is considered very dangerous for the health of a pregnant woman. The reasons may be hormonal changes in the body, calcium deficiency, severe toxicosis, hypertension, heat stroke, infection, as well as prolonged exposure to the sun.
In men
Experts often associate bleeding with nasal injuries. It is generally considered to be a direct consequence of active play in adolescence or childhood. In addition, the state of the body and the health of the nasopharynx can be affected by smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages and hypertension, which is diagnosed in men more often than in the fair sex. This is what distinguishes them from other groups of patients.
If the bleeding is repeated, abundant, and accompanied by painful sensations, then it is necessary to examine the body.