Blood in urine: causes
When wondering why urine contains blood, it is important to understand that there are more than 150 reasons for this phenomenon. It can enter the biological fluid from the bladder, urethra, ureters and kidneys - it is through these organs that urine passes before being excreted from the body. The most common reasons why blood appears in the urine are presented in our table below:
| Etiology | What diseases does it appear in? Features |
| Pathologies of infectious nature |
|
| Neoplasms of benign and malignant nature | Cancerous tumors appear after forty years and, in addition to blood clots in the urine, are rarely accompanied by other clinical manifestations. Neoplasms of a benign nature in the organs of the urinary system develop extremely rarely in the form of angiomyolipomas and renal cysts. |
| Traumatic injuries of the pelvic organs |
|
| MChB | Stones in the kidneys or bladder not only create optimal conditions for the development of inflammatory processes, but can also damage the mucous membrane of the kidneys, ureters, and also the urethra (upon exit). |
| Genetic abnormalities | Polycystic kidney disease affects not only the kidneys themselves, but also the liver, and is characterized by cystic degeneration of functionally active epithelial cells. |
| Pathological conditions in which blood clotting disorders are observed |
|
| Pathological conditions of the renal vessels |
|
| A number of kidney diseases |
|
The above reasons for the appearance of blood in the urine are common to men, women, children and elderly patients. However, there are also specific reasons characteristic of representatives of different groups.
| Group | Diseases in which this symptom is observed |
| Women |
|
| Men |
|
| Children | Blood in a child's urine may occur due to:
|
| Elderly people |
|
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of conditions that are accompanied by hematuria, you need to:
- Avoid uncontrolled use of any medications and do not exceed the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
- Dress according to the ambient temperature and avoid hypothermia.
- Avoid damage to the body - at home, during sports training or work.
- Normalize the diet and quality of nutrition.
- Avoid significant physical activity and do not lift heavy objects.
- Carry out hygiene measures carefully and regularly.
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Improve or change working and living conditions, avoid staying near sources of intoxication.
If you have a hereditary predisposition to the development of any disease, you need to undergo regular diagnosis by a specialist in the appropriate field. Timely examination and, possibly, identification of pathology will allow it to be stopped without consequences for health. It is important to eliminate all diseases in the acute form of their development, preventing them from taking a chronic course.
Bloody urine always indicates health problems. The main reason may be disease or damage to the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. To avoid the development of negative consequences and maintain reproductive status, a woman needs to visit a doctor and not deviate from his recommendations.
Blood in urine during pregnancy
The reasons for the appearance of blood in the urine during pregnancy have not yet been identified, despite the fact that this phenomenon is not considered normal. It can occur at any time and, according to experts:
- in the early stages may be caused by hormonal changes;
- in later periods - by the growth and descent of the fetus, which increases pressure on the organs of the urinary system and leads to impaired blood flow in the kidneys.
It is important to understand that such conditions are associated with a threat to the fetus and mother, and are therefore considered dangerous. They may be accompanied by oxygen starvation of the fetus and, as a consequence, dysfunction of the placenta. In turn, the latter can lead to complications such as:
- miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- weakening of labor.
In addition, the expectant mother may develop uterine bleeding.
Possible complications
If the disease or condition that caused the development of hematuria is not eliminated for a long period of time, the level of hemoglobin may decrease and the formation of anemia. Other potential risks:
- Miscarriage, premature onset of labor. Develops due to partial or complete detachment of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus.
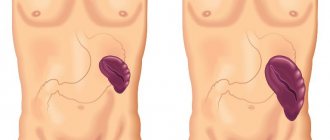
- Hydronephrosis, or dropsy of the kidney, is the expansion of its membranes due to a stone blocking the outflow of urine. If the obstruction is not removed, the risk of organ loss increases.
- Infertility. Occurs due to adhesive disease. It develops against the background of prolonged inflammation in the urogenital tract, endometriosis, or previous trauma to the pelvic or abdominal organs.
In almost 100% of cases, these complications can be avoided.
Classification of hematuria
The classification of hematuria is carried out taking into account the factors that led to its development and the amount of blood in the urine.
| Types of hematuria | Characteristics |
| Classification by factors of occurrence | |
| Postrenal | The symptom appeared as a result of kidney pathologies or injuries. |
| Extrarenal | The symptom appeared as a result of other pathological conditions. |
| Classification by the amount of blood in the urine | |
| Macroscopic | The amount of blood is enough for the urine to be colored red. In addition to blood, it may contain other impurities and pus. |
| Microscopic | The amount of blood is minimal, so it has virtually no effect on the color of urine. Abnormal changes can only be detected by special tests. |
Preventive measures and treatment prognosis
The best way to avoid hematuria and pain during urination is prevention. You need to start taking care of your health. Expert advice will help you make the right lifestyle changes:
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- choose underwear from natural fabrics;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- use contraceptives if there is no regular partner;
- immediately go to the toilet when the urge arises;
- try to avoid hypothermia;
- undergo a preventive examination once a year;
- observe drinking regime;
- Healthy food;
- completely cure diseases, especially infectious ones.
Similar measures are also suitable if there is blood and pain during urination. According to experts, the prognosis for recovery will depend on the cause of symptoms and the effectiveness of the treatment regimen.
Many diseases and pathological conditions cause pain and are manifested by blood during urination. The patient will need to see a doctor to prescribe laboratory and instrumental examination methods. Based on the diagnostic results, a course of therapy will be drawn up aimed at combating the causative factor and relieving symptoms.
Blood in urine as one of the clinical manifestations
Blood in the urine is one of the symptoms of a number of diseases and can be combined with other clinical manifestations. So, with:
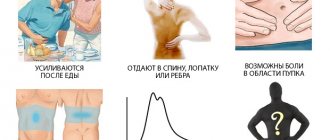
- inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), it is accompanied by pain localized in the lumbar region and side and radiating under the scapula;
- In addition to blood, urine contains other impurities such as sand and stones;
- significant blood loss is indicated by rapid fatigue, frequent dizziness, general weakness, pallor and persistent thirst;
- liver pathologies, the appearance of discharge in the form of pinkish or yellowish clots is observed;
- cystitis, there is a frequent urge to urinate, pain when emptying the bladder, pain and burning, and sometimes purulent discharge from the urethra appears;
- In the development of malignant neoplasms, large blood clots are released with urine.
Using traditional medicine techniques
The basis of traditional medicine is medicines. If necessary, other more radical methods are prescribed. It all depends on the cause of hematuria:
- A bacterial infection can be treated with antibiotics. Additionally, drugs with anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and diuretic effects are prescribed. For general strengthening of the body, it is recommended to use immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
- Oncology is treated only by surgery. After the operation, courses of chemotherapy and radiotherapy are prescribed.
- The treatment regimen for urolithiasis depends on the size of the stones. Stones up to 5 mm can come out on their own. Patients are recommended a course of diuretics. Additionally, uroantiseptics are prescribed to avoid the development of inflammation. Larger formations will have to be crushed or cut out.
- Hematuria caused by trauma resolves on its own after the damaged tissue heals. Drugs are selected individually. In serious cases, the use of hemostatic medications will be required. The operation is prescribed if there are indications.
- Erosion and prolapse of the uterus are treated surgically. In the first case, cauterization is necessary, and in the second, vaginoplasty. Other methods are less effective.
During pregnancy, pain when urinating with blood in women does not always indicate a dangerous malfunction in the body. If the problem still lies in the development of pathology, then the doctor should prescribe treatment, taking into account the duration of pregnancy and the patient’s condition.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine helps speed up tissue repair, remove excess moisture from the body and relieve inflammation. Medicines are prepared from natural ingredients, so the risk of adverse reactions is minimal.
Several effective recipes are presented in the table:
| Name | Ingredients | Cooking method | Features of application |
| Barberry decoction | • 250 ml boiling water; • barberry root or bark. | • pour boiling water over the ingredients; • let it brew for 20 minutes. | Drink 70 ml in the morning, lunch and evening. |
| Blackberry infusion | • 125 ml red wine; • 1 tbsp. l. blackberry roots. | • pour wine over the roots; • boil the resulting mixture on fire for 10-15 minutes. | Take 50 ml 3 times a day. |
| Bearberry powder | • powdered sugar; • bearberry leaves. | • mix the components 1:1. | Use the product every 4 hours for 1 hour. l. |
Advice! Despite the positive effects of medicinal herbs, before using traditional medicine at home, you should consult a doctor. In addition, such recipes can only be used as a supplement to the main treatment regimen.
Blood in urine: diagnosis
Hematuria is insidious in that it is not always possible to determine the presence of blood in the urine by eye. In the absence of other symptoms, the patient does not consult a doctor while the disease progresses. At the same time, it is necessary to understand that sometimes the color of urine changes due to eating food with dyes or certain medications. There are three ways to determine the presence of blood in urine:
- organoleptic - not accurate enough, since during visual determination the red dye can be mistaken for blood;
- rapid test - may give an incorrect result if there is hemoglobin in the urine;
- using a microscope - gives the most accurate result.
In order to determine the etiology of blood in the urine and prescribe appropriate treatment, the following diagnostic tests are performed:
- examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis;
- general and bacterial urine analysis;
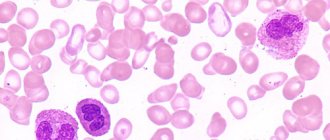
- examination of urine with a microscope to identify cancer cells;
- ultrasonography;
- CT scan.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose the disease, laboratory tests are performed. By comparing the test results with the picture of the disease, a diagnosis can be made. Based on the signs of urination, the doctor can determine the disease.
Timely consultation with a doctor significantly increases the patient’s chances of a full recovery.
To identify the disease, a comprehensive examination is necessary. If the doctor finds it difficult to diagnose the disease based on the test results, then a diagnostic method is used using functional devices.
Our doctors
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Blood in urine: treatment
Treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused such a phenomenon as blood in the urine. Specialists at the multidisciplinary CELT clinic individually develop a treatment plan depending on the etiology of the pathology.
| Etiology | Treatment |
| Trauma to the pelvis or abdomen with damage to the bladder or kidney | They resort to drug therapy methods, if possible, but most often they are treated through surgery. |
| The presence of benign or malignant neoplasms in the kidneys | Surgery aimed at removing the tumor. |
| Urolithiasis disease | A surgical intervention aimed at removing the stone or crushing it using ultrasound. |
| Infection in the bladder and urethra | It is advisable to use antibiotic therapy methods. |
| Prostate pathologies | Therapeutic techniques and drug treatment with antibiotics are used. If they do not give the desired results, surgery is performed. |
Blood in the urine is a sign of serious pathologies, so specialists at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic recommend seeking medical help immediately after identifying it or suspecting a health condition.
Remember: the earlier a disease is detected, the greater the chance of curing it. Often, timely contact with our specialists allows you to avoid surgical intervention and eliminate the existing problem using conservative methods. Contact CELT!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What is the urinary tract?
The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for removing waste and excess fluid. The urinary tract includes:
- two kidneys
- two ureters
- bladder
- urethra
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine. Each day, the kidneys filter 120 to 150 liters of blood to produce 1 to 2 liters of urine, which consists of waste and excess fluid. Children produce less urine than adults. Urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters. The bladder stores urine until it is released through urination. When the bladder empties, urine flows out of the body through a tube called the urethra at the bottom of the bladder.