Hydrocephalus: ICD-10, general description of the disease
The word “hydrocephalus” itself is formed by combining two Greek words meaning “water” and “head”. By the way, this is why the disease is often called dropsy of the brain.
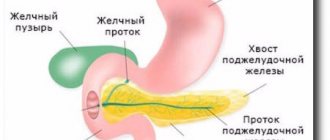
Before finding out what hydrocephalus is, it is worth considering some anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the human body. CSF constantly circulates between the brain and spinal cord - cerebrospinal fluid in the brain is concentrated mainly in the ventricles (there are four in total), and also enters the subarachnoid space that separates the meninges.
Liquor performs a number of important functions. It is with this fluid that many nutrients are supplied to the nerve tissues, and toxins and metabolic products, on the contrary, are removed from the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid also protects nerve structures from compression, adhesion and mechanical stress.
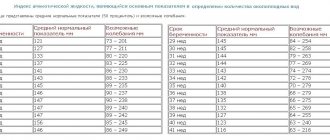
Normally, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid in infants is about 50 ml, and in an adult - no more than 150 ml. If, for one reason or another, much more cerebrospinal fluid is formed than necessary or its circulation is impaired, then hydrocephalus develops.
ICD-10 assigned the pathology code G91. Against the background of the disease, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles of the brain, which leads to a sharp increase in intracranial pressure. Since the skull of an adult consists of hard bones, the abundance of fluid puts pressure directly on the nerve structures.
How is hydrocephalus formed?
Hydrocephalus is water on the brain. In the process of brain activity, metabolic processes occur. For their implementation, liquid is required. It contains essential nutrients. It circulates inside the skull, washing the brain, and is constantly renewed.
The liquid is called cerebrospinal fluid. The child's volume is 50 ml. In adults, this figure is 3 times higher (120-150). It is constantly updated. In infants - 8 times a day, in adults - 3. The hematopoietic system, spinal cord and brain are involved in production. In the brain, the ventricles are responsible for the renewal function. The veins in the parietal region are responsible for absorption.
Liquor nourishes and protects the brain from mechanical shocks and injuries, and creates the necessary microenvironment. It maintains the pressure necessary for life, which ranges from 70 to 180 mm Hg. Art. If changes occur in the body, circulation is disrupted and fluid is poorly absorbed. The amount of liquid increases. Hydrocephalus in a child occurs from an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull.
Interesting: Fever and headache in a child
Causes of congenital hydrocephalus
Who is a hydrocephalus? This is a man suffering from dropsy. It should be understood that the disease can develop at any age. But as statistics show, very often hydrocephalus is congenital. So what is the reason for the appearance of dropsy of the brain in a child? The reasons may be as follows:
- congenital malformations of the system responsible for the synthesis and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (stenosis of the Sylvian aqueduct, abnormal structure of the subarachnoid space);
- craniovertebral anomalies;
- infections suffered during fetal development (for example, rubella, toxoplasmosis, cytomegaly, syphilis);
- head injuries during the birth process.
Acquired forms of dropsy: causes and risk factors
The disease can develop after the birth of a child or already in adolescence, adulthood, or old age. The causes of hydrocephalus of the brain can be different.
- The accumulation of fluid is most often associated with inflammation of certain parts of the central nervous system. Dropsy is often complicated by encephalitis, meningitis, and arachnoiditis.
- The list of causes includes vascular disorders, including the formation of intracerebral hematomas, hemorrhage into the ventricles, and stroke.
- Hydrocephalus can result from severe traumatic brain injury.
- Cysts and intracerebral tumors often grow into the cerebral ventricles, thereby blocking the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Features of replacement hydrocephalus
Replacement (atrophic) dropsy, as a rule, develops in old age. It is classified as a separate group, since the development of the disease is associated with age-related atrophy of nerve tissue. The brain shrinks, and the cerebrospinal fluid, in fact, simply fills the free volume of the skull.
In elderly patients, atrophic hydrocephalus may be associated with severe forms of hypertension, atherosclerosis of the vessels carrying blood to the brain and back, and macroangiopathy due to diabetes mellitus.
Classification of the disease
There are many types of hydrocephalus. For example, depending on the development mechanism, they distinguish:
- open form (either hypersynthesis of cerebrospinal fluid or impaired absorption is observed);
- closed (develops against the background of impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid).
The location of the cerebrospinal fluid accumulation is also important. Stand out:
- internal dropsy (cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles);
- external (cerebrospinal fluid is concentrated in the subdural and subarachnoid spaces).
Depending on the course of hydrocephalus, it can be:
- acute (development is very rapid; no more than 3 days pass from the onset of cerebrospinal fluid accumulation to the appearance of the first symptoms of decompensation);
- subacute (progresses over a month);
- chronic (the disease develops slowly, the symptoms are not noticeable at first, since their intensity increases gradually; the disease develops over 6 months or longer).
Depending on the nature of development, two more types are distinguished:
- compensated (stabilized) hydrocephalus is said to exist if intracranial pressure does not reach critical limits, the flow of cerebrospinal fluid is gradually restored, and the disease does not develop;
- Increasing (progressive) dropsy of the brain is caused by a sharp increase in pressure inside the skull, is accompanied by atrophy of nerve tissue and is very difficult to respond to conservative therapy (sometimes taking medications does not give any result at all).
Classification of pathology
Dropsy is classified according to numerous criteria. The most commonly used:
- By location. Divided into external and internal hydrocephalus. The internal one is localized in the ventricles, the external one - in the subarachnoid space. There are mixed types.
- According to the form. Open and closed dropsy are determined. When the form is open, nothing prevents the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid; when it is closed, there are adhesions and neoplasms. It is called occlusal. The occlusive form of hydrocephalus affects infants with brain tumors.
- According to the nature of the course, four forms are distinguished. Acute symptoms appear very quickly: within a few days. With this development, surgical intervention is necessary. Symptoms of the chronic form are blurred and visible after 6 months. With compensated dropsy, the cavities remain dilated, but the pressure drops. In this form, dropsy returns after injury to the skull. External dropsy is easily identified. It is large, the fontanel protrudes above the skin. With this form, the baby often throws back his head and arches his back. The internal closed form of leakage is considered dangerous.
Interesting: Why does a 12-year-old child have a headache almost every day?
Dropsy in adults: features of the clinical picture
The space of the cranium is limited. That is why the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid leads to an increase in intracranial pressure - this is how very characteristic symptoms of hydrocephalus of the brain appear. Patients (adolescents and adults) complain of severe headaches that cannot be relieved with analgesics. In addition, severe nausea is observed, leading to vomiting attacks. Patients note a feeling of pressure on the eyeballs.
The only exception is atrophic dropsy - there are no signs of increased pressure inside the skull with this form of the disease.
As the cerebrospinal fluid begins to compress the structures of the brain, neurological symptoms appear. Many patients suffer from vestibular ataxia, which is accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness. A person's gait becomes unsteady.
If, due to the disease, the optic nerves are damaged/compressed, then a decrease in visual acuity is observed. In some patients, the field of vision is significantly narrowed. If we are talking about chronic hydrocephalus, then there is a possibility of developing atrophy of the optic nerves and complete loss of vision.
Dropsy can lead to impaired tendon reflexes, muscle hypertonicity, paralysis and paresis. Some patients complain of a complete loss of skin sensitivity - they stop feeling pain, pressure, temperature, touch.
Sometimes the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid causes mental disorders. The illness, as a rule, affects the emotional sphere: a person’s mood often changes, he loses emotional stability. Sometimes causeless euphoria appears, which, however, quickly turns into deep apathy and a state of complete indifference. A sharp increase in cerebrospinal fluid levels can lead to aggressive behavior.
Causes of the disease
Prevalence – 1 case in 2-3 thousand newborns. This figure is small. But the diagnosis of “hydrocephalus” is considered the most common developmental disorder in preschool children.
Girls get sick less often than boys. The disease is detected in the first months of a baby's life. Dropsy in moderate form goes unnoticed. Over time it becomes chronic. The disease manifests itself differently in a child and an adult.
In an adult, the skull is formed and the bones are strong. Excess cerebrospinal fluid leads to increased intracranial pressure. In children under 2 years of age, the bones are soft and flexible. An excess of fluid causes an abnormal expansion of their head circumference.
Water forms in a child's head for many reasons. The disease can be congenital or acquired. Congenital factors include:
- injuries caused by difficult childbirth;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia);
- genetic disorders;
- infections transmitted in the womb.
Symptoms of the disease in children
In newborns, the disease occurs differently. The fact is that a child’s skull bones are more flexible, pliable, and the fontanelles have not yet had time to heal. This is why intracranial pressure does not increase, but the shape of the child’s head changes. The fontanel swells, and sometimes its pulsation can be seen with the naked eye. The veins of the scalp become very swollen, and the movement of the eyeballs is impaired, which is associated with swelling and compression of the optic nerves. The baby is slightly behind in development - later he begins to hold his head up, sit, crawl, and roll over.
If treatment was not started on time, the child’s head takes on a very characteristic shape. The skull of a hydrocephalus is spherical, too large. The patient's eyes are deep-set, ears protrude, and the skin becomes thin.
Who is hydrocephalus and how does hydrocephalus affect the child’s well-being? Unlike adult patients, children rarely suffer from emotional and mental disorders - most often there is a delay in intellectual development. A small patient with this diagnosis is usually apathetic, inactive, and often suffers from obesity.
Hydrocele in a child is very rarely accompanied by psychotic attacks, epileptic seizures and hallucinations, but this possibility should not be excluded.
How does the disease manifest?
In children under 2 years of age
In children under 2 years of age, the presence of the first signs will indicate the presence of hydrocephalus. This:
- deterioration of appetite and sleep;
- refusal of breastfeeding;
- moodiness, nervousness;
- decreased vision, squint, rolling of the eyeball;
- thin, shiny skin of the head with pronounced blood vessels;
- abnormal size of the skull;
- convulsions;
- muscle weakness;
- difficulty holding the head;
- growth retardation.
An experienced doctor will be able to identify dropsy based on the presence of minor symptoms. For minor problems, medication treatment is sufficient. For more severe symptoms, surgery is necessary.
In children over 2 years old
It happens that the disease begins later. The symptoms are characterized by intracranial pressure. The child has:
- severe pain in the head;
- vomit;
- violation of movement coordination;
- fatigue and drowsiness;
- nervousness;
- vision loss and blindness.
School-age children do not adapt well to a group, have difficulty understanding the program, study poorly, and lose their memory. They suffer from nervous disorders. The causes may be various types of lesions:
- tumors;
- meningitis;
- aneurysm;
- renal failure;
- heart and vascular disease;
- hypertension;
- skull injuries.
Diagnostic features
You already know who hydrocephalus is, what symptoms accompany the disease and what you need to pay attention to. If you have any suspicions, it is better to consult a doctor immediately.
When it comes to dropsy of the brain in a child, the external signs, as a rule, are so characteristic that a specialist can make a diagnosis based on a general examination alone. But even in such cases, additional examinations are necessary, because it is important to determine the causes of development and the form of hydrocephalus.
First of all, ultrasound is performed - echoencephalography. This quick and painless procedure assesses the degree of pressure build-up inside the skull. Children in the first year of life are usually sent for ultrasonography - ultrasound scanning is carried out through the fontanelle.
X-rays of the skull are informative - in the images the doctor can see the separation of the sutures between the bones of the skull, as well as the thinning of the bone tissue itself. On the inner surface of the bones you can see a kind of “indentation”. Additionally, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain are performed - such procedures allow not only to confirm the presence of hydrocephalus, but also to determine the nature and causes of the disease, detect cysts, tumors, and anatomical features.
The patient is also sent to an ophthalmologist so that specialists can evaluate the condition of the optic discs, assess the acuity and field of vision, as well as some other characteristics.
If there is reason to believe that the illness is caused by an infection, the patient may be referred for a lumbar puncture. This procedure is unpleasant, but it allows you to obtain samples of cerebrospinal fluid and check it for the presence of certain pathogens and markers. For congenital dropsy, doctors recommend PCR diagnostics. MRI of cerebral vessels is performed if serious vascular disorders are suspected.
Possible complications
You already know what hydrocephalus is and what symptoms accompany the disease. This is a serious pathology, because any effect on the brain is fraught with complications. If we are talking about congenital forms of the disease, then the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid leads to compression of the nerve tissues - the baby’s brain cannot develop normally.
In addition, rapidly progressing hydrocephalus can lead to consequences such as:
- cerebral edema;
- epileptic seizures;
- bleeding in the brain (stroke);
- displacement and compression of certain parts of the brain;
- comatose states;
- failure of the respiratory system.
Sometimes the accumulation of fluid in the skull can result in the death of the patient, so in no case should you delay the start of therapy.
Acquired hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult: treatment with drugs
Modern medicine offers patients a lot of treatment options. If a couple of decades ago more than half of the patients died, today the mortality rate is about 5%.
Therapy in this case directly depends on the causes of the disease, the stage and reasons for its development. If hydrocephalus is the result of an inflammatory or infectious disease, then the patient is first prescribed a course of antibiotics or antiviral agents. Sometimes the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain is not too large - in such a situation, excess fluid is eliminated with the help of diuretic drugs (Furosemide, Acetazolamide).
But, according to statistics, surgery for hydrocephalus is necessary in the vast majority of cases.
Diet features
Hydrocephalus of the brain is a disease that is accompanied by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. That is why patients with this diagnosis are recommended to adhere to a special diet. First of all, they need to completely exclude from the diet foods that retain fluid in the body. Potentially dangerous are salty foods and dishes, sausages, smoked meats, fatty poultry and meats, sweets and other confectionery products, white bread, hot spices. Before purchasing a product, be sure to study its composition - it should not contain sodium gluconate.
You can include foods that have mild diuretics in your diet (for example, lemon, oatmeal, cranberry juice, ginger, celery, eggplant, watermelon, parsley). Diet is not a way to get rid of dropsy - it is only auxiliary.
Some traditional healers recommend taking an alcoholic tincture of black elderberry root, as well as powder made from buckthorn bark or berries. But, again, such folk medicines can only be used as an auxiliary therapy, and they can only be taken with the permission of the attending physician.
Treatment
After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
Conservative treatment
In the initial forms, medications are prescribed to relieve pressure. Diuretics are used. The child is being treated in hospital. Ultrasounds are performed regularly. Help from osteopaths is possible if there is a trauma during childbirth. They use massage and the correct technique for realigning bones.
Surgical treatment
In advanced stages, surgery is required. A shunt is inserted, and with its help the cerebrospinal fluid is drained out. This operation is unsafe as it can cause infection. It is necessary to carry out several of them to achieve results. Current technology allows the use of advanced methods. The operation of endoscopic ventriculostomy provides a complete cure and does not cause infection during the intervention.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are used for treatment. Recipes for tinctures and decoctions contain herbs that help remove excess water from the body: mint, lemon balm, calamus, cornflower, black elderberry, garlic and radish, buckthorn berries. Herbal medicine is used after consultation with a doctor.
Surgery
The nature of the surgical intervention depends on what caused the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. It is possible that during the operation the neurosurgeon will remove a tumor, cyst, intracranial hematoma, hide and clean the abscess, and separate adhesions that have arisen between the walls of the channels for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
If it is impossible to eliminate the cause of cerebral hydrocele, shunting is performed. For hydrocephalus, a similar procedure helps reduce intracranial pressure by creating additional pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Prognosis for patients
How dangerous can hydrocephalus be? The prognosis directly depends on how quickly the disease was diagnosed and how appropriate the choice of therapy was. Very often, dropsy can be, if not completely cured, then at least the further progression of the disease can be controlled.
How long do people live with hydrocephalus and how does the disease affect a person’s condition? If we are talking about timely detected hydrocele of the brain in a newborn, then there is a high probability that the baby will develop at a normal pace and live a completely normal life. Yes, there may be problems associated with the maintenance of shunts installed in the brain, but they can also be solved.
If the disease was diagnosed at later stages, complications are possible. The child’s brain will not be able to develop normally, which can lead to speech disorders and delayed intellectual growth in the future. Sometimes damage to the central nervous system is so severe that it causes disability.
Hydrocephalus - symptoms and treatment
To date, the method of surgical treatment of hydrocephalus has proven its effectiveness.
Two types of surgical interventions are used: liquor shunting and neuroendoscopy. Such operations are performed by a neurosurgeon, i.e. a surgeon specializing in the treatment of diseases of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.
CSF shunt surgery
In a CSF shunt, a thin tube called a shunt is inserted into a ventricle of the brain. Excess cerebrospinal fluid contained in the brain flows through the shunt to another anatomical region of the human body.
When installing the drainage end of the system into the abdominal cavity, the shunt is called ventriculoperitoneal . In this case, excess cerebrospinal fluid entering the abdominal cavity is absorbed into the bloodstream.
When the draining end of the system is installed into the chamber of the heart (usually the right atrium), the shunt is called ventriculoatrial . They are typically implanted in children because growth has less impact on their functioning and requires replacement less often, unlike ventriculoperitoneal shunts.
Lumboperitoneal are rarely used . They drain cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid space of the lumbar spinal cord into the abdominal cavity.
In the system of tubes through which cerebrospinal fluid flows from the brain, there is a valve with a given throughput. Depending on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure, an appropriate valve is selected for the patient before the operation, which makes it possible to control the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity, i.e. having a given capacity. The neurosurgeon planning surgery determines the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain and selects the appropriate valve. It usually appears as a raised “bump” under the scalp.
Today, two types of valves are used:
- with given (preset) parameters that have a certain throughput for cerebrospinal fluid;
- adjustable magnetic valves. When choosing such valves, the attending physician, using special equipment, can remotely, without making additional incisions, change the pressure of the valve and achieve an optimal clinical result, eliminating such adverse side effects as insufficient or excessive drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid.
CSF bypass operations are performed under general anesthesia and take from one to two hours. After surgery, patients usually remain in the hospital for several days.
If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid through the shunt is disrupted or infection occurs, repeated surgery may be required.
Endoscopic ventriculostomy of the third ventricle
This operation is an alternative to liquor shunt surgery. Instead of installing a shunt, the surgeon creates a hole in the lower wall of the third ventricle and creates a bypass for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid to the surface of the brain, where its unhindered absorption occurs.
This operation is not universal for all patients with hydrocephalus, but can be used to block the cerebrospinal fluid pathways - occlusive hydrocephalus. In this case, the cerebrospinal fluid flows through an artificially created hole - bypassing the clogged cerebrospinal fluid pathways.
The operation of endoscopic ventriculostomy of the third ventricle is performed under general anesthesia. The neurosurgeon makes a burr hole in the skull with a diameter of about 10 mm and uses an endoscope to examine the ventricles of the brain from the inside. An endoscope is a long, thin tube with a light source and a miniature video camera at the end.
Through the channel located inside the endoscope, it is possible to carry out special surgical instruments to perform operations on the deep structures of the brain. After installing the endoscope into the third ventricle, a hole is formed in its lower wall. Through the newly formed anastomosis, cerebrospinal fluid enters the subarachnoid space. After removing the endoscope, sutures are placed on the aponeurosis and skin. The duration of the operation is about one hour.
The risk of infectious complications is much lower after endoscopic surgery compared to cerebrospinal fluid shunting.
Endoscopic ventriculostomy of the third ventricle has no advantages over cerebrospinal fluid shunting in long-term follow-up. After endoscopic intervention, as well as after cerebrospinal fluid shunting, hydrocephalus can develop again, even several years after the operation.
Treatment of normal pressure hydrocephalus
In case of normal pressure hydrocephalus, which usually develops in older people, the condition can be improved by performing a cerebrospinal fluid shunt operation. Although not all patients with this diagnosis have surgical treatment that is effective.
Due to the risks associated with any surgery, specific tests (stopping lumbar drainage and/or performing a lumbar infusion test) are necessary to assess the potential benefit of surgery, which should outweigh the risk of adverse effects.
According to the literature, more than 80% of patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus who responded positively to preliminary testing reported significant improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunting. Visible clinical improvement after surgery usually occurs within a few weeks or even months.
A timely and correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment, even in patients who have suffered from hydrocephalus for several years.[1][7]
Preventive actions
If we are talking about congenital forms of the disease, then it is almost impossible to predict the likelihood of their development. Nevertheless, expectant mothers are advised to take vitamins, eat right, and avoid contact with potential carriers of infectious diseases (rubella is especially dangerous in this case).
As for acquired hydrocephalus, here too doctors recommend avoiding the risk of contracting one or another infection (syphilis). Remember that when the first symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, meningitis, or encephalitis appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Any disease is much easier to treat in the early stages of development. Do not forget to undergo a routine medical examination and tests once a year (even if there are no problems with your health at all).
Diagnostics
In children, the diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is revealed during examination. The specialist will pay attention to the symptoms that are characteristic of the disease. If suspected, the baby is referred for examination to a neurosurgeon. In order not to confuse increased intracranial pressure and increased cerebrospinal fluid volume with other diseases, MRI and radiography are performed. An ultrasound examination is performed. Examine the fundus. Endoscopic methods are used.
Interesting: Headache in a 5-year-old child: causes and treatment