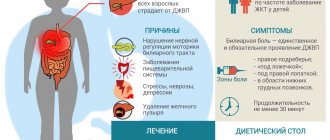
A very common disease of the gastrointestinal tract, which is characterized by impaired contraction of the digestive organ, is called gastric dyskinesia. The pathology often occurs in young people, in people with organic and functional changes in the functioning of the nervous system, as well as in children. At the same time, the patient develops sharp abdominal pain, heartburn, and rotten belching. This disease causes discomfort to a person and is accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.
The essence of the pathology of JVP
The liver, a digestive gland, continuously synthesizes bile. Through small ducts, it accumulates in a bladder under the liver, which is called the gall bladder. The circular muscle (sphincter of Oddi), which remains in a contracted state, prevents it from pouring out of the bile just like that, for no reason.
This kind of valve opens when a bolus of food enters the duodenum from the stomach. Bile rushes to it and helps the digestion processes.
Accordingly, biliary dyskinesia can occur for two reasons:
- The Oddi valve is not working properly. Either this muscle weakly blocks the duct that removes bile, which continuously flows into the intestines, or the sphincter does not allow digestive fluid to pass through at the right time due to high tone or anatomical changes in it.
- The expelling ability of the bubble itself is weakened. He does not “supply” bile when needed, or is hypotonic, his muscles are weak (1).
The motility of the bladder and Oddi is regulated by the autonomic nervous system. And, when dyskinesia occurs against the background of an apparently healthy bladder and liver, the disorder is considered functional (2). And for dyskinesia there are both anatomical and physiological prerequisites.
Prevention
Prevention of gallbladder dyskinesia includes the following measures:
- Strengthen your nervous system in every way, try to take care of yourself.
- A food regime is necessary (don’t eat at random, remove all unhealthy food filled with toxins).
- The diet is constant throughout your life.
- Eat slowly and chew your food well.
- Eat often, but keep portions small, bile will stop stagnating.
- Add vegetable oil to salads, it is choleretic.
- Proteins (animal, vegetable) are useful.
- Last meal approximately 2.5 hours to three hours before you go to bed.
- Before going to bed, drink a glass of compote, jelly, or yogurt.
Treatment of gallbladder dyskinesia is permanent and lifelong - this needs to be understood. You get used to everything, we’ll get used to this too. Therapy is mandatory to avoid more serious complications.
Reasons for the development of JVP
In recent years, the prevalence of biliary dyskinesia in adults has been increasing. Moreover, regarding the causes of the pathology, everything is still not clear: there are often patients with dyskinesia, which cannot be explained (3).
However, a number of provoking factors were identified:
- anatomical anomalies of the gallbladder - stenosis of its neck, bending;
- chronic inflammation in the gallbladder region – cholecystitis, pancreatitis;
- stagnation of bile - irregular nutrition, consumption of food rich in cholesterol, which provokes the formation of sand in the bile, scratching the mucous membrane of the bladder and ducts, fueling inflammation;
- insufficiency of thyroid function - hypothyroidism; mild forms of this pathology can be treated without hormones;
- features of higher nervous activity - psychasthenic states, against the background of which the autonomic regulation of the digestive glands is disrupted (4).
This problem is more common among women. Therefore, there are scientists who consider estrogens to be one of the causes of dyskinesia. But this point has not yet been confirmed by clinical studies.
At the moment, psychovegetative disorders (usually caused by stress) can be considered a typical trigger for dyskinesias. Since it is the autonomic nervous system, the vagus nerve, that regulates the tone of the sphincter of Oddi and contracts the muscles of the gallbladder.
Classification
Biliary tract disorders are classified according to several criteria. The forms are divided depending on the location of the lesion, the cause, impairment of motor function and nervous regulation of tone. The types of dyskinesia of the gallbladder are shown in Table 1.
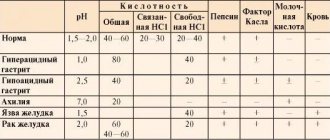
Table 1. Classification of gastric dyskinesia
| Options | Options |
| According to etiological factor |
|
| By localization |
|
| By dysfunction | Hypertonic-hyperkinetic (hypertonic):
Hypotonic-hypokinetic (hypotonic):
Dissociated |
| With the flow |
|
| Stages |
|
In clinical practice, simplified criteria based on the characteristics of motor function are more often used.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
Symptoms of biliary dyskinesia are not clearly expressed (5). Irritable bowel syndrome can also be disguised as them, for the treatment of which there are traditional methods.
The following manifestations indicate that the disorder is associated specifically with the biliary tract (6):
- pain and discomfort, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, as a rule, begins to bother you after a meal rich in fat, and persists for half an hour or longer;
- painful spasms in the right side;
- nausea and vomiting, after which some relief is noted;
- bloating, belching;
- frequent digestive disorders - constipation is replaced by diarrhea;
- loss of appetite, aversion to foods with fats;
- the pain does not subside after taking sorbents, defecation or heartburn medications.
A characteristic manifestation of biliary dyskinesia in adults is a periodic taste of bitterness in the mouth and heartburn. A similar phenomenon indicates that the sphincter of Oddi is incompetent, bile is thrown into the duodenum, then into the stomach.
Danger and complications
Unfortunately, many people prefer to sit out such episodes at home and do not see any danger in them. In fact, the complications of untreated dyskinesia are quite serious:
- calculous cholecystitis or cholelithiasis;
- the likelihood of acute inflammation of the pancreas (biliary pancreatitis);
- hepatic colic - complete cessation of the outflow of bile from the bladder; as a rule, stones block the efferent duct.
The risk of a dangerous complication – ascending cholangitis – increases. This is an acute infection of the common bile duct (7)
Complications of dysfunction
Poor functioning of the biliary tract leads to a whole range of adverse consequences. Impaired emulsification of fats from food and weak activation of pancreatic enzymes lead to inadequate digestion of fats with the development of steatorrhea (excretion of fat in feces), vitamin deficiency (lack of fat-soluble vitamins).
Due to changes in the circulation of fatty acids, the composition and properties of bile are disrupted, and its bactericidal properties are weakened. As a result, there is an excessive growth of bacteria in the intestinal lumen with the involvement of the duodenum (where there should be no microbes) in the process, which increases the risk of infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Useful information: Increased stomach acidity: treatment (15 drugs, 9 groups), more than 5 symptoms, diet, permitted and prohibited foods. How to downgrade
Lack of bile and its defective composition lead to increased pressure in the lumen of the duodenum, this is fraught with the development of duodenogastric and gastroesophageal reflux, which also leads to organic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the amount of bile is insufficient or its release is inadequate, normal intestinal motility suffers. Constipation can lead to mechanical irritation of the walls of the large intestine and the appearance of hemorrhoids. Diarrhea leads to disturbances in water and electrolyte balance. Both symptoms worsen the quality of life of an adult.
Diagnostics
At the present stage of development of medicine, diagnosing biliary dyskinesia in adults is not difficult. A medical examination and collection of complaints, the typical ones we described a little above, help to suspect a pathology.
The diagnosis is clarified using instrumental examination methods and laboratory tests (8):
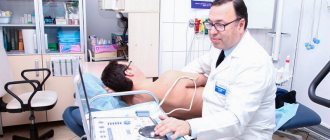
- Ultrasound - shows the anatomical structure, features of the location of the gallbladder, whether there is stagnation of bile, stones in it;
- biochemical blood test - increased bilirubin is found in it, which does not leave the bladder, but stagnates and is absorbed into the bloodstream;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - the patient is given a thin probe and with its help they can find bile in the small intestine that should not be there;
- MRI is a fast, informative, but not cheap method of examining the gallbladder;
- cholescintigraphy - the patient drinks a substance labeled with a radioactive isotope, which accumulates in the bile, and then a choleretic drug, after which they look at how much the bladder’s ability to empty (tone) is maintained.
The latter method is rarely used; ultrasound becomes an alternative. Ultrasound measures the volume of bile before and after taking a choleretic drug, based on this difference the contractility of the bladder.
After clarifying the diagnosis, the issue of treatment is decided.
The following approaches are allowed:
- Conservative, when medications, physiotherapy, nutrition therapy, etc. are used.
- Surgical – used if dyskinesia occurs due to stones and the patient has already had attacks of hepatic colic. The gallstone is simply removed.
We will consider the most effective methods in individual cases. Since dyskinesia can have many causes, it must be treated differently.
Types of biliary dyskinesia
The main signs of biliary tract activity are motor role and muscle activity. Based on the nature of the disorder, there are 4 types of disease:
- Hypotonic – reduced sphincter activity;
- Hypertensive – increased activity;
- Hypokinetic – slow decrease in bile;
- Hyperkinetic – rapid decrease in bile.
In medical practice, a double classification is used, but for patients it is enough to know the last two types.
Treatment without surgery - 9 ways
Treatment of biliary dyskinesia in adults should begin in advance, before the complications described above develop. Then you can count on the restoration of normal bile passage.
Method 1. Organizing a healthy diet
The main principle is to optimize fat in the diet and use different diets at different times. You shouldn’t give up fats completely: lipid deficiency itself leads to a disruption in the composition of bile. Nutritionists recommend consuming, first of all, olive and flaxseed oil. Add fats to your diet little by little - you need to see how the body reacts to them.
During a painful attack, it is better not to eat anything for up to 24 hours. You can only drink clean water. After the attack, you can begin to heal the liver and gall bladder with the help of nutrition. Preference is given to plant products:
- artichokes – have a choleretic effect, reduce stagnation and the risk of stone formation;
- garlic is a spice that reduces cholesterol levels and the number of crystals in bile (9);
- Jerusalem artichoke (earthen pear) – 1-2 tubers per day help detoxify the body;
- beets in any form, 1 large fruit per day.
In addition to the listed products, during an attack, zucchini, celery, and green beans normalize the passage of bile.
Read more about proper nutrition in our article.
Method 2: Reduce stress
Animal experiments have proven that psychological stress contributes to disruption of bile flow, bladder tone, and sphincter of Oddi (10).
In humans, it has long been known that psychological balance contributes to the normal functioning of the autonomic nervous system. But it is she who regulates digestion and many other functions of the body. Therefore, if you have symptoms of dyskinesia, you need to get rid of stress using available methods. This may be enough to normalize digestion and quality of life.
Method 3. Coffee enemas
The effectiveness of coffee enemas is based on the fact that they dilate the bile ducts. Thus, they promote the outflow of bile and reduce its stagnation.
Also, caffeine from enemas is believed to have a stimulating effect on the vagus nerve and increase the tone of the bladder, sphincter of Oddi. Thus, the main causes of dyskinesia are eliminated (11).
Method 4. Periodic intake of choleretic drugs
This method has been confirmed in a clinical study (12). This means that you should not refuse to take choleretic drugs. It is possible, but only in the remission phase, without pathological manifestations, to take choleretic drugs:
- Kholosas – healthy rosehip syrup;
- allohol – a complex of dry bile, garlic and nettle extracts;
- nicodine – hydroxymethylnicotinamide.
We see no point in listing all the drugs and dietary supplements; the main thing is to take choleretic drugs strictly according to the instructions and at the first sign that they are not suitable, stop using these drugs.
Method 5. Osteopathic intervention
An innovative approach that is still difficult to accept by traditional medicine. The main principle of osteopathy in the treatment of bile ducts is the normalization of the regulation of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Osteopathic practices are widely used in the treatment of the digestive tract - functional dyspepsia, reflux disease. That is, in situations where smooth muscle tone plays a decisive role. Osteopathy also helps in case of biliary dyskinesia (13).
The only problem is that finding a good osteopath in our country is a big problem. Today, everyone who is not too lazy goes to osteopaths, including charlatans and bioenergetics specialists. Or ordinary massage therapists who changed the sign above their office to increase prices by 2-3 times. Therefore, it is perhaps easier and cheaper to find a good physiotherapist with specialized education.
Method 6. Treatment of underlying diseases
If biliary dyskinesia in adults is a symptom of a particular pathology, this disease must be treated. For example, intolerance to certain foods (14). Hypothyroidism, which we already wrote about above, needs to be further examined, the TSH level determined and figured out what this means.
Method 7. Antispasmodic drugs
They are recommended to be used along with choleretic agents, this will better drain the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Doctors will advise their medications, but let's not forget that they have side effects. As an alternative, we suggest using essential oils from the following plants (15):
- fragrant mint;
- ylang-ylang;
- fennel;
- tarragon or tarragon;
- ferula.
You can use aromatherapy for biliary dyskinesia in adults in a convenient way: aroma candles, oils, air humidifiers.
Method 8. Ursodeoxycholic acid
This is a medication that has a complex effect:
- reduces the tendency of bile to form stones;
- has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- stabilizes the motility of the muscles of the bladder and excretory ducts;
- increases the sensitivity of the biliary tract to natural stimulants (cholecystokinin).
The medicine is taken in the form of courses, from 2 weeks to 2 months. This helps to avoid complications in certain forms of dyskinesia, with cholestasis (16).
Method 9. Antidepressants
As mentioned above, dyskinesia in adults is often triggered by stress or depression. If natural methods - rest and relaxation do not help or are not available, you can try antidepressants.
These drugs are of different groups; you need to select a specific one in contact with your doctor. Moreover, without consulting a doctor, you cannot be sure that biliary dyskinesia can really be cured without surgery.
I would like to draw special attention to the fact that depression is often a consequence of hormonal imbalance. You simply don't have enough certain substances in your body that are supposed to combat these symptoms. And if you want to seriously “pump up” your hormones and increase your energy levels, I recommend it for free. In it you will learn what specific steps you need to take today to get quick results.
Folk remedies
Treatment is carried out with the help of medicinal herbs, seeds, vegetables, fruits. When choosing an effective medicine, you need to take into account the type of dyskinesia and the properties of the components of the drug.
If dyskinesia develops according to the hypertensive type, the following options are appropriate:
- Peppermint. To ease spasms, eliminate nausea, improve appetite and activate the gastrointestinal tract, brew fresh or dried leaves at the rate of 10 grams per glass of boiling water. After infusion for half an hour, take 80 ml twice a day 20 minutes before meals.
- Liquorice root. The decoction is prepared similarly to the above option, cooled, filtered and the final volume is increased to 200 ml with boiled water. After taking it, there is an effective relaxation of the muscles of the ducts and the bladder itself.
For hypotonic disorders, choose the following recipes:
- Immortelle flowers to normalize the composition of bile, local disinfection and improve peristalsis. Pour 3 tablespoons of herbs into an enamel pan and add 250 ml of boiling water. Heating in a water bath is continued for half an hour with constant stirring. Then the broth is cooled and filtered. Drink the medicine 100 ml three times a day before meals for 21 days.
- Corn silk helps to liquefy bile and lower bilirubin and cholesterol levels. To prepare the infusion, pour a teaspoon of chopped herbs into a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, and filter. The finished composition is drunk 3 times a day before meals, maintaining a half-hour interval.
- Oregano for normalizing the functioning of the nervous system, reducing inflammation, increasing bile flow. For 200 ml of boiling water take 30 grams of raw materials. The infusion is kept for at least 20 minutes. The medication is taken in the same way as the previous prescription.
For dyskinesia, it is recommended to eat pumpkin seeds, grapefruit, apricot, drink jelly, dried fruit compote, and milk.
Surgery
Unfortunately, you cannot always count on the effect of conservative treatment. If stones appear in the gallstones and they cause hepatic colic, the gallstone must be removed. For this, it is better to use the endoscopic technique; it is well developed and studied.
If the cause of dyskinesia is too high a tone of the sphincter of Oddi or its lumen is blocked by papilloma, therapy will not help restore its normal functioning. It is necessary to do a sphincterotomy - minimal endoscopic intervention restores patency and normalizes the outflow of bile.
Physiotherapy
To increase the effectiveness of therapy, the treatment regimen is supplemented with special procedures:
- To correct hypomotor disorders, electrophoresis is performed using Pilocarpine. They also carry out amplipulse therapy.
- If hypertensive dyskinesia is diagnosed, Papaverine and Platiphylline are taken for electrotherapy. Laser and paraffin applications are introduced into the scheme.
For hypotension, exercise therapy is prescribed with a set of exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles. When remission occurs, a course is planned in a sanatorium with mineral water therapy.
How to choose the best way?
It can be seen that problems with bile passage can occur in a person in two opposite directions:
- constant leakage of bile and irritation of the intestines and stomach;
- lack of bile movement, stagnation.
Therefore, in therapy, we recommend starting with the first, universal method - organizing nutrition. If this does not help or is not available, try other methods. If there is no effect or attacks of sharp pain appear in the right hypochondrium, consult a doctor and get examined. Because the different mechanisms by which biliary dyskinesia develops, symptoms and treatment in adults, require clarification of the form of pathology in a particular person.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your digestive system is disturbed, consult a gastroenterologist
Treatment of dysfunction of the digestive system involves:
- gastroenterologist;
- surgeon.
According to indications, consultations with a gynecologist, neurologist, or endocrinologist are possible.
Who is at risk?
There are quite a few factors that cause the gallbladder to become hyperkinetic. And the more there are, the stronger and faster the pathology develops:
- genetic predisposition if parents had problems with the biliary system;
- vitamin deficiency;
- improper diet, lack of food intake, excess foods with animal fats, insufficient volume of fluid intake;
- diseases of parasitic etiology, damage by lamblia or helminths, infections in the intestinal tract;
- the patient is overweight;
- insufficient level of physical and motor activity;
- allergy;
- muscle dystrophy.
Diagnostic criteria for the disease
The main task of diagnosis is to exclude organic changes in the stomach in the presence of clinical symptoms. A gastroenterologist, based on patient complaints and the nature of the pain, assumes the development of hypertonic or hypotonic dyskinesia, identifies the cause and helps in selecting the correct diet, work and rest, and prescribes treatment. The doctor conducts an examination, palpates the abdomen, and the patient experiences pain and discomfort.
With deep palpation, in the absence of peristalsis, an expansion of the size of the organ is detected. Hypotonic and hypertensive dyskinesia is detected by electrogastrography. The method is based on the occurrence of electrical potential when contractile activity of muscle fibers occurs. If there are changes, the electrogastrogram will show a different result of the examination over a certain time.
The most accurate method is fluoroscopy of the stomach using contrast agents, such as barium suspension. Thanks to the method, it is possible to distinguish hypotonic dyskinesia from hypertensive or complete atony. The study shows the development of gastroesophageal reflux (return of a bolus of food from the stomach into the esophagus), a change in the topical location of the stomach, and spasm of a certain part of the organ.
The gastroscopy method helps to see changes in the mucous membrane, manifested by thickening of the folds. During the examination, attention is paid to the occurrence of a spasm when a small amount of air is introduced. A small amount of the latter can provoke spasms during dyskinesia. When performing EGDFS, biological material is necessarily taken for histological examination (biopsy). The result will show the absence of changes at the cellular level, which will confirm the diagnosis.
List of sources
- Maev I.V. Irritable bowel syndrome: a manual for doctors / I.V. Maev, S.V. Cheryomushkin. - M., 2012.
- Ivashkin V.T., Komarov F.I., Rapoport S.I. A short guide to gastroenterology. M.: M-Vesti Publishing House LLC, 2001.
- Callie E. Digestive system: diseases and their treatment. - St. Petersburg: Norint, 2000.
- Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko A.V. Clinical gastroenterology. M., 1998.
- Gracheva N.M., Yushchuk N.D., Chuprinina R.P. and others. Intestinal dysbacteriosis, causes, diagnosis, use of bacterial biological preparations: A manual for doctors and students. M., 1999.
General information
Intestinal dyskinesia is a term that defines a complex of intestinal disorders that arise as a result of disturbances in the motor functions of the intestines. Mostly such disorders occur in the colon .
Intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by the absence of organic changes, but the organ cannot perform its functions normally. According to the World Health Organization, about a third of all people on the planet suffer from this disease. In most cases, the disease is typical for women.
FAQ
Question: Is it possible to reduce or increase gallbladder activity with diet?
Answer: Yes. With hypomotor dyskinesia, you should eat a lot of vegetables, vegetable oils, fermented milk products, and eggs. Such products enhance the formation of bile and stimulate the contractile activity of the biliary tract. In case of hypermotor variant, broths and spices should be excluded. These foods may increase bladder contractions. Fats, thermal, mechanical and chemical irritants are excluded in both diet options to prevent smooth muscle spasms and increased pain.
Question: Products allowed for weak bile peristalsis should be completely excluded in case of hypertensive dyskinesia?
Answer: No. There is no need to limit the consumption of vegetables, vegetable fats, and dairy products. It is important to maintain a balanced diet. So, with increased bladder peristalsis, the menu should contain no more than 70 g of fat per day, among which vegetable oils should predominate. Vegetable and meat dishes are best consumed in the form of purees.
Question: Why do doctors prescribe antibiotics for biliary dyskinesia?
Answer: Antibacterial agents are most often prescribed for bacterial overgrowth to reduce the risk of cholecystitis. Antimicrobial agents may be prescribed based on stool microscopy results. If there is confirmation of helminthiasis, antiparasitic drugs are mandatory. However, such remedies cannot be used independently; they are always prescribed by a doctor. The logical conclusion of antibiotic therapy is taking probiotics to restore normal intestinal flora (Linex, Hilak-Forte, Bifi-form and others).
Adjuvant therapy
In addition to the main treatment, auxiliary therapy is also used:
- To improve treatment, your doctor may refer you to physical therapy, including electrophoresis and UHF therapy. Such methods improve tissue nutrition, increase regeneration, and improve access to medicines.
- Hirudotherapy. Nowadays, treatment with leeches is increasingly gaining popularity.
- Referral to sanatorium-resort treatment.
Use of medicinal herbs. In folk medicine, the use of corn silk, motherwort herb, chamomile flowers, nettle leaves, rose hips, chamomile, and peppermint for preparing decoctions and infusions is widespread.
Mineral waters for diseases of the biliary tract are also used in treatment. Essentuki 17, 4, 20, Narzan.
Symptoms of gastric dyskinesia
The main manifestation of the pathology is pain in the abdominal area without clear localization. Pain can occur in the epigastrium, hypochondrium, and peri-umbilical region, and the duration of the attack varies - from several minutes and hours to weeks. The nature of the sensations may also differ: some patients describe intense cramping pain, others describe aching, pressing pain (this depends on the nature and degree of motor impairment). The occurrence of such signs is not associated with food intake or lack thereof, but more often with a neuropsychic factor.
In the presence of antiperistaltic contractions of the muscular layer of the stomach and the reflux of acidic contents into the esophagus, patients are bothered by heartburn and sour belching. A pronounced decrease in the contractile activity of the stomach leads to stagnation of its contents and the appearance of rotten belching. Dyskinesia, which developed against the background of central nervous system pathology and irritation of the vomiting center, is accompanied by profuse repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief.
All of the above-described signs of impaired gastric motility can have varying intensity and are not specific - patients present such complaints with many other diseases. But gastric dyskinesia is characterized by a connection between the development of symptoms and mental trauma and stress, the presence of general manifestations of neurosis, variability of complaints and their reduction at night, as well as the absence of signs of organic pathology during endoscopic and histological examination.