What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
River fish is a popular product that can be eaten in any form. It contains up to 16% easily digestible protein, minerals: phosphorus, iron, iodine and calcium, vitamins: E, D, A and other valuable components. But dishes made from it can be deadly, and not only because of the bones that get stuck in the throat. With insufficiently processed fish, the larvae of cat (Siberian) fluke enter a person and he becomes ill with opisthorchiasis. Symptoms of opisthorchiasis are nonspecific, and sometimes may be absent altogether, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease, and therefore treatment.
For Russians, among whom more than 2 million are infected, this is a pressing medical problem. “Aboriginals” living in endemic areas are usually repeatedly infected with cat flukes, so opisthorchiasis in them is chronic, erased, but can appear even after 20 years.
What is opisthorchiasis?
Opisthorchiasis is a serious helminthiasis that affects the liver, bile ducts and pancreas. It is caused by a small flatworm from the family of flukes. On the front of the body it has 2 suckers, which are organs of nutrition and attachment.
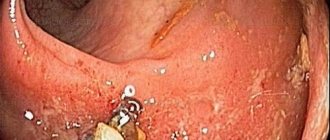
Photo of a parasite in opisthorchiasis in humans
Worms feed on glandular epithelium and cellular decay. The epithelium of the bile ducts gradually exfoliates, bleeding wounds form on their walls, which become entry points for infection. Massive invasion blocks the bile ducts, which provokes cholestasis and cholelithiasis.
Complications
As with any other disease, the possible consequences of opisthorchiasis cannot be ruled out.
Most often, infected people develop allergies. It occurs as a result of long-term poisoning of the body with waste products of parasites. Local complications include pancreatitis, cholecystitis, liver cirrhosis and peritonitis.
In addition, the cat fluke is able to migrate with the flow of lymph and blood, causing damage to other systems. In this case, opisthorchiasis can provoke manifestations of the following diseases, which cannot be called infectious, but despite this, parasites remain their primary source:
- arthrosis;
- psoriasis;
- low-grade fever;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- mental retardation in children;
- weight loss;
- anemia.
But the most dangerous complication of this type of helminthiasis is oncology.
Its development begins with necrosis of the epithelium in the bile ducts and liver, resulting from the active activity of flukes. Constantly clinging and injuring tissue, the parasites tear off individual cells, leaving behind bleeding, erosive lesions. It is because of them that a malignant process in the organ can begin.
How can you get infected?
The Siberian fluke is characterized by a complex development cycle. Humans, as well as piscivorous mammals (cats, dogs and foxes) are its definitive hosts. They are parasitized by an adult worm that lays up to 4 thousand eggs daily.
The life cycle of the fluke begins in a fresh water body, where helminth eggs fall along with the feces of the final host. The eggs are swallowed by bitinidia mollusks, inside which tailed larvae (cercariae) develop. After 2 months, they leave the mollusk and penetrate into the muscles of fish of the carp family. A metacercaria is formed in them - a larva covered with a double protective shell. A person becomes ill in one single way - by eating fish infected with metacercariae. In the human stomach, the larva emerges from the membranes, penetrates the biliary system and begins laying eggs. The eggs are then hatched, released into the river, and the cycle repeats.
Attention! From the above it follows that opisthorchiasis is not transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms of acute opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis can be acute or chronic, which depends on a number of factors:
- number of larvae;
- the state of immunity and general well-being of the infected person;
- duration of fluke parasitism, etc.
Incubation of the pathogen lasts about 3 weeks. With immunodeficiency, the incubation period may be prolonged. The human body reacts to the presence of a parasite:
- cough, runny nose, shortness of breath;
- an increase in the size of the spleen, lymph nodes, as well as the pancreas and liver with the manifestation of symptoms of hepatitis and pancreatitis;
- excessive sweating, chills, intermittent sleep, changes in behavior, irritability, weakness and other signs of asthenovegetative syndrome;
- discomfort in the abdominal area due to movements made by worms in the gallbladder, which ultimately lead to damage to the mucous membrane, the development of inflammation and swelling in it;
- vomiting and nausea as symptoms of body poisoning;
- increased body temperature;
- intermittent pain in muscles and joints;
- loose stools containing mucus and undigested food, as well as flatulence, heartburn, loss of appetite;
- allergies in the form of Quincke's edema and urticaria.
Notes
- Ilyinskikh E. N. “Current issues in studying the problem of opisthorchiasis in Siberia” // “Bulletin of Siberian Medicine”. - 2002. - Issue. 1. - pp. 63-70
- Bocharova T. A. “The causative agent of opisthorchiasis and other muscle parasites of carp fish of the lower Tom basin” / Tomsk: Tomsk State University Publishing House, 2007. - 66 p.
- ↑ 123456
V. V. Podyapolskaya, V. F. Kapustin. "Human helminthic diseases." — M.: “Medgiz”. 1958. - 663 p. - Beer S. A. “Biology of the causative agent of opisthorchiasis.” - M.: “Association of Scientific Publications KMK”, 2005. 336 p.
- Young ND, Campbell BE, Hall RS, Jex AR, Cantacessi C, et al. (2010) Unlocking the Transcriptomes of Two Carcinogenic Parasites, Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4(6): e719. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000719
- King S, Scholz T. Trematodes of the family Opisthorchiidae: a minireview // The Korean journal of parasitology. - 2001. - Vol. 39. - No. 3. - P. 209-221
- ↑ 123456
SanPin 3.2.569-96 “Prevention of parasitic diseases on the territory of the Russian Federation” (approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia dated October 31, 1996 No. 43) - Rusinek O. T., Kondratistov Yu. L. Study of infestation of trematode metacercariae in the focus of opisthorchiasis (Taishetsky district, Irkutsk region, Russia) // News of Irkutsk State University. Earth Science Series. - 2010. - T.3 - No. 1. - P. 132-142
- On the sanitary and epidemiological situation in the Russian Federation in 2010: State report. M.: Federal Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor, 2011. - 431 p.
- Ilinskikh et al, 2007.
- Residents of the Moscow region suffered from fish infected with opisthorchiasis / Moskovsky Komsomolets. February 24, 2021.
- ↑ 12
Vasilkov G.V. Parasitic diseases of fish and sanitary assessment of fish products. - M.: Publishing house VNIRO, 1999. - 191 p. - ↑ 123
Ichthyopathy / N. A. Golovina, Yu. A. Strelkov, P. P. Golovin, etc. - M.: Mir, 2007. - 448 p. - ↑ 1234567
Vozianova Zh. I. Infectious and parasitic diseases. T.1. Kyiv: Health, 2001. 904 p. - Chemich N. D., Ilyina, N. I., Zakhlebaeva V. V. et al. Opisthorchiasis in Ukraine: epidemiological and clinical features // Journal of Infectology - 2011. - T. 2, no. 2. - pp. 56-62
- Martynova N. A., Odintsova I. N. Liver cancer in the region of Siberia and the Far East // Siberian Journal of Oncology - 2003. - Issue. 2. - pp. 77-78.
- IARC Monographs - Classifications - Group1
- Opisthorchiasis in adults: symptoms and treatment
- ↑ 1 2 Bronshtein A. M., Luchshev V. I.
Liver trematodes: opisthorchiasis, clonorchiasis // Russian Medical Journal. - 1998. - T. 6, issue. 3. - ↑ 1 2 Edited by Eli Schwartz.
Chapter 31. Intestinal Helminths // Tropical diseases in travelers. - Blackwell Publishing, 2009. - P. 313. - ISBN 978-1-4051-8441-0. - ↑ 123
Lippincott's Guide to Infectious Disease. - Lippincott William & Wilkins, 2011. - P. 222-223. — ISBN 978-1-60547-975-0. - K. Darwin Murrell, Bernard Fried.
Chapter 1. Liver Flukes // Food-Borne Parasitic Zoonoses. - Springer Science + Business Media, LLC, 2007. - P. 34-37. — ISBN 978-0-387-71357-1. - ↑ 1234
Zavoykin V.D., Zelya O.P. Opisthorchiasis: clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment / DOCTOR.RU. — 2007. — No. 3. — P. 49-52 - ↑ 1234
Pustovalova V. Ya., Stepanova T. F., Shonin A. L. Opisthorchiasis Tyumen: Publishing House TGMA, 1999. 10 p. - SanPiN 3.2.1333-03 “Prevention of parasitic diseases on the territory of the Russian Federation” (approved 05/25/2003)
- ↑ 12
Konyaev S. V. Opisthorchiasis - S. K. Shibitov, R. T. Safiullin.
Recommendations for the Control of Opisthorchiasis in Carnivores in Western Siberia // Russian Journal of Parasitology. - 2010. - Issue. 3. - pp. 115–118. — ISSN 2541-7843 1998-8435, 2541-7843.
Chronic form of helminthiasis
Chronic opisthorchiasis develops when a mature helminth parasitizes inside a person. The symptoms of the disease are the same, but less pronounced:
- skin rash, possible manifestation of psoriasis, development of allergic bronchitis;
- slight periodic increase in temperature, up to a maximum of 37.5 ° C;
- increased discomfort in muscle and cartilage tissue with the gradual development of arthrosis and arthritis;
- deterioration of myocardial nutrition and, as a consequence, heart pain and tachycardia;
- liver damage and icteric staining of the mucous membrane and skin. Possible development of cholecystitis, enteritis, ulcers, gastritis, cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- decreased immunity, development of malignant neoplasms, tendency to frequent infections.
Skin rashes with opisthorchiasis
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in women are supplemented by menstrual irregularities, more intense discharge, severe pain during menstruation, which is not relieved by conventional antispasmodics. A woman’s appearance also suffers: hair falls out, skin condition worsens, and her face constantly swells.
Important! Opisthorchiasis is especially dangerous during pregnancy and lactation. Women can suffer from severe toxicosis. Miscarriages, premature birth, lack of milk, the birth of a child with developmental disabilities, exacerbation of pancreatitis, pyelonephritis and diabetes are possible.
How to treat opisthorchiasis?
The treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis in adults is selected by the doctor taking into account:
- results of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics;
- severity of the disease;
- the general condition of the patient and the presence of chronic diseases.
If the patient's condition is satisfactory, treatment at home is possible. The exacerbation stage, severe intoxication and other complex clinical situations are indications for treatment in a hospital. It is possible to defeat the cat fluke and recover from its harmful effects only through complex multi-stage therapy.
Medicines
- During the first three weeks, the patient is medicated for anthelmintic therapy. The doctor prescribes:
- treatment with drugs that neutralize the effects of allergies;
- short-term (weekly) course of antibacterial therapy that relieves inflammation;
- antispasmodics for pain relief;
- hepatoprotectors that protect the liver;
- choleretic drugs and enzymes to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- sorbents for removing worms and their metabolites;
- a special diet excluding fried, spicy foods, and fatty foods. Vegetable soups, porridges, low-fat fish and meats, and dairy products are allowed.
- At the second stage, anthelmintic therapy is carried out using special medications, for example, Biltricide, which contains praziquantel as an active ingredient. Biltricid tablets can only be purchased with a doctor's prescription. As a result, the parasites' processes of absorption of nutrients are inhibited, causing them to lose strength, break away from the walls of the affected organs and leave the person. Due to the toxicity of anthelmintic drugs, it is better to take them directly in a hospital and under the supervision of a parasitologist. Self-medication or non-compliance with the regimen of taking antihelminthics, as well as breaks in the treatment course, are unacceptable.
- The rehabilitation stage is aimed at restoring the patient's performance. To do this, the doctor prescribes:
- enzymes;
- vitamins;
- laxatives;
- choleretic compounds;
- hepatoprotectors;
- physiotherapy sessions.
ethnoscience
Treatment of opisthorchiasis with folk remedies is possible as an addition to drug therapy. For example, herbal decoctions, the components of which are:
- St. John's wort;
- dandelion;
- celandine;
- caraway;
- nettle;
- pumpkin seeds.
They have choleretic and anthelmintic properties, but they can only be taken after the approval of a parasitologist. Treatment with birch tar is also carried out in compliance with the dosages recommended by the attending physician. Birch tar is combined with milk or grated apple and taken in courses lasting 9-12 days.
To assess the effectiveness of treatment for helminthiasis, an examination is carried out after six months, based on the results of which we can already talk about the complete cure of the patient. For those who have had opisthorchiasis, dispensary control is required for six months.
Treatment with traditional methods
If opisthorchiasis is in the initial stages of development, then you can use folk remedies to speed up recovery.
Important! Don't forget about traditional treatment. Traditional methods are auxiliary. It is also better not to use questionable medications, so as not to harm your own body.
Traditional medicines can remove toxins, help during the recovery period, and improve the health of the liver and gallbladder.
The following folk remedies are used to treat opisthorchiasis:
- Birch tar. There is more than one scheme for using this medicine. The glass is filled a quarter full with milk, to which 3 drops of birch tar are added. This drink must be drunk for 9 days in the morning before meals. After this, a break is taken for 3 weeks and the course is repeated again. You can use a different regimen. Initially, only 2 drops are added, gradually it is necessary to increase their quantity by 2 pieces. When the number reaches 10 drops, you need to start reducing their number. Therapy is completed when 2 drops are drunk again.
- Young aspen bark. This component is crushed and 20 g is taken to prepare the medicine. 2 cups of boiling water are poured into a thermos and bark is added. This drink should last until the morning. It is drunk strained 3 times a day, half an hour before meals.
- St. John's wort. Dry grass is crushed. 1 tsp. added to a glass of boiling water. The mixture should stand for half an hour, after which 1 tbsp is drunk, strained. l. about 6 times a day.
- Seed material of nettle and caraway. Such components are combined in equal quantities. About 4 times a day you need to consume 1 tsp. take this medicine with water.
Diet for opisthorchiasis
If opisthorchiasis has been detected in an adult, it is necessary to adhere to dietary rules. It is recommended to eat small meals. In addition, the patient should drink a lot of fluid, which speeds up the cleansing of the body. All dishes must be boiled, stewed or baked. It is not prohibited to consume honey and vegetable oil. In addition, the diet should consist of:
- lean meat;
- well-cooked fish;
- dairy products;
- porridge;
- fruits and vegetables.
Some foods should be avoided. It is prohibited to consume eggs in various forms, baked goods, smoked foods, fatty foods, and carbonated drinks. The patient is advised to drink a lot of plain water.
Important! Cucumber pickle brings great benefits. This drink can cleanse the body of parasites.
If you do not follow a diet, then the effect of drug treatment is significantly reduced.
Prevention of opisthorchiasis
It is easier to avoid a disease than to treat it later. Therefore, doctors advise following some rules of prevention. The most important of them concerns the proper preparation of fish. For such a product it is worth having separate boards and knives.
There are certain medications that are prescribed as prophylaxis. You can consult a doctor to prescribe the appropriate medicine. It is recommended not to eat in questionable places.
You can cleanse your body using different methods. To do this, they use medications or lean towards traditional medicine recipes. But initially it is recommended to consult a doctor to avoid complications. After all, opisthorchiasis is a complex disease that requires timely treatment.
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis
Making a diagnosis is difficult, especially at the initial stage, since mature individuals begin to produce eggs a month after infection. Therefore, the basis of diagnosis is: the clinical picture of helminthiasis and its epidemiological data. To make a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor uses biochemical and clinical blood tests, as well as serological testing. The final diagnosis can be made after 1.5 months, when stool is analyzed for opisthorchiasis and worm eggs are found in the biomaterial.
Patient reviews
Elena: “I am one of those who treated opisthorchiasis using folk methods. Various decoctions, tar, tubages and probing techniques were used. I don’t know if I took the medications correctly, but they didn’t bring any results. After that, I went to the hospital, and I still had to buy drugs at the pharmacy and be treated according to the instructions. I was afraid that these drugs would have a lot of side effects, but, surprisingly, everything went well. Then I took the tests again and managed to get rid of the worms.”
Anna: “I decided to leave my review after I managed to completely get rid of parasites. Those who have cured opisthorchiasis know how long and unpleasant this course is. I had to undergo treatment three times before the negative tests came back. Honestly, now I’ll think twice before trying some unfamiliar delicacy.”
Prevention of opisthorchiasis
Important! To prevent infection with cat fluke, it is enough to follow one basic rule - cook fish well, including predatory ones, such as pike.
To do this, fish should be cooked for at least 20 minutes from the moment of boiling, and small fish should be fried for the same amount of time. It is better to cut large fish into pieces up to 100 g. Bake the pie with fish filling for about an hour at a temperature of 180-200°C. Additional precautions are necessary when cutting fish, for which it is better to use a separate knife and board, as well as when salting it, for example, keep large specimens in brine (200 g of salt / kg of fish weight) for 40 days.
A person can love river fish and at the same time fear for his health, and this is normal and correct. If you follow the basic rules when preparing fish dishes, you can truly enjoy their great taste and not worry about your health.
Disease in animals
In carnivorous predators, infection occurs when eating fish infested with metacercariae. After an incubation period lasting from 5 to 21 days, the animals’ temperature rises, general weakness appears, and eosinophilia occurs. In severe cases of the disease, animals may experience fever, jaundice, and hepatosplenomegaly. The liver becomes lumpy to the touch. Vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, hair loss, and ascites may also occur. After some time, the animal’s condition improves, the disease passes from the acute stage to the chronic stage and is manifested by biliary dyskinesia, chronic cholangiocholecystitis, and chronic pancreatitis[26].
The diagnosis is made based on the detection of opisthorchid eggs in feces. Praziquantel is used for treatment. Hexachloroparaxylene, hexichol and polytreme can be classified as obsolete drugs[26].
Since domestic animals (cats, dogs) play an important role in the spread of the disease, for the purpose of prevention in foci of opisthorchiasis it is necessary to feed them only thoroughly cooked fish[7].
It has been established that animals and humans can be carriers of the parasite for several years and release helminth eggs into the environment with feces. Therefore, accurate and timely diagnosis, identification of carriers, adequate high-quality treatment of patients, as well as protection and disinfection of water bodies are important preventive measures against opisthorchiasis. However, the main importance in preventing infection with opisthorchiasis is the exclusion of raw, insufficiently salted or insufficiently heat-treated fish from the diet. In farms, nurseries, clubs located in areas unfavorable for opisthorchiasis, measures are taken to prevent infection of animals: sanitary-epidemiological, treatment-and-prophylactic and sanitary-educational work. Fish from reservoirs unfavorable for opisthorchiasis is fed to animals only in pieces weighing no more than 100 g, boiled for 30 minutes after boiling water or frozen at a temperature of −10 ºС for four weeks, at −20 ºС - 72 hours, −28 ºС - 32, − 35 ºС - 14, −40 ºС - 7 hours. When salting fish, the temperature of the brine should be 16-20 °C, and the fish should be in it for at least 14 days. To salt 10 kg of fish, you should use 2.7-2.9 kg of table salt. These measures should be observed especially carefully in Western Siberia in the basin of the Ob, Irtysh rivers and their tributaries. In these areas, it is necessary to completely exclude non-neutralized freshwater fish from the diet of carnivores. Preventive deworming of adult foxes and arctic foxes is carried out 1 month before the rut and after the litter is deposited, puppies - from 3 months of age; therapeutic deworming - if indicated. Pregnant females are dewormed no later than 1 month before whelping. Starting from the age of one month, carnivores are accustomed to specially prepared ready-made rations for small animals (dry, wet), and adult animals should also be transferred to ready-made rations. It is necessary to organize the disposal of corpses of carnivorous animals, periodically conduct diagnostic studies of fur-bearing animals, dogs, cats and, if necessary, deworm them. [27] Video Opisthorchis felineus (marita, marita inside the gallbladder, metacercariae,)