Women's health can rightfully be recognized as a fragile world that needs to be protected from a young age. Very often, women suffer, first of all, from gynecological diseases, the reasons for the formation and development of which are completely unknown to many.
Women often complain of abdominal pain. The causes of pain may not always be problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Very often the problem lies in “gynecological matters.”
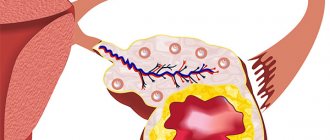
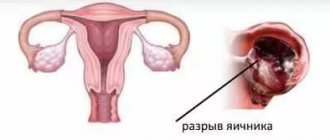
What is an ovarian corpus luteum cyst?
The corpus luteum is a gland that forms follicles in the zone that develops after the period of ovulation. The corpus luteum is small in size and can grow up to 30 mm in the process. If growth does not stand still and the corpus luteum begins to grow further, then this is the first sign that there is a corpus luteum cyst.
Development progresses more and more, and in this situation the corpus luteum ceases to produce progesterone, which subsequently leads to an increase in the size of the corpus luteum.
The occurrence of cysts is often found and observed in women who have reached the age of ready for offspring and also in that category of girls who are going through puberty.
In such situations, it is usually easy to detect hormone imbalances. Particular attention should be paid to such a hormone as the pituitary gland, which is a prerequisite for the formation and development of cysts.
In most cases, the occurrence of a neoplasm is concentrated on the corpus luteum, occurs and develops without symptoms or any pathology, and does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient.
Features of a corpus luteum cyst
The appearance of an ovarian cyst is formed from the so-called corpus luteum, which does not undergo a regression process. As a result, the blood flow process is disrupted and this leads to the appearance and accumulation of fluid of the serous type, as well as hemorrhagic.
Often, the size of the cyst reaches from six to eight cm, no more. About five percent of women who have reached reproductive age and who have a two-phase menstrual cycle are susceptible to cyst formation.
So, some facts that you need to know:
- The cyst differentiates both normally and during the period of pregnancy;
- Often a cyst of a unilateral type, as well as a single-cavity type, is formed;
- The cyst has a capsule, which is lined from the inside with granular cells;
- Resorption of the cyst is possible over the next two to three menstrual cycles;
- Resorption of the cyst may occur during the second trimester when carrying a baby.
Most often, when such a luteal cyst occurs, a woman does not feel any symptoms, only sometimes minor pain in the lower abdomen and disruption of the menstrual cycle are possible.
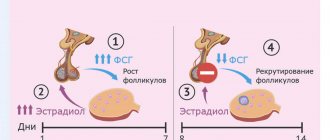
Ovulation
Ovulation is the process by which an egg is released into the fallopian tube from a mature follicle as it disintegrates.
Corpus luteum in the ovary
Then the influx of fluid and muscle peristalsis propel it towards the fallopian tube. If within 3 days before and one day after ovulation a woman has sexual intercourse, during which active sperm enter the vagina, fertilization is likely. It begins in the lumen of the fallopian tube. The embryo moves further. The sperm dies after 3 days, and the egg is active for 24 hours.
During normal development, the follicle becomes a gland where progestins are actively produced. Then it resolves, undergoes reverse development, as a result, the secretion of progesterone drops, and bleeding begins, namely menstruation. After menstruation, new follicles begin to mature. Another menstrual cycle occurs.
The menstrual cycle varies from person to person, with a normal duration ranging from 25 to 30 days. Throughout life, the ovary changes. Even during the intrauterine period, embryos develop millions of germ cells. During life, there are fewer of them. The childbearing period for women is shorter than that of men, ranging from 15 to 45 years. A woman's eggs are not renewed.
Causes of ovarian corpus luteum cyst formation
The reasons that contribute to the formation of cysts have not been studied and are unclear to this day. The occurrence of a cyst is explained primarily by hormonal imbalance. In addition, blood circulation and lymphatic drainage located in the ovarian tissues play an important role.
One way or another, all neoplasms and diseases occur for a reason. There are reasons and prerequisites for everything.
In fact, the occurrence of a cyst is associated with the following reasons:
- disruption of the hormonal system of a woman;
- poor circulation in the ovarian area;
- negative impact of medications, the purpose of which is to increase the period of ovulation when diagnosed with infertility;
- with moral fatigue;
- in stressful situations;
- with nervous breakdowns;
- when lifting heavy objects and increased physical activity;
- with previous infections that can be transmitted sexually;
- in case of disruption of the thyroid gland;
- if the pituitary gland is imbalanced;
- with menstruation that began in the early period;
- when taking medications used as contraception.
In addition to the reasons listed, it should be noted that a woman is susceptible to acquiring a cyst due to her individual predisposition to this type of disease. It often happens that a patient acquires many diseases at the genetic level, which are passed on from generation to generation.
Symptoms of a left or right ovarian cyst
During the development process, the neoplasm does not become active and does not interfere with the patient during the first three months. It often happens that after several menstrual cycles, the cyst is capable of voluntary removal from the body.
If a doctor has diagnosed a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy, then in this situation the level of danger of exposure and the influence of education directly on the development of the baby and on the woman’s health in general is determined first.
If there is no danger, then such a neoplasm may disappear by the eighteenth week of pregnancy. It is extremely rare that a cyst begins to manifest itself as pain in the area of the uterine appendages, as well as causing discomfort and bloating, as well as a delay in the menstrual cycle.
If even the slightest signs of a cyst are detected, you must immediately consult a specialist doctor.
So, what symptoms may indicate the appearance and development of a cyst:
- feeling of heaviness on the right or left;
- discomfort in the abdominal cavity, right or left;
- delay of critical days;
- leg torsion;
- acute stomach;
- vomit;
- gas and stool retention;
- intoxication.
When diagnosing a cyst, doctors often use the technique of palpation of the abdomen, which allows them to feel the tumor. During the procedure, the specialist feels the tumor in the right or left ovary by touch.
As mentioned earlier, the neoplasm usually reaches small volumes and when pressing on the cyst, the woman does not feel any pain.
Inflammation of the appendages (salpingoophoritis) and tubo-ovarian abscess
Tubo-ovarian abscess usually occurs as a complication of an ascending (from the vagina to the cervix and fallopian tubes) chlamydial or gonorrheal infection. CT and MRI reveal a complex cystic formation of the ovary with a thick wall and lack of vascularization. Thickening of the endometrium or hydrosalpinx makes the diagnosis of tubo-ovarian abscess more likely.
An axial contrast-enhanced CT scan reveals a complex cystic formation on the left, resembling an abscess, with a thick wall accumulating contrast and gas inclusions inside.
On a CT scan in the sagittal plane (left), it can be seen that the ovarian vein approaches the mass, confirming its nature (arrow). On the coronal tomogram (right), the anatomical relationships of the mass and the uterus can be assessed. A gas bubble is visualized in the uterine cavity, which suggests an infectious onset here, with subsequent spread of infection through the fallopian tube to the ovary.
Possible complications of a corpus luteum cyst
As with any other disease, in the presence of a tumor in the form of a corpus luteum cyst, complications can arise that lead to adverse consequences.
Some of the most common consequences:
- Torsion of ovarian tumor. The occurrence of leg torsion can become a threat to the life of the woman herself. If acute pain occurs, you must immediately consult a gynecologist to solve the problem. If treatment is not promptly addressed, a focus of inflammation may occur, called acute peritonitis. In this situation, the blood flow directly to the resulting cyst is disrupted and then a symptom appears: intense pain in the ovarian area; (increasing or sharp)
- pain in the legs or lower back.
- stool retention;
In case of complications, immediate medical attention is required and immediate surgical intervention is inevitable. If the urges from the body are ignored, complications can result in death.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is an important stage for any disease.
How to diagnose an ovarian corpus luteum cyst? Diagnostics is carried out using:
- medical history;
- patient complaints;
- gynecological studies;
- Ultrasound;
- laparoscopy
A vaginal examination by a gynecologist can also diagnose the presence of a cyst.
Ultrasound is best performed during the first follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Using color Dopplerography, it is possible to exclude vascularization of the internal structure of the cyst, as well as differentiation of retention type formation.
In addition, a study of the tumor marker CA-125 is used. Diagnostic laparoscopy is also widely used.
Treatment of corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy
Very often, a cyst forms during the period when a woman is carrying a baby.
Unfortunately, pregnancy is not protected from diseases and various types of formations of pregnant women. As a rule, during pregnancy, the cyst that arises can be one-sided and after some time it can disappear on its own without surgical intervention.
As a rule, the cyst disappears in the last trimester of pregnancy. If the cyst continues to develop and grow, and has also reached a size of more than five cm, then in this case, doctors can decide without hesitation that surgical intervention is necessary.
It is through surgery that a tumor such as a cyst is removed. However, this happens extremely rarely due to the fact that during pregnancy, at the eighteenth week, the placenta begins to take over all functions, including the production of progesterone.
This process does not allow the tumor to develop further and already at the twentieth week of gestation, the cyst spontaneously disappears.
In the future, the woman also retains the ability to become pregnant.
Serous cystadenocarcinoma
Ultrasound reveals a complex cystic-solid formation in the left ovary, and another large complex formation containing both a solid and a cystic component in the right half of the pelvis
A CT scan of the same patient reveals a complex cystic-solid formation with thickened septa accumulating contrast in the right ovary, extremely suspicious for a malignant tumor. There is also bilateral pelvic lymphadenopathy (arrows). Histopathological examination confirmed serous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma (the most common variant)
CT scan and macroscopic photograph of serous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma.
Ultrasound (left) shows a large multilocular cystic formation in the right parametrium; Some of the chambers are anechoic; in others, uniform low-level echogenic inclusions are visualized, caused by protein content (in this case, mucin, but hemorrhages can also look similar). The partitions in the formation are mostly thin. No blood flow was detected in the septa, the solid component was also absent, and no signs of ascites were detected. Despite the absence of blood flow during Doppler ultrasound and a solid component, the size and multilocular structure of this formation allows us to suspect a cystic tumor and recommend other, more accurate diagnostic methods. Contrast-enhanced CT scan (right) shows similar changes. The formation chambers have different densities, corresponding to different protein contents. Histopathological examination confirmed mucinous cystadenocarcinoma with low malignant potential.
What is strictly prohibited for an ovarian corpus luteum cyst?
Of course, with a disease such as ovarian corpus luteum cyst, there are a number of restrictions that must be observed.
However, a cyst is a formation that can easily be negatively affected. Even the slightest overheating of the body is prohibited with this diagnosis, but the list of contraindications does not end there. For ovarian corpus luteum cyst, the following is prohibited:
- exercise stress;
- body heating;
- various types of body wraps with seaweed;
- sexual activity;
- lift heavy objects and things;
Prevention of occurrence
To protect against the possible development of the disease, it is recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations, promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, and monitor hormonal levels.
After discovering a cyst, it is advisable to avoid heavy lifting, active sports, eat a balanced diet and be less nervous, and ensure sexual rest.
To prevent gynecological disorders that can cause the development of a corpus luteum cyst, use the correct feminine intimate hygiene products. The “Ginocomfort” line of washing gels includes 6 different products for daily delicate cleansing of the intimate area. Specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX worked to develop the composition of each of them. You can choose a gel that best suits your composition: they all support the physiological level of acidity of the vagina and external genitalia, thereby counteracting the development of pathogenic microorganisms that can cause inflammatory processes. Gels have a moisturizing, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect.
Also, the restoring gel “Gynocomfort” with lactic acid and tea tree oil is well suited for normalizing and maintaining the balance of vaginal microflora.
It has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, promotes rapid regeneration of microtraumas. This product underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenereology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University under the leadership of A. V. Ignatovsky and E. V. Sokolovsky. During testing of the product, its good tolerability and the absence of allergic reactions were proven. Like other Ginocomfort products, the gel has a full list of necessary documents and certificates. Sources:
- Age-related clinical and morphological characteristics of the ovarian appendage. Voytsovich, A.B. // Diss. Ph.D. honey. Sciences A.B. Wojtsovich. – Tomsk. - 1998. - P. 157.
- Diagnosis and therapy of ovarian formations. Savelyeva G.M., Solomatina A.A., Stepanov K.I. // Practical gynecology (clinical lectures) ed. IN AND. Kulakova and V.N. Prilepskaya. - 2002 - P. 75-88.
- Clinical features of a group of patients with reproductive dysfunction and benign ovarian tumors. R.G. Gataulina // Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases. – 2001. – T. L. – Issue. 4. – pp. 38-42.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sostoyanie-reproduktivnogo-zdorovya-zhenschin-posle-operativnogo-l…
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-printsipy-diagnostiki-i-lecheniya-oslozhnennyh-opuhole…
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/klinicheskaya-kartina-i-morfologiya-yaichnikovogo-pridatka-pri-raz…
Treatment methods for corpus luteum cyst
If this type of tumor is detected, surgical intervention is not at all necessary. As a rule, in the preoperative period, doctors prescribe various treatment methods to get rid of the cyst in some other way.
The first thing doctors start with is observing the tumor over the next few cycles. Since, in most cases, the cyst resolves on its own, the menstrual cycle usually contributes to this.
If the cyst disappears and is eliminated on its own within a few months, then no surgical procedures will be required.
This happens most often. This is one of the features inherent in cystic neoplasms in the corpus luteum. To achieve this effect, it is necessary to apply the following procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
If the tumor has not reached a large size, then this procedure must be carried out over the next few months. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to diagnose the disease. In the first stages, the cyst is usually similar to all other ovarian tumors that can arise.
In such situations, the doctor prefers to prescribe color Doppler ultrasound. It is with the help of this procedure that you can determine whether there are venous vessels on the cyst. If there are no blood vessels, then this is a sign that a cyst has formed on the corpus luteum.
Tumors can also be detected using an ultrasound procedure and a basic examination by a specialist. After the doctor prescribes treatment, the patient must comply with all conditions and recommendations prescribed by the doctor. The most important thing is to avoid physical activity, not to carry heavy objects and to abstain from sexual intercourse.
If after the procedures the cyst has not resolved within several months, then the doctor decides to remove the cyst through surgery. Very often, a corpus luteum cyst is removed using laparoscopy.
This method of tumor removal is one of the most common. Neoplasms are excised from the site where the cyst was found, and subsequently, upon completion of the operation, the formation of adhesions and scars is minimized.
With the help of this type of operation, you can get rid of other pathologies that cause infertility. If the operation was prescribed by a doctor, then under no circumstances should it be delayed. With timely surgical intervention, inflammation of the tumor and its further rupture can be avoided. Also, the chosen treatment method of laparoscopy will not cause harm to the woman’s body.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy involves examination by a gynecologist, a procedure such as Doppler corting, and diagnostics using ultrasound over several cycles.
The following methods are used as conservative therapy:
- hormonal drugs;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- treatment with mineral waters;
- electrophoresis sessions;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy
When treating with conservative methods, it is necessary to exclude:
- visiting the bathhouse and sauna;
- Avoid tanning and avoid spending long periods of time in the sun;
- It is also prohibited to carry out procedures such as seaweed wraps and procedures that have a heating effect.
If a corpus luteum cyst is detected, as well as after its removal, it is necessary to see a gynecologist on a regular basis. This will allow you to get rid of relapse and complications in the future.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is very often used due to the circumstances that sometimes there is no point in using conservative therapy and the cyst has not resolved on its own.
In such situations, to avoid mistakes and adverse consequences, it is better to use surgical intervention.
This type of therapy is chosen after the process of cyst development has already passed three months. Indications for this type of treatment are regression of the cyst or reduction in size. What is noteworthy is that the cyst can either grow or shrink.
This is not the norm. The norm is growth and then resorption of the formation. If the cyst begins to shrink, then this is clearly not a reason for joy. In this case, you will have to use surgical treatment.
The need for surgery lies in the fact that the corpus luteum located in the ovary can begin to unevenly reject the endometrium. In the future, uterine bleeding may occur. It is better not to delay the removal of the cyst due to the high risk of rupture and torsion.
In the absence of necessary therapy, the cyst may undergo changes. This can really cause a lot of problems for a woman if the cyst develops from a benign neoplasm into a malignant one. Thanks to all modern methodologies in surgery, injuries are minimized, and there is really nothing to worry about.
Laparoscopy is often used for surgery. In some cases, doctors choose a type of operation such as resection (that is, removal of the cyst itself with full preservation of the ovary), as well as suturing. Which method will be chosen depends entirely on the gynecologist.
Often, doctors, when choosing the type of surgical intervention, are guided by such aspects as:
- the patient’s choice and preference whether to use an organ-sparing type of surgery;
- The use of the laparoscopic method is used if the patient does not have any complications.
- if the patient undergoes menopause, then in this case the ovaries are removed in full.
- Resection is chosen when the tumor is located in a place that is difficult to access and inconvenient for the doctor.
Folk remedies
Self-medication very often involves treatment using folk remedies. Traditional medicine is no less in demand and is still developing to this day.
Very often, people suffering from any diseases use herbs and their decoctions.
What can be done using traditional medicine to get rid of a cyst:
- Dandelion tinctures;
- Burdock juice;
- Herbal tincture
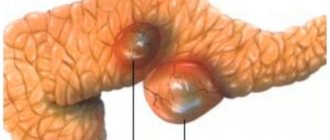
Types of cysts
More often, the cyst is located on one side of the right or left ovary. Neoplasms are distinguished:
By form:
- Single-cavity - the formation of one cavity.
- Multi-cavity - several cavities are formed on the ovary. More often complicated by ruptures.
By location:
- Right-sided - on the surface of the right ovary. Formed more often, a large aortic blood vessel is located here.
- Left-sided - from the side of the left ovary. Formed less frequently.
By stages:
- Proliferation – continuous maturation of follicles and high production of estrogen.
- Vascularization - proliferation of epithelial cells, blood supply to the cyst.
- Blooming - the formation of a cyst from the corpus luteum.
Cyst on the ovary
Prognosis for ovarian cyst
Many people are interested in the future forecast, and for good reason.
A cyst is one of the neoplasms that can develop from benign to malignant. Therefore, to avoid problems, you need to be examined in a timely manner, take measures, and be treated according to doctor’s prescriptions.
Often, a cyst begins to form during pregnancy. What is the prognosis and is there any reason for concern? With a developing pregnancy, there is no threat to pregnancy.
However, this does not mean that you can forget about the diagnosis and move on with your life with peace of mind. It is necessary to visit a doctor regularly to examine and evaluate the condition of the tumor.
It also often happens that the cyst begins to grow sharply and this frightens many. In this case, many decide to undergo surgical interventions. You need to take care of your health and not delay it, because the cyst can behave differently.
As you know, it can burst, or a torsion can form, which is also unsafe for the female body. If all is well, then after three months the cyst may resolve on its own. In this case, no medical intervention will be required.