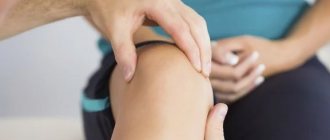
The knee joint is most susceptible to inflammatory diseases. It is difficult to say what causes this, but almost every arthritis (rheumatoid, ankylosing, gout, etc.) can affect its cartilage tissue. This process is accompanied by a number of symptoms that significantly reduce the quality of life of patients. Although they often overlap in different diseases, it is important to correctly determine the cause of arthritis. This is of fundamental importance when prescribing treatment.
Classification
In medicine, it is customary to divide knee arthritis into types, which are characterized by a specific cause and symptomatology. So, these types have the following names:
- Arthritis is reactive. It is formed due to the penetration of infections into the joint cavity. The infection enters the body primarily through the genital tract or through the digestive system. If a person has a chronic disease provoked by a viral pathogen, then the development of knee arthritis cannot be ruled out. The reactive type of the disease does not appear immediately, but a month after the virus enters the body.
- Sharp look. A sign of this type is severe cutting pain that occurs in the area of the knee joint. Acute arthritis of the knee joint is formed due to damage to bone tissue by infection. The acute form is characterized by the formation of purulent arthritis in the future, so it is very important to start appropriate treatment on time.
- Infectious type. It is formed due to the entry of infected blood into the knee joint. Infection can also enter the cavity of the joint mechanism through surgery.
- Rheumatoid appearance. It is one of the most severe forms of the disease and is accompanied by weak and stiff knee joints. This type of disease is more often diagnosed among females of various ages, and is less common in males. The danger of this type lies in the fact that the reasons for its formation remain unknown even today, which is why treatment of knee arthritis with antibiotics sometimes does not give any effect. In most cases, especially in the absence of treatment methods, a person develops a disability.
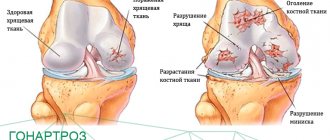
- Arthrosis-arthritis. It is characterized by the appearance of deformation of the knee joint, bone tissue and cartilage. The reason for the formation of this type of disease is primarily a failure of the body’s blood circulation. If the patient is not treated with medication, then the symptoms of the disease develop, which causes cartilaginous modifications. In addition, compactions and thorns begin to grow on the surface of the bone tissue, and deformation and curvature of the bones occur.
- Post-traumatic appearance. The reasons for the formation of this type are mechanical, household and even physical injuries. As a result of damage, cartilage destruction is observed, which is manifested not only on an x-ray, but also in the form of severe pain.
These are the main types of knee arthritis, which have different causes. Let's talk about these reasons in more detail.
Medicines and medical devices
Arthritis of the knee joint is in most cases characterized by inflammation and pain. Acute inflammation can be relieved by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are Ibuprofen and Naproxen. Prednisone can not only relieve inflammation, but can also support the rehabilitation treatment of arthritis of the knee joints . Drugs must be selected with special care, because many may be accompanied by side effects, especially if long-term use is required. Treatment of knee arthritis is almost never performed without special support or support devices. An ordinary cane, knee brace, orthopedic shoes will help facilitate movement and make it possible to painlessly bend and straighten the knee joint.
Causes of arthritis
Infectious arthritis occurs due to the penetration of the following pathogenic organisms into the “capsule” of the joint: fungi, viruses, bacteria (Gram-negative), streptococci, staphylococci and gonococci.
As for arthritis of non-infectious origin, their development is due to many factors:
- degenerative transformations of cartilage tissue (most often age-related changes occur);
- injuries of varying severity;
- inflammatory processes occurring in tissues located in close proximity to the joint capsule and caused by immunological disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- the formation of crystallized salts located in the synovial secretion. This phenomenon is evidence of a disturbance in calcium metabolism in the body.
It is important to know! Predisposing factors for the development of inflammation in the joints are constant emotional overload, stress, and endocrine diseases, such as diabetes.
Why does pathology occur?
The inflammatory process can occur for a number of reasons:
- injury - post-traumatic arthritis of the right knee joint is more common;
- this condition can complicate the infectious process - reactive inflammation;
- streptococcal infection in the form of sore throat, erysipelas leads to the development of rheumatoid arthritis;
- hereditary burden - juvenile arthritis - observed in children over 8 years old;
- Metabolic disorders in the joint capsule provoke gouty arthritis.
In addition, there are some other predisposing factors: systemic pathologies, increased stress, age-related changes, chronic diseases of joint tissues, hypothermia, viral infections, allergic reactions. If both knees are affected at once, this is polyarthritis.
The lesion can be bilateral
Symptoms
The following symptoms of the knee joint are distinguished:
- stiffness, stiffness of the knee joints due to severe swelling and accumulation of effusion when going up/down stairs, squats, driving a car and any movements in which the sore knee is involved in any way, i.e. the volume of passive and active mobility is greatly reduced;
- pain in the anterior part of the knee, aggravated in positions with the greatest tension on the tendon (of a “mechanical” nature);
- heaviness in the leg;
- massive swelling of soft tissues - dropsy;
- accumulation of exudate in the joint cavity;
- sprain of the capsule and ligaments;
- hypertrophy of the synovial membrane in the fungous form;
- weakness, lethargy;
- decreased appetite;
- periarticular phlegmon in advanced cases (death is very likely);
- atrophy of adjacent muscles, for example, the quadriceps femoris muscle - Alexandrov’s symptom;
- osteoporosis;
- bone destruction of the condyles, patella and tibia, jaggedness, appearance of focal irregularities at the articular ends;
- rheumatic carditis;
- rheumatic chorea;
- redness and local increase in skin temperature within 5-7 cm;
- spindle-shaped appearance of the sore leg;
- proliferation of villi with infiltration, swelling and fibrous degeneration;
- symptom of voting of the patella (ballot cup) - when the leg is straightened, it seems to sink into the area of exudate accumulation, and when flexed, it “pops up” again;
- Bonnet position of the joint (forced half-bent at a right angle due to muscle tension);
- fever, hectic body temperature;
- chills;
- sweating;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- general malaise, feeling of weakness;
- drowsiness;
- rheumatic dense, painless, sedentary nodules in the subcutaneous tissue, fascia, aponeuroses and bursae;
- abscesses - boils;
- fistulas;
- necrosis of soft tissues and cartilage;
- fibrosis due to connective tissue degeneration of the bursa;
- compaction and thickening of periarticular tissues;
- filling the joint with scar tissue;
- erosion of articular surfaces;
- ankylosis due to the soldering of articular surfaces by connective tissue.
The signs of arthritis of the knee joint are very similar to the symptoms of many bone diseases, as well as tumor-like neoplasms:
- fibrous osteodystrophy;
- giant cell osteoclastoma;
- sarcoma;
- pigmented villonodular synovitis;
- synovioma.
The listed pathological signs appear blurry or pronounced. They are usually divided into local and extra-articular. It is not necessary to manifest the entire symptom complex at once. It all depends on the type of disease and associated pathologies.
The patella or kneecap is a small bony “shield” that covers the top of the knee. It is linked to the thigh muscle and enhances its action. The patella is only part of the powerful stabilizing frame of the knee joint. It begins to bulge forward when there is excessive accumulation of effusion in the cavity of the diseased joint. In this case, the knees acquire a spherical shape. Condyles are semicircular protrusions of the thigh and tibia.
Surgery
If conservative methods do not bring significant results, patients are recommended to undergo surgery. The most popular surgical methods include:
- Aspiration method - removal of joint fluid from the joint. Prescribed for arthritis with purulent complications.
- Arthroscopy is recommended to remove salt deposits in the joint capsule.
- Installation of a prosthesis (endoprosthetics) is the replacement of a destroyed joint with an artificial implant.
To alleviate the symptoms of the disease, various compresses and rubs made at home are used as an addition to the main therapy. Bandages made from cabbage leaves, compresses made from table and sea salt, clay, and potato gruel help a lot.
After warming up procedures, it is good to use an ointment made from vodka and butter, rubbing based on apple cider vinegar, horse chestnut, and a solution of camphor alcohol.
Stages
If the disease is not treated, chronic arthritis develops in most cases. Experts distinguish three main stages of its development:
- First (initial). Pain and discomfort are wave-like in nature, most often disturbing in the morning, at night or when the weather changes. Images of the joint show the first signs of thinning of the bones, thickening of the muscle tissue, as well as a slight narrowing of the lumen of the joint space.
- Second. Pathological changes in the joint are more noticeable, swelling and pain are more pronounced, and leg mobility is limited. The X-ray image shows erosion, drying out of the cartilage with simultaneous thickening of the capsule, and narrowing of the lumen of the cartilage.
- Third. There is extensive muscular dystrophy, signs of bone deformation, increased growth of connective tissue and bone osteophytes, and salt deposition in the joint. The tissues of the articular cartilage are severely destroyed.
If the disease is not treated, chronic arthritis develops in most cases.
How to treat arthritis, and what modern methods are effective?
Arthritis (Latin - inflammation of the joint) is a disease that is extremely common among people over 40 years of age, but today there are also rare types of arthritis that typically manifest in childhood and adolescence. What causes the development of the disease, how to recognize its symptoms in time and choose the most effective treatment method?
Many people do not see the difference between arthritis and arthrosis, although these are two fundamentally different joint diseases. Arthrosis is an age-related chronic degenerative disease in which deformation of the joints occurs; it manifests itself as pain during the daytime and during movement; arthritis is the result of inflammatory processes throughout the body, leading to acute pain in the joints, mainly at night and regardless of movements. In some cases, arthrosis is a complication of advanced arthritis.
Arthritis can develop slowly and gradually (chronic forms) or suddenly and suddenly (acute forms). Arthritis is often accompanied by a fever. With arthritis, joint pain is always observed, but their presence is not always a sign of arthritis.
Diagnostics
The main criterion for differentiating gonarthritis is an in-depth examination, including both laboratory and instrumental methods:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- conducting diagnostic tests to establish or exclude various infectious, viral and fungal infections;
- clinical urine analysis to identify mineral metabolism disorders;
- X-ray examination of the area of the affected joint;
- ultrasonography;
- if it is necessary to obtain a more accurate idea of destructive changes in the structure of the elements of the affected joint, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may be prescribed.
The need for such an extensive study is due to the existence of a wide variety of nosological forms of gonarthritis. The most accurate determination of pathological changes in the affected joint helps the attending physician choose the right tactics in the question of how to treat arthritis of the knee joint.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a necessary aid in the treatment of knee arthritis. The following procedures help well:
- Laser and infrared therapy, ultrasound treatment. Such methods help reduce inflammation and eliminate pain.
- Hydrotherapy and electrophoresis help to activate the regeneration processes of cartilage tissue.
- Massage will help disperse the blood and activate metabolic processes.
- Plasmophoresis is prescribed for arthritis of the infectious and rheumatoid type.
- Paraffin and ozokerite heating help relieve pain and swelling and help activate blood flow.
- Cryotherapy – restores tissue metabolism, reduces joint pain.
Treatment of knee arthritis
Treatment of the disease is carried out in several areas: pharmacological correction, physiotherapy, lifestyle modification. Surgical treatment methods are used not only when conservative treatment is ineffective; there are a number of manipulations carried out even in the early stages of the disease in order to minimize clinical manifestations.
Lifestyle modification is understood as changing the stereotype of physical activity, eliminating risk factors, rational work and rest, reducing body weight through diet, and giving up bad habits.
Therapy for rheumatoid arthritis
The main (basic) group of drugs for the treatment of arthritis are cytostatics - substances that reduce the production of immune cells. They have serious side effects, such as pancythemia (insufficient production of all blood cells), vulnerability of the body to infections, liver damage, etc. Despite this, the need to use cytostatics has been proven even in the early stages of the rheumatic process. If they are not used, patients develop irreversible deformation of the knee and other joints, and their general condition worsens. You can reduce the likelihood of negative effects of medications by choosing the right dose and drug. Currently prescribed: Sulfasalazine, Methotrexate, Azathioprine, Hydroxychloroquine.
To reduce pain and stiffness, it is recommended to use NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketorolac, etc. A common side effect of non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs is the formation of ulcers in the stomach/duodenum and the development of gastritis. To prevent it, together with NSAIDs, patients are prescribed medications that reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach (Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole).
If therapy is ineffective, you can additionally use glucocorticosteroids - these are strong anti-inflammatory hormones that can be used locally (by injection into the joint) and systemically (by tablet or injection). Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone, and Dexamethasone are used in clinical practice.
The latest developments are drugs that act selectively on the body's inflammatory substances (TNF-alpha), reducing their amount. The most common is Infliximab (synonym: Remicade). It quickly relieves symptoms, in combination with a cytostatic, stops the progression of the disease and has a minimum of side effects. A significant disadvantage of Infliximab is the price. The cost of one bottle (100 mg of medicine) is about 50,000 rubles.
Gout therapy
Since the occurrence of “joint attacks” provokes an increased amount of uric acid in the patient’s blood, its level should be reduced to normal values. This can be achieved in two ways, which are combined for severe gout. The first is a strict diet, which involves the exclusion of meat and dairy products, alcohol, and legumes. The second is the prescription of Allopurinol. This is a medicine that reduces acid levels by inhibiting a special enzyme (xanthine oxidase).
Directly during the period of “joint attack,” Colchicine is recommended, which quickly eliminates the symptoms of arthritis due to its anti-gout effect.
Ankylosing arthritis
This form is slower than rheumatoid arthritis and responds better to treatment. It must be comprehensive and include the following elements:
- Physical education classes. Moderate load allows you to maintain mobility for a long time and slows down the formation of ankylosis (complete overgrowth of the joint);
- Use of medications. The basis of therapy for ankylosing spondylitis is glucocorticosteroid hormones. The same drugs are used as for rheumatoid arthritis, but in a lower dosage (most often). To eliminate pain, patients are prescribed NSAIDs - Indomethacin or Diclofenac. Sulfasalazine is used only in severe cases and rapid development of the disease;
- Physiotherapy. Improving blood circulation in the joint area helps slow down ankylosing arthritis. The optimal method is electrical stimulation according to Gerasimov, but this technology is widespread only in the Urals. An alternative can be considered galvanic currents, magnetic therapy, and ultraviolet radiation. As traditional methods of treatment, it is recommended to use “warming” procedures on the affected area: applying compresses, taking baths.
If the patient comes in at the final stage of arthritis, when the joint has become “overgrown,” the only treatment option is surgery. During the operation, the patient is fitted with a prosthesis whose functions do not differ from its biological counterpart. Unfortunately, the reserves of polymer materials are exhaustible, so after 5-7 years a second joint replacement is necessary.
Treatment of reactive arthritis
This is one of the few arthritis that can be completely cured with timely treatment by the patient. To do this, it is enough to eliminate the source of infection (urogenital, intestinal or pulmonary), after which the symptoms of inflammation of the knee joint will begin to decrease. The standard treatment regimen for the reactive form includes antibiotics and NSAIDs.
Other types of arthritis (Psoriatic, Enteropathic, Lupus and Scleroderma) are treated according to similar principles. The greatest importance in their therapy is the use of anti-inflammatory drugs of all groups:
- Cytostatics – Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine;
- Glucocorticosteroids – Methylprednisolone and Hydrocortisone;
- NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketorolac. When the disease activity is low, Nimesulide is used.
Symptoms and treatment of knee arthritis depend on the form of the disease, so it is important to carry out a comprehensive examination in a timely manner. Early diagnosis is the key to successful therapy and a prerequisite for maintaining knee mobility. If the patient does not seek medical help or it is provided unqualifiedly, the patient’s quality of life may irreversibly decrease due to joint deformation and the formation of ankylosis.
Therapy for tuberculous arthritis
Treatment of this form is carried out by a TB doctor. The patient is sent to a tuberculosis clinic, where, after diagnosis, he is prescribed a course of chemotherapy drugs. Currently, the duration of therapy for arthritis ranges from 9 months to 2 years. It should be noted that anti-tuberculosis drugs are often poorly tolerated by patients, and intolerance to some drugs occurs. The most common side effects include constant dizziness, a feeling of nausea and weakness, drowsiness, abdominal pain, allergic reactions, possible mental disorders, etc.
A healthy lifestyle is the best addition to therapy
Rheumatoid arthritis is curable, and there are cases of complete relief. It is necessary to approach treatment comprehensively and make every effort. In addition to mandatory drug therapy and proper nutrition, it is worth adding physical exercise, walks in the fresh air, hardening, and giving up bad habits.
It will help complement effective treatment and forget about rheumatoid arthritis forever:
- Swimming. The load on the joints during swimming is minimal, all muscles work. The muscles of the legs and back are strengthened. A strong muscle corset reduces stress on joints and supports the spine.
- Massage. Increases blood circulation, strengthens muscles, relieves stress.
- Bathhouse. A useful habit for joint diseases. It is not advisable to go to the steam room at the time of acute exacerbation or elevated body temperature. In other cases, a bathhouse will be beneficial.
- Spa treatment. It is useful for patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis to visit a sanatorium once a year. When the disease has subsided, preventive measures will not hurt.
The case of the disease is individual, it is impossible to say for sure whether it is possible to get rid of rheumatoid arthritis forever. Everything is in your hands; there are cases when you forgot about the disease forever. For this, some people need to move out of town, into fresh air, eat natural foods, go to the bathhouse; for some, yoga, meditation helped, for others, a full course of medication treatment. Don't give up, fight for your health!
Folk remedies
Arthritis is a disease known since ancient times. People rightly classify it as a joint disease and treat it in ways that are largely similar to the treatment of arthrosis and rheumatism.
- Take juice from burdock roots (you can buy the extract at the pharmacy) and mix it with vegetable oil: 2 parts juice and 1 part oil. The resulting ointment will be used to lubricate the sore joint.
- Decoction of elderberry leaves. 20 g of raw materials are boiled in a liter of water and allowed to brew. You need to drink up to three glasses of decoction per day.
- For treatment, you need to melt the paraffin to a temperature no higher than 510C (so as not to get burned), then dip your knee into a container with paraffin for 1-2 minutes 5-6 times. Afterwards, carefully wrap the knee in cloth and cellophane and hold until it cools completely.
- Baths with a decoction of birch buds or leaves. You can replace the ingredients with sea salt or pine needles.
- Applications with mustard. Prepare a mixture of 50 g of mustard powder, an equal amount of melted paraffin and salt (100 g each). The composition is applied to the sore knee, secured with a bandage and left overnight. The procedure will help relieve inflammation and reduce pain.
- Potatoes are good because they are available fresh all year round. For treatment you will need unpeeled tubers, which should be green. To do this, you can simply leave them in the room for several days. Then the greened tubers need to be washed well, grated on a fine grater and a compress made. It is better to carry out the procedure in the evening. For a compress: place the grated mass in warm water and heat it to 380, lay it out in a layer of up to 2 cm on a clean cloth and make a compress on the sore knee. After 25 - 30 minutes you will feel warm; if the compress does not start to warm up, it is placed incorrectly. Potatoes relieve pain and reduce inflammation. The compress is applied until the pain disappears.
Treatment of arthritis of the knee joint with folk remedies should be carried out after consultation with your doctor, this will help avoid unwanted complications.
Diet
Treatment of knee arthritis involves the need to adjust the diet. An important condition is to avoid overly salted, pickled, fried foods and canned food. The food is prepared without salt; you are only allowed to add a little salt to the portion when serving.
Preferred cooking methods are boiling, stewing, baking, steaming.
The patient needs to regularly consume jelly-like dishes - aspic, aspic, jelly. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of proteins that promote the restoration of cartilage and bone tissue.
Products recommended for arthritis:
- Beans, potatoes (preferably baked), bananas.
- Vegetables.
- Kefir, cottage cheese, bifidoc, acidophilus - in a word, all low-fat fermented milk products.
- Chicken, lean beef, turkey, rabbit.
- Citrus.
- Buckwheat and rice cereals.
To get rid of the symptoms of the disease, the patient must completely eliminate the consumption of alcohol and tobacco products.
Recommendations for patients
To avoid developing knee arthritis, you need to carefully monitor your health. You can’t stay in cold water or in the cold for a long time and overload your knees. You need to monitor your daily routine, diet and lifestyle. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to spend more time on your immune system, harden yourself, take vitamins, exercise, promptly treat infectious diseases, and undergo a full medical examination at least twice a year.
- Nutrition. For diseases of the musculoskeletal system, no special diet is required, with the exception of gout. If gout is detected, this imposes certain restrictions on the patient: it is necessary to exclude “red” meat (beef, veal, lamb), tomatoes, smoked meats, spices, fresh leafy greens, and alcohol from the diet.
- Physical therapy, swimming, cycling. Sufficient physical activity is vital for those who are faced with the problem of osteoarthritis.
- Treatment of the underlying disease, the manifestation of which is arthritis of the knee joint. It is worth setting yourself up for a fairly long-term, perhaps several months or even years, treatment with repeated courses. But the easy walk is worth it, isn't it?
- The fight against excess weight is the cornerstone for most patients with osteoarthritis. We must remember that human joints are “designed” by nature for a certain weight, and not the one we like.
- When walking, it is strongly recommended not to go up and down stairs; this increases the “wear and tear” of the knee joints.
It is also worth purchasing good quality, orthopedic shoes if possible, or ordering orthopedic insoles based on an individual impression. Like physical education, swimming pool classes or taking prescribed medications, this is a financial investment in your own body, which will reciprocate in response to care!
Exercise therapy
How to treat knee arthritis with physical therapy? Doctors warn: exercises are allowed only after the exacerbation has ceased, during the period of remission or chronic course of the disease, as well as in the initial stages.
An approximate complex of physical therapy:
- Sit on a chair with a hard back. Raise your right and left legs alternately parallel to the floor, holding each limb in the air for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times on each leg.
- Lie on your back, put your legs straight and slightly tense. Raise your limbs one by one to a height of 30-40 cm, holding them in the air for 5 seconds. The number of repetitions is 10 for each leg.
- Bicycle from a prone position – 1 minute.
- Lie on your stomach, one leg should be bent at the knee. Lift it up 7-10 times. Repeat the exercise with the other leg.
- Sitting on the floor and straightening your legs, reach your fingertips towards your feet.
To increase comfort and reduce pain, you can use special knee pads.
Avoid overly intense exercise: squats, especially loaded ones, heavy lifting, team sports: volleyball, football, long-distance running.
Forecast
Unlike coxarthrosis, which leads to disability, arthritis of the knee joint is much easier, however, due to developing synovitis, a decrease in performance is possible, and social activity also suffers, sometimes quite significantly.
The favorable prognosis directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the start of drug and physiotherapeutic treatment. The prognosis worsens when the decision on surgical treatment of the disease, if necessary, is delayed.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint Bursitis of the knee joint Synovitis of the knee joint Gout: signs and complex treatment Ankylosing spondylitis Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis): symptoms, treatment, photos
Basic therapy as a path to cure
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis should begin with basic therapy. The effect is noticeable after a couple of months; today it is a way to cure the disease. Drugs that make up the basic therapy:
- Aurotherapy - treatment with gold. The drugs are used if the body does not tolerate Methotrexate. Gold has advantages, for example, drugs help children and adolescents, inhibit the development of the disease, use is allowed for inflammatory processes, malignant tumors. Methotrexate is a drug included in basic therapy.
There are medications for rheumatoid arthritis. The problem lies in the regularity of taking medications and constant monitoring by a doctor. Treatment of the disease depends on the patient's desire to get better. If there is no faith in healing, it is difficult to achieve a positive result. Depression and stress are provocateurs of the disease and should be excluded with the help of a psychologist.