- History taking
- Drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis
is a chronic disease of blood vessels, in which “bad” cholesterol and other LDL are deposited on their inner walls in the form of plaques and plaques, and the walls themselves become denser and lose their elasticity. The vessels gradually become hard due to the sedimentation of fats and lime on the walls, lose their elasticity and, as a result, narrow, which reduces blood access to the organs. Eventually, the vessel may close completely. And when this is accompanied by a blood clotting disorder, there is a tendency to thrombosis and ischemic damage to organs occurs.
Atherosclerosis is considered one of the most dangerous diseases that leads to death. Atherosclerosis is recognized most often when problems with the blood supply to the heart, limbs and brain already appear, i.e. the disease is diagnosed in the last stages. Atherosclerosis is one of the main causes of the development of cardiovascular diseases: coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
The percentage of people with atherosclerosis increases depending on their age, i.e. this disease is typical for older people. Therefore, doctors call it a disease of old age, but every year it becomes younger, which is associated with the modern lifestyle.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko - the true causes of plaques on the walls of blood vessels, preventive measures:
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
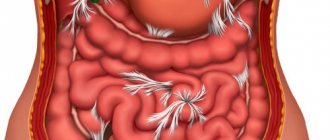
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease, so it usually affects all major blood vessels of the body. It follows from this that the manifestations are also diverse. As a rule, the heart, brain, and limbs (most often the lower ones) are affected. The symptoms are specific, but they do not always manifest themselves clearly enough to unambiguously diagnose atherosclerosis.
Symptoms depend on which organ suffers from lack of blood circulation to a greater extent. In any form of atherosclerosis, two symptomatic periods are distinguished. In the preclinical period, the process is just beginning, so there are no specific manifestations. Significant problems with blood supply and organ functioning begin when the lumen of the artery closes more than 1/2.
Symptoms of heart vessel damage
Heart pain occurs with a frequency of 75%. Atherosclerosis affects the coronary vessels and reduces the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium. The heart is one of the organs most sensitive to changes in nutritional intensity. In this indicator, it is second only to the brain. However, symptoms develop immediately; it is important to correctly interpret the patient’s sensations.
Disruption of the normal blood supply to the heart is manifested by angina pectoris syndrome.
Cardiac symptoms occur periodically and include:
- Pain in the chest area. Pressing, dull, aching or burning (which is characteristic of an ischemic process). Pain sensations radiate to the shoulder blade, left forearm, hand or fingers (along the entire length of the circulatory system);
- Feeling of pressure on the chest (as if a heavy weight was placed on the chest);
- Painful sensations when breathing (both on inhalation and exhalation);
- Respiratory disorders.
Angina pectoris, as a characteristic syndrome for atherosclerosis, manifests itself in attacks. The attacks are accompanied by instability in blood pressure levels.
Somewhat less frequently, the following symptoms appear with atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels:
- Pain in the lower jaw, ear, neck on the left side (irradiation, but in the opposite direction);
- Back pain;
- Feeling of weakness in the limbs;
- Feeling of cold, increased sweating and chills (“goosebumps”);
- Tachycardia or bradycardia (heart rhythm disturbance);
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Confusion of consciousness up to complete loss of consciousness for a short period of time.
The intensity and frequency of symptoms depends directly on the degree of tension in the body (stress, overeating, substance abuse, etc.).
Find out more:
Atherosclerosis of the aorta of the heart
[Video] Educational films Eureka (Eureka) - what is an atherosclerotic plaque and thrombus, how do they form?
Symptoms of vascular lesions of the upper and lower extremities
The symptoms are as follows:
- Feeling of cold (chilliness) in the hands or feet;
- A feeling of “goosebumps” running down your arms or legs, as if after a long stay in the same uncomfortable position (“numbness”);
- Paleness of the skin: the skin takes on a deathly pale color and the vascular pattern is clearly visible (marble-colored skin).
In the later stages of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities, more severe manifestations occur:
- Degeneration of tissues that receive insufficient amounts of necessary substances (thinning of the fat layer, irreversible hair loss);
- Pain in the extremities. In the case of damage to the arteries of the legs, the so-called “intermittent claudication” is observed. The pain is localized in the thighs, buttocks and calves and is paroxysmal in nature, as a result of which the patient begins to limp;
- Formation of wounds on the legs (trophic ulcers associated with lack of tissue nutrition);
- Redness of the toes or hands, development of persistent swelling;
- Tissue necrosis (gangrene).
Find out more:
Obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
Symptoms of cerebral vascular damage
It is most susceptible to nutritional disorders, but the primary symptoms are characteristic not only of atherosclerosis. Thus, problems with cerebral circulation are observed with osteochondrosis, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, etc.
Symptoms appear gradually, increasing:
- Cephalgia (or unspecified headache). Covers the entire head without the ability to determine the exact location. Has a bursting or pressing character;
- Ringing and noise in the ears;
- Sleep problems. A person suffers from insomnia, or vice versa, he is constantly sleepy. During sleep, severe or nightmare dreams often occur (which is associated with brain activity and diffuse changes due to lack of blood circulation);
- Deterioration of a person’s character (changes in personality);
- Nervousness, high excitability, increased anxiety;
- Lethargy and fatigue;
- Violations of the basic functions of the body: breathing, speech, nutrition. The person may speak slurredly, often choke on food, etc.;
- Impaired coordination of movements, problems with independent movement and orientation in space (due to damage to the cerebellum).
Find out more:
Cerebral atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels
Homeopathy
Homeopathic doctors claim that taking statins, sequestrants and nicotinic acid are effective, but after completing the course of treatment the disease begins to progress again. And with the help of homeopathic medicines, atherosclerosis can be defeated by affecting the cause of the disease.
Herbal preparations trigger self-regulation processes in the body, helping to get rid of acute signs of atherosclerosis. They act at the cellular level, restoring tissues affected by the disease. The blood is cleansed of “bad” cholesterol, the formation of plaques and blood clots is prevented, and the lumen of blood vessels expands.
Most often, homeopaths recommend taking the following remedies:
- Cholesterol;
- Golden iodine;
- Arnica;
- Konium;
- Krategus;
- Edas.
Is it possible to cure atherosclerosis with homeopathy, many patients ask. Therapy with herbal preparations initially differs from traditional
Patients with severe signs of atherosclerosis are prescribed drugs that improve venous blood flow - Botrops, Helleborus, Ginko Biloba, Lachesis. But only a homeopathic specialist can recommend any treatment.
Causes of atherosclerosis
The causes of atherosclerosis are high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high blood cholesterol. But the main cause of atherosclerosis is a violation of cholesterol metabolism. The formation of atherosclerosis is a natural process that begins at approximately 10–15 years of age. With age, it may slow down, or it may speed up.
The following risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis are identified:
- Floor.
Men are more susceptible to developing atherosclerosis than women. The first signs of this pathology can appear as early as 45 years of age, or even earlier, in women - from 55 years of age. This may be due to the more active participation of estrogens in the metabolism of cholesterol and low- and very low-density lipoproteins;
- Age.
This is a natural risk factor. With age, atherosclerotic manifestations worsen;
- Heredity.
Of course, this is one of the reasons for the appearance of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a multi-cause disease. Therefore, hormonal levels, hereditary dyslipoproteinemia (impaired plasma lipid profile), and the activity of the immune system play important roles in accelerating or slowing down the development of atherosclerosis;
- Bad habits.
Smoking is poison for the body. This habit is another reason for the development of atherosclerosis. If you want to have healthy blood vessels, quit smoking! As for alcohol, there is an interesting dependence: drinking small doses of alcohol - about 50 g of vodka, 100 g of wine or 0.5 liters of beer daily is an excellent prevention of atherosclerosis. True, the same dose also contributes to the development of liver cirrhosis. So we treat one thing and cripple another. But large doses of alcohol accelerate the development of atherosclerosis;
- Excess weight.
This factor increases the likelihood of atherosclerosis. Obesity can lead to diabetes, and this pathology is a direct path to atherosclerosis;
- Poor nutrition.
Fatty, unhealthy foods are a major risk factor. Eating is a very important physiological process in our lives. Our future health will depend on how healthy the foods we consume are. Few people know that not a single diet, except for therapeutic and balanced diets, is approved by the World Council of Food Hygiene. You need to eat rationally and adequately to your needs and energy costs.
The average life expectancy of the Japanese is 90 years, and the Russians are about 60. Why is there such a difference? The answer is simple: look at what the Japanese and other eastern peoples eat. Their menu includes a variety of grains, vegetables, herbs, beans and fresh fish. Every day, the market in Tokyo is filled with seafood that contains valuable fatty acids. Why treat a disease if it is easier to prevent it? Start eating right from an early age so that in old age you can thank yourself for it.
Video: formation of atherosclerotic plaque
Types of atherosclerosis
Depending on the location of cholesterol plaques, the following types of atherosclerosis are distinguished:
- Coronary - the vessels of the heart and all vessels located nearby are affected.
- Cerebral - means damage to the blood vessels of the brain.
- Brachiocephalic - means damage to the carotid, vertebral or subclavian arteries;
- Obliterative - damage to the arteries of the lower extremities.
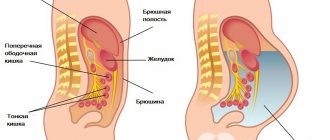
- Renal - damage to the blood vessels of the liver.
- Mesenteric - damage to the intestinal vessels.
Forms can manifest themselves independently, but more often they do so systematically.
Risk factors
They do not directly cause the onset of the disease. But they increase its likelihood, and if there is already a diagnosis, they accelerate progression.
- Large body weight.
- Being male. The ratio of demographic groups by incidence is 4:1 (m/f)
- History of hypertension.
- Improper diet with a predominance of fatty foods.
- Hypothermia of the lower extremities.
- Caffeine consumption. Drug addiction.
- Addiction to alcohol. Ethanol also causes severe vasoconstriction.
- Burdened heredity.
The reasons are taken into account in the system. Often they are combined with each other. Risk factors should be considered as part of the development of recommendations for prevention in a particular person and generally as an epidemiological measure.
Cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis
Cholesterol is a special chemical compound, by its nature a fatty alcohol. The role of cholesterol in the synthesis of cellular structures and organelles has been proven (cholesterol is known to be involved in the formation of cell membranes). However, an increase in the level of the substance in the blood directly increases the risk of developing atherosclerotic pathology and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, since it indicates the onset of disorders of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in the body.
It is possible to prevent the development of this terrible disease only by giving up bad habits and maintaining the concentration of fatty alcohol in the blood at the same normal level constantly. However, cholesterol is atherogenic only in excess.
Its normal content is necessary not only to perform the structural function, but also:
- For normal digestion. With the participation of fatty alcohol, the liver synthesizes digestive juices necessary for processing fat-containing compounds;
- For stable synthesis of sex hormones and pancreatic hormones.
Cholesterol enters the bloodstream in several ways:
- Synthesized by the liver
. The liver produces the most cholesterol. Typically, its more active production is associated with a deficiency of the compound and the inability to replenish it with cholesterol from food. If liver function is impaired, interruptions and problems with regulating the level of the substance in the blood are also possible;
- Comes with foodstuffs
. This cholesterol is no more than 25%. Cholesterol is found in products containing animal fats. Its highest concentration is found in egg yolks, offal (brains, liver, kidneys), shrimp, margarine, and bacon. The cholesterol they contain enters the blood in a free state and only then is transferred by chylomicrons to the liver, where, depending on the functional characteristics of the body and the usual diet, it is converted into two types of lipoprotein complexes: “good” (or HDL) and “bad” (LDL). The former cleanse the walls of blood vessels from layers of fat, and the latter form them.
In addition to the fact that cholesterol is actively synthesized and used by the body, it is also actively removed beyond its boundaries. Most of the compound is released naturally through the digestive tract. A slightly smaller amount is excreted through the death (desquamation) of the upper layers of the skin and intestinal mucous membranes.
An increased level of cholesterol in the blood proportionally increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis - this phrase can often be heard, but is it really so? Research from the journal Neurology. The normal level of cholesterol in the blood is far from a guarantee and is not insurance against the formation of pathology for other reasons.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko explains why there is no need to lower cholesterol:
Atherosclerosis is directly related to the presence of concomitant diseases (hypertension, obesity, neuroendocrine form of hypothalamic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, substance abuse, etc.). They act as equivalent risk factors for the development of the disease.
One way or another, cholesterol plays a key role in the development of atherosclerosis. To reduce the risk, it is necessary to adhere to a hypocholesterol diet and maintain the concentration of the substance at approximately the same normal level.
Find out more:
High cholesterol - what are the causes? What is the norm? How to lower cholesterol levels?
Preventive actions
To avoid the development of pathology, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right.
Exclude from your daily diet fried, fatty foods, pickles and marinades, smoked foods, fast food, mayonnaise, foods high in sugar and fat, pasta, cakes, pastries, and carbonated drinks.
Recommended for use:
- Dishes from low-calorie meat of turkey, rabbit, chicken and veal, steamed or boiled.
- Fruits, vegetables and a variety of greens.
- Sea and river fish baked in foil.
- Soups with vegetable broth.
- Seafood.
- Cereals of all kinds.
- Compotes and decoctions of dried fruits, herbal teas, fruit drinks and juices from freshly squeezed fruits.
- Only olive or sunflower oil.
- Boiled eggs.
- Low-fat dairy products.
In addition to your diet, you will have to give up tobacco products and drinks with high alcohol content. You can drink a glass of red or dry wine before eating.
You will also have to change from tight high-heeled shoes and sneakers to more comfortable ones. In the winter season, do not allow your feet to become hypothermic.
Do not feel sorry for yourself, and try to do as much physical exercise as you can.
Suitable activities for this include visiting the pool, Nordic walking, yoga for beginners, cycling and water aerobics.
Atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus
Cholesterol is actively involved in the synthesis of digestive juices and pancreatic hormones, and, despite the fact that it is not the cause of diabetes, it still significantly affects the course of the disease.
Diabetes mellitus is considered an increased risk factor for the development of vascular atherosclerosis (the likelihood of development increases by more than half). Also, vascular atherosclerosis increases the severity of diabetes. In the presence of diabetes mellitus, the incidence of atherosclerosis is set at equal limits in both men and women (although without diabetes, men are more likely to get sick).
Diabetes mellitus, in turn, seriously complicates the course of atherosclerosis:
- Atherosclerosis can also form at a young age if you have diabetes. Although the disease usually develops after 45-50 years;
- There is a high probability of aneurysms;
- The vessels not only become clogged, but also become extremely fragile, which increases the likelihood of strokes;
- The process becomes systemic, equally severely affecting the heart, brain, and limbs.
Atherosclerosis begins in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is associated with digestive and lipid metabolism disorders, which causes a stop in normal metabolism. The walls of blood vessels become extremely permeable to fatty fractions, and therefore much more “bad cholesterol” penetrates into the bloodstream. It forms fat deposits on the walls of large arteries, gradually closing the lumens of the artery.
Over time, the layer of fat is encapsulated by connective tissue and crystallizes under the influence of calcium deposits. This entire structure becomes “stony” and the lumen of the artery closes even more. The vessel becomes brittle and loses its conducting function. The result is impaired circulation in the affected area, increasing ischemia, vessel rupture and tissue necrosis.
Patients with diabetes are 4 times more likely to simultaneously suffer from diseases of the cardiovascular system, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease and angina. In addition, with atherosclerosis in diabetics, the likelihood of rapid development of necrosis (gangrene) of the lower extremities increases almost seven times. These factors must be taken into account during treatment.
Find out more:
Diabetes mellitus: causes, symptoms and treatment
Why is atherosclerosis dangerous? Stages of development
According to statistics, atherosclerosis is the most common disease of the cardiovascular system and the main cause of death for the vast majority of patients around the world. Atherosclerosis is variable, and, despite the fact that the essence of the disease is the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, it significantly affects the entire body. Lack of blood circulation affects the heart, brain, abdominal organs, lower and upper (rarely) limbs. Disturbances in blood flow in the arteries also affect smaller blood vessels, causing secondary ischemia.
Atherosclerosis is a polyetiological disease. The exact reasons are not fully known, but it is known that the mechanism is based on a disorder of lipid metabolism. This dysfunction is the trigger for the onset of a dangerous illness.
There are several stages in the development of pathology:
- The stage of formation of fat stains (or lipid stains).
At this stage, no specific symptoms are observed, and the patient does not suspect the presence of atherosclerosis. The essence of the stage lies in diffuse changes in the walls of the arteries (molecules of lipoprotein complexes penetrate the structure of the arterial wall and form a thin layer). Externally, these changes appear as yellowish-brown stripes along the length of the affected area of the vessel. Not the entire tissue of the bloodstream is affected, but only individual segments. The process is developing quite quickly. It is accelerated by existing cardiovascular pathologies, diabetes and obesity;
- The stage of formation of lipid layering.
The tissue underneath the lipid bands becomes inflamed. The body thus tries to fight the imaginary intruder. A long-term focus of chronic inflammation is formed. Constant inflammation leads to the decomposition of the lipid layer and tissue germination. As a result, the fatty accumulation is encapsulated and rises above the artery wall;
- Stage of development of complications.
This is the last stage in the formation of atherosclerosis. At this stage, complications develop, and symptoms appear most clearly. There are two main types of complications: rupture of encapsulated fatty deposits (plaques), which entails the release of a large amount of blood, and blood clots. Blood clots, together with plaque products, get stuck in the lumen of the vessel, completely clogging it. In such a situation, the development of a stroke is possible. If blood clots block large arteries that provide necessary nutrition to the limbs, tissue necrosis and gangrene are likely to occur.
The timing and speed of development of atherosclerosis is quite difficult to predict. We can talk about years or a few months. It all depends on the characteristics of metabolism, metabolic rate, the presence of a predisposition to atherosclerosis and diseases that increase the risk of its development, and many other factors.
Theories of the appearance of the disease
There are several theories for the development of atherosclerosis, but they all meet two basic rules:
- the primary disorder leading to the disease is a disorder of lipid metabolism, and the violation of the integrity of the vessel wall is secondary;
- Damage to cellular, connective tissue and other structures of the vessel wall is the main link in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
The cholesterol theory, developed by Dr. Anichnokov, suggests that the development of the disease is caused by excess amounts of fat and cholesterol. Subsequently, the doctor put forward another, combined, theory of the development of the disease. In it, cholesterol is already considered as a factor provoking atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. According to the combined theory of atherosclerosis, the disease develops due to:
- disorders of lipid regulation and metabolism;
- alimony factors;
- hemodynamic and other mechanical effects on blood vessels;
- age-related and other primary changes in blood vessels.
The main provisions of the combined theory formed the basis of the combined-infiltration theory . She says that the disease develops incl. due to increased concentrations of lipids in the blood. The endothelial theory considers the occurrence of atherosclerosis due to damage to endothelial cells. Violation of lipid metabolism in it only as a condition promoting atherogenesis. The monoclinal theory of disease development considers atherosclerotic plaque as a benign tumor that appears as a result of exposure to viruses and mutagens. The membrane theory is close to monoclinal. According to it, proliferation of smooth muscle cells occurs due to excess intake of cholesterol.
The autoimmune theory has begun to actively develop in recent decades. The theory suggests that the pathological process is provoked by autoimmune complexes, which include lipoproteins as an antigen.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis
Diagnosing advanced atherosclerosis is relatively easy. It is a completely different matter to clarify the localization of the process and accurately determine the source of the lesion. This requires a lot of work. Only an experienced doctor can cope with such a difficult task.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Taking anamnesis;
- Initial examination of the patient using special functional tests;
- Laboratory analyzes and instrumental studies. Thanks to them, it is possible to establish the very fact of the presence of the disease, determine the stage and localization of the process, and assess the general condition of the patient’s body.
History taking
The primary analysis of the patient’s condition begins with a survey regarding complaints and heredity.
Firstly, with this pathology, there will be at least three specific symptoms in the anamnesis; in addition, there will most likely be signs (and maybe a confirmed diagnosis) of a disease that provokes atherosclerosis.
Among them:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Previous myocardial infarction or stroke;
- Angina syndrome, ischemic heart disease;
- Kidney pathologies.
Such a diagnosis does not provide a complete picture, but it allows one to determine in general terms the condition of the body and draw up a plan for diagnostic measures.
In addition, it is important to establish the presence of risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, psychoactive substance use, obesity.
Initial examination
In addition to functional tests aimed at assessing the blood supply to the extremities, an experienced doctor pays close attention to the following factors:
- Disappearance of hair on the legs or arms;
- Sudden decrease in the patient's body weight;
- Heart murmurs, increased blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances;
- Hyperfunction of the sweat and sebaceous glands;
- Nail deformation;
- Constant development of edema in the absence of kidney disease.
Laboratory and instrumental methods
- Venous blood donation to assess indicators such as atherogenicity coefficient, total cholesterol;
- X-ray examination and angiography. X-rays allow you to evaluate the condition of the aorta, since plaques are clearly visible in the images. Angiography involves injecting a special contrast agent into the bloodstream and further monitoring the blood flow;
- Ultrasound. Allows you to evaluate the speed of blood flow in a particular part of the artery. Thanks to this method, it is possible to identify the slightest deviation and determine the degree of insufficiency of blood supply.
There are other diagnostic methods. Specific methods are determined by the doctor based on the clinical picture.
Treatment of atherosclerosis
As a rule, in 80% of cases, drug therapy is sufficient to eliminate the cause of atherosclerosis and its harmful consequences. Treatment with special drugs is combined with the prescription of a diet and an optimal regime of physical activity.
Drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis
Among the drugs for atherosclerosis, drugs of several groups can be distinguished:
- Statins
. The most popular statin drugs are still used today. Their effect is to inhibit the liver's function in producing cholesterol. These include: Rosuvastatin, Lovastatin, Atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Simvastatin. In parallel with statins, patients with atherosclerosis are prescribed medications to maintain the activity of the heart and digestive organs (since statins have the most negative effect on them). At the present stage of development of medicine, reputable scientists and practitioners question not only the effectiveness of statins, but also the very fact of the role of cholesterol in the development of atherosclerosis, considering the danger of this substance to be unreasonably overestimated. Read more about statins;
- Lipid-lowering drugs
. Vasosponin is a natural drug that normalizes cholesterol levels by increasing the excretion of cholesterol in bile from the body and limiting the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. The drug has no effect on the liver; according to research results, it helps reduce the level of total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides and the atherogenic coefficient. It can be taken in monotherapy and in complex therapy with other lipid-lowering drugs. Vasosponin combines well with statins, allowing in combination with them to achieve an additional reduction in lipid profile values up to 30% [1]. The drug helps reduce the risk of atherosclerosis by preventing the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaques in the arterial vessels of the heart, brain and lower extremities;
- LCD sequestrants
. Significantly inhibit the function of bile acid synthesis by the liver. In this regard, the body has to more actively consume cholesterol in order to ensure normal and stable digestion. With prolonged use, disorders of the digestive system are possible. Prescribed at the initial stage of the disease or to prevent pathology;
- Fibrates
. They destroy neutral fatty structures - triglycerides. They are quite effective in the fight against atherosclerosis, but are strictly contraindicated for people with liver problems. When taking fibrates, the level of neutral fats decreases by 20-55%, cholesterol by 10-25%, LDL by 10-35%, and the concentration of HDL increases by 10-30%. Read more about fibrates;
- Nicotinic acid preparations (vitamin B3)
. Despite the fact that they do not fight cholesterol, they have a vasodilating and antispasmodic effect. Niacin will reduce cholesterol levels by 10-15%, LDL by 5-25%, triglycerides by 20-35%, and increase HDL levels by 15-35%. They are used in combination with other medications and form an important part of drug therapy (on the topic: record-breaking products for vitamin B3 content). However, due to frequent side effects, niacin is rarely used in the treatment of atherosclerosis. The therapeutic dosage is 1000-6000 mg, which is 50-300 times more than the usual daily intake.
- Omega-3
. This is the safest remedy of all drugs for atherosclerosis. It can be used as an alternative to fibrates or an addition to statins. (more details: benefits of omega-3 + TOP products of record holders);
- Ezetimibe-SZ (ezetrol)
is a cholesterol absorption inhibitor; it inhibits the activity of a specific carrier protein, without which dietary cholesterol cannot be absorbed. Reduces low-density cholesterol content by 18%.
- Cumabs (evolocumab and alirocumab)
- antibodies to the enzyme that regulates the rate of absorption of cholesterol contained in the blood by liver cells.;
- Thrombolytic therapy. With atherosclerosis, the risk of thrombosis increases, so antithrombic drugs are often prescribed. These include: Fibrinolysin, Streptokinase, Urokinase and others. More information about anticoagulants, list of drugs
Conservative therapy also includes physical therapy. This method is indicated for persons with atherosclerosis of the extremities.
Best Herbal Remedies
Inflaminat . The composition of the drug includes tricolor violet, calendula and black elderberry. All plant components have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. The drug has a pronounced antiatherosclerotic effect. Taking inflamint for two years reduces atherosclerotic progression in the carotid arteries by 45% [1].
Nattokinase is an enzyme that dissolves blood clots. The 2021 study included 82 patients. They took nattokinase for 26 weeks, and at the end of this time, atherosclerotic plaques decreased in the first group by 36.6%, in the second by 11.5% [2]. Goes well with seppeptase.
Revital Garlic Pearls. These are chewable “candies” containing allicin (garlic extract). Allicin has been shown to lower LDL and increase HDL.
Pumpkin oil. Reduces cholesterol levels, prevents blood clots, and promotes the secretion of bile.
Ravisol . This is a tincture that is made from medicinal plants that have been proven effective against atherosclerosis in numerous studies. It contains mistletoe, horsetail, Japanese sophora, hawthorn fruits, red clover flowers, chestnut fruits, and periwinkle grass. Reduces the level of bad cholesterol, improves blood circulation in the heart and brain, and resolves blood clots.
On this topic:
7 folk remedies for atherosclerosis with proven effectiveness
Useful supplements for atherosclerosis
- Magnesium . Able to relax muscles, balance the amount of minerals in the body. Research results have established that a decrease in magnesium causes dysfunction of the endothelium, which provokes the development of atherosclerosis [3].
- Beta-sitosterol is a drug created on the basis of plant sterol. The active substance inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol and reduces the levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood. Sesame is considered the record holder for beta-sitosterol content - 210 g of the active component was found in 100 g of seeds. Despite their high concentration, sesame seeds do not fully provide the body with beta-sitosterol. Beta-sitosterol inhibits the absorption of beta-carotene and vitamin E. Depending on the indication, the recommended dose can vary from 800 mg to 6 g per day. The volume is divided into three doses and taken 30 minutes before meals.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) . Multiple observations have shown that Coenzyme Q10 has antioxidant effects. Subjects who were offered CoQ10 supplements in the first three days after a heart attack reported a decrease in chest pain. Continuous use of CoQ10 significantly reduces the likelihood of another heart attack. Deaths from heart disease were less common in these patients than in those who did not take supplements.
- Selenium. Medical studies have proven that people who are offered 100 to 200 mcg of selenium per day are less likely to develop cardiovascular disease.
Surgery
In modern medical practice, three main methods of surgical treatment of atherosclerosis have been developed.
Highly invasive:
- Shunting.
The essence of bypass surgery is to suture the affected vessel to a healthy one, due to which a new blood line is formed and the blood supply to the tissue is gradually restored;
- Endarterectomy.
Used to remove plaque in the carotid arteries (neck) or peripheral arteries;
- Vascular prosthetics.
Modern materials make it possible to completely replace the affected vessel and restore blood supply functions.
Minimally invasive method:
- Angioplasty.
The essence of the method is to insert a specialized catheter through the femoral artery, which, under camera control, is advanced through the bloodstream by an endoscopist to the affected area. After this, the necessary manipulations are performed to clean or expand the vessel.
- Atherectomy.
A procedure to remove plaque from the arteries. To do this, use a laser catheter or a surgical rotating razor.
Thus, atherosclerosis is an extremely controversial and complex disease, which, however, requires maximum attention, since it can lead to life-threatening and health-threatening consequences. The symptoms of the disease are quite pronounced, and with the proper level of training, the doctor will easily establish a diagnosis, as well as determine the localization of the process and prescribe competent and effective treatment. A wide arsenal of tools and methods for diagnosing atherosclerosis, even in the early stages, helps the doctor with this. The specialist will determine the specific examination strategy himself, based on their feasibility and the degree of confidence in the diagnosis.
Treatment of atherosclerosis at the present stage of medical development does not present any great difficulties. In the vast majority of cases, it is possible to get by with “little bloodshed.” If conservative treatment methods are not sufficiently effective, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Correct and competent diagnosis combined with an effective course of treatment is the key to a favorable outcome.
The best diet
The best diet for atherosclerosis is the Mediterranean diet, which focuses on whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, olive oil and moderate daily wine consumption. The Mediterranean diet is not low in fat. Instead, it is low in saturated fat but high in monounsaturated fat. It's good for the heart. In a long-term study of 423 heart attack survivors, those who followed a Mediterranean diet had a 50% to 70% lower risk of recurrent heart disease than people who did not receive special dietary advice.
More details:
Mediterranean diet: pros and cons
TOP 8 most useful foods for atherosclerosis
To maintain healthy arteries, you should introduce the best foods that have a healing effect into your diet:
- Asparagus. An excellent herbal product that helps cleanse arteries. The active substances of plant fiber have a hypotensive effect and suppress thrombus formation, which causes serious consequences. The effect of asparagus extends to the veins and arteries, where it suppresses signs of inflammation. The product stimulates the production of its own antioxidant - glutathione, which can reduce inflammatory manifestations, prevent oxidative reactions that cause stenosis and clogging of the lumen of the arteries. Alpha-linoleic and folic acids, which are found in asparagus, prevent the development of atherosclerotic signs.
- Avocado. Avocado fruits contain large quantities of vitamin E, which can suppress oxidative processes involving cholesterol. Potassium - has antihypertensive properties. In general, eating avocado promotes the growth of “good” cholesterol and the removal of “bad” cholesterol, which helps clear lipid deposits from the arteries.
- Whole grains. Whole grains are high in soluble plant fiber, which can bind LDL and naturally remove it from the body.
- Broccoli. Broccoli is loaded with vitamin K, which protects arteries from calcification and blockage. The product inhibits oxidative processes. Vegetable fiber, which is contained in broccoli, lowers blood pressure and normalizes the tone of the vascular walls. Pronounced tone leads to rupture of the arterial wall. Broccoli contains sulforaphane, which stimulates protein metabolism in the body. The combined effect of the active substances helps prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arterial lumens.
- Pomegranate. Pomegranate fruits contain ellagic acid, which has an anti-inflammatory effect and facilitates the elimination of cholesterol. There is even a very interesting study where people took pomegranate juice or a placebo every day for a year. In the placebo group, intimal thickness (the inner layer of blood vessels) increased by 9%, while in the control group it decreased by 30% [4].
- Olive oil. One of the most valuable vegetable oils. The product is rich in essential acids that regulate the balance of “good” and “bad” cholesterol. Ideal for dressing salads and preparing dishes.
- Coffee. One of the most favorite morning drinks. A long-term medical experiment showed that just three cups of coffee a day can reduce the likelihood of atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis [5].
- Tea with bergamot . Bergamot has the same properties as statins. The drink lowers cholesterol levels while maintaining healthy arteries [6].
On topic: Diet for atherosclerosis for every day
Surgical intervention
In some cases, atherosclerosis of blood vessels is treated surgically. The intervention is indicated for patients in whom there is a real threat of complete occlusion of the artery by a thrombotic formation or plaque. After conducting high-quality diagnostics (coronary angiography, angiography, ultrasound examination of blood vessels), the specialist selects the most appropriate method of surgical treatment.
Endarterectomy
This type of surgical treatment is suitable for patients with severe atherosclerotic changes in the legs and arms. It is the excision of a plaque along with a small section of the internal tissue of the vessel from a peripheral blocked artery.
Endarterectomy is recommended for arterial lesions when the occlusions range from 7 to 9 cm and are segmental. Open surgery involves a longitudinal arteriotomy, in which the vessel is cut lengthwise. The changed masses of the capillary along with the plaque or thrombus are excised, the process is controlled visually using powerful equipment.
The hole left after the cut is closed with a vascular suture or the surgeon applies a patch. A semi-closed operation to relieve arterial occlusion is performed with a small transverse incision of the vessel. In this case, the changed tissue is peeled off and removed instrumentally.
Peripheral artery stenting
This method of therapy involves X-ray endovascular expansion of the clogged lumen of the capillary. This is done using balloon angioplasty followed by installation of a stent inside the vessel. The operation is indicated for patients with a specific area affected by occlusion, when the narrowing of the artery is local.
Stenting - principle of operation
An artery is punctured in the thigh or armpit area, monitoring the process using x-rays. Next, the affected vessel is dilated by inserting a balloon catheter into it. If necessary, a mesh tube (stent) is installed into the artery cavity and secured, thereby ensuring the patency of the capillary.
Laser treatment
Laser therapy for atherosclerosis is a method that was tested in the 80s, and is now widely used for existing indications. The main effect on the arteries is produced by the beam, which creates a high temperature. A quartz thread is first inserted into the cavity of the affected vessel, it is advanced to the place where the artery is narrowed by a plaque and cannot fully move blood.
After connecting the laser, the plaque dissolves under the influence of temperature, turning into a gas.
The procedure is simple but effective; similar methods are used in the treatment of varicose veins of the lower extremities. Laser treatment is popular in Israel, while simultaneously prescribing the patient anticoagulants, Omega-3 and Omega-6 supplements, new generation statins and drugs that prevent further blockage of the arteries.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
Cardiac surgery, which is performed on patients with diagnosed stenosis (narrowing) of the coronary arteries and signs of ischemia of the main muscle of the heart - the myocardium. In this case, a bypass path of blood flow is created through venous or arterial shunts. The radial artery or vein on the leg, located under the skin, is fixed directly to the aorta, and on the other hand - to the artery below the stenotic area of the vessel.
During the intervention, the patient must maintain artificial blood circulation, and it is also necessary to provide high-quality extracorporeal gas exchange. For this purpose, surgeons use “heart-lung” equipment if the operation is performed on a non-functioning heart.