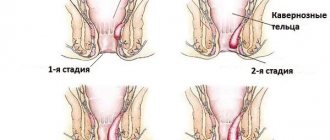
The deep veins, which are located under the muscles, can be affected by acute disease. Yes, this is precisely thrombosis of the lower extremities, which can poison the life of any person.
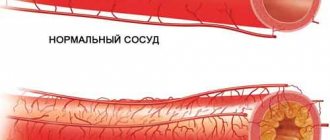
The disease manifests itself in the form of the formation of clots, which can reach a size capable of completely blocking the lumen in the vessel.
If it progresses rapidly, the disease leads to disability. If measures are not taken to eliminate the pathology, then everything can end in death.
The vessels of the lower leg are more unable than others to resist the formation of such clots. The resulting blood clots try to attach to the vascular wall. The first day they are still very weak and often migrate with the bloodstream.
After the clot gains sufficient hardness, its body adheres tightly to one of the walls of the veins. This is where deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities occurs.
Simply put, the disease is an inflammatory process at the site where the blood clot has formed. After which, due to severe inflammation, additional clots appear. Their localization occurs above the place where the primary phlebolith is fixed. The transformation of thrombosis into thrombophlebitis occurs within 7 days.
general information
One of the biological systems responsible for the normal viability of the human body is hemostasis. Its main task is:
- dissolution of blood clots;
- stopping bleeding in case of damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- keeping blood in a liquid state;
The formation of blood clots is one of the mechanisms of hemostasis, i.e. its appearance is necessary to stop bleeding.
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms in the lumen of a vessel when it is damaged. It covers the affected area and thus prevents bleeding. This process is called thrombosis. So, on the one hand, thrombosis protects the individual’s body from blood loss, and on the other hand, it is a provocateur of pathological conditions associated with a malfunction in the blood flow system. Causes of thrombosis:
- damage to the walls of blood vessels as a result of surgery or injury;
- change in blood flow speed;
- high blood viscosity.
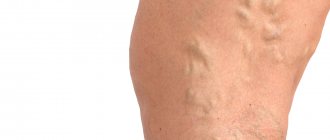
There are venous and arterial forms of thrombosis. Next we will talk about thrombosis of the leg veins (photo below). It has two forms: thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis, in which a blood clot breaks off and blocks a pulmonary artery.
The clot can completely cover the lumen of the vessel or only the edge of the wall. In the second case, it is called parietal and most often affects the veins of the lower extremities. Its presence provokes an inflammatory process called thrombophlebitis. Complications of thrombosis are precisely the result of untreated thrombophlebitis. Therefore, it is important not to miss the first symptoms of a blood clot.
Why does thrombophlebitis occur?
The disease is referred to as an inflammatory process, which can manifest itself as a complication of varicose veins of the lower extremities if it is not treated properly.
In most cases, thrombosis occurs on one side without affecting the second limb. Inflammation in the problem area occurs precisely due to the formation of phlebolith.
Factors contributing to the development of thrombosis:
- oncological diseases;
- long bed rest;
- hereditary predisposition;
- high blood clotting;
- constantly being in a standing or sitting position;
- advanced age or overweight;
- period of bearing a child.
Classification according to the form of thrombosis
- Migrating thrombophlebitis. It is characterized by simultaneous damage to a group of vessels. Inflamed lesions occur regularly, but can disappear after a period of time. Moreover, after they are absorbed, there are no traces left of them.
- Acute thrombophlebitis. It can develop in just a few hours, and all the symptoms will be sharply expressed.
- Chronic thrombophlebitis. The course of the disease is gradual, the development of pathology is almost imperceptible. Exacerbations occur quite rarely.
Development of the disease in the lower extremities. First signs
How to identify leg thrombosis at an early stage? This is a question asked by many patients. At the development stage, a blood clot is quite difficult to identify, since during its formation it is securely attached to the walls of blood vessels. As it grows, there is a high risk of separation and complications. A small blood clot does not interfere with the nutrition of soft tissues, since it does not block blood flow. However, even during this period, signs are observed indicating the beginning of problems with the nutrition of the soft tissues of the lower extremities. As a result, local immunity is reduced, and, as a result, the limb becomes vulnerable to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Often the affected leg is attacked by a fungus. An individual should pay attention to the following symptoms of leg thrombosis:
- a feeling of fullness and increased local temperature in the affected limb;
- thickening of the dermis;
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- aches in the calf;
- pain when bending the foot inward.
It has been proven that early symptoms are characteristic of females. The reason is that girls prefer to wear high-heeled shoes, which is a provocative factor in the occurrence of various pathologies of the lower extremities. In men, early signs of a blood clot are invisible, i.e. absent.
Late signs
Under favorable conditions, the clot increases in size and blocks the blood flow. The individual experiences severe symptoms of leg thrombosis:
- at the location of the thrombus, a compaction is felt during palpation;
- severe pain can be only at the site of the clot or can be felt throughout the entire length of the blood vessel located below the clot;
- intense swelling gives the dermis an unhealthy appearance.
If a person does not go to a medical facility and the clot remains in the vessel for a long period, then the temperature on the affected limb decreases and the skin turns pale. Lack of treatment is fraught with the development of gangrene.
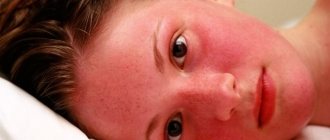
In addition, the blood clot itself serves as a provocateur of the inflammatory process. In this case, the dermis over the affected area acquires a distinct vascular pattern and becomes red and painful. The individual experiences:
- Strong headache;
- increased sweating;
- general malaise;
- nausea.
Reasons for the development of thrombosis
Under the influence of various factors, clots may form in the lower extremities. However, the main cause of their occurrence is considered to be a malfunction in the blood clotting system. Provocative factors are:
- insufficiently active lifestyle;
- impaired blood circulation;
- genetic predisposition to the appearance of blood clots;
- cardiovascular abnormalities, for example, arrhythmia, atherosclerosis;
- hormonal imbalance caused by endocrine diseases, pregnancy, and long-term use of hormonal medications;
- tumor processes;
- damage to vascular walls;
- overweight;
- blood clotting disorder;
- paresis and paralysis of the legs;
- surgery, trauma or injury to the lower extremities;
- septic conditions.
Regardless of the reason that provoked the formation of a clot in a venous vessel, it must be identified and removed. Only in this case will the treatment be effective.
What to do if a blood clot breaks loose
If a blood clot breaks loose, immediate hospitalization is required. This must be done when it is detected, especially a mobile, floating species. Prescribe complete rest and urgent treatment:
- installation of a trap - vena cava filter;
- suturing a vessel (vein);
- administration of drugs for resorption - enzymes (Streptokinase), low molecular weight heparins (Fraxiparin).
We recommend reading the article about thrombosis and thrombophlebitis. From it you will learn about the similarities and differences of pathologies, causes of development and risk factors, diagnostics and treatment methods. And here is more information about the prevention of thrombosis of the veins and vessels of the lower extremities.
The formation of a blood clot in blood vessels occurs with circulatory disorders, congestive processes, atherosclerosis, changes in the rheological properties of blood, and its clotting ability. In a chronic course, blood clots disrupt blood flow with the development of ischemic syndrome. Acute blockage when a blood clot breaks off leads to heart attacks and gangrene.
Venous thrombosis is accompanied by edema and congestion of the veins with expansion of the visible network of vessels and impaired outflow. A complication of blood clot movement from the extremities can be pulmonary embolism.
Varieties
Blood clots in the lower extremities have a different nature. Depending on the etiology, thrombosis is distinguished:
- inflammatory;
- stagnant;
- caused by a malfunction of the blood coagulation system.
Depending on the location, thrombosis can be superficial or deep. In addition, the following forms of clot are distinguished:
- Parietal - considered less dangerous, since the thrombus is attached to the wall and does not interfere with blood flow.
- Occlusive - the vein is completely blocked.
- Multifocal - clots form in different places.
- Floating - in this case, the clot goes along the wall, and its tip floats in the venous lumen. It comes off quite easily and gets into small vessels and clogs them.
- Mixed - the thrombus moves up and down the vein.
If floating thrombosis of the leg is detected, what to do? It should be remembered that this is the most dangerous form of the disease, since if it breaks off along with the blood flow, the clot easily enters the pulmonary artery. When identified, the individual must:
- strict adherence to bed rest;
- strict adherence to medical prescriptions, including taking anticoagulants.
Depending on the location of the clot, the doctor decides on emergency hospitalization of the patient and surgical intervention.
Signs of blood clots in the lower extremities
As mentioned above, at the initial stage the disease is quite difficult to detect. Clots form in both deep and superficial veins. An individual may suspect signs of thrombosis in the legs when the following clinical picture appears:
- frequent inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- trembling in the body;
- swelling;
- the legs become dark blue;
- heaviness in the limbs;
- compaction in the affected area, which is clearly palpable upon palpation;
- general malaise;
- weakness, fatigue;
- the dermis below the site of formation of the clot is burgundy and shiny.
In some cases, the blood clot grows slowly, while in others it grows quite quickly, which requires prompt medical attention.
If the superficial veins are affected, then symptoms of thrombosis of the blood vessels of the legs may appear immediately. In this case, the individual experiences:
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- redness of the affected area;
- the venous pattern becomes bright;
- pain when moving;
- edema;
- compaction at the site of the clot.
Stages of thrombosis
Several successive stages of thrombus formation have been identified:
- Injury to the inner lining of the vessel.
- Release of tissue coagulation factors.
- Fixation of platelets at the site of injury.
- The release of platelet substances, which trigger a chain of sequential reactions to form fibrin threads.
- A mesh of fibrin strands traps blood cells.
- A clot forms.
- The thrombus contracts with the release of plasma and becomes denser.
Symptoms of deep and superficial vein thrombosis
Typically, with thrombosis, pain in the leg appears sharply and suddenly. The limb swells and there is a feeling that it is being torn. At the same time, the body temperature rises, chills and weakness appear. External manifestations of the disease can be different, as they depend on how severely the vessel is affected and the location of the blood clot. For example, if a clot forms in the iliac or femoral vein, the entire leg swells. At the same time, blood flow worsens, and a venous network appears on the abdomen. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply. General weakness, chills appear, and the temperature rises. Let's look at the differences in the symptoms of leg thrombosis (see photo in the article) when deep and superficial vessels are affected. In the first case:
- the dermis of the diseased limb takes on a pale and sometimes bluish appearance;
- legs increase in volume due to swelling;
- the feeling of heaviness in the legs increases in the evening;
- an inflamed vein provokes an increase in temperature to thirty-nine degrees;
- pain in the lower leg of a bursting nature;
- the lower limb loses sensitivity, a feeling of goosebumps appears;
- the pain syndrome spreads along the inner side of the thigh, lower leg and foot.
In case of damage to the superficial veins:
- the foot and lower leg swell;
- the dermis turns red above the thrombus;
- there is a feeling of heaviness in the lower extremities;
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- “goosebumps run down my leg”;
- pain in the leg due to thrombosis along the vein increases with physical activity;
- skin sensitivity increases.
Symptoms of a detached blood clot
How can you tell if a blood clot has broken off? Immediately after the separation of a dense clot, a person experiences an increase in heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure. The blood supply to the organs deteriorates, collapse occurs, accompanied by chest pain. Such symptoms are characteristic of myocardial infarction. The patient experiences urinary retention, difficulty pronouncing words, swallowing food, and sometimes the person loses consciousness. Due to the malfunction of the stomach and the fullness of the internal organs, abdominal pain is felt.
Lack of air and shortness of breath cause respiratory failure, which provokes cyanosis. Often, infarction pneumonia develops or pleurisy is detected, in which the body temperature increases. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by hemoptysis. If the blood clot is not treated, then after a while reactions of the immune system appear: a rash appears on the skin, reactive pleurisy develops, and the concentration of eosinophils in the blood increases.
Diagnostics
Thrombosis of the lower extremities is diagnosed by a doctor trained in phlebology or vascular surgery. Diagnostic methods:
- MRI and CT - identify areas with blood clots. They are also used to identify complications.
- Impedance plethysmography - changes in the electrical resistance of tissues determine the rate of filling of blood vessels with blood.
- X-ray contrast venography is an accurate way to detect the disease. A contrast agent is injected into a vein of the lower extremities, then photographs are taken to evaluate the patency of the blood.
- Ultrasound duplex angioscanning and Doppler ultrasound are considered the gold standard for detecting thrombosis. With their help, the nature of the attachment of a blood clot to a vein is determined, the degree of narrowing of the vessel is assessed and analyzed, as well as the location, type, extent and mobility of the blood clot.
- Radionuclide scanning - a radioactive substance is injected into a vein in the foot, which can be deposited in blood clots. The areas affected by the thrombus are not visible on the images.
- Blood analysis.
How to check your legs for thrombosis during an outpatient doctor's visit? To confirm the diagnosis, the following functional tests are performed:
- Mayo-Pratta - initially the doctor gives the individual a massage, then applies a tourniquet for thirty minutes. If thrombosis is present, there will be pain and a feeling of fullness in the limb.
- Homansa - the doctor asks the patient to lie on the couch and bend his legs. When bending the foot, pain appears in the lower leg.
- Marching - an elastic bandage is applied to the entire leg from the toes to the groin. After some time it is removed, and if the patient has pain in the lower leg area, then there is a possibility of a blood clot.
- Lowenberg - a cuff from a tonometer is placed on the lower limb and air is pumped up with a bulb, if the numbers are about 90 mm Hg. Art. If the individual feels pain, then he has a clot in the vessel. In a healthy leg and at 150 mm Hg. Art. there is no pain.
If PE is suspected, an X-ray of the lungs is taken using a radioactive marker.
Diagnostics carried out by a highly qualified specialist, as well as regular examinations, will save an individual at risk from irreversible consequences.
What causes a blood clot to break off in a person?
At first the clot is soft, but over time the structure becomes denser. Under the pressure of blood, the clot breaks away from the vascular wall, breaking into fragments. Some of them undergo destruction, others move to the organs, posing a serious danger to the further functioning of the body. Blood clots that form in large veins are especially dangerous. After tearing off, they migrate through the bloodstream, causing stroke, heart attack, pulmonary embolism, and death.
The risk group includes the following group of people:
- men over 40 years old;
- women during menopause;
- with obesity;
- with malnutrition;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- with reduced activity (physical);
- pregnant women;
- after surgery on large joints or the abdominal cavity;
- coffee abusers;
- smokers;
- cancer patients;
- taking hormonal drugs.
Treatment methods for leg thrombosis
Treatment for this disease must be comprehensive.
The following methods exist:
- Conservative includes physical activity, leg bandaging with elastic bandages, compression therapy, medication, nutritional therapy, a special daily routine, the use of traditional recipes, as well as minimally invasive procedures.
- Surgical.
Let us consider in more detail how to treat leg thrombosis using a conservative method. For superficial thrombophlebitis, physical therapy, wearing compression garments and bandaging the limb with an elastic bandage are indicated. In order to eliminate the purulent or inflammatory process, the doctor recommends a course of antibacterial treatment. You can reduce the formation of blood clots using special anticoagulant drugs that thin the blood:
- "Heparin";
- "Warfarin";
- "Fragmin";
- "Clexane."
When taking them, blood clotting should be monitored by regular testing. The dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the doctor individually.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used in different dosage forms will help reduce pain and inflammation: injection solution, ointments, gels, capsules or tablets:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ketoprofen";
- "Voltaren";
- "Indomethacin".
Fibrinolytics are suitable for clot breakdown:
- "Urokinase";
- "Streptokinase".
Improves blood circulation:
- "Trental";
- "Flexital";
- "Pentoxifylline."
To improve the rheological properties of blood, use:
- "Reosorbilact";
- "Refortan";
- "Reopoliglyukin".
Detralex and Antistax will do an excellent job of strengthening the walls of blood vessels.
When treating leg thrombosis, in order to increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, the doctor recommends using other methods, for example, minimally invasive manipulations. If a floating clot is detected that has the ability to move through the vessel, special vena cava filters are installed. They are otherwise called traps; they prevent the blood clot from penetrating into vital organs.
After relieving the inflammatory process, physiotherapy is possible. If there are contraindications to taking anticoagulants, hirudotherapy is prescribed, which reduces blood viscosity.
First aid for a blood clot
It is impossible to independently save a person who has suffered a separation. You should call an ambulance and try to determine the area of the blockage.
It is recommended to give the patient a semi-sitting position, provide access to fresh air and prevent any movement, since stress can lead to the development of bleeding or further advancement of the blood clot.
In the event of loss of consciousness or when the victim dies, it is necessary to immediately begin resuscitation measures until paramedics arrive.
If a vessel has burst and there is bleeding, a tourniquet should be applied to the limb to stop blood loss.
Surgical treatment
Now let’s look at how to treat leg thrombosis surgically. It is indicated for:
- ascending thrombophlebitis;
- the threat of pulmonary embolism;
- when floating clots are detected and conservative therapy is ineffective;
- when a blood clot melts with purulent contents.
The following methods are used for this:
- Stenting.
- Thrombectomy – removal of a clot.
- Troyanov-Trendelenburg operation, during which the great saphenous vein is clamped.
In particularly difficult situations, they resort to removing a section of the affected vein. This operation is performed under general anesthesia. After surgery, the individual should begin to move as quickly as possible, i.e., walk. This is necessary to prevent the formation of repeated blood clots.
Mechanism of blood clot formation
When a vessel or its walls is damaged, components that inhibit anti-aggregation processes begin to be produced. Platelets undergo changes and disintegrate, procoagulants are released into the bloodstream - elements that promote blood plasma clotting. Under the influence of thrombin, febrinogen is transformed into fibrin, which forms the base of the thrombus as a mesh of threads. Aggregated platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes accumulate in the cells. After a while, the structure is compacted, the stage of clot formation is completed and the leakage of blood plasma is leveled out.
Possible complications: hidden and obvious
Delayed contact with a doctor and inappropriate treatment of symptoms of leg thrombosis (see photo below) is considered a predisposing factor to serious consequences.
For example, the occlusive form of the clot can lead to gangrene. Fortunately, this is a fairly rare occurrence. The following complications of thrombosis are known:
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) - blood circulation and breathing are impaired. If the small branches are blocked, the patient develops signs of hemorrhagic pulmonary infarction.
- Painful blue phlegmasia - as a result of occlusion of the femoral and iliac veins, the outflow of blood is completely blocked. In such a situation, there is a danger of developing gangrene.
- Purulent expansion of the clot - with thrombophlebitis in the acute stage, an abscess forms.
- Painful white phlegmasia - artery spasm occurs next to the affected vein.
- Postthrombotic disease is damage to the deep veins of the lower extremities with complete destruction of the valves as a result of previous thrombosis, as well as changes in perivascular tissue.
Consequences
Sometimes blood clots resolve on their own. This happens with a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, and abstinence from drinking alcohol and smoking. However, this does not happen immediately. Sometimes it takes several years to get rid of a blood clot. If the disease is not treated, poor circulation can lead to poor skin condition, dry mucous membranes, and autoimmune changes. As a result of insufficient nutrition of tissues, their death will gradually occur - gangrene will occur, which will lead to the loss of a limb.
Postpartum thrombosis of the lower extremities
Often, after delivery, women are diagnosed with diseases of the venous system, including acute thrombosis of the legs. The reasons for this phenomenon lie in the following:
- Changes occurring in the blood coagulation system. Both during normal childbirth and during caesarean section there is a lot of blood loss. The body, trying to stop it, produces several times more factors that contribute to increased clotting. As a result, clots form in the lumen of the vessels. In addition, during the period of delivery, the walls of blood vessels are damaged, which also provokes an increase in coagulability.
- Low vascular tone of the lower extremities, as well as the pelvis, is present in women after childbirth. As a result, the speed of blood movement decreases and the mechanisms of thrombosis begin to actively work.
- After the baby is born, the hormonal levels change dramatically, which also contributes to the development of venous clots.
- Pathologies of the coagulation and cardiovascular systems, excess weight, anemia, late toxicosis, as well as age after forty years increase the risk of thromboembolic complications.
In addition, the risk of developing this pathology is especially high in women with varicose veins.
What to eat if you have thrombophlebitis?
One of the causes of the described disease is obesity. Therefore, everyone who is susceptible to any disease of the venous system needs to limit themselves in the consumption of certain foods.
For example, the diet for thrombophlebitis (for the period of treatment) recommends avoiding fried, spicy, too salty and spicy foods. It is advisable to refrain from fatty fish and meats and include dietary varieties in your diet: chicken breasts, rabbit, turkey. There should always be fresh vegetables and fruits on the table, except bananas, peas and beans.
In winter, take multivitamins. Make it a rule to eat a clove of garlic every day, and be sure to eat onions. [adsen]
Signs of postpartum illness
Symptoms of leg thrombosis appear on the fifth or sixth day after delivery. When superficial veins are affected in the first days, the following is observed:
- redness of the dermis along the thrombosed vessel;
- increase in local temperature above the clot;
- when touched the vein is dense;
- deterioration in general health;
- pain in the affected leg when moving or walking.
When deep veins are affected, the symptoms are minor. The main symptom of this type of leg thrombosis is swelling, which is increasing and quite painful. The pain is bursting in nature and intensifies when lowering the legs down and when standing. The dermis in the affected limb becomes milky white or blue. In general, deep vein thrombosis is practically asymptomatic and is detected incidentally during ultrasound. The danger of an undiagnosed and untreated disease provokes its transition to postthrombophlebitic syndrome, in which the subcutaneous tissue is destroyed, the color of the dermis changes and quite dense swelling appears.
How to recognize a blood clot
A blood clot can be recognized if it interferes with blood circulation and symptoms of thrombosis appear:
| Type of thrombosis | Symptoms |
| Deep veins of the leg | Distension, pain, it becomes stronger when palpated in the area of the affected vessel, swelling, redness or bluish color of the skin, an increase in its temperature, a pronounced venous network, congested veins. |
| Pulmonary artery | Sudden onset of shortness of breath, bluish skin with a gray tint, drop in pressure, chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances, bulging neck veins, fainting, cough, wheezing, pinkish sputum, increased body temperature, pain in the right hypochondrium. |
| Coronary arteries of the heart | Pain behind the sternum, radiating to the back and neck, occurs during stress, physical activity, and is accompanied by shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. |
| Arterial network of the legs | Chilliness, numbness of the feet, burning, pain when walking, which stops when you stop, the skin becomes pale, and then the fingers turn blue. |
| Cerebral arteries | Dizziness, unsteadiness, various visual disturbances, unclear speech, decreased muscle strength and sensitivity in the arm and leg, memory loss. |
Treatment and prevention of postpartum thrombosis
Correctly selected therapy will help to completely cope with this problem. It is important to remember that self-treatment and the use of alternative medicine in the postpartum period, as well as in pregnant women, are contraindicated. If you notice the symptoms described above, you should immediately visit a vascular surgeon or phlebologist. What does thrombosis look like on the legs? Photos are presented in the article. In the treatment of the disease, an integrated approach is used, including:
- Taking medications. The main anticoagulants are the heparin group, which are approved for use by nursing women. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated for severe thrombosis and only after stopping breastfeeding. Venotonics are also contraindicated when breastfeeding a baby.
- Wearing special underwear. Compression tights, stockings or knee socks help reduce the diameter of blood vessels, normalize and increase blood flow through the veins. As a result, venous congestion and the risk of pulmonary embolism are reduced. Your doctor will help you choose the right knitwear.
- Physiotherapy. Electrophoresis, laser therapy, cryo-wraps, and phonophoresis are effective in treating symptoms of leg thrombosis in the postpartum period. Massage, hot wraps, baths, compresses, and wave forms of physical therapy are contraindicated.
In order to exclude postpartum thrombosis, preventive measures should begin during the planning period of conception. If a woman in this position has varicose veins, then wearing compression garments and a special bandage will be mandatory. If this disease is detected in the second trimester, the use of venotonics - Detralex, Antistax, Phlebodia - is indicated. If a woman has high blood clotting, she is recommended to administer injectable anticoagulants, which significantly reduce the risk of a blood clot.
How to check blood vessels for plaques and blood clots
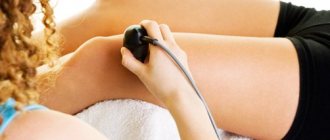
In order to check the vessels for the presence of plaques and blood clots, an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound is performed. Using this method you can evaluate:
- the presence of an obstacle to the movement of blood;
- the total diameter of the vessel and its patency;
- blood flow speed;
- thrombus density;
- its danger (mobility).
Dopplerography of vessels
If the data obtained is not enough to select a treatment method, then angiography is used. It involves the introduction of a contrast agent. Most often it is prescribed before surgery. One method of searching for a blood clot is the injection of fibrinogen labeled with radioisotopes. He will indicate hidden blood clots, but will not be able to determine their structure, size and risk of rupture.
Prevention
Preventive measures are especially indicated for persons who are overweight, have varicose veins, and lead a passive life. To prevent leg thrombosis you should:
- rest daily with your lower limbs raised up;
- drink at least two liters of plain water per day;
- do swimming or yoga;
- perform a set of therapeutic exercises selected by the doctor;
- regularly monitor cholesterol and blood glucose;
- do a contrast shower;
- take salt baths for your feet;
- perform self-massage of the legs and feet;
- wear compression garments;
- walk barefoot on a textured surface;
- exclude the use of oral contraceptives and anticoagulants;
- do cold foot rubs;
- wear comfortable shoes, the heel should not be higher than four centimeters;
- quit smoking;
- exclude alcohol-containing drinks from the diet.
The occurrence of a clot in the lower extremities is a very dangerous condition that poses a threat to life. What thrombosis looks like on the legs is shown in the photo. Having noticed the first symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor, who, after diagnosis, will select a course of therapy.
ethnoscience
Treatment of thrombophlebitis with folk remedies involves the use of natural products and substances. Ready-made formulations allow you to normalize blood flow in the area of deep veins and the vascular network.
These decoctions and ointments can be used for home treatment of thrombophlebitis. For this you will need:
Treatment of atherosclerosis: ways and methods of how to cure blood vessels. The best remedies and drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis (120 photos)Celandine tincture - treatment with celandine, recipes and application (video + 105 photos)
Treatment of chronic runny nose - step-by-step description and treatment in adults and children (105 photos)
- Honey 200 gr;
- Garlic 150 gr;
- Deep capacity.
The first step is to melt the honey in a water bath. Next, mix the liquid mass with grated garlic. Infuse the resulting liquid for 1 week.
Take one tablespoon of the finished mixture before eating. On average, the course of treatment ranges from 20 to 40 days.
This product has proven itself to be a highly effective and antiseptic agent that destroys the viral and microbial environment.
Causes of pain in the veins
Often, pain in the legs or calf muscles is caused by inflammatory processes in the blood vessels. If a vein in your leg hurts, then most likely a blood clot has formed. As a result, the outflow of blood is disrupted, the walls of the vessel stretch and expand. Pain in the lower extremities is caused by compression of tissues adjacent to the affected vessel. How do veins in the legs hurt due to thrombosis? The individual feels a dull, nagging pain. Prolonged walking and standing causes pain in the veins, as well as tension and loss of sensation. With deep vein thrombosis, pain manifests itself on palpation. With thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins, one of the first complaints of the patient is pain in the vessels of the lower extremities.
What is the difference between thrombophlebitis and varicose veins?
Thrombophlebitis and varicose veins have similar symptoms, but different nature. With varicose veins, the vessels are constantly dilated, and their walls become thinner. The disease leads to disruption of blood flow and the formation of nodes in the vessels. With thrombophlebitis, the walls of the vein become inflamed and a blood clot forms. Blockage of the lumen of the vessel causes circulatory disorders and swelling of the affected vessel.