A gastric polyp is a benign formation on the gastric mucosa. It is rare and usually does not manifest itself clinically. Most often it is discovered by chance during examination for other reasons.
The size of stomach polyps ranges from 0.5 to 8-10 cm. They can develop in any area of the stomach, but most often they are localized in the pylorus - near the exit from the stomach, where the duodenum begins.
Most polyps are benign, although some increase the risk of developing stomach cancer. Treatment of such polyps involves their removal; in other cases, the doctor is limited to observation only.
Polyps in the stomach
General information
Having analyzed the pathologies of internal organs, we can conclude that gallbladder diseases occupy a fairly significant place in this list. However, there are also diseases that are not detected for a long time, even if the patient attends preventive examinations. Among these are polyps in the gallbladder, a relatively common disease. According to statistics, it is most often diagnosed in women over the age of 30. Against the backdrop of improvements in the overall quality of diagnostics, doctors often make this diagnosis recently. The main feature of this disease is the absence of pronounced clinical manifestations. In most cases, patients with polyps complain of pain of varying intensity in the right hypochondrium. If an infection joins the pathological process, then the symptoms resemble acute cholecystitis .
The ICD-10 code for gallbladder polyp is K82 (other gallbladder diseases).
What are polyps in the gallbladder, is it dangerous, is it necessary to remove these formations and what treatment is appropriate in such a situation will be discussed in this article. In addition, the article provides the opinions of experts on why such a diagnosis is dangerous.
Surgical treatment
Types of gallbladder operations:
- Videolaparoscopic cholecystectomy (VLC) is considered the most gentle for the patient and uses modern endoscopy technologies.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder without an incision, as in a traditional cholecystectomy using instruments for endoscopic operations. It is considered the “gold standard” of modern surgery, but in five percent of cases the operation cannot be completed and a traditional cholecystectomy is performed.
- Traditional cholecystectomy (TCE) - by open surgery, access is through an upper midline incision or a Kocher incision in the right hypochondrium. The disadvantage of this method, in comparison with laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is that it is traumatic - the incision cuts through the skin, fatty tissue, linea alba and peritoneum.
- Endoscopic polypectomy – used to remove gallbladder polyps while preserving the organ. This type of operation is performed using a diathermy loop, which is placed over the stalk of the polyp and trimmed. Formations without a stalk are removed by fragmentation. An electrical charge is passed through the loop to coagulate the blood vessels, which helps prevent bleeding. This method is used to remove polyps in the intestines, but it is rarely used in the treatment of gallbladder polyposis, so the consequences can be unpredictable.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination to avoid possible complications and choose the optimal method of cholecystectomy.
Pathogenesis
The gallbladder is an organ that is located next to the liver. Accordingly, the liver synthesizes bile , which accumulates in the gallbladder, and during the digestion process it is released into the small intestine. Due to the influence of various factors, pathological growths called polyps appear inside the gallbladder. In almost 90% of cases they are safe. However, in other cases we are talking about so-called true polyps, which can sometimes be malignant.
It is still not known for certain why polyps appear in the gallbladder. Sometimes such formations are parasitic in nature. If parasites settle in the ducts of the gallbladder, a worm-like tumor may be identified as a polyp during ultrasound examination. The development of cholesterol polyps is associated with the accumulation of cholesterol .
About the disease
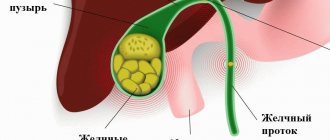
A biliary polyp is a benign formation in the cavity of an organ. It is attached to the wall with a leg, and can also have a fairly wide base.
People first started talking about this disease back in the 19th century, but it was possible to clarify its nature and differentiate it from others after ultrasound began to be used.
Approximately 6% of people suffer from this disease, and most of them are women over 36 years of age. In men, polyps are of a cholesterol nature; in women, the hyperplastic type is diagnosed.
Classification
4 types of polyps are formed in the organ:
| Cholesterol type | It occurs more often than others and is formed from excess cholesterol, which occurs as a result of lipid metabolism disorders. They occur latently and are discovered accidentally during ultrasound. |
| Inflammatory appearance | The reason is inflammatory processes caused by a bacterial component. |
| Adenomatous type | The most dangerous from the point of view of degeneration into a malignant tumor. They arise from the glandular layer, every tenth case of gall cancer is associated with these polyps. For this reason, this type of education requires close monitoring. |
| Papillomatous appearance | It consists of small multiple growths. |
Also, neoplasms are divided into small (6-8 mm) and large (more than 10 mm). Based on their numbers, they are divided into single and multiple. The latter tend to degenerate into a malignant tumor in 80%.
Based on the type of attachment, growths are divided into pedunculated polyps and parietal polyps (having a wide base). The parietal ones also have a high probability of degeneration.
Classification
Depending on the nature of such formations, the following types are determined:
- A cholesterol polyp is a formation that appears due to hyperplasia of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder. The name “cholesterol” is due to the fact that the polyp consists of cholesterol deposits. These are so-called false polyps, which respond to conservative treatment and completely resolve. However, ultrasound most often reveals a true polyp in this case, so diagnosis in this case is quite complicated. Develops against the background of fat metabolism disorders. By visiting this or that forum, you can find many stories about how such polyps were completely cured.
- Inflammatory – a consequence of the inflammatory reaction of the gallbladder mucosa. Develops as a proliferation of granulation tissue. These are peculiar pseudotumor formations that grow because the mucous membrane reacts to inflammation in this way. Also factors that provoke such formations are parasitic infections and calculi.
- Adenomatous is a benign formation that develops as a polyp-like growth of glandular tissue. In this case, there is an increased risk of developing a malignant tumor (in approximately 10% of cases).
- Papilloma is a benign formation that develops as papillary growths. However, when exposed to certain factors, such growths can become malignant.
Based on the number of growths, the following are determined:
- Singles.
- Multiple.
What it is?
These formations are a consequence of the proliferation of the surface epithelium or the accumulation of harmful masses. It is possible to form small or large structures with a diameter of the order of several centimeters. Another option is a large-scale mesh formation. By their nature, polyps are benign, but lack of treatment is fraught with the development of an oncological process.
There are four forms of neoplasms:
- Cholesterol - the main element of the tumor is a combination of calcified inclusions and cholesterol itself. Initially, the process develops in the submucosal area, then the tissues grow, acquiring a convex shape.
- Inflammatory – occurs when a bacterial infection enters the body. The location of the granulomatous structure is the inner lining of the bile duct.
- Papillomas. Their peculiarity is their small size and the presence of papillary growths.
- Adenomatous. Such polyps are benign tumors formed from glandular tissue. They often degenerate into oncological structures and require constant monitoring.
Causes of polyps in the gallbladder
Most often, the reasons for the appearance of such formations are associated with metabolic disorders. We are talking about lipid metabolism, leading to an increase in cholesterol levels in the blood. As a result, cholesterol is deposited on the walls of the gallbladder, forming false polyps.
However, other factors can determine the appearance of polyps:
- The presence of gallbladder pathologies associated with inflammation. Polyps often form in people with chronic cholecystitis , when the flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted.
- Hereditary factor.
- Genetic anomalies.
- Hypatobinary pathology, which provokes dyskinesia of the gallbladder .
- Improper and irregular diet, abuse of food containing large amounts of cholesterol.
Reasons for development
There are factors that contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- Heredity. A high risk of developing the disease occurs in people whose relatives have suffered from this disease.
- Chronic cholecystitis. Stagnation of bile leads to an increase in the tissue of the internal organ.
- High-calorie food. High cholesterol content in food provokes the development of the disease.
- The hormone estrogen. An increase in the production of this hormone entails the growth of the epithelium in the gallbladder (abbreviated gallbladder). Because of this, women suffer from this disease more often than men.
- Inflammatory process. During inflammation, the body turns on protective processes in tissues and organs, and this contributes to the onset of pathology.
- Impaired metabolism. Improper nutrition or heredity leads to disruption of the outflow of bile, as a result of which the tissue of the internal organ begins to grow.
- Dyskinesia. Improper functioning of the biliary tract directly affects the development of pathology.
- Hepatitis and papilloma virus. Both of these diseases can cause tumors.
Infections and stress, physical inactivity affect the functioning of internal organs and digestion. A congenital anomaly in the structure of the gallbladder can affect the digestion process and cause pathology.
Symptoms of gallbladder polyps
Polyps in the gallbladder present with nonspecific symptoms. Very often, patients are completely free of any complaints, and the formation itself is discovered by chance, during a preventive examination or ultrasound of the abdominal cavity when diagnosing other diseases. Such studies can be carried out if a person complains of a feeling of heaviness, flatulence , belching, etc.
Symptoms of a cholesterol polyp appear along with signs of other diseases. In this case, the most dangerous condition is when such formations are located in the neck or ducts of the gallbladder. With such localization, the normal process of bile outflow may be disrupted, which leads to the development of obstructive jaundice .
Thus, symptoms that indicate this disease may include the following:
- Jaundice, in which yellowing of the skin is visually detected. This indicates an increase in the level of bilirubin in the body.
- If there are mechanical obstacles to the normal outflow of bile, it can penetrate into the blood. As a result, blood pressure increases, skin itching, nausea and vomiting are noted.
- Liver spasms – develop in the area of the right hypochondrium. This symptom is typical for polyps with long stalks. This condition can cause very severe pain and requires immediate treatment.
In general, the development of such formations can lead to disruption of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Due to inflammatory processes, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and corresponding symptoms can develop.
Who is at risk from polyps?
Polyps are most often found in middle-aged and elderly people. Their appearance is expected when infected with Helicobacter pylori, since this bacterium increases the risk of developing chronic gastritis, and gastritis is considered one of the causes of polyps.
Multiple polyps are five times more likely to cause malignancy than single polyps. There is a close relationship between the size of the polyp and the risk of malignant neoplasm - a formation with a diameter of 1.5 cm is repeated in malignant disease in 6.8% of cases, and with a diameter of 3 cm - in 73.7%. Polyps with flat stalks are three times more likely to become cancerous than polyps with long stalks.
Tests and diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing the disease is ultrasound. In the gallbladder, a polyp is defined as a round or oval formation.
Types of polyps
In addition, if necessary, other studies are used:
- Endoscopic ultrasonography (endosonography) - makes it possible to more accurately determine the location of the formation and its structure.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiography - a study that allows not only to determine the location and characteristics of the polyp, but also to identify or exclude other diseases of the gallbladder.
- Computed tomography - in the process of such a study, it is possible, among other things, to differentiate space-occupying formations in the liver.
Health effects
The effect of polyps on human health depends on their type and size. The least dangerous are cholesterol and papillomatous polyps. The most dangerous are adenomatous, as they are prone to magnesiumization.
If the formation is small and occupies no more than 25% of the volume of the bladder, then it does not pose a health hazard. However, the following complications occur:
- Blockage of the bile ducts, resulting in obstructive jaundice.
- Large growths cause pain in the right side. They can be so very strong or aching.
- Digestive disorders: frequent diarrhea, attacks of nausea, vomiting.
- The growths contribute to the deterioration of bile outflow, which leads to cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
Find out from the video whether polyps in the gallbladder are dangerous or not:
Treatment of polyps in the gallbladder with folk remedies
Very often, people with this pathology look for the answer to the question of how to stop the growth of a polyp in reference books on traditional medicine. It should be noted that not a single folk method can stop the growth of education and save the patient from the problem. Therefore, folk remedies can be treated in parallel with the main therapy and only if they are approved by the doctor.
- Celandine . 1 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs and strain after two hours. Drink 2 tbsp before meals. l. three times a day.
- Chamomile with celandine . 20 g of celandine and chamomile herbs mixed in equal proportions should be poured with 200 ml of boiling water and left for 6 hours. Strain and drink 20 ml three times a day. The drug is taken for a month, after which a break is taken for a month and treatment is resumed.
- Herbal infusion . To prepare it, mix 20 g of St. John's wort, plantain, immortelle, coltsfoot, corn silk, knotweed, shepherd's purse, blackberries, and strawberries. To this mixture add 15 g of string and dill seeds, as well as 40 g of rose hips. Mix everything, take 2 tbsp. l. mixture and add 0.5 liters of water. Leave for half an hour, drink 100 ml before meals three times a day for a month.
Prevention
To avoid the development of this pathology and prevent problems associated with it, it is important to adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- If you have a genetic predisposition to this disease, undergo preventive examinations regularly (once every six months).
- Take measures to normalize fat metabolism. To do this, it is necessary to adjust the diet in order to reduce the amount of fats and simple carbohydrates in it, as well as lead an active lifestyle. A sedentary and inactive lifestyle provokes stagnation of bile.
- Treat gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner. In case of inflammatory diseases, immediately practice the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor.
- Do not abuse alcohol.
Video
Some experts tell you that surgery is required for tumors, while others say that treatment is possible. Watch the video and you will become familiar with the risk factors and causes of the disease. You will understand under what conditions surgical intervention is necessary.
About the most important things: Polyps and gallstones, arthrosis of the joints
Diet
Diet for polyps in the gallbladder
- Efficacy: no data
- Timing: permanently/from 3 to 6 months after surgery
- Cost of products: 1300-1500 rubles. in Week
Proper nutrition is an important element in the treatment of gallbladder polyps. Therefore, when confirming such a diagnosis, it is very important to adhere to some general recommendations:
- Don't skip breakfast.
- Eat small meals - 5-6 times a day. In this case, one serving should weigh approximately 200 g.
- Do not snack on unhealthy foods such as fast food.
- Avoid fatty and fried foods and simple carbohydrates in favor of healthier foods.
- Drinking regime is also important - you should consume a sufficient amount of water per day - about 1.5 liters.
- Food should be consumed warm.
- The amount of salt should not exceed 1 tsp. in a day.
- It is recommended to eat boiled and steamed foods, and you can also bake food.
It is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- Fatty broths.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Confectionery.
- Corn.
- Garlic, radishes, onions, spinach, legumes.
- Soda, store-bought juices.
- Chocolate, cocoa, coffee.
- Marinades.
- Alcohol.
- Mushrooms.
- Spicy dishes.
- Smoked meats.
Answers to popular questions
- Can a polyp in the gallbladder resolve? In 95% of cases, the detected polyps are loose cholesterol formations, which makes it possible to treat them conservatively with choleretic drugs, which include Ursosan and Ursofalk. Medicines that dilute bile promote the resorption of polyps in the submucosal layer of the gallbladder.
- Is it possible to remove only the polyps themselves while maintaining a functioning gallbladder? It is impossible to remove a polyp without damaging the walls of the gallbladder, so even if the doctor saves the organ, its function will be impaired, and the polyps will appear again after some time, possibly in greater numbers than before the operation. This practice was abandoned quite a long time ago. Already in the 70s of the last century, operations that preserved the gallbladder after removing tumors from it were no longer performed. In addition, at one time, the technique of crushing stones (lithotripsy) was popular. However, this treatment method turned out to be meaningless, since after a while, 99% of the patients experienced a relapse of the disease. In the future, the only thing that helped them was surgery to remove the organ. Therefore, the optimal treatment method is surgery, namely laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
However, removal of the gallbladder is not the only solution; most tumors can be treated conservatively. The patient is required to undergo regular diagnostic testing twice a year to prevent malignancy of polyps and the onset of the cancer process. The danger comes from growths larger than 10 mm that do not stop growing; if a small polyp has increased over the course of a year and has become twice its original size, this may indicate the onset of malignancy. Neoplasms with a wide base and without a pronounced stalk are more prone to malignant degeneration. For polyps larger than a centimeter, surgery is prescribed to remove the gall bladder. In other cases, you can get by with choleretic drugs and correction of your diet and lifestyle.
- Can a polyp in the gallbladder hurt? Pain from gallbladder polyps is usually associated with the formation of cholesterol stones or are symptoms of cholecystitis. Typically, polyps in the gallbladder do not cause pain.
- Is it possible to visit a bathhouse or sauna if you have polyps in the gallbladder? If you have polyps in the gallbladder, you cannot warm up the area of the organ, so it is not recommended to go to the bathhouse or sauna or spend a lot of time in the sun.