Zinc deficiency is actually an epidemic that most people are not even aware of. Zinc deficiency is a global problem. According to WHO, it affects 31% of the world's population.
We live in a bubble of fortified and fortified foods sold freely on store shelves, and do not think about the scale of this global problem that millions of people face every day. However, we often don't realize that just eating a nutrient-rich food doesn't mean our bodies are fully absorbing it. And everyone can be at risk. Even those who live in developed, industrialized countries are not protected from zinc deficiency !
Forms of the disease
Zinc is involved in the regulation of nucleoproteins and helps eliminate the development of inflammation. A deficiency of the element provokes disruption of metabolic processes, causing multiple clinical signs. A skeletal development disorder may develop, as well as a malfunction of the reproductive and immune systems. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms.
Chronic
Zinc deficiency (symptoms manifest differently in women) of a chronic nature develops with a rare metabolic disorder in the body (enteropathic acrodermatitis).
The pathology is congenital. The disease is characterized by morphological changes in the skin, hair loss and gastrointestinal upset. A polymorphic rash around the oral cavity often appears. Severe microelement deficiency is rarely diagnosed in medical practice.
Acute
Zinc deficiency, the symptoms of which in women are acute, is usually caused by an unbalanced diet or age-related factors. The subclinical course is provoked by prolonged consumption of foods low in the element. Also, a deficiency of the substance manifests itself with active skeletal growth. A high need for zinc in girls is observed at 10-12 years of age.
A reduced marker in the pubertal phase can provoke a disturbance in the development of the axial skeleton and the deposition of minerals in bone tissue.
A deficiency of the element occurs in women who adhere to parenteral nutrition, as well as in patients with chronic pathologies (Wilson-Konovalov disease, sickle cell anemia, nephritis, cirrhosis). The condition can also be triggered by bariatric surgery and mercury or tartrazine poisoning.
Zinc deficiency (symptoms in women are described in this article) may be the result of a mental disorder.
Repeated diagnostic measures to study the marker of the element in the blood are indicated to monitor therapy when the patient is using medications that contain zinc.
Insufficient zinc content in the body does not always indicate a lack of microelement. Its concentration decreases during acute infectious and inflammatory processes, traumatic injuries, increased physical stress and stress. Normally, the marker decreases after eating.
Zinc and the postoperative period.
After gynecological surgery, women usually stay in the hospital for about a month, and sometimes longer. If they started taking zinc a week before the operation, then discharge would have occurred 2 weeks earlier. This means that zinc speeds up healing. This also applies to the period after tonsil removal.
Zinc is extremely beneficial in treating various skin conditions. But the skin is not only the surface that separates us from the outside world, it is also the shell of every cell, and all organs, any gland, our brain are made up of cells. And zinc is a faithful guardian of the health of our cells, our well-being.
It seems that no one doubts the beneficial effects of zinc on the human body. Meanwhile, doctors extremely rarely recommend zinc to patients.
Therefore, we will continue our conversation about the importance of zinc in order to know more about ourselves, our health, and the health of our children.
The table is normal
The table shows normal indicators for women of different age categories.
| Age | Norm | Pregnancy period | Lactation period |
| 0—6 months | 2 mg | ||
| 7-12 months | 3 mg | ||
| 1-3 years | 3 mg | ||
| 4-8 years | 5 mg | ||
| 9-13 years | 8 mg | ||
| 14-18 years old | 9 mg | 12 mg | 13 mg |
| 19+ | 8 mg | 11 mg | 12 mg |
Vitamins with zinc for children
For development, a child from the age of 4 is allowed to take vitamins with zinc.
In order to grow and develop normally, children from the age of 4 vitamins with zinc by pediatricians . In addition to boosting immunity, improving vision, skin and hair, regulating the metabolic process, zinc improves mental abilities and physical development in children .
Medicines for children:
- Vitrum
- VitaZhuyki
- Multi-Tabs for children
- VitaMishki
Vitamin E+zinc . These drugs are prescribed to children who are growing slowly and are developmentally behind their peers:
- Rock oil with zinc and vitamin E
- Polivit
- Centrum
- Alphabet
- Duovit
Possible causes of deficiency
Zinc deficiency (symptoms in women appear at different levels) is most often a consequence of an unbalanced diet. Representatives of the fairer sex resort to various diets that exclude the consumption of meat and dairy products. As a result, vitamin deficiency is provoked.
Low levels of the microelement are diagnosed in people who eat a vegetarian diet. Representatives of the fairer sex, who prefer sweets, coffee, and marinades, also suffer from a lack of metal.
The main provocateurs of the pathological condition include:
- Irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. With this pathology, zinc is not absorbed by the body.
- Diabetes. The pathology is provoked by a violation of the functionality of the pancreas, which causes a violation of the absorption of microelements. With this disease, zinc is excreted in large quantities in the urine.
- Kidney failure. A sharp decrease in the level of the element is observed in patients on hemodialysis.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol interferes with the absorption of the element. With their systematic use, zinc deficiency becomes more pronounced.
- Gestation and lactation. In pregnant women, the consumption of all elements proceeds very quickly. For this reason, zinc deficiency is often observed.
- Age category above 65 years. Older women have decreased absorption of nutrients. In this case, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes.
- Sickle cell anemia. People with this pathology suffer from a lack of many elements. The provocateur is a reduction in the level of red blood cells in the blood and metabolic disorders.
Zinc deficiency in women is often associated with improper use of diuretics, antibiotics and antidepressants. Regardless of the provoking factor, a woman must take measures to eliminate the deficiency of the element. The lack of this element has a particularly negative effect on the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
Potential Side Effects of Zinc
Negative symptoms accompany not only zinc deficiency, but also its surplus. Most doctors agree that it is probably unsafe to consume elevated amounts of zinc for extended periods of time. It can cause cough, fatigue, fever, abdominal pain and a number of other health problems. Therefore, if you are trying to supplement zinc deficiency in adults or children, you should consult an experienced nutritionist to avoid excessive zinc intake.
Some sources claim that taking more than 100 mg of supplemental zinc per day for 10 years or more doubles the risk of developing prostate cancer. There are also concerns that taking large amounts of multivitamins and single zinc supplements increases the likelihood of dying from prostate cancer.
Regular over-doses of zinc—450 mg or more per day—are also known to affect blood iron levels, and taking too much zinc can also affect copper levels.
In addition to this, here are some key recommendations for women:
- Pregnant women over 18 years of age should limit their zinc intake to 40 mg per day.
- Pregnant women under 18 years of age should limit their zinc intake to 34 mg per day.
- Breastfeeding women over 18 years of age should limit their zinc intake to 40 mg per day.
- Women under 18 years of age who are breastfeeding should limit their zinc intake to 34 mg per day.
Final Thoughts
According to the World Health Organization, millions of people around the world may have insufficient levels of zinc in their diet. In fact, zinc deficiency, the symptoms of which go undetected for a long time, ranks fifth in the ranking of risk factors for disease worldwide.
Zinc deficiency occurs when you don't have enough zinc-rich foods in your diet or you have trouble absorbing zinc from food due to digestive disorders or poor gut health.
What are the symptoms of zinc deficiency? Zinc deficiency affects many organ systems, including the immune, gastrointestinal, skeletal, reproductive, integumentary, and central nervous systems.
If you're wondering if you need a zinc supplement and want to know the signs of zinc deficiency, look for problems like diarrhea, allergies, thinning hair, weak immunity, and poor neurological function.
Symptoms
Zinc deficiency often occurs in a latent form. Symptoms in women are observed in 1/3 of cases. Pathology is detected by examining blood or urine.
The most striking signs of microelement deficiency include:
- Taste defects. It usually feels like the food tastes great. In some cases, preferences change: a craving for salty and sour foods appears.
- Metabolic disorder. Women can suffer from obesity or significant weight loss while maintaining their diet.
- Intense hair loss. Sometimes even baldness is observed. A decrease in zinc levels provokes a disruption in protein production, which has a bad effect on the condition of the hair. A reduced amino acid marker provokes a lack of nutrients.
- Diarrhea and other digestive problems. If there is a deficiency of the element in a person, the production of enzymes is reduced. Food begins to be processed with difficulty. Constipation may also occur.
- Functional disorder of the nervous system. With low levels of zinc in the body, the transmission of nerve impulses in neurons slows down, which negatively affects mental processes such as memory and attention.
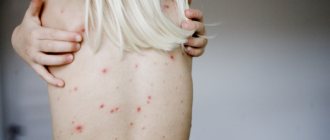
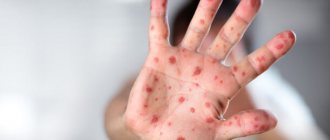
- Violation of the morphology of the dermis. A clear sign of zinc deficiency in women is acne. The trace element is involved in the regulation of the sebaceous glands. With a lack of substance, sebum begins to be produced intensively and contributes to clogging of pores. As a result, comedones form.
- Infertility. In some cases, with a low zinc content in the female body, there is an inability to conceive a child.
All signs develop with a significant decrease in the level of the microelement.
Properties and Functions
As mentioned, zinc plays a key role in the development and functioning of the body. Its main properties include:
- Improving metabolic processes. It has been proven that the microelement is involved in the breakdown of dietary fatty acids coming from food, helping them to be absorbed.
- Strengthening the immune system. Thanks to the action of Zn, antibodies, leukocytes and hormones work better, which activates the body's defenses and accelerates healing in case of damage. In addition, zinc plays the role of a “detoxifier”, removing harmful carbon dioxide from the body.
- Forms enzymes. Research has shown that Zn is contained in more than two hundred enzymes. For this reason, the microelement is involved in many physiological processes occurring in the body.
- Normalization of the hormonal system. The chemical element plays a key role in the synthesis and excretion of insulin, which is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates coming from food. Also, zinc in the blood protects the beta cells of the pancreas and participates in metabolic processes occurring in the ovaries, thyroid gland, adrenal glands and other organs. The sufficiency of the microelement is especially important for the male body (for the health of the prostate and the formation of hormones).
- Improving the absorption of tocopherol. It is known that the normal content of this microelement guarantees optimal absorption of tocopherol and retinol, which has a positive effect on health.
- Skin restoration. It is believed that the deterioration of the condition of the skin is directly related to a lack of zinc in the body. The reason is that Zn improves the absorption of vitamin A, accelerates tissue regeneration and wound healing, and effectively eliminates emerging inflammatory processes.
- Strengthening teeth and bone tissue. This function is associated with the presence of Zn in the structure of these body parts.
- Help during pregnancy. The results of numerous studies have shown that Zn affects the development of the baby in the womb: it helps in the formation of the organs of the genitourinary system, heart, bones, eyes and brain.
- Acceleration of cell growth. The main function of the microelement is to participate in cell division, DNA production and stabilization of its structure. This is why the supply of Zn is so important for the normal growth of living tissues.
- Improving liver performance. The supply of microelements guarantees normal liver function and the production of retinol in it.
- Normalization of the nervous system and brain. A lack of zinc is believed to lead to the development of Alzheimer's disease.
Modern diagnostic methods
The basis of diagnosis is the determination of zinc marker in blood plasma, red blood cells, urine and hair. The most informative way is to determine the level of the element in the blood serum. An indicator of 13 µmol/l is regarded as a deficiency state, and a marker below 8.2 µmol/l is unfavorable.
It should be noted that a deficiency in the blood does not always manifest itself with clinical symptoms, since the concentration of the substance falls and rises throughout the day. The indicator varies depending on the food consumed, stress, infectious process, and disruption of blood plasma collection.
During diagnostic manipulations, it is necessary to take into account not only the level of the element in the blood, but also the positive dynamics of clinical signs, as well as an increase in the marker in response to treatment with drugs containing zinc.
The biological material is blood taken from a vein. No special preparation is required for the test. It is forbidden to consume food 2-3 hours before the manipulation, as the level of the substance decreases after eating. This may cause incorrect results. In 30 min. You should stop smoking before the test
Interpretation of the results is carried out taking into account data from another study. Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is indicated. Presents a method for quantitative urine analysis.
Based on the ability of atoms to absorb light of a certain wavelength (resonant absorption) and influence signals emanating from other atoms contained in the atomizer. Approximately 60 chemical elements (mainly metals and a number of transition elements) can be determined using the AAS method.
In Moscow, a blood test for zinc content will cost 700-970 rubles. The research method using ACC, including sample preparation, will cost 1,300 rubles.
In Samara, a blood plasma test will cost 430–650 rubles. Analysis using the ACC method will cost 1000-1200 rubles.
Zinc and old age.
What can I say, old age is a depressing thing, and one of the most unpleasant diseases that accompanies it is senile insanity, when a person lives, realizing almost nothing. Many people think that this is the result of natural aging of the body. But senile insanity is a disease, and it is curable. And zinc is needed for treatment. But not only him: the brain must receive enough nutrition and oxygen, it should not be poisoned by alcohol, drugs, or excessive doses of medications. It is believed that zinc prevents damage to blood capillaries and protects the brain. People undergoing zinc treatment regain their memory, coordination ability, etc.
Drug therapy
The most popular medicines that replenish the lack of zinc in the body include “Zincteral”, “Zincit”, “Bio-zinc”.
The drug "Zincteral" is taken 1 tablet after 2 hours of food. The tablets should not be split or chewed.
The recommended dose depends on the severity of the pathology. As a rule, take 1-3 tablets 1-3 times a day. The cost of the drug 124 mg is 269-385 rubles. There are 25 tablets in a package.
"Bio-zinc" is taken 1-2 tablets per day with meals. The drug is taken for a month. The cost of the drug 0.3 mg is 450 rubles. There are 60 tablets in a package.
In cases of severe metal deficiency, complex dietary supplements “Complivit Selenium and Zinc”, “Duovit”, “Antioxicaps” are used.
The product “Complivit Selenium and Zinc” is taken 1 capsule 1 time per day after meals. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The cost of the drug is 278 rubles. There are 60 capsules in a package.
Antioxicaps is taken after meals. For the purpose of prevention, the drug is prescribed to adults, 1 capsule 1 time per day for 1-3 months. The course is repeated several times a year.
Therapeutic doses of the drug "Antioxicaps" are established by the doctor depending on the nature and severity of the pathology. The cost of the drug is 900-1000 rubles. There are 60 capsules in a package.
Typically in dietary supplements, zinc is presented in the form of picolinate, gluconate, sulfate and acetate. Picolinate has high bioavailability.
With prolonged use of high doses, copper levels may decrease, as competitive absorption of elements by red blood cells occurs. Before using dietary supplements, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Why is excess dangerous?
It was mentioned above that microelement deficiency leads to negative consequences. But not only a shortage is dangerous, but also an excess. In this case, the following problems are likely:
- weakening of the immune system;
- nausea and vomiting;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea);
- secondary copper deficiency;
- development of pathology of hair, skin and nails;
- malfunctions of the prostate, liver and pancreas.
A lack of zinc in the body is always caused by certain reasons. A similar situation arises with an excess of microelements. Only reasons are different:
- Excessive intake of foods rich in Zn, as well as zinc-containing preparations (ointments).
- Disruptions in zinc metabolism.
- Direct contact with zinc (optionally, during operation).
Nutrition correction
In parallel with taking various medications to eliminate zinc deficiency, diet correction is indicated.
Advised:
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages, coffee, marinades, or foods high in salt.
- Stick to fractional meals. For the body to fully absorb the necessary elements, you should consume food in small portions.
- Consume baked or steamed foods.
Approximately 20–30% of the microelement is lost during defrosting and cooking foods.
To preserve the mineral, it is recommended:
- Defrost meat in the refrigerator only on the bottom shelf, placing it in a saucepan with a lid.
- When cooking fish, use only a sharp knife. This preserves the juice of the product, which is rich in minerals.
- Pour water into the pan over meat and fish so that it slightly covers the product.
- Place the fish only in boiling water.
A balanced diet, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, as well as timely elimination of pathologies helps the body preserve essential microelements.
If a deficiency occurs, you should consume the following foods:
- Dried pumpkin seeds. A glass contains the daily dose of the element.
- Beef or lamb. 100 g of product contains 1/3 of the daily dose of metal.
- Cashew nuts. It is recommended to eat 2 glasses a day.
- Mushrooms. High microelement content is found in varieties such as shiitake, oyster mushrooms and champignons.
- Yogurt and kefir. A glass contains 10% of the daily dose of the element. The content of a glass of spinach juice is the same.
- Cocoa. It is necessary to consume dark chocolate.
It is also recommended to include buckwheat and oatmeal, bran, peas and beans in your diet.
The table shows the element marker in various products.
| Product | Level in mg/100 g |
| Fish | 78,8 |
| Calf meat | 12 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 7,6 |
| Beef meat | 6,31 |
| Nuts | 3,57 |
| Dark chocolate | 3,31 |
| Yogurt | 1 |
| Champignon | 0,9 |
| Eggs | 0,6 |
| Cocoa | 0,3 |
| Peas | 2,5 |
| Lamb meat | 4,5 |
| Chicken's meat | 2,25 |
| Oysters | 32 |
Only 20-40% of the microelement enters the body from food. The element is absorbed faster from animal products than from plant foods.
Beans, grains and oilseeds contain phytates, which interfere with the absorption of the element. To increase bioavailability in vegetarian foods, it is necessary to consume sprouted foods or soak them.
The daily norm for women and men is 15 mg. The requirement for children is 3-12 mg. Vegetarians will need 50% more zinc than the indicated marker.
Making dietary changes to increase zinc levels is advisable in cases of mild deficiency. If there is a violation of the body’s absorption of the element, they resort only to medications.
The role of zinc in the body
Eating foods rich in zinc helps your body:
- Fight harmful bacteria and viruses
- Increases the body's immunity
- Zinc is essential for athletes to build muscle mass.
- Pregnant women need zinc , especially if they are expecting a boy. In the first 3 months, the placenta develops and the fetus's genitals form.
- need zinc during puberty . It is responsible for the production of testosterone, the male hormone, in the body. The body of a young man contains more than 2g of zinc, and mainly in the testicles. Lack of zinc affects sexual potency . In adulthood, zinc deficiency leads to diseases such as impotence and prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland)
- A woman’s sex drive depends on zinc – it helps produce lubrication, which is so necessary during sexual intercourse
Both men and women need zinc for procreation
Possible consequences and complications
A reduced level can provoke:
- Stunted growth.
- Immune failure. With a low zinc marker, the respiratory system often becomes inflamed.
- Disorder of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract. Irritable bowel syndrome is provoked, manifested in systematic inflammation. The process is triggered by an allergic reaction to food. Diarrhea, bloating and gas may occur on a regular basis.
- Thinning hair structure and hair loss.
- Inflammation of the dermis.
- Complications of pregnancy. Premature birth or abnormal development of the embryo may be triggered.
- Development of diabetes mellitus.
- Hematopoiesis disorder.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Development of depression.
- Macular degeneration. With age, the zinc marker in the retina decreases, which contributes to a deterioration in the functionality of the visual system.
Zinc deficiency in the body in women is unacceptable. The microelement allows representatives of the fair sex to maintain beauty and physical activity. Prevention of substance deficiency makes it possible to prevent unpleasant symptoms and possible problems with conception and gestation.
Zinc and hair.
If you have hair loss, a rash on your skin, or diarrhea, do not take medications that can have a negative effect on other organs (eyes, liver, kidneys) and do not help much in treating the underlying disease. Only zinc treatment brings relief! Yu. Aleksandrovich describes the following case: “A 22-year-old woman, whose skin was covered in wounds, could not wear shoes and could only move by leaning on a stick, the doctor prescribed her zinc daily. The patient’s condition began to improve within a week, and she quickly recovered: her skin became clear, her hair grew back, the absence of which was a real tragedy for her.”
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency (Dietary Zinc Insufficiency):
Ensuring the body's optimal need for this mineral has allowed nutritional medicine to achieve revolutionary successes in curbing a wide range of consequences of its deficiency - a list of these ailments includes schizophrenia and other mental disorders, diabetes, prostate adenoma, cataracts, heart disease, brain and nervous system damage, disorders immune system functions, poor digestion, ulcers, food allergies, toxic metal accumulation, poor wound healing, osteoporosis, skin diseases, fatigue, loss of appetite, hearing problems, eating disorders and a host of symptoms of blood sugar imbalance. Our earth is becoming increasingly poor in zinc, and a high-carbohydrate diet leaves us with even less. Calcium supplements and calcium-rich diets can reduce zinc absorption by up to 50%. Zinc is quickly eliminated from the body under stress (physical, emotional or chemical), as well as under the influence of toxic metals, pesticides and other environmental pollutants. Aging inevitably puts us at a disadvantage because the stomach does not produce enough acid to absorb this mineral. Based on the prevalence of zinc deficiency among sick elderly people, the use of supplements should probably be considered mandatory for all older people.
A whole range of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders can be associated with zinc deficiency - epilepsy, schizophrenia, multiple sclerosis, Huntington's disease, dyslexia, acute psychosis, dementia, pathological aversion to food, attention problems and depression.
Zinc supplements may help prevent Alzheimer's disease. The zinc-dependent thymus hormone, thymulin, is almost undetectable in people affected by this disease, implying that zinc deficiency may play a role in the disease process.
People affected by AIDS are almost invariably zinc deficient , which contributes significantly to the ongoing decline of an already damaged immune system.
Malignant tumors develop more easily against the background of low zinc levels.
Symptoms of almost all skin diseases decrease or disappear when the body's zinc stores increase. In doses of 100 mg or more, it is particularly effective in treating acne, which some researchers believe is a condition caused by a deficiency of zinc, an essential fatty acid. The effects of supplements do not appear immediately - it may take weeks or months before you notice results on your skin.
Benign enlargement of the prostate gland (prostate adenoma), which has now reached almost epidemic proportions among men over fifty years of age, is inextricably linked with inadequate zinc intake throughout previous life. Urinary frequency and other symptoms of BPH are reliably reduced by using zinc supplements, especially when combined with saw palmetto (saw palmetto) extract, essential fatty acids, and several amino acids, including glycine, alanine, and glutamic acid. Zinc deficiency can also impair sperm production and testosterone production, while when a group of men over sixty were treated with zinc , their serum testosterone levels literally doubled.
Zinc deficiency can lead to a variety of pregnancy complications, including miscarriage, morning sickness, fetal growth restriction, and obstructed labor. Even a moderate daily dose of 22 mg tested in one study allowed women to give birth to significantly larger babies. Zinc doses of about 10-60 mg per day are completely safe to take during pregnancy.
Zinc levels in the body tend to be low in women experiencing premenstrual syndrome. It is possible that a deficiency of the mineral leads to a decrease in progesterone production, which, in turn, can cause cravings for sweet and salty foods. It is possible that zinc deficiency makes a certain contribution to one of the most common causes of blindness - macular degeneration. Taking supplements in doses of 100 to 200 mg may slow the progressive destruction of the retina that causes this condition. Forty percent of people with Crohn's disease are deficient in zinc , and replenishing your body's supply of this mineral is critical to overcoming this common digestive disorder. zinc supplements to the diet of children deficient in this mineral can reduce the incidence of dysentery and diarrhea. For those affected by rheumatoid arthritis (an inflammatory joint disease), the body's zinc reserves tend to be severely depleted. When zinc levels in the body decrease from optimal levels, we become more vulnerable to the toxic effects of environmental pollutants. In one study of two hundred randomly selected people with chemical hypersensitivity, 54% had low zinc levels.
Total information
Location on the periodic table D.I. Mendeleev: in the old version - IV period, V row, II group, in the new version of the table - 12 group, 4 period.
- Atomic number – 30
- Atomic mass – 65.38 g/mol
- Electronic configuration – [Ar] 3d10 4s2
- Melting point (°C) – 419.6.
- Boiling point (°C) – 906.2.
- CAS: 7440-66-6.
Read also Diet No. 1b (table No. 1b) - nutrition for gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers during their exacerbation
Physicochemical characteristics. Pure Zn is a silvery-white metal, plastic to the touch, which crackles slightly when bent due to friction between the crystals. When heated to 100 degrees, plasticity increases significantly, but as soon as it contains impurities of other minerals, fragility increases sharply.
Upon contact with air, it becomes covered with a thin oxide film, and when exposed to high temperatures it gradually burns.
Pathogenesis (what happens?) during Zinc Deficiency (dietary zinc deficiency):
As you know, zinc is one of the essential microelements. Its reserves in the body are not large. So, an adult contains only 1.5-2 g of zinc, which, for example, is 2 times lower than the iron content. Zinc is found in all organs and tissues of the body, but its highest concentrations are found in skeletal muscle, which contains 62% of its amount. The skeletal system, prostate gland, and cornea are also rich in zinc. In newborns, 25% of zinc can be present in the liver. The main amount of incoming zinc (40-45%) is absorbed in the duodenum through the mechanism of controlled diffusion. It has been established that the absorption of zinc is inversely proportional to its concentration in the intestinal lumen. Having entered the enterocyte, zinc combines with metallothionein, which, according to some data, regulates not only the absorption, but also the release of zinc. In the bloodstream, the main ligand of zinc is albumin, which carries up to 2/3 of the metabolically active trace element. Small amounts of zinc are transported to the brain by histidine and cystidine
The daily requirement for zinc is 8-10 mg, only 20-30% is absorbed from food. The richest foods in zinc are meat, dairy products, seafood, nuts, and eggs. It should be borne in mind that the qualitative composition of products can significantly affect the absorption of microelements. Thus, the absorption of zinc is prevented by phytin, which is contained in large quantities in products of plant origin, which forms an insoluble complex with zinc in the presence of calcium, which is not absorbed in the intestine. Hemicellulose, chelating agents, and calcium also inhibit the absorption of zinc.
Zinc is released mainly through the intestines (10 mg per day), with urine (0.3-0.6 mg), with sweat (in hot weather up to 2-3 mg). Zinc is also excreted in human milk (1.63 mg/kg),
Biological role of zinc
The biological role of zinc is diverse. It is necessary for cell growth and division, bone development, regeneration processes, reproductive function, brain development and behavior. Being a component of more than 300 enzymes, zinc takes part in all types of metabolism and is part of the genetic apparatus of the cell, representing about 100 zinc-containing nucleoproteins. Zinc plays a significant role in the functioning of the immune system. Thymulin, a thymic hormone necessary for T-lymphocytes, is zinc-dependent, as a result of which, with zinc deficiency, the total number of T-lymphocytes and T-suppressors, as well as the phagocytic activity of neutrophils, decreases. Zinc takes an active part in regeneration processes, as it is necessary for the synthesis and stabilization of DNA. Superoxide dismutase, which is involved in the regulation of lipid peroxidation, is also a zinc-containing enzyme, and therefore many authors classify this trace element as an antioxidant.
Zinc deficiency conditions
The indispensability of zinc for the course of fundamental life processes is clearly manifested when its deficiency occurs. A classic example of zinc deficiency is acrodermatitis enteropathica. It is a rare, autosomal recessively inherited disease. Manifests in infancy and without treatment leads to death. It is believed that as a result of a genetic defect in Paneth cells, the absorption of zinc in the intestine is impaired. Clinically, acrodermatitis manifests itself with typical signs of zinc deficiency. Skin lesions come to the fore in the form of chronic erythematous-bullous dermatitis on the extremities and around the natural orifices of the body, often accompanied by secondary infection, pathology of nail and hair growth, and alopecia. Characterized by severe gastrointestinal disorders with malabsorption syndrome, eye symptoms (blepharitis, conjunctivitis, photophobia, corneal opacities), neuropsychiatric disorders, growth retardation, hypogonadism, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly, decreased acuity of taste and smell. Zinc deficiency experienced by a woman during pregnancy leads to a wide range of congenital deformities in the fetus - cleft jaw, upper palate, microcephaly.
What is Zinc Deficiency (Dietary Zinc Deficiency) –
Zinc is a structural component of biological membranes, cellular receptors, proteins, and is part of more than 200 enzymatic systems. Zinc-dependent are such vital hormones as insulin, corticotropin, somatotropin, gonadotropins; it is necessary for the formation of red blood cells and other blood elements. Zinc is believed to have antioxidant properties and also improve the effects of other antioxidants. For normal functioning, the human body needs about 15 mg of zinc per day.