Causes
Excess zinc in the human body cannot be formed due to excessive intake of this substance from food. After all, food contains a very small amount of microelements. Even daily consumption of foods high in zinc cannot lead to an overdose.
Doctors call excess zinc in the body hyperzincosis. The following reasons for this condition can be identified:
- Taking medications. Long-term use of high doses of zinc-based medications can lead to an excess of the microelement in the body. This applies not only to oral medications, but also to topical agents. Many skin ointments contain zinc, as this substance has wound-healing properties. Long-term use of such drugs can cause hyperzincosis.
- Vitamin abuse. Zinc is part of many vitamin and mineral complexes. Patients often mistakenly believe that such dietary supplements are absolutely harmless. Under no circumstances should you exceed the permissible dosage of dietary supplements. Excess zinc in the body after taking vitamins is not uncommon. Signs of hyperzincosis do not appear immediately, but as the microelement accumulates in the body. With long-term use of high doses of vitamin complexes with zinc, chronic intoxication develops. Acute poisoning can result from taking more than 150 mg of zinc per day.
- Consumption of foods stored in zinc containers. There have been cases of poisoning from such food. Packaging materials may contain zinc salts, which have a toxic effect on the body. At home, it is not recommended to store food in galvanized containers; this can also lead to intoxication.
- Work in hazardous production. Zinc compounds are used in the manufacture of paints, matches, ceramics, glass and man-made fibers. Workers at such enterprises have an increased risk of acute or chronic zinc intoxication. Zinc vapor poisoning can occur when carrying out electric welding work without a respirator and in a closed space.
- Disorders of zinc metabolism in the body. Hyperzincosis is observed in chronic alcoholism, diabetes mellitus and liver cirrhosis.
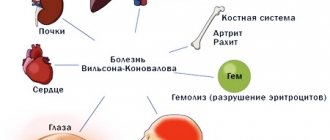
Excess and deficiency of zinc in the human body are equally harmful to health. Microelement deficiency leads to dermatitis, as well as deterioration of vision, hearing and smell. Excessive accumulation of zinc causes intoxication and damage to various organs.
Why is zinc dangerous? Harm of zinc
The harm of zinc begins with a significant overdose of the metal in the body - 150-600 mg is already poison for humans, and 6 g guarantees death. With metal intoxication, weakness, nausea and other signs of poisoning are observed. Of course, we rarely encounter the metal in such doses, but the harm of zinc can manifest itself unnoticed by us through indirect contact with the element. For example, drinking standing water from galvanized vessels is not recommended - soluble zinc compounds will have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Metal dust can cause lung pathology. Zinc phosphide used for rodent control is extremely dangerous for humans. The harm of zinc mainly manifests itself in contact with modifications of the element into complex compounds. Although zinc metal itself is neutral for humans.
Zinc is a fragile silvery bluish-white metal that cannot be replaced by anything; its properties are unique to industry and even to medicine. The thirtieth element of the periodic table of Mendeleev belongs to the transition metals. This means that it is able to change its oxidation state, it has a slight electronegativity, and, in general, is a little similar in properties to its nearest neighbor with the previous atomic number 29 - copper. At the end of the 18th century, it, together with copper, was used as elements of a voltaic column, which was capable of producing direct current. Therefore, zinc can be considered an important substance that stood at the origins of the study of electricity.
Acute poisoning
If a large amount of zinc and its compounds enters the stomach, the patient experiences acute poisoning. High doses of this trace element cause a burn to the gastrointestinal mucosa. The deterioration of health occurs within 2-3 minutes. The following symptoms of excess zinc in the body occur:
- acute pain in the esophagus and stomach;
- bloody vomiting;
- convulsions;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- copious secretion of saliva.
Acute intoxication is accompanied by renal and liver failure. Patients often experience collapse and loss of consciousness. The patient needs immediate medical attention.
Possible consequences
The harm of zinc oxide depends on the dose received by a person. Exceeding the permissible volume provokes respiratory arrest and brain dysfunction in allergy sufferers. In chronic poisoning, the bronchi and lungs, liver, and kidneys are most affected. Therefore, the consequences can be severe:
- pneumonia;
- atrophy of the mucous membranes of the pulmonary alveoli;
- anemia;
- renal failure.
In some situations, in the absence of medical assistance, the death of the victim is possible. Doctors do not recommend stopping treatment at the first positive results. The patient needs to additionally undergo a course of oxygen cocktails and inhalations with plant decoctions. A visit to the salt room or a trip to the sanatorium has a good effect.
Read what phthalates are and what harm they cause here.
Inhalation of vapors
Poisoning by vapors of zinc compounds is called foundry fever. This type of intoxication is observed among workers of metallurgical enterprises. Inhalation of harmful substances leads to irritation of the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchi. In this case, the symptoms of excess zinc in the body are similar to the manifestations of respiratory diseases. Signs of respiratory poisoning are as follows:
- coughing;
- temperature rise to +40 degrees;
- thirst;
- chills;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the throat and chest;
- redness of the face and eyes.
A rise in body temperature is quickly replaced by a sharp drop and increased sweating.
Chronic intoxication
Chronic intoxication is observed much more often than acute poisoning. In this case, zinc accumulates in the body over a long period of time. This is observed in patients who systematically abuse medications and vitamins, as well as in people working in hazardous industries.
Symptoms of excess zinc in the body during chronic intoxication are less pronounced than during acute poisoning. The patient experiences the following signs of hyperzincosis:
- constant weakness;
- noise in ears;;
- anemia;
- hearing impairment;
- poor condition of skin and nails;
- hair loss;
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system;
- constant drowsiness and lethargy.
Zinc compounds accumulate in the pancreas. As a result, organ tissues undergo fibrotic changes, and insulin secretion worsens. This leads to increased blood glucose concentrations and the development of diabetes.
A symptom of excess zinc in the body in men can be reproductive dysfunction. This microelement has a negative effect on prostate tissue and spermatogenesis. With hyperzincosis, patients often experience deterioration in the quality of seminal fluid and infertility.
The appearance of symptoms of excess zinc in the body in women is especially dangerous during pregnancy. This element is necessary for the body of the expectant mother for normal gestation. However, excess zinc is toxic to the embryo. The risk of having a child with various developmental anomalies increases. Therefore, pregnant women should never abuse dietary supplements with zinc.
Dosage
Zinc supplements should be prescribed to children by a pediatrician. In some cases, supplements are prescribed for infants. But always for objective reasons: for prevention or treatment. The dosage cannot be calculated independently, especially when it comes to babies.
If it is impossible to consult with a specialist, the daily dose of a zinc-containing drug is calculated based on general recommendations. But remember: you do this at your own peril and risk:
- children under 8 years old – up to 4 mg of zinc;
- primary schoolchildren – 8 mg;
- adolescents over 14 years old – 11 mg.
In some cases (for example, with skin injuries, weak immunity and muscle diseases), the dosage is increased to 20 mg. But this can be done only after the approval of the pediatrician.
Complications
Hyperzincosis can cause dangerous complications. Patients often experience the following consequences of excess zinc in the body:
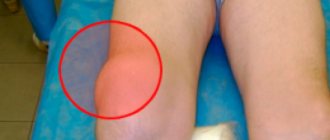
- Increased bone fragility. Excessive zinc content impairs the absorption of other microelements: cadmium, iron, manganese, copper. This leads to deterioration of the bone tissue.
- Slow growth. This complication is observed in children. With hyperzincosis, the activity of bone tissue cells decreases. As a result, the child grows very slowly.
- Muscle weakness. Excess zinc and deficiency of other microelements negatively affect the condition of the muscles. In advanced cases, the patient has no tendon reflexes.
- Malignant tumors. It has now been established that zinc compounds have carcinogenic properties.
- Autoimmune pathologies. With hyperzincosis, serious disturbances in the functioning of the immune system are observed. This can lead to diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pneumonia and pulmonary edema. Such complications occur with constant inhalation of zinc vapor.
- Heart diseases. Zinc intoxication negatively affects the contractile function of the myocardium.
- Urolithiasis disease. Excess zinc leads to increased salt content in the urine, and then to the formation of kidney stones.
First aid
In case of acute zinc poisoning, the patient needs urgent hospitalization and detoxification. At the pre-medical stage, the patient must be provided with the following assistance:
- The victim should be removed from the area of exposure to the toxic substance.
- The patient needs to be put to bed. Until the doctors arrive, the patient must remain completely calm.
- In case of vapor poisoning, you need to open a window or window to allow fresh air into the room. It is useful to inhale with soda solution, this will help neutralize toxins.
- If zinc enters the body through the gastrointestinal tract, then it is necessary to rinse the stomach with a soda solution. The patient needs to drink as much fluid as possible (alkaline mineral water or milk).
Further assistance to the patient is provided by the ambulance team and doctors in the hospital.
Natural sources
Despite the fact that many parents consider vitamin supplements in children's diets a good idea, the best option is to get the substances the child's body needs through food.
There are quite a lot of tasty and affordable foods containing zinc, including:
- any meat;
- poppy seeds;
- black currant;
- celery;
- pumpkin seeds;
- liver;
- milk;
- lobsters;
- pears;
- carrot;
- sesame;
- plums;
- oysters;
- fish;
- sunflower seeds;
- nuts;
- mustard;
- beans;
- apples;
- wheat germ;
- beet;
- cabbage.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of excess zinc in the body may resemble manifestations of other pathologies. Therefore, it is very important to carry out differential diagnosis. This is especially necessary in case of chronic intoxication, when the symptoms of poisoning are often erased.
The most reliable diagnostic method is a blood test for zinc content. At the same time, the concentration of copper is also examined, since in hyperzincosis there is a deficiency of this microelement.
Additionally, a urine test is performed to determine the concentration of zinc. However, this test is less informative. An increased content of this microelement in urine can be observed not only with hyperzincosis, but also with cardiovascular diseases, as well as with oncological pathologies.
Flu-like symptoms
Taking more zinc than the prescribed UL may cause flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, headache and fatigue ().
These symptoms occur in many conditions, including poisoning from other minerals. Therefore, diagnosing zinc overdose can be difficult.
Your doctor may need your detailed medical and dietary history, as well as blood tests to suspect mineral poisoning.
If you are taking supplements, be sure to tell your doctor.
Summary:
Flu-like symptoms can occur due to excess intake of several minerals, including zinc. Therefore, to ensure proper treatment, it is important to report all supplements you are taking to your healthcare provider.
Therapy
Treatment of zinc intoxication is carried out in a hospital setting. Antidotes are administered to patients:
- "Unithiol";
- "EDTA";
- "Dimercaprol."
Additionally, the drug “sodium thiosulfate” is prescribed. It has a laxative effect and helps eliminate toxins.
In case of poisoning by vapors of the substance, oxygen therapy sessions are indicated. As symptomatic therapy, bronchodilators and antipyretic drugs are prescribed.
After discharge from the hospital, the patient should regularly visit the doctor and undergo all necessary examinations. This will help to identify possible complications of hyperzincosis in a timely manner.
Prevention
The following recommendations will help prevent chronic and acute zinc intoxication:
- when working with zinc compounds in production, you must follow safety rules;
- during welding work, you should use a respirator and ensure air flow into the room;
- do not store food in galvanized containers;
- do not abuse vitamins and zinc-based medications;
- store chemicals with zinc compounds out of the reach of children
These measures will help avoid severe poisoning and the dangerous consequences of hyperzincosis.