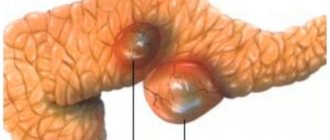
Gallstone disease (cholelithiasis) is considered one of the most common diseases. It is characterized by the formation of hard stones of different sizes and shapes in the gallbladder. More often, women suffer from the disease, as well as people who abuse fatty and protein foods.
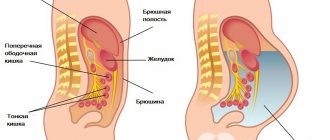
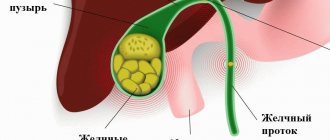
The gallbladder is an important organ involved in the digestion process. It accumulates bile produced by the liver, which is necessary for digesting food. It has narrow ducts that open into the small intestine and deliver bile to it for digesting fatty foods, cholesterol, and bilirubin. It is from bile that rocky formations are formed that block the bile ducts.
What is gallstone disease
The disease is characterized by the formation of hard stones in the gallbladder or ducts. Pathology appears as a result of a disorder in cholesterol metabolism. Bile consists of bilirubin and cholesterol, and stones in the bladder are formed due to its stagnation. In this case, cholesterol is retained in the body and forms a dense sediment in the gallbladder, from which sand is formed.
Over time, if treatment is not started, the grains of sand stick together, forming solid conglomerates. The formation of such stones takes from 5 to 25 years, and the patient does not experience discomfort for a long time.
The risk group for cholelithiasis includes older people, as well as patients taking medications that affect cholesterol metabolism. The development of the disease can be triggered by hereditary disposition, unhealthy diet (overeating and starvation), some gastrointestinal diseases, and metabolic disorders.
Watch the video about the effects of fasting on the gallbladder:
Possible complications
The exacerbation of the disease is provoked by a number of reasons, which are:
- diet violation;
- alcohol abuse;
- hard physical labor;
- stressful situations.
If the pain is constant, then this indicates an inflammatory process, that is, cholecystitis or cholangitis. Active movements of the patient contribute to increased pain. Exacerbation of the disease provokes fever to high numbers.
If the pain syndrome is prolonged and is accompanied by temperature and changes in the blood count, then these clinical symptoms will indicate phlegmon. The calculus, putting pressure on the wall of the organ, causes dystrophic changes, which leads to its thinning.
If the bladder ruptures, peritonitis develops. This is an acute condition that is life-threatening and requires immediate attention.
A complication of cholelithiasis can be the formation of a fistula between the duodenum and the bladder. If the stone comes out of it on its own and enters the intestines, intestinal obstruction may develop, accompanied by sharp pain in the abdomen with cessation of the passage of gases and stool.
A long period of illness can lead to the development of oncology, acute or chronic pancreatitis. If the intrahepatic ducts are obstructed for a long time or partially, secondary cirrhosis of the liver may develop.
Any complication during the course of the disease poses a threat to the patient's life. Early treatment of the disease avoids the spread of the pathological process.
Symptoms of gallstones
The severity and degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the size of the stones and their location. The longer the disease lasts, the more painful the symptoms. One of the most pronounced signs of gallstone disease is severe and acute pain, called hepatic or biliary colic.
It is localized in the right hypochondrium, and a few hours after the onset of the attack, it covers the entire area of the gallbladder. The pain can radiate to the neck, back, under the shoulder blade and to the heart.
Main symptoms:
- heartburn;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching;
- pain under the ribs on the right;
- general weakness.
The cause of the attack is often the consumption of fatty, spicy and fried foods, and alcohol. Pain can be caused by stress, physical overload, and spasm of the gallbladder caused by the movement of stones. Blockage of the bile ducts is accompanied by constant nagging pain and a feeling of heaviness in the right side.
Characteristic symptoms include severe nausea and vomiting, abnormal bowel movements, and bloating. In some cases, there is an increase in temperature, fever, and if the main bile duct is completely blocked, jaundice and white feces are observed.
Main symptoms in women and men
The main symptom of gallstones is pain in the right hypochondrium. They can be sharp or dull, occur periodically or only occasionally. During the first years of stone-bearing, there is usually no pain syndrome. A person leads a normal lifestyle, without even realizing the presence of stones. And they, in turn, lead to persistent impairment of motor skills and functionality of the organ, negatively affecting the condition of the liver and the entire digestive system.
It is precisely because of the gradual destruction of the gallbladder and dangerous complications in the form of acute cholecystitis, perforation of the walls, when even minor symptoms of gallstones appear, treatment is carried out predominantly surgically. Cholelithiasis is a disease in which it is dangerous to follow a wait-and-see approach.
The main symptoms of gallstones in women and men:
- dull or sharp pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dyspeptic manifestations: nausea, vomiting, presence of bile in the vomit;
- increased body temperature;
- heartburn, heaviness in the stomach;
- bloating, periodic abdominal pain;
- discoloration of stool with the development of obstructive jaundice when the common bile duct is blocked by a stone and the development of obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi.
Symptoms of gallstones depend on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage of stone formation, the ratio of bile components only changes, but this does not manifest itself clinically. The stone-carrying stage continues for many years, and at this stage it is possible to detect stones in the gall bladder using instrumental research methods.
If you do not effectively treat gallstones before attacks of colic and the onset of pain, the disease subsequently progresses to the stage of acute or chronic calculous cholecystitis. The functionality of the organ will rapidly deteriorate.
If at the initial stage, when there are no symptoms of gallstones, conservative treatment can give good results or at least stop the growth of stones, then in the cholecystitis phase only surgery is indicated.
Causes of stone formation
The gallbladder has a volume of no more than 70-80 ml, and the bile contained in it should not linger or accumulate. The process of its movement to the intestines must be continuous. With prolonged stagnation, cholesterol and bilirubin precipitate, where they crystallize. This process leads to the formation of stones of various sizes and shapes.
Causes of cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis):
- obesity;
- taking hormonal medications;
- heredity;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- alcohol abuse;
- irregular meals, prolonged fasting;
- taking medications that affect cholesterol metabolism (Octreotide, Cyclosporine);
- inflammatory process in the gallbladder;
- women have multiple births;
- diabetes;
- intestinal surgery;
- increased levels of calcium in bile.
Often, cholelithiasis is caused by eating fatty and spicy foods, endocrine pathologies, and toxic liver damage.
Causes of stones
The reasons for the formation of stones or the occurrence of acute attacks when stones form in the gallbladder ducts turn out to be different, each to a certain extent depends on the individual qualities of the patient, from medical history to genetics.
Among the most common reasons are:
- interruptions in food intake: first - overeating (the cause is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting), then, on the contrary, prolonged fasting;
- problems with excess weight, including obesity;
- sedentary work that does not allow movement during the working day;
- side effect of hormonal-based contraceptives;
- pathology of the pancreas.
The occurrence of stones in the gallbladder ducts is an unpleasant thing, not recognized in time, and provokes serious complications. For example, cholelithiasis can easily lead to biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
Stones in the gallbladder ducts
The composition of the stone stuck in the duct
Based on the nature of the pain, it is impossible to determine the composition of the stone that caused cholelithiasis. Cholesterol stones, for example, often contain an admixture of calcium, which is not fully processed in the body and is forced to be excreted through roundabout routes.
Sometimes lime gets into the stones - a rather rare phenomenon, but known. The presence of a substance in stones is determined using a diagnostic method - cholecystography.
Stones in the liver ducts often appear as a parallel disease: damage to the first organ of the excretory system leads to damage to the second. Of course, treating two diseases at the same time complicates the process; it is better to monitor the timely passage of stones in advance, preventing the appearance of new ones.
Types of gallstones and what sizes they reach
There are several types of stones that differ in composition. This depends on the constituent components of bile.
Types of stones:
- cholesterol;
- limestone;
- mixed;
- bilirubin.
Cholesterol stones are round, smooth formations with a uniform structure. They can reach a size of about 15-20 mm in diameter, and the reason for their formation is metabolic disorders in obese people. They are localized exclusively in the gallbladder and appear in the absence of an inflammatory process.
Calcareous, composed of calcium, and the cause of their formation is considered to be inflammation of the gallbladder. Around bacteria or small particles of cholesterol, calcium salts accumulate, which quickly harden and form stones of various shapes and sizes.
Mixed stones occur as a result of increased inflammation in the liver and gallbladder. Calcium salts are layered on cholesterol and pigment formations, forming solid heterogeneous formations with a layered structure.
Bilirubin is formed regardless of the presence of inflammation, and the reason for this is a violation of the protein composition of the blood or congenital defects associated with increased breakdown of red blood cells. These stones are small in size and are often located in the bile ducts.
The least common are calcareous stones, and more often mixed ones, the size of which ranges from 0.5 mm to 5-6 cm.
Diagnostics
When there are complaints about problems with the digestive system, the patient often has a question about which doctor should be consulted. For an initial examination, the patient is sent to a therapist, who will collect anamnesis and objective data of the disease.
Then, taking into account the polymorphism of symptoms, laboratory research methods are carried out for clarification and differential diagnosis:
- blood for ESR, hemoglobin, leukocytosis;
- general stool analysis;
- urine for general analysis;
- blood biochemistry for liver tests.
After the initial and laboratory examination, the patient is referred to a gastroenterologist, who prescribes instrumental examination methods to clarify the diagnosis:
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray or fluoroscopy of the abdominal cavity;
- CT or MRI;
- oral cholecystography is an alternative ultrasound method, but less informative.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis
GSD is asymptomatic for a long time, and patients consult a doctor only when they experience severe pain. Hepatic colic requires examination by a gastroenterologist to confirm the diagnosis. The doctor is required to prescribe a general blood test and biochemistry.
On a biochemical study, an increased level of bilirubin is clearly visible, and on a general basis - an increase in leukocytes and a rapid ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Further diagnosis requires an ultrasound of the gallbladder, which shows the presence of stones in the gallbladder and ducts in 90-95% of cases, as well as choledochoscopy. Calcareous formations are clearly visible on x-rays, and ultrasonography using an endoscope allows you to see stones in the gall bladder in very overweight, obese patients.
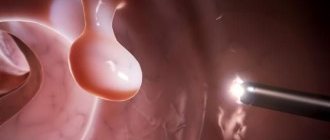
ERPG (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) effectively identifies stone formations in the bile ducts.
Surgical treatment
Every year in our country hundreds of operations are performed to remove gallstones during laparoscopy: reviews about the method vary, but most of them are positive. Patients get tired of the constant exacerbation of calculous cholecystitis and eventually decide on surgical treatment. Negative consequences after removal of the gallbladder with stones occur in those who cannot maintain a fairly strict diet in the first 3-6 months of the recovery period.
But dietary restrictions can gradually be softened by giving up only excessively fatty, fried foods, spicy foods and alcohol. Cholecystectomy involves removing the gallbladder along with stones. After several years of gallstone disease, the organ can no longer perform its functions, so it is better to remove it.
In most cases, cholecystectomy is performed through a laparoscopic approach - small punctures in the abdominal wall. This operation is easily tolerated, is not accompanied by blood loss and does not require difficult and long rehabilitation.
When is it better not to touch gallstones?
A surgeon will help get rid of large stones, but if the disease does not manifest itself in any way, then there is no need to treat it. The main thing that needs to be done is to follow a diet, lead a healthy lifestyle, and give up bad habits.
Small stones can be dissolved with the help of medications, but treatment will take a very long time, and the effect is short-lived. In addition, the use of such drugs destroys liver cells and causes multiple complications.
If 1-2 small pebbles are found, they can be crushed using a shock wave. After which, the resulting fine sand leaves the body on its own. Under no circumstances should you use choleretic drugs (including herbal ones). Uncontrolled movement of stones through the gallbladder can lead to dangerous complications.
Diagnostic methods
If a patient is suspected of having deposits, the attending physician prescribes:
- Clinical blood test. During the inflammatory process, the study will show an increase in ESR.
- Blood chemistry. The basis for further diagnosis is increased levels of cholesterol and bilirubin.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). To conduct the study, a probe with a camera is inserted into the patient's digestive tract. Then, using a special catheter, a contrast agent is injected into the bile ducts. After this, X-rays of the diseased organ are taken. To prepare for ERCP, the patient should not eat for several hours. Possible consequences of the method include perforation of the walls of the esophagus, stomach pain, and infection.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiography. Using the method, you can determine the presence of small deposits that do not yet bother the patient. Magnetic resonance cholangiography helps identify the duct filled with stones. The study is carried out in the morning. The evening before cholangiography, the patient is prohibited from eating after 20:00. In the morning before visiting the doctor, smoking and drinking liquids are prohibited. The method does not affect the patient’s immunity and does not contribute to the development of cancer.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examinations can be performed repeatedly over a short period of time, since the patient is not exposed to radiation. It is necessary to prepare for the diagnostic procedure 2-3 days in advance. All foods that cause gas formation should be excluded from the diet. The last meal should be 8 hours before the test. The evening before the procedure, it is recommended to take 1-2 tablets of activated carbon and do an enema.
- Computed tomography. The patient takes a contrast agent, and then it is placed inside the tomograph. The device takes pictures of the diseased organ. The patient should abstain from the evening meal on the eve of the tomography. It is recommended to take a laxative. If the patient suffers from asthma, diabetes, heart or kidney disease, it is necessary to warn the doctor about this. Tomography is not performed during pregnancy.
Treatment methods
Drug treatment is used only at the initial stage of development of cholelithiasis.
In this case, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
| Ursofalk | Medicines that normalize the composition of bile. |
| Creon, Mezim | Digestive aids. |
| No-Shpa, Platafillin, Pirencipin | Muscle relaxants and antispasmodics. |
| Zixorin | Stimulators of bile production. |
The addition of a secondary infection requires the use of antibiotics, and to dissolve cholesterol stones, Ziflan and bile acid preparations are used. The latter contain different active substances and are divided into two groups: ursodeoxycholic (Ursosan, Ursofalk) and chenodeoxycholic (Chenosan, Henochol).
Taking such drugs requires compliance with certain conditions:
- small size of stones (5-15 mm in diameter);
- the gallbladder contracts on its own;
- There are no stones in the bile ducts.
You will have to take these medications for a long time, more than 2 years, and they can cause many complications.
There is a rather interesting technique called contact dissolution. Its essence is that a special substance that dissolves stones (Propionate) is injected into the gallbladder and ducts. After such a procedure, the patient requires long-term maintenance therapy.
No less popular is spraying (shock wave therapy), which turns stones into small grains of sand. But this method of treatment can only be used if there are no stones in the ducts.
Find out in the video about a powerful remedy that helps remove stones from the gallbladder:
ethnoscience
Treatment of gallstones with folk remedies is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. The principles of dissolving stones are similar to those used when using acids in preparations. Herbal remedies can break down stones, and if there are too many of them or they are large, then the risk of blockage of the ducts will be high. Be careful when using traditional medicine, especially if you have previously had attacks of biliary colic.
Beetroot infusion
Boil the beets without peels until a thick infusion is obtained. Take 0.5 cups 30 minutes before each meal (at least 3 times a day). The course of treatment is long - 4-6 months. But the effectiveness of the method is high, as confirmed by people on specialized forums where they solve problems of the gallbladder, including the course of calculous cholecystitis.
Horseradish leaf tincture
Wash the horseradish leaves (enough to fill a 3-liter jar), dry and cut with scissors into 2-3 cm pieces. Place them in a jar, fill with vodka, or better yet, homemade moonshine. The jar will take approximately 2 liters. Place in a dark place for 2 weeks. Shake the jar of horseradish leaves periodically. After 2 weeks the tincture is ready. Drink it 1 tablespoon an hour after meals or on an empty stomach (if there are no stomach problems). Take the product until it runs out. After dissolving gallstones, drink the tincture for prevention every 2 years.
Bear bile
Bear bile is actively used to dissolve gallstones. It has unique healing properties and is even used to fight cancer. The dry gall bladder of a bear must be crushed and poured with vodka in a ratio of 25 g of bile per 0.5 liter of vodka.
The product will be ready in 2 weeks. All this time it should stand in a dark place. It is recommended to shake the container with tincture daily. Take half a teaspoon one hour after meals or on an empty stomach (if your stomach health allows). The course of dissolving gallstones with this remedy is 2-3 months.
When is gallbladder removal surgery necessary?
Complete removal of the gallbladder is carried out with the development of acute calculous or chronic cholecystitis. In this case, open abdominal surgery (classical cholecystectomy) or surgery using laparoscopy (laparoscopic cholecystectomy) can be used.
In some cases, surgical removal of stones by laparoscopy may be required without removing the gallbladder. It is carried out in cases of frequent relapses and the presence of large stones.
Treatment options
You should consult a specialist at the first symptoms of the disease. You should not take folk choleretic remedies on your own, which can cause the movement of stones. Modern medicine offers both surgical intervention and non-surgical treatment, such as stone lithotripsy.
Drug treatment
In the treatment of cholelithiasis, drugs such as:
- Ursosan. The drug is released in the form of capsules. Treatment with this remedy can last up to two years. Ursosan is used for dyskinesia and inflammation of the bile ducts. The drug can be used as a choleretic agent for bile stagnation. With its help, you can remove sand and small stones almost painlessly. Side effects of the medication include nausea, diarrhea, or constipation. The drug is not prescribed for liver failure and liver cirrhosis.
- Karsil. Produced in the form of dragees and capsules, the drug contains milk thistle extract. The medicine is used as a choleretic agent. Karsil is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age. Possible side effects include nausea, skin rash, itching, diarrhea.
- Allohol. The drug is produced in the form of tablets. The medicine is prescribed for cholecystitis and impaired motility of the biliary tract. The tablets help normalize the process of bile formation. Taking Allochol without a doctor's prescription is prohibited, despite the almost complete absence of side effects. Allochol is not prescribed for certain liver diseases (hepatitis, liver dystrophy).
- Odeston. The drug in tablet form acts on smooth muscles. Thanks to this effect, bile promptly enters the duodenum for further participation in digestion. Odeston can be used as a prophylactic agent. The medicine is contraindicated in certain diseases (Crohn's disease, hemophilia, ulcerative colitis) and in patients under 18 years of age.
- Heptral. The drug in tablet form normalizes the excretion of bile, preventing its stagnation. The medicine is contraindicated in certain genetic diseases (hyperhomocysteinemia). Possible side effects include joint pain, flatulence, shortness of breath, nausea, headaches, and dizziness.
- No-shpa. The medicine is used in cases where it is necessary to relieve pain as soon as possible. No-spa is available in the form of capsules, injection solutions and tablets and has a wide range of applications. The antispasmodic can be taken without a doctor's prescription. It should be remembered that the drug is intended for temporary relief of the patient’s condition. If you feel better, you should consult a doctor.
As an aid, it is permissible to use dietary supplements, for example, products from Tentorium. But before you start using it, you must obtain the approval of your doctor. Tentorium uses medicinal plants and bee products in its production that can cause an allergic reaction.
Surgical intervention
It is impossible to do without surgery if:
- the presence of large stones;
- frequent colic;
- loss of contractile function of the gallbladder;
- complications.
Surgical intervention may be indicated in the presence of cholecystitis and frequent exacerbations of this disease. The surgical option is selected individually for each patient. This could be cholecystectomy, cholecystostomy, etc.
Other methods
You can also get rid of stones using:
- Cholelitholysis. The patient has a catheter inserted into the deposit-containing organ through the skin and liver tissue. A mixture of medications is delivered through a catheter to the diseased organ. The drugs dissolve stones, regardless of their composition and size. Cholelitholysis is used both in asymptomatic cases of the disease and in the presence of signs of the disease. To achieve the desired effect, the procedure must be repeated. Within a month, at least 90% of the stones can be dissolved. Despite its effectiveness, cholelitholysis is used infrequently.
- Ultrasonic crushing. The deposits are exposed to ultrasonic waves. The stones crumble into small fragments, which are easily removed from the body. To achieve the desired result, at least five sessions are necessary. The procedure can be carried out only with a small number of stones. The deposits must be cholesterol. The disadvantages of the method include possible injuries that the patient can receive from stone fragments or an ultrasonic wave. The procedure is prohibited for certain gastrointestinal diseases.
- Laser crushing. To carry out this procedure, a special device is inserted into the diseased organ through a small puncture in the anterior part of the peritoneum. Within 20 minutes, the beam crushes the stones. The indications for using the procedure are the same as for ultrasonic crushing. The method is not used in the presence of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system. Laser crushing is not suitable for patients over 60 years of age and weighing over 120 kg. Possible complications include damage to the mucous membranes from stone fragments or radiation.
Diet for gallstone disease
The first signs of the appearance of stones require a transition to a strict diet. In this case, table No. 5 is assigned, and you will have to stick to it for life.
The following are completely excluded from the menu:
- any meat and fish broths;
- fried, fatty and salty;
- marinades, smoked meats, seasonings;
- eggs;
- rich pastries and fresh rye bread;
- strong tea and coffee;
- alcohol and soda;
- canned meat and fish.
You should eat in small portions, at least 5-6 times a day, and food should be boiled or baked without butter or fat. The diet should contain a large amount of vegetables and vegetable oils.
Diet
After clarifying the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. But, first of all, for gallstones, a diet is indicated. Since there is a disorder of cholesterol metabolism, therapeutic nutrition is a prerequisite for preventing exacerbations and complications during the course of the disease.
Without diet, drug treatment will not be successful. Patients with biliary tract disease must follow the following dietary rules:
- meals are fractional, up to six times a day;
- adherence to food intake;
- single servings of food are no more than 300 grams;
- food processing is carried out only by steaming, stewing or boiling;
- the food is warm, no higher than 30 - 35 degrees;
- a reduced salt regime is introduced, no more than 10 grams of salt per day;
Patients with gallstones are recommended to eat a diet corresponding to table No. 5, the energy value of which is 2500 kilocalories.
The diet for liver patients is based on foods that can or cannot be consumed.
Prohibited Products
The presence of stones requires exclusion from the diet of certain foods that increase bile production. These include:
- fatty beef, lamb, pork;
- strong meat and mushroom broths;
- fresh wheat bread and pastries;
- peas, beans;
- smoked and canned products;
- sharp cheeses;
- coffee and colored carbonated drinks;
- white and Brussels sprouts;
- hot sauces;
- spices and herbs.
Authorized Products
The diet of a patient suffering from gallstone disease must be complete and nutritious, including everything necessary.
Products allowed for consumption include:
- dietary meat of chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- buckwheat, rice, semolina, oatmeal porridge cooked in water;
- yesterday's dried bread, biscuits;
- pasta;
- lean fish varieties (pike perch, cod, pollock);
- low fat dairy products;
- chicken protein;
- boiled vegetables;
- compotes or jelly;
- mineral water without gas such as Borjomi, Essentuki.
Prevention
To prevent cholelithiasis, you need to eat right, normalize weight, exercise, or simply provide regular physical activity.
If cholelithiasis has already been diagnosed, in order to avoid repeated relapses, it is necessary to take litholytic drugs for six months, be wary of taking certain medications, and lose excess weight. Prolonged fasting and irregular eating can also trigger the formation of stones.
Types of stones
Before starting treatment, the doctor must determine the structure and composition of the stones. According to their structure, stones can be:
- amorphous;
- crystalline;
- fibrous;
- layered.
According to the composition they are distinguished:
- Calcareous (calcifications). The rarest type of stones is formed from potassium salts, which when ingested into the body are layered on top of each other. Calcifications are often observed during inflammatory processes. Limestone stones are distinguished by their brown color.
- Cholesterol. Depending on the stage, cholesterol stones come in small and large sizes. Such stones are considered the most common type. Possible causes: diabetes mellitus, systematic consumption of fried and fatty foods, long-term use of oral contraceptives, liver disease. Cholesterol stones are yellow in color.
- Bilirubin (pigment-calcareous). Black, gray or dark green stones occur after taking certain medications, chronic or autoimmune diseases. The formation of stones can be a consequence of the breakdown of hemoglobin.
- Mixed composition. Stones of mixed composition are formed when calcium salts, cholesterol and bilirubin combine.
Concretions are also divided into:
- Primary, formed over a long period of time when the composition of bile changes.
- Secondary, occurring when the outflow of bile is disrupted.
Exercising when sick
If cholelithiasis is detected, you should limit yourself in physical activity. This also implies the exclusion of household physical activity. Physical activity during the course of the disease can help:
- rapid formation of bilirubin (this is dangerous for people with bile stagnation);
- movement of stones (if there are stones, then physical activity will move them out of place);
- likelihood of complications of cholelithiasis;
- complications after surgery.
According to the doctor's indications, daily 30-60 minute walks, gymnastics without stress on the abdominal area and sudden movements, swimming without diving are allowed. These loads are considered to prevent the occurrence of gallstones and also promote recovery after surgery. Professional sports involving heavy loads are prohibited for patients with cholelithiasis.
List of references: https://rg.ru/2012/07/05/zhelch.html https://52gkb.ru/press-tsentr/besedy-s-vrachom/1204-chto-nuzhno-znat-o-zhelchekamennoj- bolezni-zhkb https://www.alfazdrav.ru/zabolevania/zabolevaniya-gepatobiliarnoy-sistemy/zhelchekamennaya-bolezn/ gp7.by/news/simptomy-kamnej-v-zhelchnom-puzyre/ https://www.smclinic.ru /diseases/zh/zhelchnokamennaya-bolezn/ https://www.tasmc.org.il/sites/ru/ichilov/Statji/Pages/kamni-v-zhelchnom-puzire.aspx https://dialine.org/articles/ kamni_v_zhelchnom_puzyre https://www.ckb2rzd.ru/departments/territory1/1hiro/jkb/ med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/kamni-v-zhelchnom-puzyre-simptomy-i-lechenie/ https://www.pravda .ru/health/234296-holecist/ Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/09/2020