The phrase gastrointestinal tract disorder refers to a variety of diseases, both those directly affecting the gastrointestinal tract and those related to disruption of other body systems. Such diseases are among the most common today. In general, all of them can be divided into three large groups: functional, organic disorders and psychosomatic disorders. Let's take a closer look at each of the groups.
Functional disorders
As the name speaks for itself, with this type of disorder the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. Moreover, this disorder is not accompanied by any organic changes in the structure of the organs themselves. So, what functions may be impaired?
- Motor. It is performed by muscles and is responsible for chewing food, swallowing it, moving it throughout the digestive tract and removing it from the body.
- Secretory. It consists in the production of various secretory fluids (saliva in the mouth, gastric juice in the stomach, intestinal juice in the intestines, etc.).
- Excretory. Responsible for the release of metabolic products (salts, heavy metals) into the cavity of the digestive tract.
- Suction. It is necessary for the body to absorb nutrients that were released from food during the digestion process.
Each of these functions or several at once can be disrupted due to various reasons, which leads to gastrointestinal disorder. The failure of organs affects a person’s sensations, which makes it possible to identify certain symptoms.
Heartburn
This irritating symptom appears when the patient experiences an excessive release of gastric juice, that is, increased acidity. Heartburn is a kind of uncomfortable burning sensation in the upper part of the esophagus. Sometimes people suffering from heartburn feel a lump in the throat, which puts a lot of pressure and causes very unpleasant sensations. They especially annoy a patient with gastrointestinal disorders when a person bends down to pick up or do something. In this position of the body it only intensifies and irritates even more.
But keep in mind that something as common as heartburn can cause holes in the stomach, intestines (ulcers) and even cancer of the digestive system.
Symptoms of functional disorders:
- Pain, discomfort, pressure, heaviness in the abdomen. Most often indicates diseases of the stomach or intestines.
- Chest pain (can sometimes indicate heart disease).
- Heartburn and/or belching (may indicate problems with the duodenum or stomach).
- Intestinal dysfunction (colic, bloating, diarrhea or constipation, gas).
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Decreased or complete absence of appetite.
- Difficulty swallowing food, which may be accompanied by pain (signals inflammation in the oral cavity or cancerous formations).
As you can see, the symptoms are very common and can indicate many different diseases.
Nausea
Another pestering “messenger” for almost all people suffering from “stomach” problems. Nausea is a rather unpleasant sensation, which usually leads to vomiting, another dangerous symptom. It usually occurs in the chest or oral cavity and is a manifestation of many common diseases: gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, ordinary poisoning or overeating, and even the most serious diseases. In a word, this symptom is accompanied by all gastrointestinal abnormalities, even infection by parasites, bacteria and viruses.
Reasons for violations
The causes of functional disorders can be very diverse, ranging from the unfavorable influence of the external environment to other diseases in the body that provoke complications in the gastrointestinal tract. The most common of them:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Diseases of internal organs located near the digestive tract.
- Lack of eating routine and/or unbalanced diet.
- Polluted ecology.
- Great physical activity.
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Bacterial infections.
Most often, the reasons lie in poor nutrition. Often, eating dry, fatty, spicy and fried foods requires the release of more secretion than is normally necessary. Over time, the glands “get tired” and can no longer secrete the required amount of juices to process less heavy food. This condition leads to irritation of the mucous membrane, gastritis can occur, and so on. In other cases, the motor function of organs is disrupted, the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract is slowed down or accelerated, which causes discomfort and pain in the patient.
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
A common occurrence in disorders of the human digestive system. Characterized by frequent, mostly watery bowel movements. A patient's diarrhea occurs when food, being poorly digested, moves very quickly through the gastrointestinal tract without having time to be absorbed properly. This condition is usually caused by viruses and bacteria present in the inflamed intestine. And a similar manifestation accompanies pancreatitis, intoxication or cholestasis.
By the way, diarrhea is also a symptom of other disorders of the human body, for example, stress, a change in climate or diet, or taking certain medications. In any case, such an important sign cannot be ignored, because it can provoke an even more serious illness.
Diagnostics
An accurate determination of the location of discomfort in the abdomen helps bring the doctor closer to making an accurate diagnosis. Conventionally, the entire abdomen can be divided into 9 sections, which is illustrated in the picture below. At first glance, this seems very difficult, but let's figure it out. The division begins by drawing two horizontal lines that connect the upper ends of the thighs and the lower ends of the costal arches. Thus, the abdomen can be divided into three levels, from upper to lower: epigastrium, mesogastrium and hypogastrium. Further, each of these levels lasts for another 3 parts, which are distinguished by drawing two vertical lines that are drawn along the rectus abdominis muscles. Also, to limit the diagram, a solid line is drawn from above along the costal arches. The dotted line in the picture indicates the dome of the diaphragm.
Why is it necessary to divide the body into sections? The fact is that in each of these sections certain organs are located and, by defining the sections, we significantly narrow the range of possible diseases. For example, in area No. 7 the appendix is most often located, and in areas 6 and 4 the kidneys are located.
These methods are used only for primary diagnosis. Ultrasound, stool, blood and urine tests are used for confirmation.
Hiccups
Specific contractions of the diaphragm, characterized by the involuntary expulsion of excess air that entered the stomach along with food or resulting from increased gas formation. Therefore, hiccups are one of the main symptoms of many gastrointestinal disorders, for example, the stomach is full of food or severe intoxication. In any case, if the hiccups are not long-lasting, then apart from unpleasant sensations and annoyance, they will not cause much trouble. But when such a physiological reaction is too long and exhausting, it is better to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo an appropriate examination.
The most common diseases
Of course, in this article we will not cover the entire variety of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore we will briefly consider the most common:
- Gastritis (violation of stomach acidity).
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Chronic bronchitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis (refers to gastrointestinal disorders when caused by the entry of stomach contents into the bronchial tree.
- Non-ulcer dyspepsia syndrome.
Pathological impurities in feces
But the appearance of this symptom already indicates more serious ailments. In modern medicine, these include pieces of undigested food, mucus, blood, and pus. The last two “contents” in the stool of a sick person indicate a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. Also, blood and pus may be present in the stool when a person has dysentery, has an ulcer, hemorrhoids, or a fissure in the rectum.
This is a fairly serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment
Basically, the standard therapy regimen includes methods of traditional and traditional medicine, as well as diet. All patients are advised to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking) during treatment, and to carefully follow the treatment.
In most cases, treatment is limited to taking medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs to restore intestinal microflora, drugs that normalize stomach acidity. In extreme cases or in advanced stages, surgical intervention may be required.
Bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SIBO)
SIBO develops when bacteria from the large intestine enters the small intestine, causing symptoms such as:
- bloating
- diarrhea
- constipation
Some evidence suggests there may be some connection between IBS and SIBO. A 2000 study found that eliminating bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine effectively treated IBS symptoms in 48% of study participants. Treatment includes taking antibiotics, but it may also include medications to aid digestion and address the underlying cause.
Treatment
Organic dyspepsia is diagnosed in the same way as functional dyspepsia. However, the therapy will be different. In this case, more intensive and prolonged treatment is required. Patients are necessarily prescribed antibiotics (often even two at once), as well as drugs that support the microflora in the intestines. For severe pain, antispasmodics and painkillers are used.
Important! These drugs are prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis! You should not take painkillers for abdominal pain without consulting a doctor; they can hide the symptoms of serious diseases.
If an infection has been diagnosed, which is accompanied by a high temperature, then antipyretics are prescribed.
In case of a severe course of the disease, the patient must remain in bed, overload himself physically, and temporarily give up work and study.
You need to drink plenty of fluids and watch your diet.
It is best to go on a diet: eat only boiled, non-spicy and low-fat foods.
Under no circumstances should you eat hot or cold food; everything should be at room temperature. You should eat small portions several times a day.
If you like tea, it is better to replace it with herbal infusions.
If serious complications develop, surgery may be required.
Prevention
Intestinal diseases can be avoided by following a basic list of rules:
- proper nutrition. Eliminate everything harmful from your diet (fast food, salty, fried, fatty, baked goods). Include: vegetables, fruits, lean meats and poultry, fish;
- avoid stressful situations;
- completely eliminate alcohol and tobacco;
- for women, closely monitor the pelvic organs (if any manifestations of symptoms occur, immediately consult a doctor);
- wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly;
- engage in physical education;
- take vitamins;
- drink more fluids.
Psychosomatic disorders
In most cases, they mean the same diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but caused by a person’s mental state. The theory of this effect was developed by Hans Selye, who studied wounded soldiers and conducted experiments with rats. In the course of his research, he discovered that the level of stress and the duration of its impact on the body significantly affect life expectancy and health.
Today, such dependence is not a secret for doctors, and especially gastroenterologists, because nervous tension most often affects the gastrointestinal tract.
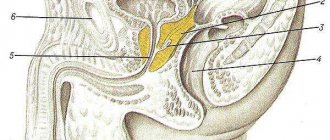
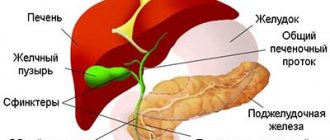
Cholelithiasis
The gallbladder is a small sac of bile that the body uses during digestion. Gallstones form in the gallbladder. In most cases, a person may not know that they have gallstones as they usually do not cause symptoms. However, symptoms may occur if gallstones block the opening of the gallbladder.
Symptoms may include:
- constant pain under the ribs, on the right side of the body
- jaundice
- heat
- nausea
- vomit
- sweating
Treatment for gallstone disease may include surgical removal of the gallbladder or a procedure that removes gallstones from the bile duct.
Causes of the disease
As mentioned above, the main reason is nervous tension and stress. However, how do they affect digestion? The fact is that man is a biological being, in whom many natural instincts are embedded. When any changes occur in life that entail strong feelings, the body can behave in two ways:
- Prepare to “defend”, that is, fight.
- “Run away”, that is, hide from problems.
The first strategy requires activation of all body systems and obtaining additional energy. To obtain it, it is necessary to speed up the process of digesting food, by releasing more secretion and increasing organ motility. In the second case, the entire body, on the contrary, is inhibited, all processes slow down, accordingly, less secretion is released, motor skills slow down.
Both situations negatively affect the condition of the organs: in the first case, they are depleted, and in the second, they release an insufficient amount of resources for digesting food and the body does not receive enough nutrients.
Sources
- Meenakshi Rao, Michael D. Gershon. The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, Sep: 13(9):517-528. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5005185/
- Joel C. Bornstein, Serotonin in the Gut: What Does It Do? Front Neurosci. 2012; 6: 16. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3272651/
- Chris Mavrangelos, Melissa A. Campaniello, Jane M. Andrews, Peter A. Bampton, Patrick A. Hughes. Longitudinal analysis indicates symptom severity influences immune profile in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2021. URL: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/06/170620122901.htm
- Brian E. Lacy, Nihal K. Patel. Rome Criteria and a Diagnostic Approach to Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021 Nov. 6(11): 99. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5704116/
- Wathsala S. Nanayakkara et al. Efficacy of the low FODMAP diet for treating irritable bowel syndrome: the evidence to date. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2016; 9: 131–142. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4918736/
- Instructions for medical use of the drug Duspatalin® (Mebeverine) 135 mg, film-coated tablets dated May 24, 2017
- Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Baranskaya E.K. et al. Recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of cholelithiasis RZHGGK 2016; 3:64-80 2.
- NICE. Clinical Practice Guideline. Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: Diagnosis and management of irritable bowel syndrome in primary care. February 2008. Updated March 2021. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61/evidence/full-guidance-pdf-196701661 (accessed 09.21.18)
- Minushkin O.N., Elizavetina G.A., Ardatskaya M.D. Drug therapy for functional disorders of the intestines and biliary system, occurring predominantly with abdominal pain and flatulence. Clinical pharmacology and therapy. 2002;1:24-26.
- International foundation for gastrointestinal disorders. Statistics. 10 May 2016 https://www.aboutibs.org/facts-about-ibs/statistics.html
More: https://www.aboutibs.org/facts-about-ibs/statistics.html https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/37063.php https://www.emedicinehealth.com/irritablebowelsyndrome/articleem htm#howdoyouknowifyouhaveibs-tests https://www.news-medical.net/health/Irritable-Bowel-Syndrome-(IBS)-and-Stress-Response.aspx https://s3.gi.org/patients/cgp/ pdf/ibs.pdf https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/06/170620122901.htm https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/gut-second-brain/
Symptoms
Typical manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are complemented by insomnia, loss of appetite, “emptiness” in the head, chaotic thoughts, difficulty concentrating and other signs of high nervous tension. If the impact of a stressful situation is prolonged, then other symptoms begin to appear:
- sweating of the extremities and armpits;
- “numbness” of fingers and toes;
- headaches and heart pain;
- weakness and fatigue.
Often the patient himself may not notice that he is in a state of stress.
Complications
Loss of strength and decreased blood pressure are a consequence of constant diarrhea.
If an intestinal disorder is not treated in a timely manner, it can lead to dysbiosis, which will affect a person’s immunity - it will weaken. Then the body will become more susceptible to even the most common cold, not to mention a viral infection.
Also, an untreated or advanced digestive disorder that causes diarrhea can lead to dehydration and loss of electrolytes, which sometimes puts a person in a critical condition requiring urgent medical attention.
Also, a consequence of constant diarrhea can be a loss of strength and a decrease in blood pressure. Therefore, it is important to quickly respond to the first symptoms of the disease and begin treatment in a timely manner, but this should only be done under strict medical supervision.
Digestion process
What is the mechanism of this process? Food that enters the body is subjected to not only mechanical but also chemical processing. Part of it is absorbed and assimilated, while the other undigested (as well as decay products) is excreted. Moreover, digestion is only the initial stage in a long chain of metabolic processes. In the form in which carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals enter the body, they cannot be absorbed by its cells. Therefore, in the gastrointestinal tract they are divided into small molecules devoid of any specificity.