It is important to understand that the liver does not have nerve endings, so it cannot hurt. However, pain in the liver area may indicate liver dysfunction. After all, even if the liver itself does not hurt, the organs around it, for example, when it is enlarged or dysfunctional (accumulation of bile), can hurt.
If symptoms of pain in the liver or discomfort appear, it is necessary to diagnose it, consult a doctor, and also, as prescribed by a doctor, use hepatoprotectors.
Liver, what kind of organ is it?
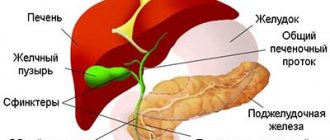
The liver is the largest digestive gland in animals and humans, which produces bile.
The liver performs a recycling, cleansing function. Removes toxic substances. The gland takes part in vitamin metabolism, as well as hematopoiesis. Pathologies of this organ can lead to disruption of functions important to life. The normal functioning of this organ directly depends on a person’s daily lifestyle.
Almost every person knows in which area of the abdomen this gland is located. On the right side, under the ribs (see photo above). In addition to the gland, other organs are located there, namely the digestive and respiratory systems. How to find out what is bothering the gland specifically?
Important point! The gland itself in the right hypochondrium does not hurt; its membrane or organs, pressure on which is exerted by the enlarged exocrine gland, are disturbing.
Clinical manifestations of pathologies
Everyone needs to know what the liver is for, how important it is, and how long it takes to suspect liver dysfunction. During the diagnosis, the patient is interviewed, the size, density, surface of the organ is analyzed, and liver function is assessed.
The gland can be affected by:
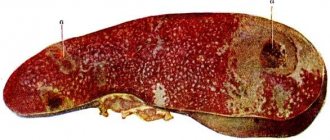
- Cirrhosis. The structure of the liver is represented by a pathological proliferation of fibrous (connective) tissue, which replaces functional hepatocytes. Liver dysfunction may be caused by:
- chronic alcoholism;
- hepatitis of viral etiology;
- infection of the gland by helminths, Trichomonas.
- Oncological process – cancer. The reasons for its occurrence are not fully known, however, among the predisposing factors it is worth highlighting:
- cirrhosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- alcoholism;
- contact with carcinogenic substances;
- hereditary predisposition.
- Hemangiomas, or abnormalities of vascular development.
- Cysts (parasitic - echinococcosis, as well as non-parasitic).
As soon as it is noticed that the liver hurts, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will examine the body, especially carefully palpate the area of the right hypochondrium, and prescribe the necessary examinations. Palpation can be carried out on the back or side. In addition, you should pay attention to the main symptoms indicating possible organ dysfunction:
- weakness, feeling of constant fatigue;
- weight loss;
- vomiting, nausea, bloating, indigestion;
- yellowing of mucous membranes and skin;
- causeless increase in temperature;
- itchy skin;
- spider veins;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- excessive sweating;
- hypersensitivity to odors;
- change in color of stool and urine.
The listed symptoms are the basis for contacting a gastroenterologist, who, through a full examination, will identify abnormalities in the functioning of the gland and prescribe effective therapy. Only a specialist will be able to figure out what is the cause of liver dysfunction, so you should not self-medicate.
Liver diseases: causes of pain
Abscess
A formation with purulent accumulations appears in the tissues of the gland. It appears due to cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. The location of the formation can be determined by pain in one area or another. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, because if the formation breaks through, there will be serious consequences.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process. It can be viral, toxic or autoimmune. It can be determined by the enlarged size of the liver. Due to changes in the structure of the liver, cirrhosis develops.
Cirrhosis
This disease has the potential to be fatal. The gland enlarges due to the proliferation of connective tissue in its structure. And also, the exocrine gland stops functioning. Liver cirrhosis is asymptomatic for a long time. But at the beginning of the development of the disease, minor changes in the person’s condition may appear: fatigue, lethargy, irritability.
Liver failure
With liver failure, yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes appears (the disease is called jaundice)
“Wonderful network” or a little about blood circulation in the liver
Both venous and arterial blood can simultaneously circulate in the liver parenchyma. A single capillary network, covering each lobule, unites numerous interlobular arteries and veins of the same name, emanating from the hepatic artery and portal vein, respectively. From the capillaries, the blood collects into the central veins, which combine to form several more massive hepatic veins.
This type of blood circulation, which has received the unofficial name of the “miraculous network,” is explained by the complex interaction of two venous systems:
- the portal system, flowing from the portal vein, brings blood to the liver from the abdominal organs;
- The caval system, on the contrary, carries blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava.
The two venous complexes are connected by the arterial system of the hepatic artery and the capillary network. Thanks to such a complex complex, stable biochemistry of the liver, as well as the body as a whole, is maintained.
How to find out what exactly is bothering the liver?
The first step is to establish the nature of the pain:
- Dull pain - talks about the following diseases: hepatitis B, C and A. Or the presence of bacteria and an abscess, accompanied by a feeling of fullness.
- Aching pain – cholecystitis. Also hepatitis A, B or C. In addition, this is a sign of hepatomegaly or a developed liver abscess.
- Throbbing pain is a cyst or parasites in the human body.
Symptoms of liver disease
The accompanying signals will help prove the fact that the pathology occurs specifically in the liver:
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- constant belching;
- enlarged belly on the right side;
- severe weight loss;
- yellowness of the skin
- discolored urine and stools;
- itching and dry skin;
- swelling.
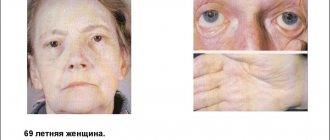
Liver pathology is visible externally. The quality of hair, nail plates and epithelium deteriorates due to the fact that iron does not cope with complete cleansing; toxins and waste accumulate in the body. The epithelium on the face dries out and becomes dull, rashes form, hair falls out, and the nail plates break and peel.
The most important thing you need to know: if these symptoms appear, you must immediately consult a doctor; self-medication in this situation is strictly prohibited.
Itchy skin
When the liver hurts, a person is faced, as already mentioned, with various rashes. The fact is that any rash that appears is accompanied by severe itching. It has an enhanced effect in cases where there is a rash on the skin, as well as their inherent yellowish color. How can one interpret the appearance of itching?
The fact is that the liver must neutralize bilirubin. If she fails to complete this task, it is deposited in the skin. As a result, the result is visible - irritation. Another impetus for itching is other metabolic products that find a secluded place in the human skin. When people come to the doctor with liver complaints, they often notice scratching of itchy areas. To a greater extent it is:
- forearms;
- belly on the sides.
Complications of liver diseases
Patients with liver diseases are at risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma, and vision deteriorates. Since the gland fails to cope with its role, cholesterol begins to accumulate, which leads to the development of cardiovascular diseases. Blood pressure increases, which leads to the development of myocardial infarction and stroke.
Prevention
Infectious hepatitis can be prevented by avoiding questionable and unprotected sexual contacts. Hepatitis C is easier to catch because the infectious dose is very small. Therefore, you need to be very careful when visiting dental clinics, tattoo parlors, manicure and pedicure rooms, saunas, and hairdressers.
Prevention of infection by parasites involves selective, careful consumption of meat and fish. These products should be subjected to sufficient heat treatment.
Toxic liver damage can be avoided by monitoring liver function indicators and continuous use of medications. You should be more careful with alcohol and drinks based on it, especially weak ones.
Diagnostics
Using laboratory tests of diagnostic procedures, a qualified specialist can identify liver pathology in the early stages of disease development. The treatment system will be determined depending on what caused the pain after diagnostic measures.
Types of diagnostic procedures that a doctor will prescribe for patients with liver pain:
- Laparoscopy;
- Biopsy;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- CT;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Tests for viral hepatitis and cancer;
- Genetic research;
- Immunological tests.
Treatment is selected individually, based on the results of these tests.
Anatomical features
Here's how to describe the liver:
| Index | Organ characteristics | ||
| From | Before | Units | |
| Length | 20 | 30 | cm, centimeters |
| Width | 10 | 21 | |
| Height | 7 | 15 | |
| Weight | 1400 | 1800 | g, grams |
The liver is divided into two lobes:
- right, larger;
- left
The organ also includes:
- sectors (5 in number);
- segments (8 sections).
The structural and functional unit of the liver is the lobule (from Latin lobulus hepatis). It, in turn, consists of rows of cells - hepatocytes.
The liver is penetrated by bile ducts - starting with a small caliber and ending with a common one, connecting in the wall of the duodenum with the excretory mouth of the pancreas. Together they form an extension - an ampulla, the opening of which is regulated by a complex of smooth muscle bundles - the sphincter of Oddi.
Innervation is carried out through such structures as:
- Branches of the vagus nerve.
- Hepatic (sympathetic) plexus.
Blood supply occurs through large vessels, which, after entering the parenchyma (tissue) of the organ, branch into structures of smaller caliber:
- proper hepatic artery;
- portal vein;
- interlobular vessels;
- capillaries-sinusoids.
The outflow of blood from the organ is carried out through the hepatic vein system.
Treatment
Most illnesses are treated in a hospital. And many diseases can be treated in simple ways. If this is alcoholic hepatosis, then you should forget about alcohol and choose a diet. In case of toxic poisoning, poisons are removed from the blood through detoxification. Other diseases can be cured by taking antibacterial and antiviral drugs. Surgeon intervention is necessary in the presence of cysts and tumor formations.
And if pain in the gland is due to injury or physical activity, then you should just rest. No treatment as such is required.
Pain relief medications (first aid for liver pain)
The following special drugs are used to help relieve spasm and severe pain in the liver:
- No-shpa
You can take tablets, but it is advisable to administer the medicine intramuscularly, because in this form the drug can relieve suffering in a shorter time than tablets. But we must also forget that No-spa is not used for liver failure.
- Papaverine
Its injections are also used to suppress pain. The direct purpose of the drug is to relax the smooth muscles of the digestive and genitourinary systems. But, again, the use of this drug for liver failure is prohibited.
This drug is administered in various ways.
- Analgin
You cannot take analgin yourself, because... it may mislead your doctor by dulling pain or changing signs of pathology. And also, Analgin additionally loads the exocrine gland.
However, the doctor may prescribe injections of this drug if he considers it necessary.
How to cleanse the liver with folk remedies
Although it was indicated that you cannot self-medicate for pain in the liver, it is still worth noting a couple of points about alternative medicine. You can try liver herbal teas, they are sold in pharmacies and do not require a prescription from a doctor.