Sphenoiditis [sphenoiditis; anatomical (sinus) sphenoidalis sphenoid sinus + -itis] is an infectious inflammatory disease of the sphenoid sinus and its mucous surface. It is considered one of the rarest and most dangerous inflammatory processes that occurs in the paranasal cavity. Due to the fact that the sphenoid sinuses are located at the base of the skull, their inflammation can cause serious consequences.
Causes
The cause of sphenoiditis is acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid (sphenoid) sinus caused by an infectious agent.
Common causes of narrowing of the natural excretory duct are:
- anatomical narrowness of the sphenoid sinus and its small size;
- congenital anomalies of the nasal cavity (curvatures, additional septa, absence or overgrowth of ducts);
- congenital or acquired (due to injury) curvature of the posterior part of the nasal septum;
- space-occupying formations in the sphenoid sinus (cysts, polyps, malignant tumors);
- volumetric formations of the nasopharynx in close proximity to the anastomosis of the sphenoid sinus (cysts, polyps, malignant tumors);
- foreign bodies that enter the anastomosis of the sphenoid sinus during a sharp inhalation.
In men and women, the disease manifests itself for the same reasons.
Sphenoiditis may not always develop as a primary disease, but manifests itself as a complication of such ailments:
- flu;
- scarlet fever;
- angina;
- rhinitis.
It is worth noting that the infectious agent itself, which has penetrated the sphenoid sinus, does not play a decisive role in the occurrence of the disease. There must be a so-called trigger mechanism or provoking factor, which will serve as an “impetus” for the development of the disease.
Symptoms in children
Some doctors believe that in children under 6 years of age, the sphenoidal sinuses are not fully formed, so they cannot become inflamed. Naturally, children are not treated. In fact, this opinion is wrong.
Despite the fact that in young children the sphenoid sinuses may still change, inflammation is quite possible. The symptoms of sphenoiditis in children are the same as in adults, except that not every child can accurately describe what is happening to him. Parents should be concerned when their baby:
- persistent runny nose with pus;
- no desire to play or eat;
- elevated temperature;
- labored breathing.
Sphenoiditis in children mainly occurs against the background of inflamed adenoids and redness of the tonsils.
Symptoms of sphenoiditis
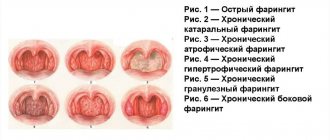
In adults, symptoms and signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus are usually considered according to the forms of the disease:
Acute sphenoiditis most often begins with the appearance of a headache, which intensifies at night. This is a characteristic symptom for this disease. At first, the pain is localized in the back of the head, but already on the second or third day from the onset of the disease, it begins to radiate to the forehead or temples. In some cases it radiates into the eye sockets.
The main symptoms of acute sphenoiditis:
- Pain in the head, localized in the occipital region, but radiating throughout the entire facial part.
- Copious discharge from the nasal cavity of a mucous, purulent or mucopurulent nature.
- Impaired sense of smell.
- Heat.
- There is a smell of rot.
- Weakness and fatigue.
Chronic sphenoiditis is an unfavorable outcome of the acute form of the disease. It develops if treatment for sphenoiditis in the acute stage is not started on time, or the doctor prescribed incorrect treatment, which did not cope with the symptoms of the disease and could not destroy the pathogen. The process occurs in an isolated form or with damage to the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. Signs of sphenoiditis are usually less pronounced than in the acute form.
The main symptoms of the development of chronic sphenoiditis:
- Dull, aching pain in the occipital region.
- If pain is the only symptom, then sphenoiditis may not be detected and treatment for other diseases that do not relieve symptoms may be unsuccessful.
- Feeling of rot in the mouth.
- Discomfort in the nasopharynx.
- Unpleasant smell.
- When the optic nerve is involved in the process, the patient complains of decreased vision.
- Chronic drowsiness.
- Constant fatigue.
- Gradually decreasing appetite.
- Weakness and lethargy.
Surgical intervention
There are patients who develop sphenoiditis precisely because of the appearance of growths in the sphenoid sinuses or because of injuries in the parts of the nose. Surgery in such cases is the only correct method of treatment. Depending on the doctor's decision, either general anesthesia or local anesthesia is used. The patient's bone of the ethmoidal labyrinth is opened and an endoscope is inserted into the sphenoid sinus. This device allows you to accurately examine where a polyp has formed, where a cyst has grown, what changes are occurring in the mucosa, and carry out precise surgical manipulations. Upon completion, the patient is injected with the necessary medications into the sphenoid sinus and further treatment is prescribed.
Consequences
Because the sphenoid sinus is located near many vital structures, inflammation can lead to serious complications.
- Damage to the cranial nerves, including the optic chiasm. Due to the close location of the cranial nerves, the infectious process often spreads to them. In this case, the III, IV, V and VI pairs of cranial nerves may be affected. When the third pair of cerebral nerves is damaged, the patient experiences double vision, impaired movement of the eyeball outward, as well as upward, downward, and inward. If the IV pair of nerves is affected, then only downward and sideways eye movements are impaired. If the infection affects the trigeminal nerve (V pair), then the sensitivity of the skin of the face, teeth, and chewing muscles is impaired. The most severe consequences develop if the optic chiasm is involved in the inflammatory process. This is accompanied by the appearance of blind spots in the visual field (scotomia), blindness in one half of the visual field (hemianopsia), and in severe cases, complete loss of vision (amaurosis).
- Spread of infection to other sinuses. Usually the infection penetrates into the sphenoid sinus from other sinuses, most often from the maxillary or ethmoidal sinus. However, the disease can develop in a different scenario. Inflammation from the sphenoid sinus through natural anastomosis or through the bloodstream can spread to other airways. Thus, several sinuses can be involved simultaneously with the development of so-called pansinusitis.
- Spread of infection into the cranial cavity. Sometimes the infection breaks into the cranial cavity through the natural openings in the sphenoid sinus. In this case, bacteria (or viruses, if the inflammation is of viral etiology) can affect both the brain substance itself and its membranes. In the first case, encephalitis develops, and in the second, meningitis. In both cases, the patient's condition deteriorates sharply. Lethargy occurs, including stupor, blood pressure drops, vomiting and photophobia appear. As a rule, the spread of infection is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition, which is immediately diagnosed by doctors. In rare cases (against the background of severe immunosuppression), an infection that has penetrated the skull can be localized and persist for a long time.
- Infection of the orbital cavity. This complication most often develops against the background of sphenoiditis involving the ethmoidal labyrinth. Since the latter anatomical structure is in direct contact with the orbital cavity, microbial flora very easily penetrates into this cavity. In this case, retrobulbar (located behind the eye) abscesses and phlegmon can form. These accumulations of pus further put pressure on the eyeball, causing it to bulge. When soft tissues are involved in the inflammatory process, the skin around the eyes becomes swollen and red. Movement of the eyeballs is difficult, the patient tries to keep the eye closed.
Possible complications
Due to its close proximity to structures important for human life, the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the area of the sphenoid sinus can lead to the following problems:
partial or complete destruction of cranial nerves;- damage to the optic chiasm;
- bacteria entering the cranial cavity;
- spread of infection to other sinuses;
- infection, complete or partial, of the eye cavity.
And these are just the main complications that the disease can cause.
Important! If you begin to treat the ailment that has arisen in a timely manner, you can hope for a favorable result.
A negligent attitude will only lead to more serious problems and complications.
Diagnostics
Symptoms such as abnormal nasal discharge and prolonged headaches should prompt immediate consultation with a specialist.
The medical institution conducts:
- interviewing the patient by an otolaryngologist to find out how the disease began and what were the dominant symptoms in the clinic;
- rhinoscopy;
- puncture of the sphenoid sinus;
- its probing;
- laboratory blood tests;
- X-ray examination of the sphenoid sinus in several projections;
- CT scan.
Lifestyle Features
Treatment of sphenoiditis during an acute process requires the patient to follow special rules:
- It is important to maintain proper nutrition and drinking regime;
- procedures aimed at regularly cleansing the nasopharynx of mucus and pus;
- measures to increase the body's resistance.
Nutrition
A clear eating regimen is developed - at the same hours, in small portions, five times a day.
Foods that contribute to allergies are excluded from the diet. The allergic process in the body causes swelling in the mucous membranes, including the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
Useful products are those that help increase the body's resistance. Such products must contain:
- vitamins;
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- minerals;
- probiotics - bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Acute sphenoiditis requires limiting fluid intake so as not to increase swelling of the mucous membrane and symptoms of respiratory failure.
Cleansing the nasopharynx
It is necessary to speed up recovery and is directed against the addition of secondary microbial flora. Carried out with washing solutions:
- "Aquamaris";
- "Aqualor";
- "Physiomer";
- "Marimemer";
- "Linakvoy."
Symptomatic treatment
To normalize the patient’s body temperature and quickly relieve him of incessant headaches and other unpleasant sensations, doctors make the following prescriptions:
- Paracetamol, Nurofen, Aspirin, Indomethacin are drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Aquamarine, Quix and Aqualor are sprays made from salt sea water and necessary for regular rinsing of the nasal passages and sinuses;
- Nasobek, Beconase - drugs from the group of corticosteroids;
- Sinupret, Pinosol and Umkalor are remedies for runny nose and nasal congestion, which are made exclusively on a plant basis;
- IRS 19 and other immunostimulating drugs.
Please note: some doctors prescribe homeopathic remedies - they may have an effect, but there is no scientific evidence of the “work” of such drugs.
As soon as the acute symptoms of the development of the inflammatory process are eliminated, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures - for a speedy recovery and, so to speak, consolidation of the result. These procedures include:
- acupuncture;
- balneological procedures;
- reflexology;
- massage;
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy and others.
If the cause of the development of sphenoiditis was the anatomical features of the structure of the sphenoid sinus, then the patient will be recommended to undergo surgical treatment and correct the problem. Then the patient will have to undergo a fairly long rehabilitation period with visits to specialized sanatoriums, and subsequently will have to follow preventive measures and periodically undergo examinations by the attending physician.
Preventive actions
Sphenoiditis can be prevented in the following ways:
- constant walks in the fresh air;
- hardening (it is better to start in the summer);
- healthy lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- annual preventive examination by specialists;
- visiting the dentist.
The disease sphenoiditis is considered not a common illness; this disease is mainly caused by correct attention to one’s health, or by the body’s natural ability to respond to this infectious disease. Treatment at home takes place only in the early stages of the development of sphenoiditis. Sometimes the pathology requires surgical intervention.
Where to go? ENT clinics in Moscow:
Center for Motherhood, Natural Development and Child Health Moscow, st. Gasheka, 9 (entrance from the yard) Medical center Family clinic on Izmailovskaya Moscow, st. Pervomaiskaya, 42 Best clinic on Krasnoselskaya Moscow, st. Nizhnyaya Krasnoselskaya, 15/17 Medical Center Doctor on the House Moscow, Chistoprudny Blvd., 12, bldg. 2, office 11 Clinic of Restorative Neurology Moscow, Marshala Vasilevsky, 13, bldg. 3 Center for Traditional Obstetrics and Family Medicine - CTA Tula Moscow, st. Pavlovskaya, 18, building 2 All ENT clinics in Moscow on the map
Etiotropic therapy
If sphenoiditis is of bacterial origin, then the patient will definitely be prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs (antibiotics). Moreover, such treatment can be carried out both in a hospital setting and in an outpatient setting.
The antibacterial drug can be prescribed both in the form of injections and in tablet form. But in any case, the choice of a specific drug from the group of antibiotics is carried out exclusively on an individual basis - it all depends on the duration of the inflammatory process, the depth of its spread, and the identified pathogen.
Simultaneously with taking antibacterial drugs, the patient will be prescribed irrigation and rinsing of the nasopharynx and sinuses with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions.
Types of disease
Classification of sphenoiditis by etiology distinguishes bacterial, viral and fungal forms. By severity - mild, moderate and severe forms of sphenoiditis.
By localization:
- Left-handed
- Right-handed
- Bilateral
By form:
- Exudative: catarrhal and purulent;
- Productive: polypous, cystic, and parietal hyperplastic.
By etiology:
- Traumatic
- Viral
- Bacterial
- Fungal
- Mixed
What is healthy to eat?
The diet should include foods that are rich in vitamins, proteins, minerals, and lactobacilli. Let's look at the vitamins that help fight illness, as well as the foods that contain them:
- Vitamin A. Found in carrots, chicken eggs, beef liver and fish oil. This vitamin increases the resistance of the respiratory system to infectious agents.
- Vitamin C. Ascorbic acid is found in rose hips, sea buckthorn, tomatoes, sweet peppers, and cauliflower. During infectious processes, harmful toxic substances are released, and vitamin C weakens their negative effects.
- Vitamin E. Contained in olive oil, walnuts, dried apricots. This vitamin reduces fatigue and makes the body more resilient.
Now let's talk about the most important minerals and their content in food:
- Zinc. Contained in beef, pork, peanuts. This essential element is necessary to maintain normal functioning of the immune system.
- Iron is present in pork and beef liver, spinach, buckwheat, and oatmeal. Iron takes an active part in neutralizing toxic substances, as well as strengthening protection against harmful bacteria.
- Calcium is found in cheeses, garlic, cottage cheese, and almonds. Calcium has anti-inflammatory properties and also increases barrier functions.
Separately, I would like to say about the role of lactobacilli in the treatment of sphenoiditis. These beneficial bacteria have a detrimental effect on bacterial and fungal infections. In addition, lactobacilli improve the absorption of nutrients. They also prevent the development of dysbiosis, which can occur due to antibacterial therapy used during the treatment of sphenoiditis.
Diet
This point is mandatory in the process of fighting illness. Such meals should not include the following:
beer drinks;- alcoholic drinks;
- caffeine;
- coca cola;
- dishes with a lot of pepper or salt.
You need to eat foods that have a large amount of proteins, lactobacilli, vitamins and minerals.
It is prohibited to consume food and drinks that can dry out the nasal mucosa (they are presented above).
It is worth checking with your doctor about your future diet, since poor nutrition will only worsen the situation.
In what cases is surgery prescribed?
Surgery is a last resort. Experts resort to surgery when conservative treatment methods are ineffective and to avoid the development of serious complications.
Currently, endoscopic surgery . Based on the name, it is clear that the intervention is performed using an endoscope - a thin tube equipped with a light for easy examination of the nasal passages: during the operation, the doctor removes the tissues that block them.
An alternative to endoscopic surgery is a procedure using a sinus catheter . This painful but necessary manipulation involves alternating high and low pressure directed into the purulent focus, which promotes the evacuation of the contents, as well as the restoration of the ability to smell.
The advantage of the method is that after cleansing the pathological secretion, medications are administered through this catheter, which have a disinfecting effect, which means successful treatment. This therapeutic method is used from the age of five, and for the stability of the positive effect, a number of repetitions of three to five procedures is recommended.
Folk remedies
The disease sphenoiditis is considered severe due to the inaccessibility of the source of the disease, which is located deep in the center of the head. Traditional medicine in this case will not lead to a complete recovery, but will only worsen the situation. An important tip is to drink regularly, this will facilitate the drainage of sinus contents. As an aid in treatment, you can use the procedure of rinsing the nasopharynx with a saline solution (dilute a teaspoon of salt in 200 ml of warm boiled water).
Prevention
Those who keep the nasal mucosa sufficiently moist will prevent most problems. Inhalation of a decoction of medicinal herbs will be effective; refusal to stay in a room filled with cigarette smoke; limiting the consumption of alcohol and caffeine, known for their drying effect.
Early detection eliminates the possibility of more serious complications, which include neurological damage and, rarely, death. Given the possibility of rapid progression of the disease, you need to pay attention to any changes in your health, and if your condition worsens, immediately go to the hospital.