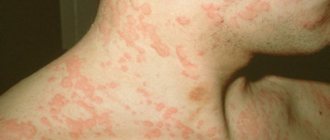
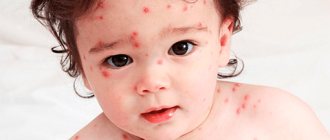
Pemphigus is a group of bullous dermatoses in which the pathogenetic role belongs to circulating autoantibodies directed against antigens of the desmosomal apparatus system of stratified squamous epithelium (skin, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, esophagus and other organs).
The disease develops under the influence of various factors (taking medications containing thiol groups; insolation; infectious agents; stress; consumption of certain foods; physical factors, etc.), but often it is not possible to determine the provoking factor.
During the disease process, antigen-presenting cells recognize their own molecules that make up desmosomes, cancel T- and B-cell tolerance to their own autoantigens, and synthesize autoantibodies.
Types of viral pemphigus
The most common type of pemphigus is the viral (infectious, enteroviral) variety. In case of timely examination and proper therapy, the prognosis is favorable. Patients recover successfully without sequelae.
There are also other types of disease:
| Name | Description |
| Vulgar (ordinary) pemphigus. | The form of the disease is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes and skin of newborns. Accompanied by blisters that break even with a light touch of clothing. In their place, painful bleeding erosions with cracked edges form. The patient sleeps poorly, becomes irritable and lethargic. Muscle pain and headaches are a concern. Extensive and purulent pathological processes lead to serious complications, even death. |
| Vegetative. | The disease is characterized by local focal lesions. Without timely treatment, the vegetative type ceases to become pemphigus vulgaris. |
| Exfoliative (leaf-shaped). | A chronic form of the disease that entails serious complications. More common in children. Shallow lesions appear on the scalp. The blisters open, peel, and give off an unpleasant odor. While the old ulcers are healing, new blisters form underneath them. In some situations, the child's body temperature rises. |
| Seborrheic (erythematous) pemphigus. | Symptoms of the pathology are similar to those of seborrheic dermatitis. The disease develops due to the use of medications (uncontrolled use of antibiotics). It proceeds easily and without complications. The rash affects the face, chest, back and scalp. First, inflamed spots appear; in their place, blisters form, which burst and leave behind a gray-yellow crust. |
Viral pemphigus affects the soles and palms of the hands. The causative agents are enteroviruses types A16 and 71. In most cases, the disease is mild. The complex course of the pathology is aggravated by encephalitis or meningitis. The patient feels unwell, sleep and appetite worsen.
Classification of the disease
Pemphigus is divided into four main types
Ordinary
Characteristic:
- affects the middle and deep layers;
- First, the lesion is noted in the oral cavity;
- the disease can affect all parts of the body.
Note: the common form is diagnosed in 70% of cases.
Vegetative
Characteristic:
- localization in the oral cavity, nostrils, lips, groin and armpits;
- frequent bleeding in damaged areas of the skin;
- the likelihood of developing intoxication.
Note: in 60% of cases it is severe.
Leaf-shaped
Peculiarities:
- the lesion is noted on the entire surface of the dermis;
- the blisters are opening quickly;
- severe redness of individual parts of the body occurs;
- after the blisters are opened, erosions remain.
In advanced types, partial or complete baldness is diagnosed, as well as rejection of the nail plates.
Seborrheic
Peculiarities:
- lighter form compared to others;
- Initially, the lesion occurs in the facial area, in particular on the nose, ears, and near the eyes;
- gradual growth of blisters throughout the body;
- the appearance of painful erosions.
The first signs of seborrheic appearance are similar to lupus erythematosus.
Mechanism of bubble formation
Pemphigus is a disease in adults, a photo of which will help in home diagnosis and will force a person to go to the hospital for examination. The pathology primarily affects the oral cavity.
Blisters form, then they burst open and painful ulcers remain in their place. The rash then affects the skin, spreading rapidly. After opening the blisters, weeping or ulcers remain, covered with a crust on top. The risk of infection in open wounds increases.
Routes of transmission
Caused by Coxsackie viruses subspecies A16 and enteroviruses subspecies 71. The first type of microorganisms mainly leads to damage to the palms and proceeds without complications. Enteroviruses of 71 subspecies lead to the appearance of a contagious infection, which is often complicated by meningitis and other pathologies. In adults, the disease occurs after 40 years of age, but children under 10 years of age are more susceptible to it.
Transmission routes:
- by airborne droplets, for example, when talking with someone who is a carrier of the virus;
- when eating from the same container with a sick person;
- after physical contact with a patient, if the contents of the vial come into contact with the skin of a healthy person:
- in case of particles of the patient’s feces entering the gastrointestinal tract of a healthy person.
The danger of the disease is that you can become infected not only from a sick person, but also:
- from a person whose disease is in an incubation period lasting up to 6 days;
- from a person who is a carrier of the virus, but feels well (no symptoms);
- from a person who has recovered from the infection – the virus is still active in the body for 3 months.
Those who have problems with the immune system are more likely to get sick, and have characteristics of the upper layer of skin, which leads to a tendency to develop the disease. The disease is seasonal: the virus is activated in the warm season; in winter, low temperatures kill microbes.
Causes of disease development in adults and children
There are certain provoking factors against which pathological processes develop. It is important to establish the cause of pemphigus, since the therapy selected by the dermatologist depends on the source of the problem.
| Name | Description |
| Neurogenic factor. | Impaired functioning of the central nervous system. |
| Endocrine disruptions. | Hormonal imbalance. |
| Infectious lesion. | Infection of the human body with a viral or bacterial agent. |
| Autoimmune disorders. | Antibodies produced by the immune system kill the body's own cells. |
Pemphigus is also inherited.
The disease occurs as a result of endogenous bacteria entering the human body through airborne droplets or household contact. The photo of adults shows that the first signs are rashes. Children are more likely to encounter pemphigus because their immunity is just developing.
Causes
The reasons for the development of pemphigus have not yet been fully studied. One of the main causes of pemphigus is a violation of autoimmune processes, thereby the cells become antibodies to the immune system.
Violation of cell structure is subject to the influence of external factors, as well as aggressive environmental conditions. As a result, the communication between cells is disrupted, which leads to the formation of bubbles. The incidence rate in people with a hereditary predisposition is much higher.
Pemphigus in newborns
The causative agents (Staphylococcus aureus) of the disease enter the baby’s body through contact and household contact. This could be the mother or a health care worker. Already on the 3rd day of life, the baby appears redness, rashes and blisters on the body with transparent or purulent contents.
The baby becomes irritated, refuses the mother's breast, and the body temperature rises. The rash affects the groin folds, legs, arms, lower abdomen and navel. In place of the blisters after they are opened, red wounds remain.
Recommendations
It is recommended to consult a dermatovenerologist, a cytological examination for acantholytic cells in imprint smears in the area of the bottom of blisters and erosions, and a histological examination of the skin.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Director of the Central Dermatovenerological Institute of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Kubanova A.A. |
Pemphigus symptoms
The first manifestations of the disease are translucent papules on the skin.
Pemphigus in children and adults is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of blisters on the palms and soles (rarely the genitals, buttocks, and thighs are affected);
- pain syndrome;
- severe itching in the affected areas;
- elongated or oval-shaped bubbles with a red rim;
- exudate is clear or contains blood;
- fever, weakness, hyperthermia;
- stool disorders;
- pigmentation at the site of blistering.
The child feels unwell, general weakness occurs and sleep deteriorates. Problems with appetite appear against the background of pain in the throat, the baby is lethargic and broken. It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own, since pemphigus in children occurs like many other skin diseases. A thorough examination and treatment by a dermatologist is necessary.
Treatment of pemphigus during pregnancy
Due to weakened immunity and hormonal changes, pregnant women have a slightly higher risk of encountering pemphigus. In addition, they separately consider the so-called pemphigus of pregnancy - an irritation that grows from the navel over the abdomen, back, buttocks, somewhat similar to herpes, but is not one.
With the development of pemphigus in pregnant women, the risk of premature birth slightly increases, while at the same time, the statistics of miscarriages and stillbirths are still assessed. Every twentieth child from a woman with pemphigus experiences irritation after birth.
It is important to carry out treatment of pemphigus in pregnant women exclusively together with specialized specialists, whose competence lies in the competent selection of the safest steroid and, if necessary, antibacterial agents.
Diagnostics
After an external examination, the dermatologist makes a preliminary diagnosis.
An additional examination of the child will help confirm the development of pathological processes:
| Name | Description |
| Serological studies (analysis of stool, cerebrospinal fluid and blood). | A diagnostic method that detects antibodies. |
| Cytological studies. | Experts study the contents of the bubbles in laboratory conditions. |
| Nikolsky's test. | A method for diagnosing pemphigus that allows differentiation of the disease. |
Therapy depends on the diagnostic results, since the examination helps determine the type of pemphigus and the extent of the spread of pathological processes. In some situations, you will also need to consult a therapist, allergist, neurologist, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist.
Forecast
The prognosis for acantholytic pemphigus is conditionally unfavorable. On the one hand, in the absence of effective treatment, there is a high probability of complications and death.
On the other hand, patients with pemphigus are forced to take glucocorticosteroids for a long time, and sometimes for life, which is fraught with the development of side effects. But hasty refusal of drugs leads to immediate relapse of the disease. Glucocorticosteroids do not eliminate the cause of the disease, but inhibit the pathological process and prevent its progression.
Treatment in children and adults
Pemphigus is a disease in adults (the photo will help identify the pathology at an early stage of development), characterized by skin rashes (papules, blisters). The main goal of therapy is to prevent the appearance of new blisters. It can also relieve clinical symptoms, improve the patient’s quality of life and achieve a positive prognosis.
Therapy for viral pemphigus
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes systematic treatment, taking into account the degree of damage to the human body and its individual characteristics.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application and effectiveness |
| Antiviral. | "Laferon", "Cycloferon". | Treatment involves the use of 1 suppository 1-2 r. per day for 5-10 days. |
| Glucocorticosteroid drugs. | "Prednisolone", "Dexamethasone". | Patients are prescribed 0.5-9 mg per day intravenously or intramuscularly. |
| Cytostatics. | "Sandimmune", "Methotrexate". | They stop the process of division of immune cells. The doctor prescribes 2.5-5 mg/kg per day for 1-2 weeks. |
| Antipyretic. | "Ibuprofen", "Nimesil". | The standard dosage of the drug is 200-400 mg per dose. The maximum course of therapy is 5 days. |
| Antihistamines. | "Fenistil", "Cetrin". | Medicines reduce itching in affected areas of the body. Patients are prescribed 20-40 drops. 3 r. per day. |
For external treatment of blisters, antiseptics (“Miramistin”, “Chlorhexidine”) and combination preparations, which include an antiseptic and an anesthetic (pharmacy mash), are used. When the oral cavity is affected by viral pemphigus, special irrigation products (Orasept, Forteza) are also used. Local medications with an antimicrobial effect.
How to treat other forms of pemphigus?
To combat non-viral types of pemphigus, the following groups of drugs are used:
| Medicines | Name | Application and effectiveness |
| Glucocorticosteroids. | "Methylprednisolone", "Triamcinolone". | Patients are prescribed 4-20 mg 2-3 times. per day. The course of therapy lasts no more than 10 days. |
| Immunosuppressants. | "Methotrexate", "Sandimmune". | The minimum dose of the drug is 15 mg. The course of therapy depends on the degree of damage to the body, but not less than 5 days. |
| Antibacterial drugs. | "Doxycycline", "Metronidazole". | The medicine is prescribed to the patient at 500 mg per day for 14 days. |
| Antifungal medications. | "Fluconazole", "Terbinafine". | The course of therapy is 2-4 weeks, 50 mg per day. |
Additionally, high-dose human immunoglobulin and anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are administered.
Medicines for the treatment of pemphigus
The doctor selects medications based on the results obtained after a medical examination. It is important to start therapy in a timely manner to prevent serious complications.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application and effectiveness |
| Corticosteroid drugs (hormonal). | "Prednisolone", "Azathioprine". | The initial dosage of the drug is 5 mg/kg in 2-3 doses over 30-60 days. Maintenance therapy includes 1-4 mg/kg per day. |
| Antihistamines. | "Loratadine", "Cetirizine", "Dimetindene". | Patients are prescribed 10 mg 1 r. per day. The course of therapy in most cases lasts 1-5 days. |
| Cytostatics. | "Methotrexate", "Cyclophosphamide". | The medicine is administered intravenously. The standard dosage for continuous treatment is 3-6 mg/kg per day. |
| Sorbents. | "Activated carbon". | The medicine is prescribed orally at a dose of 250 mg per 10 kg of body weight, 1 r. per day for 10 days. |
The patient is also recommended treatment with vitamin complexes. Additional therapy involves blood purification using plasmapheresis (blood transfusions are carried out at intervals of 1-2 weeks to remove circulating immune complexes) and hemosorption.
Local therapy
Products for external use prevent secondary infections. Used for any form of pemphigus, severity and stage of the disease.
| Name | Application | Efficiency |
| "Hydrocortisone." | The product is applied 1-2 r. per day for 7-10 days. | Reduces the inflammatory process and has an antiallergic effect. |
| "Zinc ointment". | Apply 1-3 rubles to affected areas of the body. per day for 1-7 days. | The medicine protects and softens the skin, dries it out. It also reduces the release of exudate from blisters. |
| "Methylthionium chloride." | The medicine is applied topically 1-3 r. per day for a week. | Has an antiseptic and detoxifying effect. |
Local treatment eliminates weeping and drys out the rash; medications are also used for adsorption.
Photochemotherapy
Inactivation of blood cells with G-methoxypsoralen using ultraviolet rays and reintroducing them into the bloodstream also helps reduce the negative manifestations of pemphigus. The effectiveness of this treatment method is due to blood purification and the removal of toxic substances and immunoglobulins.
Diet
Pemphigus is a disease in adults (the photo will help distinguish the pathology from other disorders in the human body and force him to undergo a medical examination), which requires proper nutrition.
The article describes pemphigus disease in detail and provides useful photos.
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
If the oral mucosa is affected, patients are advised to consume pureed soups and mucous porridges in liquid form. Hard foods will damage the blisters and slow down the healing process of the ulcers. It is recommended to eat small portions of 4-5 rubles. per day.
What medications are used to treat pemphigus?
Treatment of pemphigus is usually carried out with hormonal drugs, which are taken in loading doses, and then their concentration is sought to be minimized; it is extremely rare that it is possible to completely stop taking the drugs. Specific medication regimens are determined by the attending physician in each individual case, focusing at least on the individual tolerance of the prescribed regimen by the patient.
The following pharmaceuticals are used:
- Azathioprine - 150 mg per day,
- Heparin - 10,000 units 2 times a day intramuscularly for 15 days,
- Doxycycline - 0.1 g 2 times a day,
- Difenin - 0.1 g 2 times a day,
- Methotrexate - 20 mg per week,
- Prednisolone - from 40 to 180 mg per day,
- Cyclophosphamide - 100 mg per day.
Dispensary observation
Treatment for pemphigus should begin as soon as the first symptoms appear. All patients are advised to undergo clinical observation and take systematic medications. Timely therapy reduces the risk of disease progression and allows you to bring it under control.
Diagnosis, treatment and observation are carried out around the clock in a hospital setting. By monitoring the patient’s condition, the dermatologist assesses the dynamics of the pathology and adjusts the therapy.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - p
| Treatment of pancreatitis |
| Treatment of pancreatic necrosis |
| Treatment of tracheal papilloma |
| Treatment of parametritis |
| Treatment of paraneoplasia |
| Treatment of paranephritis |
| Treatment of pediculosis |
| Treatment of pelvioperitonitis |
| Treatment of testicular torsion |
| Treatment of a patellar fracture |
| Treatment of periarthritis of the shoulder joint |
| Treatment of pericarditis |
| Treatment of hepatic coma |
| Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy |
| Treatment of pyelonephritis |
| Treatment of pyoderma |
| Treatment of pyonephrosis |
| Treatment of pleurisy |
| Treatment of pneumoconiosis |
| Treatment of pneumonia |
| Treatment of pneumosclerosis |
| Treatment of pneumothorax |
| Treatment of gouty kidney |
| Treatment of gout |
| Treatment of subcutaneous granuloma of the face |
| Treatment of polycystic kidney disease |
| Treatment of polyneuropathies |
| Treatment of polio |
| Treatment of gallbladder polyps |
| Treatment of diarrhea |
| Treatment of portal hypertension |
| Treatment of porphyrias |
| Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder |
| Treatment of priapism |
| Treatment of leprosy |
| Treatment of prostatitis |
| Cold treatment |
| Treatment of proteinuria |
| Treatment of pseudotuberculosis |
| Treatment of psychosomatic diseases |
| Treatment of psoriasis |
| Treatment of hydatidiform mole |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Folk remedies for pemphigus
Treatment with prescriptions from witch doctors and healers is carried out strictly after consultation with a dermatologist. Components of traditional medicine can cause complications or worsen the condition.
| Name | Recipe | Application and effectiveness |
| Eucalyptus decoction. | Pour boiling water over the herb (1 tsp), leave and strain. | The resulting product is used to rinse the mouth morning and evening. |
| Herbal collection. | Mix 2 tbsp. birch buds, chamomile and eucalyptus. Add 4 tbsp. St. John's wort, 3 tbsp. yarrow. Pour boiling water (450 ml) over the resulting mixture (2 tablespoons), leave and strain well. | The medicine is taken every 4 hours for 3 months. |
| Tansy flowers. | Pour hot water (0.5 tbsp) over the plant, leave well and strain. | Patients with pemphigus are recommended to drink 20 ml 3 times a day. per day for a week. |
To treat rashes on the body, you can use fresh nettle juice. The product is applied with a cotton pad. The plant has an analgesic effect, promotes rapid healing of wounds and stops bleeding.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 2 | 56 | 56 | 94 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 108 | 108 | 201 | 96 |
How to avoid exacerbations of pemphigus?
It is currently impossible to prevent the disease.
You can avoid exacerbations and complications if you start treatment in a timely manner and remember the useful recommendations of doctors:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Healthy food;
- contact the hospital in a timely manner if concomitant diseases appear.
It is important to follow simple hygiene rules and take care of your skin.
What diseases can it be associated with?
The development of pemphigus is often accompanied by complications, especially against the background of absent or inadequate treatment. However, therapy appropriate to the diagnosis can affect health over the years, since it is usually lifelong use of corticosteroids.
Complications of pemphigus are:
- pneumonia,
- sepsis,
- cardiovascular failure,
- cachexia.
These often cause death.
Prognosis and complications
Exacerbation of pemphigus occurs with untimely treatment.
Death occurs in particularly difficult situations against the background of serious complications:
- sepsis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- stomach ulcer;
- diabetes;
- hypoproteinemia.
It is difficult to predict the development of pemphigus because the disease has not been fully studied.
There are a large number of its forms. Viral pemphigus goes away with timely treatment. Other types of disease cause complications and negative consequences (sepsis, meningitis, encephalitis). Without proper therapy, the risk of death increases, especially for young children, whose immunity is just developing and cannot resist its own antibodies.
Pemphigus is a rare disease that requires timely response from doctors and medical care. Complications lead to death. It is impossible to prevent pathology, so it is important to monitor your health. A photo symptom in adults will allow you to think about it and consult a doctor as soon as possible when the first signs appear.
Prevention
Depending on the cause of pemphigus disease, various preventive measures are taken.
Pemphigus vulgaris is difficult to prevent, because... this is an autoimmune disease - just like to prevent many other diseases, it is necessary to constantly maintain immunity. To prevent relapses, monitor the condition of the skin, monitor the level of prothrombin, blood sugar, urine, blood pressure at least 2-3 times a week, take vitamins and calcium supplements.
To prevent viral pemphigus and pemphigus of newborns, you should follow basic rules of hygiene and antiseptics.
Erysipelas disease Streptoderma Echinococcosis Tetanus in humans Listeriosis in humans Toxoplasmosis in humans
Therapy
Treatment of viral pemphigus is purely conservative. It consists of prescribing medications and certain procedures. Various types of systemic drugs are used in therapy:
- antiviral: “Viferon”, “Cycloferon”, “Laferon”;
- immunosuppressive. They can be of 2 types: glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) and cytostatics that suppress the division of immune cells (Azathioprine, Sandimmune, Methotrexate);
- antipyretics: Ibuprofen, Nimesil, Mefenamic acid, Paracetamol. “Aspirin” or acetylsalicylic acid should not be taken to reduce fever, especially for children under 10 years of age;
- for itching, antihistamines are required: “Cetrin”, “Fenistil”, “Diazolin”.
Locally, to treat the skin, antiseptics are used (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Methylene Blue), combined preparations, including antiseptics with anesthetics (Oflokain, "talkers" made in a pharmacy with local anesthetic drugs, antiseptics and vitamins). For viral pemphigus of the oral cavity, antimicrobial local anesthetic drugs are prescribed: Forteza, Orasept. Additionally, you can relieve itching using lotions with nettle juice, aloe juice or walnut leaf oil.
The procedures used are those whose essence is to purify the blood. This:
- hemosorption, when the blood is purified using a carbon filter;
- plasmapheresis is the removal of a certain amount of the liquid part of the blood and its replacement with solutions similar to it in physical and chemical properties, but free of microbes, antibodies and immune complexes.
To prevent substances that get into food from injuring the mucous membrane affected by viral pemphigus, you need to follow a diet. It consists of eliminating spicy, sour foods. You can drink juices, but non-acidic ones and those that do not cause allergies. Soups, cereals, pasta or other dishes should not be eaten hot, but at room temperature, so as not to increase the pain syndrome.
You need to eat more often, but take small portions. Intake of cold foods is indicated: ice cream, fruit ice or others, if there is no allergy to them. If you need to treat an infant, it is best to return completely to breastfeeding for the duration of the illness in order to meet the child’s energy needs and not injure his mucous membranes.
You cannot refuse feeding. If a child cannot eat, it is necessary to go to an infectious diseases hospital and not refuse hospitalization. Then, for a while, until the eruptive elements of the viral pemphigus disappear, the baby will be able to install a tube in the stomach and feed with it.