General information
Bronchial pneumonia is an acute, infectious-inflammatory disease of the lungs with the obligatory involvement of all structural elements.
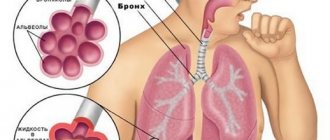
Bronchopneumonia is characterized by damage to the alveoli with the development of inflammatory exudate in them (the liquid part of the blood plasma leaves the blood vessels and permeates the surrounding tissues). With bronchopneumonia, not only the lung tissues are affected, but also the adjacent structures of the bronchial tree. The inflammation is focal in nature and spreads within the segment, lobule and acinus. Bronchopneumonia is not associated with a specific type of pathogen and, with the progression of the inflammatory process, can develop into lobar pneumonia . In children and the elderly, it can occur as an independent disease, and in mature patients, bronchopneumonia is most often a complication of another disease.
According to statistics, pneumonia ranks 4th in the structure of causes of mortality, behind diseases of the cardiovascular system, oncology and traumatic injuries. Preventive measures to prevent the development of bronchopneumonia include timely treatment of respiratory diseases. A synonym for bronchopneumonia is focal pneumonia. The most common type is right-sided focal pneumonia, which remains asymptomatic for a long time. Bronchopneumonia code according to ICD-10 is J18.0
Risk group
- The disease affects people of all ages, but most often it occurs in newborns, children under three years of age, and pensioners over 65 years of age. In these cases, the disease is more severe. Among children at risk are children with idiopathic diseases of the respiratory system and those who have immunodeficiency.
- People who have suffered other lung diseases are more susceptible to bronchial pneumonia. In addition, people suffering from heart disease or diabetes are at risk.
- Smokers are hospitalized with a diagnosis of bronchopneumonia more often than people who do not have this bad habit.
Pathogenesis
As a result of the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the smallest structures of the lung tissue and bronchial tree, local immune defense is disrupted. Weakened local immunity provokes the development of the inflammatory process. In parallel, a change in microcirculation , ischemic changes , lipid peroxidation is activated and local sensitization occurs.
Features of the disease
Bronchopneumonia refers to pathologies of inflammatory and infectious origin that affect the lungs. Its main difference from ordinary pneumonia is the penetration of bacteria and viruses not only into the lungs, but also into the bronchi. Most often, this inflammatory process occurs as a result of infection of the upper respiratory tract. The causative agents of this pathology are streptococci and pneumococci.
Classification
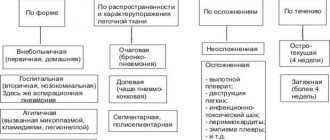
According to the conditions of development, the following forms of bronchopneumonia are distinguished:
- hospital or nosocomial;
- community-based or outpatient;
- pneumonia due to immunodeficiency.
Some classifications propose to separately distinguish bronchopneumonia caused by medical interventions.
According to etiological factors, there are:
- bacterial forms;
- viral forms;
- atypical forms.
Classification by severity:
- Easy. Symptoms of intoxication are mild, low-grade fever is recorded, pulmonary infiltration is observed in the area of one segment. Signs of respiratory failure are not recorded, there are no hemodynamic disturbances.
- Average . Symptoms of intoxication are moderate, body temperature rises to 38 degrees, pulmonary infiltrate is recorded within 1 or 2 segments. Patients experience tachycardia (increasing heart rate to 100 beats), respiratory rate increases to 22. No complications are observed.
- Heavy . Patients experience severe symptoms of intoxication, body temperature rises to 38 degrees and above, symptoms of respiratory failure of 2 and 3 degrees are recorded, and hemodynamic disturbances (pulse more than 100 beats, blood pressure less than 90/60 mm Hg) are noted. In patients, consciousness is impaired, concomitant diseases worsen, the infiltration zone increases by 50% within 48 hours.
Causes
The most common causative agents of community-acquired bronchopneumonia are:
- pneumococci (leaders, accounting for 70-90% of the disease);
- mycoplasma (affects 20-30% of patients under 35 years of age);
- hemophilus influenzae;
- legionella;
- chlamydia;
- coli;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- hemolytic streptococcus;
- Friedlander's wand;
- Moraxella.
The main causative agents of hospital-acquired pneumonia (develops within 48-72 hours after the patient is admitted to the hospital) are:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- coli;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Friedlander's wand, Klebsiella ;
- other gram-negative microorganisms.
Viruses can also cause pneumonia:
- adenovirus;
- influenza viruses;
- rhinoviruses;
- respiratory syncytial viruses;
- some types of enteroviruses (ECHO, Coxsackie).
Bronchopneumonia is characterized by polyetiology - a combination of several causative factors:
- long smoking history;
- children and old age (children aged 3-9 months are most often affected);
- heart failure with congestive lungs;
- alcohol abuse;
- secondary immunodeficiency states;
- taking immunosuppressants;
- malformations of the respiratory system;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- occupational hazard;
- chronic pathology of the bronchopulmonary system;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the ENT organs;
- conditions after surgery;
- long bed rest;
- unfavorable ecology in the area of residence.
Kinds
Considering the area of damage to the bronchi, in medicine there is a certain classification of bronchopneumonia. In each case, characteristic clinical symptoms appear, with which it is recommended to consult a pulmonologist, undergo examination and treatment.
Unilateral bronchopneumonia
The inflammatory process develops in the lungs on one side. Right-sided pneumonia is more common. On this side, the lung is located in such a way that pathogenic microorganisms quickly penetrate into its lower sections.
Bilateral bronchopneumonia
In medicine, the disease is called lobar bronchial pneumonia. The inflammatory process in the lungs contributes to the appearance of infiltration, which externally resembles grains of oat grains.
At the initial stage of bilateral bronchopneumonia, a person develops minor hemorrhages. As pathological processes progress, the affected tissues become inflamed. Bilateral bronchopneumonia is more often diagnosed in children.
Catarrhal bronchopneumonia
In this situation, the inflammatory process affects the bronchi at an early stage, then spreads to the lung parenchyma. The patient develops a severe cough, fever and pulse increase. In some situations, an infection occurs, against which purulent foci appear.
For any form of bronchopneumonia, it is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner and begin treatment. In severe situations, the risk of serious complications, including death, increases.
Symptoms of bronchopneumonia
The disease extremely rarely develops acutely, more often as a complication of respiratory infections or tracheobronchitis .
Symptoms of bronchopneumonia in adults:
- Cough with discharge of mucopurulent sputum. It all starts with a slight cough with a gradual transition to a dry and unproductive cough. Sputum begins to appear 2-3 days after the onset of the disease.
- Increased body temperature. Most often, subfebrile numbers are recorded; a rise to 38.5-39.5 degrees Celsius is rarely observed.
- Chest congestion with pain. The pain intensifies with coughing and deep breathing.
- Intoxication manifests itself in the form of lethargy, weakness, apathy, dizziness , drowsiness and decreased appetite.
In children and the elderly, the following symptoms of focal pneumonia are sometimes observed:
- shortness of breath with a respiratory rate of 25-40 per minute;
- severe headaches.
Tests and diagnostics
If bronchopneumonia is suspected, the following diagnostic measures should be carried out:
- general blood test (an increase in ESR, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, leukocytosis is detected);
- biochemical blood test (markers of acute inflammatory process are increased);
- sputum examination;
- Carrying out auscultation (moist fine bubbling rales, hard breathing, and rarely crepitus are heard);
- R-graphy of the chest organs (increased pulmonary pattern is recorded, fuzzy heterogeneous infiltrative shadows are revealed);
- computed tomography (performed in cases of severe bronchial obstruction, in cases of damage to the hilar region, for differential diagnosis with tumors in the lungs and tuberculosis ).
In some cases, polypositional fluoroscopy is performed. For uncomplicated bronchopneumonia, a control x-ray examination is carried out no earlier than after 2-3 weeks.
Diagnosis and therapeutic methods
A comprehensive examination is used to diagnose unilateral or bilateral pneumonia at different stages. It includes clinical tests of blood, urine, sputum and mucus from the throat, X-ray of the lungs, as well as auscultation.
X-ray for pneumonia
With the help of a laboratory examination, the causative agent of the disease is identified and its type is established, and the severity of the pathology is determined. To ensure the reliability of the indicators, biomaterial is collected before antibacterial therapy and two weeks after it is completed.
X-ray allows you to determine the location of the inflammation in the lungs.
Auscultation allows you to determine the degree of damage to the bronchi and inflammation of the pleura. It is carried out by listening to the chest with a phonendoscope or stethoscope.
A full-fledged diagnostic complex allows you to accurately determine the type and stage of bronchopneumonia, as well as select the appropriate treatment, which is carried out in a hospital. For the treatment of catarrhal bronchopneumonia and relief of inflammatory processes, the following is prescribed:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Taking herbal mucolytics.
- Antipyretic medications.
- Analgesics.
- Multivitamins containing macronutrients.
- Maintaining bed rest.
- Therapeutic diet.
Therapeutic course of treatment
Chest massage to ease breathing
After stabilizing the body temperature, it is recommended to undergo a course of chest massage and inhalations with drugs that make breathing easier. The therapeutic course must be prescribed by a doctor. In pediatrics, the intake and dosage of medications is strictly controlled by a pulmonologist.
To improve the dynamics of recovery and increase the effectiveness of conservative therapy, the use of alternative treatment methods is allowed. The most effective traditional medicines are those with mucolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. In acute bronchopneumonia, such methods of therapy are contraindicated.
Treatment of bronchopneumonia
Most often, focal pneumonia is treated comprehensively.
Treatment of bronchopneumonia in adults includes:
- compliance with the medical and protective regime (outpatient treatment or hospitalization depending on the severity);
- adherence to therapeutic nutrition - diets No. 10 and No. 15 with a high content of fortified drinks;
- etiotropic therapy (prescription of antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs);
- pathogenetic therapy (taking medications that help restore the drainage function of the bronchi: expectorants and mucolytics);
- immunomodulatory therapy;
- use of antioxidant agents ;
- detoxification therapy;
- syndromic treatment (anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, antipyretics and antitussives);
- carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures (breathing exercises, massage, exercise therapy, spa treatment).
Adequate treatment in adults leads to a favorable prognosis. Treatment of bronchopneumonia in children is particularly difficult, because most often occurs with complications and consequences due to inadequate and untimely therapy. Dr. Komarovsky recommends starting treatment by identifying the source and causative agent of the disease to further determine the tactics for prescribing medications - antibiotics or antivirals.
Is bronchial pneumonia contagious?
Pneumonia usually occurs upon contact with a dangerous microorganism. According to statistical information, severe forms occur in hospital settings.
Under certain conditions, pathogenic microflora, having entered the body, can trigger an abnormal process in the lungs. But this may not happen (if the immune system is strong).
Bronchopneumonia in adults does not occur immediately after infection. Microorganisms need to “get comfortable” in the body and only then do they begin to reproduce. This period is called incubation. At this time, the person already poses a danger to others. The incubation period can last from several days to several weeks, and no symptoms usually occur.
Pneumonia caused by atypical pathogens - legionella, chlamydia, mycoplasma - is very dangerous for others. Viruses are also dangerous. The risks increase significantly with close contact, including kissing.
Medicines
The main direction in the treatment of bronchopneumonia is antibacterial therapy if the cause of the disease is microorganisms. The antibiotic is selected individually depending on the characteristics of the organism and taking into account the results of bacterial culture for sensitivity ( Ceftriaxone , Clarithromycin , Amoxicillin and others). Antimicrobial agents can be administered by injection or orally. At the initial stages of the disease, antipyretics ( Aspirin , Paracetamol ) and expectorants ( Fluifort , ACC , Mucaltin ) are prescribed. If necessary, anti- allergy to help relieve swelling and ease breathing ( Suprastin , Cetrin , Tavegil ).
How is pneumonia different from asthma?
The main difference between pneumonia and asthma is that pneumonia develops as a result of infection, while asthma is not associated with infection. In asthma, the bronchi become inflamed and the airways narrow. With the help of competent therapy and good medications, asthma can be treated, but it cannot be completely cured. Over time, a person learns to avoid factors that provoke attacks of bronchial asthma - the quality of life improves.
With pneumonia, the lung tissue becomes inflamed and the alveoli are affected, which are filled with exudate - an inflammatory fluid. The bronchi and bronchioles are not affected, so the airways remain healthy. Pneumonia can be completely cured. Despite the fact that both diseases have similar symptoms, different medications are prescribed and different therapeutic approaches are used to treat each.
Treatment of bronchopneumonia with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can become an integral assistant in the fight against diseases of the bronchopulmonary system. Before using them, be sure to consult your doctor. Some traditional methods may seem ineffective at a certain stage of treatment or may not be suitable due to the individual characteristics of the patient.
Treatment of bronchopneumonia at home:
- Honey and birch buds. A remedy prepared from a decoction of birch buds with the addition of bee honey helps eliminate the main symptoms of the disease. The resulting solution should be taken 30 minutes before going to bed, 1 dessert spoon.
- Tar. Pour 3 liters of boiling water over the tar and leave for a week. The resulting remedy should be given to the patient 30 minutes before bedtime every day.
- Plantain. You can make compresses from plantain leaves. A dried, freshly picked plantain leaf should be applied to the patient’s chest and carefully wrapped in a warm blanket.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and additionally use traditional methods of treatment, then bronchopneumonia will pass without consequences or complications. After completing the course of therapy, it is necessary to undergo a control x-ray. Do not forget that traditional methods can only act as an addition to the main treatment prescribed by a doctor.
Disease prevention
To prevent bronchial pneumonia, preventive measures are recommended. Particular attention to disease prevention should be paid to people at high risk, as well as adults and children during the off-season period. To do this you should:
- Perform a set of exercises aimed at strengthening the respiratory system.
- Maintain your annual flu vaccination schedule.
- Adults and older people are regularly vaccinated against streptococcal infections.
- For children at risk, vaccination against pneumonia is required.
- When working in hazardous industries, use professional protective equipment.
- Maintain personal hygiene carefully.
- Systematically strengthen the body's immune system.
- Stop smoking tobacco products and drinking alcohol.
Prevention of pathologies that are considered provoking factors should be observed. For this, doctors recommend:
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Include daily walking in your daily routine.
- Maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
- Prevent exacerbations of chronic diseases.
- Harden the body.
- Regularly visit the gym.
- Avoid chest injuries.
Bronchopneumonia is one of the most common types of pneumonia. The disease is highly treatable at an early stage. Therefore, in order to prevent negative consequences and complications, it is recommended that when the first symptoms appear, you immediately seek qualified help from a pulmonologist. Self-medication of such a lung disease is strictly prohibited.
First aid
The patient can take certain measures to improve well-being and maintain strength in the first hours of the disease himself. After calling a local doctor to your home, you must:
- measure body temperature;
- drink herbal tea with lemon;
- go to bed.
How household members can help:
- relief from breathing problems;
- reducing the negative impact of intoxication;
- control of blood pressure and cardiac activity.
What to do first:
- put the patient in bed and raise the head end of the bed, creating optimal conditions for easier breathing;
- ventilate the rooms, do wet cleaning;
- apply cool wet compresses to the forehead, wipe hands and feet with a napkin previously moistened in cool water;
- if necessary, humidify the air in the room (during the acute period of the disease, the humidity in the room can reach 50-60%).
Regime and diet
In case of focal pneumonia, specialists prescribe bed rest. The room where the child is located needs to be ventilated and wet cleaned every day . Walking is allowed only when the temperature is stable and does not rise. But the duration of the walk should be less than under normal conditions. It is necessary to ensure that the child does not become hypothermic.
The diet should be gentle: small portions, but often . It is better to prepare food that is easily digestible, so that the body spends most of its energy on fighting the disease, and not on digesting food. The drink should be warm. The best solution is homemade compotes and fruit drinks, non-carbonated mineral water.
susceptible to dehydration than adults , especially at high temperatures. Parents must ensure that the child drinks water or other drink on time .
Bronchopneumonia in children
According to statistics, more than 1 million children die from bronchopneumonia every year, so in pediatrics the disease is considered quite dangerous. Against the background of focal bronchopneumonia, electrolyte and metabolic disturbances form in the child’s body, and the functioning of all organs and systems changes. Most often, the disease is registered in children under 3 years of age after suffering from bronchitis and is accompanied by copious discharge of purulent sputum.
Well-known specialist Dr. Komarovsky E.O. believes that it is necessary to start treatment of bronchopneumonia in children with antibiotics only as a last resort. The first steps in therapy should be aimed at eliminating foci of the disease. The prescribed drug therapy should be absorbable in nature. If, after carrying out the necessary examination and passing the appropriate tests, viral bronchopneumonia was detected, then antiviral agents are added to the treatment. Unreasonable prescription of antibiotics can only worsen the child’s condition.
Bronchopneumonia in adults is milder than in children, unless we are talking about elderly people or patients with immunodeficiency conditions . Treatment of bronchopneumonia in adults is carried out by a therapist and pulmonologist.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of bronchopneumonia:
- Fever is an increase in body temperature, first to 38 or 39 degrees, and in the absence of medical care - to higher values.
- General weakness, poor health, hyperhidrosis, muscle pain, decreased appetite, sleep disturbance.
- The cough started out dry and then wet. Mucous sputum is produced, sometimes streaked with blood.
- Shortness of breath - first when walking and other physical activity, and as the underlying disease progresses - at rest.
- Acrocyanosis is a bluish discoloration of areas distant from the heart: the nasolabial triangle, the tips of the ears and nose, and the fingers.
- Rapid breathing due to hypoxia.
- Unpleasant sensations and pain in the chest of a stabbing or pulling nature.
- Arthralgia is pain and discomfort in the joints.
- Herpetic eruptions on the lips.
- Coated tongue - the appearance of a rough white coating on it.
- Tachycardia - rapid heart rate up to 110 beats per minute.
- Shortening of the percussion sound, the presence of a tympanic tint.
- Intermittent fine bubbling and dry wheezing.
- Vesicular respiration.
- Muffling of heart sounds.
- Neutrophilic leukocytosis, increased ESR.
In children, the disease develops rapidly. This is due to the small size of the respiratory tract and not fully formed immunity. The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of the disease in adults, but are supplemented by anxiety, tearfulness, restlessness, lethargy, pale skin, drowsiness, unhealthy blush, lack of appetite, and convulsions. The disease in children often leads to complications. The disease is difficult to diagnose because fever and cough are often absent or mild. Late diagnosis delays the start of therapy. Sick children with bronchopneumonia breathe loudly and complain of shortness of breath. In such cases, the development of pathology is usually preceded by long-term bronchitis or ARVI.
In children, bronchopneumonia is very severe. This disease is dangerous to the health and life of the child. It often causes the death of young children. Water-electrolyte and metabolic processes in the body are disrupted, which leads to dysfunction of vital organs and systems. That is why children with bronchopneumonia must be hospitalized in the pulmonology department for treatment, which will prevent the development of acute respiratory and vascular failure.
In the absence of timely and adequate therapy, patients develop severe complications:
- Purulent inflammation of the middle ear,
- Purulent pleurisy,
- Pyelonephritis,
- Cardiac dystrophy,
- Pericarditis and myocarditis,
- Abscess formation and fibrosis of lung tissue,
- Acute coronary dysfunction,
- State of shock
- Bronchoobstruction,
- Inflammation of the membranes of the brain and medulla,
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome,
- Psychopathy,
- Anemic syndrome,
- Inflammation of the kidneys and liver with subsequent organ dysfunction.
In children, intoxication, diuresis retention, neurotoxicosis, exudative pleurisy, sepsis and asthenia come first.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes enormous hormonal changes. The immune system weakens several times and becomes more vulnerable. Expectant mothers most often suffer from a cough with a runny nose, which is accompanied by malaise and weakness. Sometimes it is precisely these symptoms that cause bronchopneumonia in pregnant women. It is not recommended for expectant mothers to self-medicate and hope that everything will go away on its own. In order to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and avoid complications, you must urgently contact your doctor. Bronchopneumonia is not an indication for termination of pregnancy .
Diet for bronchopneumonia
Diet for bronchitis
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 7-14 days
- Cost of products: 1600-1800 rubles. in Week
Diet for pneumonia, nutrition for pneumonia
- Efficacy: no data
- Time frame: 21 days
- Cost of products: 1500 - 1700 rubles. in Week
Nutrition for bronchopneumonia should be special and aimed at maintaining the body’s protective function, reducing the load on the immune system and unloading the digestive tract. It is extremely important to reduce your intake of carbohydrates, fats and salt during treatment. It is recommended to increase the consumption of foods rich in B vitamins ascorbic acid . You need to eat partly - up to 6 times a day, preferably in small portions. If you have no appetite, then you don’t need to force yourself. It is better to steam, boil, bake in the oven, and thoroughly grind the food until it becomes mushy. Warm, plenty of fluids are important.
Allowed products during the acute period of the disease:
- meat/chicken broth;
- lean chicken;
- low-fat fish;
- meat;
- fermented milk products;
- dried fruits;
- fresh fruits and vegetables.
During the recovery period, the menu can be slightly diversified - increase the amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats and reduce fluid intake.
What are asthma and pneumonia?
Asthma and pneumonia are diseases that affect the respiratory system. Asthma is a chronic disease in which the bronchi become inflamed and their lumen narrows, making breathing difficult. A serious complication is status asthmaticus - a condition when an attack of asthma does not stop for a long time. With status asthmaticus, the bronchioles swell and oxygen deficiency in the blood increases. This condition is a medical emergency.
Symptoms of bronchial asthma are not constant: they can come and go. Their appearance depends on the presence of pathological factors, which include:
- allergens: pollen, dust, pet hair, molds in poorly ventilated areas;
- chemical vapors;
- tobacco and industrial smoke;
- contaminated air;
- low humidity and temperature;
- powerful emotions;
- exercise stress;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- taking aspirin.
Pneumonia is a disease of the respiratory system accompanied by inflammation of the lung tissue. As a rule, pneumonia is caused by infections: pathogenic fungi, bacteria, viruses or parasites. The tissue in one or both lungs may become inflamed. Pneumonia mainly affects the alveoli - small vesicles in which the exchange of gases between blood and air occurs. At the same time, pus and inflammatory fluid accumulate in the alveoli, making it difficult for the patient to breathe.
Consequences and complications
There are pulmonary and extrapulmonary pathological conditions that can complicate bronchopneumonia.
Pulmonary complications:
- pleural empyema;
- parapneumonic pleurisy;
- bronchial obstruction syndrome;
- gangrene of the lungs;
- abscess in the lungs;
- acute respiratory failure .
Extrapulmonary complications:
- DIC syndrome;
- toxic hepatitis;
- acute glomerulonephritis ;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- acute cor pulmonale;
- nonspecific myocarditis ;
- anemia;
- meningoencephalitis;
- meningitis;
- endocarditis;
- psychoses.