For normal functioning of the body, it is necessary to maintain all its functions in a state of balance. This concerns not only the level of hormones, the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, but also the acid-base composition of the blood. Normally, the amounts of substances with low and high acidity (abbreviated as pH) are in a certain balance. Due to this, the blood has a slightly alkaline environment. When the concentration of alkalis increases, a person develops “alkalosis”; when the concentration of acids increases, a person develops “acidosis”.
Metabolic acidosis develops in various diseases that are not associated with damage to the respiratory system. It cannot occur on its own and is always a complication of some other disease. You can get all the necessary information about the causes, symptoms and treatment methods of this condition from this article.
Development mechanism
The process has a complex origin. The pathogenesis is based on the inability of the body's buffer systems, primarily blood, to normalize the acidity of the environment. Typically, even healthy people experience pH fluctuations; an adequate value is in the range from 7.35 to 7.38.
Minor deviations in both directions are possible, but short-term. This is also not considered critical.
When the pH drops below 7.35 on a long-term basis, changes in the functioning of organs develop: breathing and cardiac activity suffer, the nervous system is depressed, which ends in death without treatment.
Dynamic balance becomes impossible in a group of disorders. There are several mechanisms for the development of acidosis:
- Excessive acidification of the blood due to the intake of large amounts of gases rich in carbon compounds. For example, when exposed to smoke for a long time, in a stuffy room, with a lack of O2, possibly in high mountains. This is a relatively uncommon cause.
- Hormonal imbalance, accumulation of protein breakdown products in the body. Typically, this problem occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- The development of a gestational variant of the disorder is possible. They talk about it when the waste products of the fetus poison the mother’s body, when self-regulation and cleansing of the latter is impossible. It occurs mainly in women with somatic pathologies (renal, cardiac, respiratory failure), also in cases of multiple births and severe gestation.
There are other options. Acidosis does not always have a pathological origin. Normally, healthy people experience changes in the acidity of the blood and urine.
There are several reasons for this:
- Intense stress triggers biochemical reactions involving cortisol, adrenaline and others. The result is a temporary pH drop.
- The problem is also observed against the background of excessive physical activity.
- After surgery.
- With an ill-formed diet with a large amount of carbohydrates, protein with a minimum amount of coarse fiber.
Each situation is subject to individual assessment.
Acidosis does not always present pronounced symptoms, especially if the acidity is slightly increased.
But the disorder has the unpleasant property of progressing quickly, within a matter of hours, leading to coma and death. You need to be on your guard.
Clinical picture of acidosis
The most characteristic sign of severe acidosis is depression of the function of the central nervous system, expressed in drowsiness, stupor (see Stunning) and coma (see). With acidosis, the blood pH can drop to 7.1, in some cases of metabolic acidosis even to 6.8, which is the lowest level compatible with life. A comatose state occurs when the pH drops below 7.2.
One of the most pronounced clinical signs of acidosis is breathing problems. With metabolic acidosis, in the early stages of its development, an increase in the minute volume of respiration (polypnea) is observed, which later, as a result of a compensatory decrease in blood pCO2 and a decrease in the excitability of the respiratory center, can become noisy and superficial (see Kussmaul breathing). An increase in blood pCO2 during gas acidosis causes spasm of the bronchioles.
Changes in blood pCO2 during acidosis cause corresponding changes in central and peripheral hemodynamics (see Hypercapnia, Hypocapnia). Thus, a decrease in pCO2 (with metabolic acidosis) causes a drop in vascular tone, as a result of which blood pressure drops and cardiac output decreases, and cerebral and coronary blood flow decreases. On the contrary, an increase in blood pCO2 leads to spasm of arterioles, including kidney arterioles, increases blood pressure, and complicates the functioning of the heart. A large excess of CO2 can cause increased vagal tone and cardiac arrest. The blood vessels of the brain, under the influence of increased pCO2, dilate, which increases the formation of cerebrospinal fluid and contributes to an increase in intracranial pressure. It was noted that intravenous administration of substances that increase osmotic pressure (glucose solutions, etc.) usually does not reduce intracranial pressure in such patients.
The effect of acidosis on renal function is manifested in a decrease in urinary function: the narrowing of renal vessels that occurs under conditions of gaseous acidosis limits blood flow through the vessels of the kidneys, reduces the pressure in the afferent vessels of the renal glomeruli and reduces the volume of urine excreted. In metabolic acidosis, a drop in central blood pressure leads primarily to a decrease in urine production.
Metabolic acidosis significantly affects water-salt metabolism: the concentration of potassium in the plasma increases, the osmotic pressure of the extracellular fluid increases (due to an increase in the concentration of potassium, sodium, and chlorine ions), which causes an increase in the volume of extracellular fluid. The consequence of these changes is disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions (atrial tachycardia, atrial and ventricular extrasystole), deterioration in myocardial contractility, and the development of tissue edema. With gaseous A. the concentration of potassium in the plasma also increases.
Recognition and assessment of the severity of acidosis is facilitated by determining the main indicators of the acid-base state using the Astrup express method (see Express methods).
Classification
The disorder can be divided in several ways. Upon admission of a patient, doctors urgently examine the extent of the disorder. This involves assessing blood and urine.
The types are named according to the criterion:
- Compensated form. Accompanied by relatively normal acidity levels of up to 7.35. There are no symptoms or any signs yet, the patient is completely fine and does not suspect a problem. In this state, acidosis is usually not noticeable and the person is admitted to the hospital for another reason.
- Subcompensation gives a pH level in the range of up to 7.25, which is much more dangerous. The body is still coping, buffer systems partially correct the acidity level, but functional impairments are already present. From the heart, blood vessels, respiratory system. The central nervous system is still normal; headache, nausea, and vomiting are possible. Reflexive, not bringing relief. Without treatment, the pathological condition very quickly moves to the next stage.
- Decompensation of acidosis. Acidity levels are below 7.25, and abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and digestive tract occur. Breathing is shallow, gas exchange is significantly impaired. The phenomena of depression of consciousness and coma are rapidly increasing. Without urgent correction, death cannot be avoided.
Another way to classify acidosis is to evaluate its origin. Without elaborating this criterion, it is impossible to begin quality treatment.
Exogenous form
It is caused by the entry into the body of a large amount of acid in its pure form or substances that can be converted into acid during metabolic processes. If the buffer systems are working properly, the situation is unlikely.
Among the routes of entry of substances, the main one is considered to be nutritional. Food.
Respiratory acidosis
It's gas. It occurs more often and occurs as a result of the ingestion of dangerous mixtures from the surrounding air and environment into the body. For example, when you are in a burning room, there is a lack of oxygen in a room or office.
The same is observed with chest injuries. Carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood, which causes an imbalance in the dynamic balance.
Attention:
Respiratory acidosis most often leads to rapid changes in the lungs, endocrine system, central nervous system, coma and death.
Excretory form
Accompanied by the inability to remove protein breakdown products and acidic substances due to insufficient filtering function of the kidneys.
The same problem occurs if the concentration of alkaline compounds drops. This often happens with dysfunction of the digestive tract. Recovery involves correction of the main diagnosis.
Metabolic acidosis
Associated with insufficient metabolism. Develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and pathologies of infectious origin.
The dysfunctions are deep and systemic. Therefore, treatment may take a little longer.
A special case of the metabolic form of the disorder is lactic acidosis, caused by a drop in insulin levels and, as a result, a complex biochemical reaction with the formation of a large amount of organic acid.
Mixed process type
The pathogenesis (origin) is based not on one, but on several factors.
Attention:
All of these types of acidosis are dangerous and, without treatment, in approximately 87% of cases end in the death of the patient.
Compensated forms can regress on their own, but this does not always happen. There is no need to count on luck.
Gas acidosis
Gas acidosis - an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide and an increase in the partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2) in the blood (see Hypercapnia) - develops with a decrease in pulmonary ventilation (respiratory failure, hypoventilation), as well as with inhalation of air with a high concentration of CO2.
The causes of respiratory failure can be: 1) inhibition of the function of the respiratory center (shock, increased intracranial pressure, overdose of morphine-like drugs and barbiturates); 2) breathing disorders associated with damage to the neuromuscular apparatus of the respiratory muscles (poliomyelitis, botulism, phrenic nerve palsy, myasthenia gravis, period of restoration of spontaneous breathing after the use of relaxants); with limited mobility of the chest due to injury and a number of diseases (kyphoscoliosis, high position of the diaphragm, ossification of the costal cartilages, deformation of the ribs); 3) hypoventilation due to insufficient airway patency (foreign body in the respiratory tract, bronchospasm) or due to a decrease in the tidal volume of the lungs (pneumonia, pulmonary infarction, pneumosclerosis, scleroderma, bronchiectasis, etc.). In severe respiratory failure, the blood pCO2 value can increase to 70-120 mmHg. Art. and higher (normal 35-42 mm Hg).
Gas acidosis can occur when inhaling air or gas mixtures with high concentrations of CO2 during prolonged stay in a closed room without refreshing the air or when using an anesthesia machine with a depleted absorbent. Hypoventilation can also be observed when artificial respiration is performed incorrectly (see).
Compensation of gas acidosis is carried out primarily with the participation of the hemoglobin buffer, thanks to which the hydrogen ions formed during the dissociation of carbon dioxide are retained by reduced hemoglobin in the erythrocytes, and the HCO3- anions released in exchange for chlorine ions from the erythrocytes into the plasma contribute to the formation of additional amounts of bicarbonate in it sodium (NaHCO3). Thus, with gas acidosis, the primary increase in H2CO3 is compensated by a secondary increase in NaHCO3, due to which significant changes in the ratio of the concentrations of the components of the plasma bicarbonate buffer may not occur, and the plasma pH will remain within physiological limits. The second stage of compensation for gas acidosis is an increase in sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, providing an increase in NaHCO3 in plasma. Greater reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys during gas acidosis is facilitated by an increase in pCO2 in the blood, as well as an increased conversion of basic phosphates (Na2HPO4) into acidic ones (NaH2PO4) in the urine. The latter causes a slight increase in the titratable acidity of urine during gas acidosis. See also Alkalosis.
Symptoms depending on the type of acidosis
The clinical picture is determined by the type of disorder.
The respiratory form is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Dizziness. Occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen concentration. Accompanied by disturbance of orientation in space, unsteadiness of gait. In difficult cases, the patient takes a lying position to ease the symptom.
- Shallow shallow breathing. A typical sign of respiratory acidosis. However, such an increase in movements does not lead to compensation; hypoxia (oxygen starvation) increases.
- Change in skin tone to pale. Cyanosis.
- With the long-term existence of the pathological process, the phenomena intensify. Cardiac signs occur: tachycardia, increased number of contractions per minute, arrhythmia. Jumps in blood pressure that are not subject to qualitative correction.
Objectively, in addition, changes in urea levels are detected, calcium concentration drops, which leads to muscle spasms and cramps.
In terms of diagnosis, the respiratory form is the simplest; the causes are obvious even with a superficial examination.
Metabolic acidosis from the beginning gives cardiovascular manifestations:
- Tachycardia. Increase in the number of contractions per minute. At the same time, although the volume of pumped blood increases, the effect is minimal. Because there is not enough oxygen.
- Arrhythmias of other types. When excessive load on the myocardium occurs, group extrasystole or ventricular fibrillation occurs. Which is extremely dangerous. Against the background of such changes, the contractile, pumping function decreases.
- A characteristic symptom of acidosis in adults is increased breathing. The depth of movements increases while the frequency is formally preserved. Based on such a sign of acidosis as the nature of gas exchange, the doctor estimates the type of pathology, this saves time during further examination.
- Dizziness. Inability to navigate in space.
- Nausea and vomiting. Rare. Most often one-time, reflex.
- Impaired consciousness. When the pathological process worsens, all forms of the disorder cause depression of the central nervous system.
At first, this manifests itself as a “wobbly” body, weakness, drowsiness, a decrease in the speed of reaction to stimuli: a call, physical impact, a request, etc. Then loss of consciousness occurs.
Attention:
If brain function is not restored, coma develops. It is extremely difficult to get a person out of this situation.
Other forms of the pathological process do not have specific features. Typical symptoms: headache, nausea, vomiting, thinking disorders, loss of consciousness, respiratory and cardiac dysfunction of varying severity.
It is also worth keeping in mind that the list of manifestations is not always the same. And the formation of a holistic clinical picture, its changes, and complications develops according to an individual scenario.
Symptoms
This condition does not have any characteristic signs. A change in acidity is accompanied by a large number of different symptoms, which can be quite difficult to associate with each other. This is why it is quite difficult to identify the disease at home.
Common manifestations that can be observed with any form of the disease include:
- Constant nausea with vomiting, after which there is no improvement in well-being;
- Severe weakness that forces the patient to stay in bed;
- The appearance of shortness of breath at rest. A person cannot “breathe”, which is why his breathing becomes frequent and deep;
- Paleness of the skin and visible mucous membranes (eyes, mouth and nasal cavity);
- The appearance of cold sweat on the skin;
- Slows the heartbeat and lowers blood pressure;
- The development of convulsions, severe dizziness and loss of consciousness (even coma) is possible.
As we have already said, a change in acidity does not happen on its own. This condition is always preceded by some other disease. To put it simply, we can say that a sharp deterioration in well-being due to the disease is often the first symptom. In this case, it is necessary to call an ambulance team, which will assess the situation and, if necessary, hospitalize the patient. In the hospital, doctors will establish a final diagnosis, conduct the necessary studies and treatment measures.
Causes
Factors in the development of the disease are diverse. If we summarize the list, we can talk about such culprits.
- Increase in temperature. Accompanied by increased metabolism, breakdown of proteins and organic compounds. The body begins to intensify its own work. Products remain in the blood and acidify the environment. If the activity of buffer systems is disrupted, an increase in the thermometer reading even by a degree becomes extremely dangerous.
- Endocrine diseases. First of all, diabetes mellitus. Accompanied by instability of insulin levels or tissue insensitivity to this substance. Which ultimately, through a complex process, leads to the production of lactic acid, poisoning of the body and coma. In addition to diabetes itself, other processes are possible: thyrotoxicosis, thyroid disease.
- Renal failure and other pathologies of the urinary tract. The problem is a violation of the elimination of breakdown products of proteins and carbohydrates. If this condition persists for a long time, acidosis and dangerous consequences cannot be avoided. Therefore, nephrology patients need to carefully monitor their diet, select medications with caution, and regularly see a specialist.
- Lung dysfunction. Accompanied by insufficient intensity of gas exchange and, as a result, slow removal of carbon dioxide. It accumulates in the blood and causes an increase in its acidity. Direct causes include pneumonia, bronchitis, emphysema, COPD, and other conditions.
- Nutritional errors. Excessive consumption of protein foods may lower the pH level.
- Pregnancy. It is not so common as a factor in critical acidosis. Mainly for complications of gestation, multiple births, and diseases in the mother.
The cause of the disorder can be severe dehydration. With prolonged exposure to high temperatures, with diarrhea.
Consequences and complications
Complications of metabolic acidosis can include:
- dehydration;
- decrease in circulating blood volume;
- increased blood clotting, accompanied by a risk of thrombosis;
- circulatory disorders (including such serious ones as myocardial infarction, infarction of parenchymal organs, peripheral thrombosis, stroke);
- arterial hypo- and hypertension;
- disturbance of brain functions;
- coma;
- death.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out urgently. The hematologist takes the initial steps, then the participation of other specialists is required. Depending on the origin of the process.
Among the priority methods:
- Oral survey. If the situation allows you to talk with the patient. As fast as possible. The task is to identify all manifestations of acidosis, then it is necessary to create a complete picture and put forward hypotheses.
- Brief history taking. In order to identify the origin of the violation.
- Blood test. Urine. For acidity. It is considered the main diagnostic method. Allows you to quickly identify the problem.
Then it is necessary to urgently correct the condition.
After stabilization, you can resort to searching for the root cause of the development of acidosis.
Here the scope for medical activity is much wider:
- At a minimum, an x-ray is indicated to identify disorders of the lungs and bronchi.
- In extreme cases, CT.
- Also assessment of hormones in the blood. Thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Diagnosis of brain pathologies if necessary. EEG, MRI. There are many more options.
The examination is the task of specialized doctors.
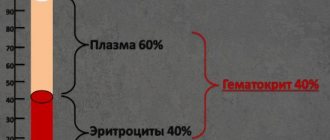
Acid-base balance buffer system
To function, the body needs energy, which it gets from food. Various metabolic processes make energy useful to muscles and organs. During metabolism, waste products accumulate and are excreted by the body through the kidneys, liver, skin, lungs and intestines. These wastes may be acidic or alkaline.
It is important for the body that the blood has a stable pH (hydrogen level). Therefore, the blood usually has a more or less stable pH level between 7.36 and 7.44. This is ensured by various buffer systems that balance the acid-base balance:
- chemical buffering;
- compensation through breathing (so-called respiratory compensation);
- compensation through the kidneys (so-called renal compensation).
Acidic metabolic waste is eliminated by the body through the kidneys, urination, or exhaled through the lungs. If the regulation of acid-base balance is disrupted (for example, as a result of impaired lung or kidney function), excess acid occurs and the body becomes acidic.
Treatment methods
It is impossible to speak generally about therapy in a nutshell.
The main task is to eliminate the underlying condition. That is, the actual disease that provoked the decrease in pH.
- Diabetes mellitus involves maintaining glucose levels within normal limits. Here you cannot do without a diet, systematic examination, and insulin is used if necessary.
- Lung diseases are treated with medication. Infectious processes require the use of antibiotics (bacterial lesions, fungal disorders), as well as stimulation of the immune system.
- If there is a suspicion of acidosis during pregnancy or the mother is predisposed to this condition, hospitalization or, at a minimum, systematic monitoring by a leading gynecologist is necessary. Changing your diet can be a good solution for nutritional problems.
- Kidney diseases can be treated with medication or require surgical correction. Hemodialysis and transplantation are practiced if it is impossible to influence the disorder in other ways.
As for dealing with symptoms. Drinking plenty of fluids and intravenous infusion of sodium bicarbonate solution (soda prepared in a special way), which neutralizes the acid, is indicated.
How to prevent acidification of the body (prevention of acidosis)
Anyone who wants to prevent acidification in the body must first pay attention to possible precipitating factors (triggers) of acidosis and prevent them. These include:
- diseases of the respiratory system (for example, bronchial asthma, emphysema, pulmonary fibrosis and other lung diseases);
- respiratory failure (for example, caused by rib fractures);
- diabetes;
- chronic kidney diseases.
In addition, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- eat a balanced diet, pay attention to physical activity;
- drink enough water (about 2 liters per day);
- drink alcohol in moderation;
- give up nicotine completely.
Forecast
The prospects for recovery depend on the nature of the disease. Compensated forms regress on their own in 76% of cases.
Physiological varieties do not require treatment; adaptive mechanisms cope on their own. For more complex forms of the process, forecasts are vague.
Survival rate for the subcompensated type is 55-60%. If the final phase is detected - 10-15% or less.
Negative prognostic signs are confusion, coma, poor response to treatment, pregnancy, late admission to the hospital, the onset of structural changes in the central nervous system. Myocardium.
Risk factors
The lifestyle a person leads has a negative impact on the level of acidity in the body. The most important factor is nutrition. The risk of metabolic acidosis increases significantly when consuming large quantities of animal protein. Acidity can also increase:
- oil;
- alcohol;
- sweets;
- coffee;
- cheese;
- eggs.
These products provoke excess levels of fatty acids, which must be eliminated. If you consume all these foods for many years, it will be quite difficult for the body to cope with their elimination.
In addition, stressful situations have a negative impact. A state of stress significantly increases the level of hormones, which significantly increase the body's acid reactions. The situation gets worse if you have bad habits. Insufficient physical activity can also increase acidity. With normal physical activity, metabolic processes in tissues and muscles proceed at a faster rate, and as a result, fatty acids are burned much faster.
Types of disease
Depending on the cause of the accumulation of acids in the blood, acidosis is divided into types:
| Type of acidosis | Violation | Causes |
| Ketoacidosis | Due to a lack of glucose, the body is forced to meet its needs by breaking down fatty acids. The process is accompanied by increased formation of keto acids. | Diabetes mellitus: type 1 – insufficient dose of insulin or a spoiled drug, type 2 – severe insulin resistance due to a long-term lack of compensation. Long-term fasting, alcoholism. |
| Lactic acidosis | Increased concentration of lactic and pyruvic acids. Their formation increases with a lack of oxygen. | Mild form - after strain on the muscles, especially in untrained people. Severe – with liver diseases, which normally cleanses the blood of acids. It can be observed in diseases that lead to oxygen starvation: cardiac, pulmonary, vascular, and with a lack of hemoglobin. The likelihood of lactic acidosis is increased by uncontrolled use of Metformin in diabetes. |
| Renal tubular | No acids are formed. Acidity increases due to lack of bicarbonates. Proximal acidosis is a violation of the return of bicarbonates to the blood. Distal – insufficient removal of hydrogen ions. | Proximal acidosis - nephrotic syndrome, hepatic vein thrombosis, myeloma, cysts, long-term use of diuretics, aldosterone deficiency. Distal acidosis - pyelonephritis, nephropathy, taking medications that can affect the rate of urine filtration in the glomeruli. |
| Acidosis due to intoxication | Acidification by breakdown products of substances, for example, oxalic acid when consuming ethylene glycol or formic acid when poisoning with methanol. | Failure to comply with safety precautions when working with toxic substances, consumption of surrogate alcoholic beverages, overdose of medications. |
A combined form of acidosis also occurs, especially in patients with chronic metabolic disorders. For example, the risk of acidosis due to high sugar in diabetes is significantly increased by alcohol consumption and diabetic nephropathy.
According to the degree of compensation, acidosis is divided into 3 forms:
- compensated acidosis: symptoms are rare, acidity is close to the lower limit of normal, the condition is stable. No special treatment is required, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the disorder;
- subcompensated acidosis: borderline condition, observation required;
- decompensated form of metabolic acidosis - blood pH is reduced to life-threatening levels or continues to decrease. Urgent hospitalization, acidity correction with special solutions, and, in some cases, resuscitation measures are required. Without treatment, decompensated acidosis can cause coma and lead to death of the patient.
Criteria for determining the degree of metabolic acidosis:
| Criterion | Compensation | Subcompensation | Decompensation |
| pH | ≈ 7,4 | 7,29-7,35 | < 7,29 |
| Buffer bases, mmol/l | 50 | 40-49 | < 40 |
| Topical bicarbonates, mmol/l | 22 | 16-21 | < 16 |
| Standard bicarbonates, mmol/l | 24 | 19-23 | < 19 |
| Pressure of carbon monoxide in the blood, mmHg. | 40 | 28-39 | < 28 |
Diet and lifestyle
To normalize acidity in the body, you must follow a special diet and also lead a healthy lifestyle. If possible, you should completely avoid pork and eat only low-fat butter. In addition, it is advisable to consume as little sugar and sweet foods as possible, as they provoke an increase in acidity levels.
You need to chew food long and thoroughly and consume fresh vegetables or fruits every day. You should avoid excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeinated drinks, quit smoking and avoid places where people smoke.
Be sure to include exercise and long walks, as this allows you to burn acidic fats faster. It is important to learn how to cope with stress using relaxation techniques, as well as get as much fresh air as possible. Every day you need to drink at least 2 liters of still mineral water with low sodium content.