Calcitonin is a peptide hormone that is involved in the processes of regulating bone formation, and special anatomical structures are responsible for its release into the bloodstream: parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland.
All connection level changes are potentially dangerous:
- On the one hand, we are most likely talking about a full-fledged pathological process. As the most obvious option, there are disturbances in the structure of the thyroid glands.
There are other possible factors in the development of the disorder; a thorough examination should be carried out.
- On the other hand, the pathological process is likely to lead to complications. As a rule, the bones are the first to be affected. Because the regulation of the production of special cells is disrupted.
A detailed examination is required. After which you can draw conclusions and prescribe special treatment.
Functions in the body
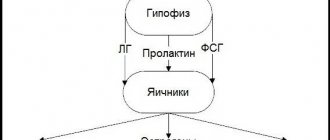
Calcitonin is a hormone produced by the parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland.
Also, a small amount of this hormone is synthesized by cells:
- intestinal mucosa (endothelium);
- lungs;
- thymus gland.
The main structural unit of the thyroid gland is follicles, consisting of two types of cells:
- type “A”, producing thyroid hormones that regulate general metabolic processes;
- type “B”, responsible for the synthesis of serotonin (neurotransmitter, or “happiness hormone”).
C-cells, in which calcitonin is synthesized, are located in the interfollicular space and make up a small part of the total volume of the gland.
Modern science believes that the main function of calcitotin is to regulate the concentration of calcium (Ca) in the blood by reducing it.
This hormone is capable of:
- partially block the process of “extracting” calcium from food by the intestines;
- by activating the work of the kidneys, accelerate the excretion of calcium through the genitourinary system;
- initiate the process of calcium absorption by bone tissue, activating the cells responsible for its “building” (osteoblasts);
- reduce the activity of osteoclasts, which perform the exact opposite function (causing bone destruction).
Structure and functions of the hormone
Calcitonin (hormone calcitonin) - what is it? This is a peptide hormone consisting of 32 amino acid units. 8 sources (from animals) of calcitonin have been identified, but 3 have received medical significance and are used: thyrocalcitonin thyroid gland from salmon, pigs and humans.
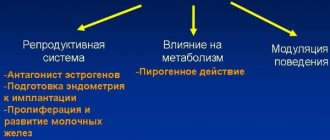
The functions of calcitonin are such that, in addition to its main control over the levels of Ca and P, the hormone performs:
- regulation of calcium absorption in the intestine, and therefore reduces it in the blood serum;
- participates in the production of vitamin D;
- increases daily urination due to the excretion of sodium ions and uric acid;
- has a slight anti-inflammatory effect;
- reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach;
- the level of phosphorus in the blood decreases slightly.
The mechanism of the hormone:
- Stimulates the functional activity of osteoblasts, helping to form bone tissue;
- Calcitonin blocks the absorption of Ca in the intestine;
- Inhibits Ca reabsorption (reabsorption of calcium from primary urine) in the kidney tubules and removes it with urine.
- Thyroid calcitonin inhibits the functioning of osteoclasts; Unlike osteoblasts, they can resorb the mineral component of bone tissue.
How and under what conditions is it produced?
The mechanism of calcitonin production is triggered by an increase in the level of calcium in the blood.
Simplified, its action can be described as follows:
- If the concentration of calcium increases (for example, after eating a meal containing this mineral), C-cells, under the influence of gastrin produced in the stomach (a hormone that regulates the digestion process), begin to work intensively, synthesizing calcitonin.
- Calcitonin, acting on bone tissue receptors (osteocytes), initiates the process of calcium absorption by it, activates osteoblasts and blocks osteoclasts.
- As a result, bone mineral density increases and the amount of calcium in the blood decreases to safe levels.
If necessary, under the influence of calcitonin, the kidneys join the process of calcium removal, absorbing more calcium from the blood, and the intestines temporarily stop absorbing this mineral.
This mechanism for regulating calcium levels protects the body from hypercalcemia - excess calcium:
- leading to disruptions in the functioning of internal organs;
- negatively affecting the functioning of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract;
- provoking the development of cardiovascular diseases.
After the calcium level drops to normal values, within a few minutes calcitonin breaks down into its components and is removed from the body. Normally, the more calcium enters the body, the more calcitonin is produced, and vice versa.
The role of substance
There are two main tasks of connection. The first concerns the actual regulation of certain processes in the body.
There are two types of bone cells found in the human body:
- Osteoblasts. They are, in fact, responsible for the normal synthesis of durable tissue. They play a major role in recovery, for example, after fractures. Promotes the formation of strong calluses and rapid regeneration.
- Osteoclasts. They work in reverse. Stimulate the destruction of bone tissue. They are especially active during the growth and development of the body in childhood and puberty. And during the course of their lives they remain a little less active.
Thyroid calcitonin is responsible for regulating the production of both cells, allowing us to maintain the very necessary balance so that bones grow, repair and do not collapse.
Without enough of it, the condition will deteriorate very quickly. It is quite difficult to cope with this pathology.
The development of osteoporosis is possible due to the rapid removal of the mineral component from the bone. And at any age. Although the disease is associated with old age.
The second and not so obvious function is artificial. In laboratory conditions, calcitonin testing can provide a lot of useful information.
For example, about the condition of the thyroid gland and some internal organs. This is not a specific indicator, but as a result it is possible to determine the vector for further diagnosis. Then you need to conduct an auxiliary examination to get a complete picture of what is happening.
If you do not go into complex biochemical details, the mechanisms of the influence of calcitonin and its work, we are talking about exactly the two named functions.
The substance also has other tasks.
To elaborate on these points:
- Strengthening bone tissue. Due to the synthesis of osteoblasts and the rapid growth of structures.
- Regulating mineral balance in the body. As a rule, substances leaving the bone are excreted into the bloodstream. Next, they need to be eliminated so that problems do not occur. For example, the deposition of calcium salts in the joints with low calcitonin leads to chondrocalcinosis. This condition is very similar to arthritis.
- Adequate body growth during childhood and puberty.
Indicator table is normal
The calcitonin norm in women and men is measured in pg per ml of blood, 1 pg = 10-12 g. The lower value of the normal level is considered to be 0.1 pg/ml. It is conditional and can temporarily decrease even to zero values.
More informatively, the value of the upper limit, which depends on age, gender, weight, and calcium level in the blood, is:
| Age | Norm pg/ml |
| Children under 12 years old | 20 |
| Women and girls over 13 years of age | 18,2 |
| Men and boys over 13 | 11,5 |
When we talk about calcitonin levels, we mean its concentration in blood taken on an empty stomach after fasting for 8-12 hours in people of normal weight. When calcium enters the body, this figure can increase several times, which is normal.
Pharmacology
Salmon calcitonin is used to treat conditions such as:
- Postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Hypercalcemia
- Paget's disease
- Bone metastases
- Phantom limb pain
The hormone calcitonin has also been investigated as a possible non-surgical treatment for spinal stenosis. Despite the knowledge available at the time of writing, many questions regarding nonsurgical treatments for spinal stenosis remain unresolved and therefore require clarification through further well-designed and carefully conducted randomized controlled trials.
General characteristics of the active substance
Salmon calcitonin is quickly absorbed and excreted from the body. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within the first hour of taking the drug. Animal studies have shown that calcitonin is primarily metabolized through proteolysis in the kidney after parenteral administration.
The metabolites do not have the specific biological activity of calcitonin. Bioavailability after subcutaneous and intramuscular administration in humans is high and is the same for the two routes of administration - 71% and 66%, respectively. Calcitonin has short absorption and elimination half-lives of 10-15 minutes and 50-80 minutes, respectively.
Salmon calcitonin is primarily and almost exclusively degraded in the kidneys, producing pharmacologically inactive fragments of the molecule. Thus, metabolic clearance is significantly lower in patients with end-stage renal disease than in healthy individuals. However, the clinical significance of this finding is unknown. Plasma protein binding ranges from 30% to 40%.
Subcutaneous injection of calcitonin
There is a relationship between subcutaneous calcitonin administration and peak plasma concentrations. Following parenteral administration of 100 IU calcitonin, peak plasma concentrations range from approximately 200 to 400 pg/ml. Higher blood levels may be associated with an increased incidence of nausea, vomiting, and secretory diarrhea.
Preclinical safety data
Traditional long-term toxicity, reproduction, mutagenicity and carcinogenicity studies have been performed in laboratory animals. Salmon calcitonin does not have embryotoxic, teratogenic or mutagenic effects.
An increased incidence of pituitary adenomas has been reported in rats treated with synthetic salmon calcitonin for 1 year. The studies concluded that this is considered a species-specific effect and has no clinical significance.
Salmon calcitonin does not cross the placental barrier. Suppression of milk production was observed in lactating animals treated with calcitonin. Calcitonin is excreted in milk.
Pharmaceutical production
Calcitonin has been extracted from the ultimobranchial glands (thyroid glands) of fish. Salmon calcitonin is similar to human calcitonin, but is more active.
Currently, it is obtained either using recombinant DNA technology or by chemical synthesis of peptides. It has been demonstrated that the pharmacological properties of synthetic and recombinant peptides are qualitatively and quantitatively equivalent.
Symptoms of increase and decrease
A significant persistent change in the concentration of calcitonin in the blood leads to disruption of the process of regulating calcium levels and can cause hypercalcemia.
Its first symptoms are gastrointestinal problems, manifested by:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- constant thirst;
- frequent urination.
In severe forms of hypercalcemia, the following are observed:
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- disorientation;
- coma.
With low calcium levels (hypocalcemia), the following are possible:
- tingling in the fingers, lips and tongue;
- breathing problems;
- muscle spasms;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- hypertension;
- general deterioration of health.
In children, hypocalcemia leads to rickets, in adults – to bone diseases.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
Increased or decreased calcitonin in women and men can be a physiological norm.
For example, its level:
- gradually decreases as one gets older;
- increases in women during pregnancy (2nd and 3rd trimesters);
- drops significantly in older people due to age-related changes in the thyroid gland.
Changes in calcitonin levels can also be caused by certain medications, for example, drugs containing this hormone, which are used in the treatment of diseases of bone tissue associated with a lack of calcium in it.
Pathologies that cause disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, as a result of which it begins to produce an excessive amount of hormone, include:
- medullary thyroid cancer. This is a rare form of cancer that develops in C cells. In the early stages of the disease, it manifests itself as pain in the neck, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness of voice, and causeless cough;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland not related to oncology;
- malignant tumors in the chest and internal organs: kidneys, stomach, liver, lungs, prostate;
- benign tumors localized in the lungs;
- kidney disease (renal failure);
- pancreatic adenoma;
- Addison-Biermer disease or pernicious anemia associated with a lack of vitamin B12;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis in the acute stage.
A persistent decrease in calcitonin levels is possible during the period of taking certain dosage forms, in particular, phenytoin (used for epilepsy) and ocreotide (a drug for the treatment of pancreatitis).
Low concentrations of this hormone can:
- indicate pathological changes in bone tissue (osteoparosis);
- talk about endocrine disorders (hypoparathyroidism);
- observed in patients who have undergone thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland).
Calcitonin is reduced
Calcitonin levels in the blood can reveal many things about cancer patients' health. This is one of those hormones that, even with a slight deviation from the norm, can indicate that health is in great danger. As a rule, oncological diseases are difficult to treat, therefore, it is very important to detect them in the initial stages. A decrease in calcitonin threatens serious problems, therefore, this particular analysis is used to make a diagnosis.
Low calcitonin: causes
A decrease in the level of calcitonin in the blood is not as common a problem as its increase. However, there are reasons for this, and if eliminated, the patient can be cured of the disease. The main reasons for the decrease in calcitonin are:
- The tissue is susceptible to swelling and does not synthesize the hormone, which leads to a level of decline that is directly proportional to the area of the affected tissue;
- Consequence of surgery on the thyroid gland, when part of it was removed;
- Consequences of taking medications that affect hormonal levels (the dose was exceeded);
- The tumor marker has not reached the required level to see diagnostic indicators.
What can low calcitonin lead to?
If the hormone level falls below the required norm, then the first signs of disease may already appear and it is necessary to begin their treatment as soon as possible. If calcitonin is below normal in women, problems may arise during pregnancy. In a normal state, it increases because the development of a new organism inside the body is required. The same applies to feeding a baby, but if at this time the level is low, then complications in the development of the child can lead to pathologies, as well as to a high probability of miscarriage. If calcitonin is low and parathyroid hormone is elevated, this may indicate secondary hyperparathyroidism.
When calcitonin is reduced, cretinism may develop. This disease is associated with an increase in other hormones and can lead to thyrotoxicosis. As a rule, when levels decrease, other thyroid hormones also suffer. When this part of the body ceases to function normally and does not work at full capacity, the body does not receive the hormones it requires. This in turn can lead to dementia. Like many other diseases in this area, they occur more often in women than in men.
Bones may become more fragile. For people who play sports and are more prone to injury than other people, this can be a very serious disadvantage. When understanding what low calcitonin means for them, it is worth highlighting two main points:
- Less resistance of bones to impacts, which can lead to frequent fractures;
- A weak level of recovery, since in a normal state, hormones are activated for bone fusion, whereas with a reduced level of calcitonin in an emergency, it can return to normal and will not give the desired effect.
Deterioration in health is only a symptom, while in fact everything can develop into a more serious nature. After all, this may be a sign of the development of more serious diseases, such as renal failure, primary osteoporosis or hypoparathyroidism. Deterioration in well-being manifests itself in decreased performance. A person gets tired quickly and cannot maintain a normal state throughout the day. In turn, frequent overwork and lack of adequate sleep can lead to a lack of the hormone.
It happens that calcitonin decreases a month after thyroid surgery. This is quite understandable if part of it was removed. When the tissue becomes smaller, the synthesis of the hormone decreases; this may be temporary, since the gland will recover over time and will work properly. But this often means that the level on its own will not return to its proper position and additional treatment will be required. For this, a recovery period is allocated, after which it will become clear how serious everything is.
How to increase calcitonin
For the most minor deviations from the norm, which sometimes happen to many people, a standard recovery procedure is also suitable, with normal sleep, good rest, and a diet with a high calcium content. Getting rid of fatigue will help you restore your health without medications or medications.
Instructions for use of calcitonin
At the same time, drug treatment is very effective and is very often used. Calcitonin is taken in tablets or by injection. Properly selected doses restore hormone levels. Other medications treat the source of the low levels. Surgery is required for large tumors. This happens in the most difficult cases.
Indications for the study
The normal calcitonin level in women and men is determined by laboratory tests.
They can be prescribed for:
- identifying the causes of calcium metabolism disorders;
- diagnosis of benign tumors capable of producing calcitonin;
- detection of medullary cancer.
Depending on the patient’s age, the analysis is prescribed by a therapist or pediatrician, as well as:
| Specialist | Indications for use |
| Surgeon |
|
| Endocrinologist | Suspicions of pathological processes in the thyroid or parathyroid glands, manifested by:
|
| Orthopedist |
|
| Oncologist | Detection of thyroid pathologies indicating malignancy:
The analysis is needed to confirm the diagnosis, as well as to assess the size of the tumor and determine the presence or absence of metastases |
Why increased
Increased levels of calcitonin are found in the following diseases:
- medullary cancer, when stimulated with pentagastrin, increases 10-25 times;
- hyperplasia of parafollicular cells - active division due to mutations, precedes benign and malignant tumors;
- calcitonin can also be produced by tumor cells of the blood, stomach, lungs, mammary glands, reproductive and pancreas;
- megaloblastic anemia;
- insufficiency of kidney and liver function;
- excessive production of hormones by the parathyroid glands;
- liver cirrhosis due to alcoholism;
- thyroiditis;
- pancreatitis;
- leukemia;
- pheochromocytoma;
- long-term chronic inflammatory processes.
For medullary cancer, the data obtained are used to determine the likelihood of tumor metastasis:
- up to 40 units – the likelihood of metastases is low;
- up to 400 units – there is short-range propagation;
- more than 400 units – increased risk of distant metastasis.
A decrease in the indicator does not have an independent diagnostic value, but it reflects the effectiveness of therapy and is regarded as a favorable sign of a tumor disease. Therefore, for C-cell tumors, calcitonin is considered a tumor marker and an indicator of the degree of cancer malignancy.
We recommend reading the article about autoimmune thyroiditis. From it you will learn about the causes of the development of autoimmune thyroiditis, the classification and stages of Hashimoto's goiter, as well as the symptoms of the pathology in adults and children, diagnostic methods, treatment of acute and chronic forms.
And here is more information about the disease and Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
Blood calcitonin is produced in the thyroid gland by parafollicular cells. Participates in calcium metabolism and maintaining bone density. Determination in the blood is prescribed if medullary cancer or its metastasis is suspected. The analysis is indicated for a rough estimate of the size, as well as after treatment of carcinoma to confirm the effectiveness of the operation.
The test is also prescribed to detect osteoporosis, low or high function of the parathyroid glands, and pancreatitis. Before diagnosis, preparation is needed. Interpretation of the data is carried out by an oncologist, endocrinologist, or therapist who referred for examination.
How to determine
Calcitonin (the norm in women and men is determined by analysis) can be determined by donating venous blood on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. The concentration of calcitonin is determined using a special device - an immunochemiluminescent or enzyme-linked immunosorbent analyzer.
The 3rd generation diagnostic devices are more advanced and provide minimal error. When using 2nd generation equipment, errors are possible, which leads to incorrect diagnosis and ineffective treatment. Therefore, when choosing a laboratory, you should find out what kind of equipment will be used.
In controversial cases, if there are symptoms of the disease but normal calcitonin levels, a provoking test can be performed. It consists of injecting the patient with calcium gluconate or pentagastrin (substances that provoke the release of calcitonin into the blood) by intravenous injection.
Calcitonin levels are measured before the procedure, as well as 3, 5 and 10 minutes after it. A provocative test is safe for the patient, gives more accurate results than a conventional analysis and allows you to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
What to do if the result is increased or decreased?
Elevated calcitonin often indicates serious health problems, therefore, if the analysis reveals such a deviation, you need to undergo additional examinations as soon as possible. Usually they are prescribed by a doctor, so there is no need to figure out on your own what to do and what not to do.
If the blood donated for analysis contains low calcitonin, the optimal solution is the same: seek the help of your attending physician to definitively establish the causes. Unlike cases when this indicator is elevated, reduced levels are much less likely to indicate serious problems.
Calcitonin in normal amounts in women indicates that the condition of the thyroid gland is good, and there is no reason to worry in this regard. If deviations are identified, you need to get tested, undergo an examination, find out the reasons and eliminate them.
Preparing and conducting analysis
A blood test for calcitonin will give a reliable result, provided that the rules of preparation for it are followed. The doctor is required to collect an anamnesis and find out whether the patient is taking medications that could distort the data obtained.
The patient will have the following:
- 10 days before the study, stop taking medications that can affect calcitonin levels;
- during the day preceding the test, refrain from drinking alcohol;
- on the last evening before the study, at least 8 hours before it, limit yourself to a light dinner of foods with minimal fat content. It is recommended to avoid fried foods;
- for 1-2 hours before donating blood, do not smoke, consume food or drink, except clean water. Refrain from actions that require a lot of physical effort, eliminate excitement and emotional stress;
- 15 minutes before the start of the examination, calm down and sit.
Before taking blood to determine calcitonin levels, you should not do the following:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- instrumental examinations;
- fluorography;
- Ultrasound;
- massage.
Any medical procedure can distort test results.
Due to the large number of restrictions, the test is scheduled for 8-11 am. Blood is taken from a vein and immediately frozen. Subsequently, serum is separated from the blood and examined using chemiluminescent immunoassay or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results are ready the next day.
After conservative or surgical treatment, the patient may be scheduled for re-examination to monitor the dynamics of changes.
In this case, the patient is offered:
- carry it out after completing the course of drug treatment. About 2 weeks should pass after the last dose of the medicine;
- donate blood for analysis every 3 months for a year after surgery to remove a malignant tumor, and then every six months for life. This is performed for timely diagnosis of disease relapse and the appearance of metastases.
Please note: the result of the analysis may be distorted if the requirements for preparation for it are not met.
For example, when:
- high physical activity preceding blood sampling;
- carrying out medical procedures before taking blood;
- treatment with drugs containing calcium;
- consuming large amounts of sweets shortly before sampling;
- taking estrogen-based medications.
Why do you need a provocative test?
A specific analysis provides more accurate results than an independent study of calcitonin levels. Additional components are needed for testing: pentagastrin or calcium gluconate.
The study is carried out if characteristic signs of progression of medullary cancer are identified, but the tumor marker has not yet been elevated to critical values. With an integrated approach, false positive and false negative results can be avoided.
How the test works:
- first, the patient donates blood for a standard test to determine calcitonin levels,
- the second stage is intravenous injection of an auxiliary substance for the active release of tumor markers,
- Blood sampling is repeated after 5-15 minutes. If the increase in calcitonin values is in the range from 30 to 90%, then oncopathology is not confirmed. With the development of medullary carcinoma, the deviation from the initial result ranges from 100 to 1000% or more.
Decoding the results
You can decipher the analysis result yourself.
Usually there are 4 columns on the form:
| Count | Decoding |
| Test name | Calcitonin |
| Result | For example, less than 2.0 |
| Units | Pg/mg |
| Reference values | Normal for a given age and gender. For example, 0.1-5.0 |
Calcitonin.
Normal Reference values largely depend on the equipment used and may vary significantly between laboratories. Therefore, if it is necessary to undergo several tests in order to determine the dynamics of changes, it is important to perform the procedure in the same institution.
By comparing the numbers in the 2nd and 4th columns, you can find out whether the calcitonin level is normal or too high/low.
Too high readings may mean:
| Calcitonin level (pg/mg) | Possible reason |
| Less than 40 | The presence of small nodes in the thyroid gland that do not metastasize |
| 100 | Malignant tumor of the thyroid gland |
| Less than 400 | Low probability of metastases |
| More than 400 | High probability of metastases |
| About 60 | The body's reaction to taking medications, eating food, etc. |
Forecast
Donating blood to detect calcitonin levels helps in early detection and determining the correct treatment of the disease. It is dangerous to refuse this analysis if you suspect the development of cancer. The prognosis may worsen if the patient does not accurately identify the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
While having your blood drawn can be unpleasant, and some lab technicians leave bruises, it's still better to take care of your health rather than avoiding anything that scares you. This will help prolong life and cure the disease in time.
When to see a doctor
The obtained analysis result is not the basis for making a diagnosis, since the method for determining calcitonin levels is not perfect enough, as a result of which errors are possible. In addition, various factors can influence the concentration of the hormone in the blood. For example, anxiety or taking a test in the middle of the day.
However, if the test results show a multiple excess of calcitonin levels, it is necessary to consult a doctor to conduct further research to determine the cause, make a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Consultation with a specialist is urgently required if, despite a nutritious diet, high levels of calcitonin are accompanied by symptoms that may indicate hypo- or hypercalcemia.
This:
- fragility of bone tissue, frequent fractures of limbs;
- joint pain;
- frequent muscle spasms;
- tingling sensation in fingers and feet;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- gastrointestinal problems, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
An immediate visit to a doctor is necessary for any signs of the development of medullary cancer, which, in addition to a multiple increase in the concentration of calcitonin in the blood, is indicated by:
- sore throat not associated with a cold;
- difficulty swallowing;
- the presence of subcutaneous seals in the neck area, which can be easily detected independently.
Medullary cancer is a rare form of cancer (it accounts for 5-6% of all thyroid cancers), develops extremely slowly, is easily diagnosed, but is dangerous because it can metastasize in the early stages. The earlier the pathology is detected, the higher the patient’s chances of successful treatment.
Blood test for calcitonin
The concentration of calcitonin can now be determined in many laboratories, which use various equipment for this purpose. The most reliable information about the content of this hormone can be obtained using 3rd generation analyzers based on the immunochemiluminescent method. More common 2nd generation analyzers using enzyme immunoassay methods are cheaper, but have a serious drawback - a significant error in the result. Their use may lead to inaccuracies in the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of patients.
A very dangerous malignant tumor, C-cell carcinoma, or medullary cancer, can develop from the C-cells of thyroid follicles. A feature of this tumor is its relatively slow but steady growth. Over time, medullary cancer metastasizes to the lymph nodes located in the neck and mediastinum; through the bloodstream, metastases can also reach the lungs, liver, bones and even the brain. Treatment of C-cell carcinoma presents significant difficulties, since the tumor does not respond to antitumor chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy. Only antitumor agents based on kinase inhibitors can have a minor effect on C-cell carcinoma. The only effective treatment for this type of cancer is surgery in the early stages of the process. This is the only way that gives a chance for recovery if cancer is diagnosed early.
Since C-cell carcinoma grows from cells that secrete calcitonin, its content in the blood increases sharply already in the early stages of cancer. This is why the content of this hormone is of such interest to endocrinologists and surgeons. Calcitonin concentration testing is the most reliable and early method for determining medullary cancer, which allows saving more than one thousand human lives.
Every year, approximately 100-150 new cases of C-cell thyroid carcinoma are registered throughout Russia. Statistical studies have shown that in 16 densely populated regions of the European part of Russia, about 40 diagnoses of medullary cancer are made per year.
Among all cases of thyroid tumors, the most dangerous are the anaplastic and medullary forms. While effective treatment methods have not yet been developed for anaplastic cancer, C-cell carcinoma is completely curable if diagnosed early. And only a blood test for calcitonin can help with this.
In 2012, the European Thyroid Association added to its recommendations an indication of the need for a single determination of calcitonin in all patients with nodules in the thyroid gland. This analysis does not have to be performed every year; a repeat study in the case of the first normal result is prescribed only if new nodes have been registered.
This fact has led the European endocrine community to believe that the financial costs of conducting 300 studies will be justified if at least one of them reveals the presence of medullary cancer. At the same time, the American Thyroid Association still believes that such a massive scale of calcitonin research is not economically justified. This concerns only the financial part of the issue; no one doubts the clinical value of this method.
How to get it back to normal
Calcitonin is normal in women and men - this is only an indicator of how properly the thyroid gland is working. There is no point in treating him. If the levels are high, it is necessary to find the cause and cure the disease that caused the increase/decrease in the concentration of the hormone in the blood.
Depending on the type and severity of the disease, conservative or surgical methods are used for treatment
Medications
In the treatment of kidney diseases (renal failure), leading to an increase in calcitonin levels, the following drugs are used:
- diuretics that facilitate urine output (furosimed, uregid);
- eliminating excess phosphates in the blood (selamerex);
- saturating the body with the amino acids it needs (ketoaminol, ketosteril);
- accelerating metabolism (cocarbaxylase);
- enterosorbents (polyphepan);
- choleretic (chophytol).
For prostate adenoma, one of the symptoms of which is a high level of calcitonin, the following drugs are prescribed:
- preventing its growth (terazonin, doxazoline);
- blocking the production of substances that promote the development of adenoma (finasteride, dutasteride).
For pernicious anemia, which can be diagnosed based on the results of blood tests for calcitonin, the following are indicated:
- vitamin B12 injections;
- drugs that normalize the process of its absorption;
- medications that eliminate metabolic disorders.
There are a number of calcitonin-based drugs that increase its concentration in the blood.
Applicable:
- for hypercalcemia as a means of normalizing calcium levels;
- for diseases leading to bone thinning (osteoporosis) to initiate the process of mineralization and strengthening of bone tissue;
- as a prevention of degenerative bone changes during postmenopausal women.
In the list of drugs:
- Miacalcic;
- Calcitonin;
- Osteobion;
- Osteobios;
- Endocalcin
- Bonefos;
- Ostogenone.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods will help normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland and calcitonin levels, however, they should be used after consulting a doctor. It should also be taken into account that they are not always applicable: in case of severe diseases (oncology), traditional methods can only be used as an aid.
For the health of the thyroid gland and the prevention of its diseases, traditional medicine recommends:
- Grind the lemon or orange along with the zest and mix with sugar. Eat 1 teaspoon three times a day;
- drink 20 drops of liquid hawthorn extract three times a day on an empty stomach;
- prepare a rosehip decoction and drink 0.5 tbsp. before each meal;
- prepare a mixture of 1 tbsp. l. licorice root and 2 tbsp. l. madder root, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over it, leave. Drink a glass every morning.
- eat more fresh leafy greens and chokeberries.
Also remember that the main enemies of the thyroid gland are:
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- iodine deficiency;
- constant stress;
- overwork;
- lack of sleep;
- excessive use of drugs.
If these factors are not excluded, any treatment methods will not give a positive result.
Other methods
If the increase in calcitonin levels is caused by a developing medullary tumor (carcinoma), then the main form of treatment is surgery. Depending on the severity of the disease, surgical removal of the tumor and nearby tissues is performed, or in later stages of the disease and with large sizes of carcinoma, thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland).
Treatment with radioactive iodine
It is performed 4 weeks after surgery to permanently remove the remaining malignant tissue. The principle of treatment is based on the fact that radioactive iodine is absorbed mainly by the thyroid gland and destroys its tissue without causing harm to other organs.
Hormone therapy
Taking hormonal drugs (thyroxine) to compensate for their deficiency after removal of the gland.
External irradiation
Exposure of cancer cells to hard x-ray radiation. Unlike healthy tissue, tumor cells are more vulnerable and die faster, while healthy cells damaged during the procedure are restored over time.
Irradiation can be performed:
- before surgery to reduce the size of the area affected by the tumor;
- after surgery to destroy remaining malignant tumors;
- for inoperable forms of cancer to slow down the development of the tumor and alleviate the patient's condition.
Chemotherapy
Introduction into the body by drop method or in the form of tablets of poisons that destroy cancer cells and are relatively safe for healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy can be carried out:
- as a therapeutic procedure, replacing surgery in the early stages of the disease;
- to reduce tumor size before surgery;
- for complete elimination of tumor fragments after surgery;
- to prevent relapse of the disease.
What the analysis shows
A wealth of information can be obtained from the results of the study. As a rule, the procedure is prescribed to assess the condition of the body for potential disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Analysis shows:
- Osteoporosis. A dangerous disease that increases bone fragility. This is the result of calcium and minerals being removed from anatomical structures.
- How quickly a person recovers from an injury, how does treatment work.
- Calcitonin analysis shows how the thyroid gland reacts to the manipulations performed. Most often we are talking about surgical interventions. For example, regarding cancer or large nodes, diffuse growth (goiter).
- Metabolic disorders. Those related to the balance of minerals in the body. For example, when calcium is not processed enough.
- It also makes sense to take a calcitonin test if you have increased bone fragility. If injury occurs. It is rather a technique for assessing the causes and identifying the origin of the problem.
A sample list would look like this. It is not complete, but reflects the overall picture.
Possible complications
Since calcitonin is a tumor marker for the most dangerous form of cancer, by ignoring the test result showing a multiple excess of its concentration, you can miss the time when the disease can be treated with gentle methods, without removing the thyroid gland.
Calcitonin is a hormone produced by special cells of the thyroid gland. Its main role is to maintain normal calcium levels in the body of a woman, man or child.
In addition, in modern medicine it is considered a tumor marker for the most dangerous type of cancer - medullary thyroid carcinoma. Also, the concentration of calcitonin in the blood can be used to judge the presence of other diseases of bone tissue and internal organs.