A group of small arachnids, close to insects, there are about fifty thousand species in the world.
A tick can be distinguished from an ordinary insect by the following characteristics:
- Insects have three pairs of legs, and the arachnid parasite has four.
- The head and chest of the tick are fused into one system - the cephalothorax.
general information
If we talk about the period when parasites are most dangerous, then it should be said that the danger of an attack by an infected individual is present in any spring, summer and autumn. There are periods when they are most active and aggressive. The first such period begins in early spring, when they, waking up from hibernation, are very hungry and are looking for victims to satiate. The second period begins in the fall, when they need saturation before a long winter sleep.
These bloodsucking creatures do not tolerate direct sunlight, and dry and hot weather is not favorable for them. For this reason, they wait for their victims on leaves in dense grass or on bushes that are located in shaded areas. They cling to the victim with their paws, which have microscopic hooks and suction cups. You can see what the parasite looks like in the photo.
Once on clothing, they begin to seek access to the body, and then choose the most suitable place to bite, where the skin is thin and soft. The attached parasite can most often be found in the neck, behind the ears, on the elbows, armpits, and groin area. A person cannot feel a tick bite because an anesthetic substance is released during its application.
Not all individuals are infected and carry the risk of contracting diseases, but at the same time, up to 90% of uninfected ticks can provoke severe allergic reactions. There is a difference between the process of saturation with blood of females and males.
It takes an hour for a male to satisfy his hunger; he quickly becomes satisfied and falls off the body; for this reason, a person may not even know that he has been attacked by a parasite. Females attach themselves to the victim's body for several days; they require a large amount of food so that they can lay offspring.
Cautions
There are a number of precautionary measures that, when followed, can help prevent negative consequences:
- During trips to nature, you can use special preparations and products designed to combat ticks. However, before using them, you must carefully read the instructions, since some of them are intended for external application to the skin, while others are strictly prohibited from being used in this way.
- For long-term stops or outdoor recreation, it is better to choose forests consisting mostly of dry pine trees, as well as places with sandy soil or simply no grass.
- Donate blood for analysis after a bite only after a few weeks , since at an earlier period the diseases carried by these parasites cannot be diagnosed.
- Under no circumstances should you crush ticks or touch them with your bare hands.
Attack and bite
These small parasites have a well-developed oral apparatus with a hypostome, with the help of which they gnaw through the skin. The oral apparatus has microscopic growths, which in structure resemble a harpoon, which allows them to be firmly held in the wound when saturated.
Infected individuals are capable of transmitting the disease virus to humans within the first minutes of a bite. If an individual is a carrier of encephalitis, the virus is transmitted through the saliva of the tick. Even if the sucking individual is discovered immediately after it has attached itself to the body and is quickly removed, there is a risk of infection.
The Lyme disease virus is found in the insect's gastrointestinal tract, so every minute counts. The parasite can share gastrointestinal tract products with a person as early as 5-6 hours into the saturation process. The likelihood of viral infection increases significantly when the parasite is not removed from the wound correctly.
If the skin turns red at the site of an insect attack, you should not draw premature conclusions and think that an infection has occurred. Symptoms do not appear immediately, and redness and irritation are an allergic reaction to the bite.
Obvious external symptoms are observed with borreliosis, when focal erythema appears in the place where the tick was sucked, which has a regular round shape and a red border. After a day, the erythema becomes pale and acquires a bluish tint, scarring appears, as a rule, after 10-14 days it completely disappears.
The earlier the better!
A tick bite is a Russian roulette with health: although the chances of getting sick are not too high, neither you nor the doctors will be able to assess them right away. Before two weeks from the moment of the bite, your tests will not show whether infection has occurred or not, and when they do, it will mean that the disease has already developed. At the same time, encephalitis and borreliosis are extremely serious diseases, fraught with both immediate and long-term consequences for the body. The sooner preventive treatment of borreliosis is started or emergency immunoprophylaxis of tick-borne encephalitis is carried out, the higher the chances of maintaining your health.
Signs of an attack
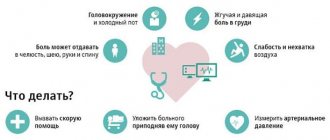
The first signs may appear several hours after the bloodsucking attack. Each person's symptoms manifest themselves individually; some may not feel any changes at all. You may experience weakness and fatigue, increased body temperature and chills, and photophobia.
Vivid symptoms are most often observed in older people, children, and also in those who suffer from immunodeficiency pathologies or allergies. Itching, headache, decreased blood pressure, and enlarged lymph nodes may appear. In severe cases, breathing problems appear, in rare cases, hallucinations are observed.
Remember that all the symptoms that occur immediately after an attack do not indicate the presence of an infection in the body; they arise, as a rule, due to the body’s reaction to the parasite’s saliva. Symptoms should be feared if they appear some time after the attack occurred. Since the virus that has entered the body goes through an incubation period and does not manifest itself at first, only after this period do signs and symptoms of the disease appear.
What happens to a tick when it drinks blood?
The tick sucks blood for several reasons - to continue development, replenish reserves, lay eggs. The larvae live in the soil where they developed into eggs. They wait for the victim to drink blood. Most often these are rodents, reptiles, and amphibians. At the end of the meal, it falls to the ground, molts, and turns into a nymph. To move to the next stage of development, blood is again needed.
Tick drunk on blood
A fertilized female will not be able to lay eggs until a sufficient amount of blood enters her body. During the feeding process, her body inflates, increasing to 1-2 cm. The female becomes clumsy and vulnerable. The main goal of a fed female is to get to the ground and lay eggs.
Does the tick die after it drinks blood - the male yes, the female not immediately - as soon as she completes her mission of laying eggs. The adult does not bite again.
What to do if you find a parasite on your body
It is quite easy to identify and recognize a blood-sucking insect that has burrowed into the skin and cannot be confused with other insects. If the female has been on the body for a long time, she increases significantly in size and resembles a small pea.
A tick embedded in the skin carries the risk of infection, so it must be removed from the wound as quickly as possible. It would be correct to go to a medical institution to carry out such a procedure, but if this is not possible, you can do it yourself at home.
It is very important to carry out the procedure correctly so as not to damage the blood-sucking. An incorrect procedure significantly increases the likelihood of infection. For the removal procedure, you can use special devices that are sold in pharmacies, or you can make do with improvised means.
Remember that the procedure must be carried out with rubber gloves; if you don’t have them, you can take a bandage and wrap your fingers. You also need to prepare a disinfectant; you can use iodine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green or any alcohol disinfectants. Prepare any container in which the removed tick will be placed; a regular jar will do.
Thread
It’s worth saying right away that this method is not the easiest; it will require endurance and patience. It is not suitable for extracting small individuals, since it will be quite difficult to fix the thread itself on them.
The procedure is carried out as follows: you need to take a thread and make a loop that is put on the insect. It is very important to fix the loop in such a way that the head of the insect is captured, and not just the abdomen. If you grab only the abdomen, you can easily tear the blood-sucking animal.
When the loop is fixed, you need to start unscrewing it with careful movements, without using force; you can use rocking movements from side to side. You cannot pull it out of the wound and make sudden movements.
When the insect is removed, it must be placed in a prepared container and submitted to the laboratory. The laboratory will conduct the necessary tests to show whether the individual is infected. The wound must be disinfected and, if possible, sealed with an adhesive plaster so that bacteria and germs do not enter the wound.
Tweezers
Using tweezers, you can remove large and small individuals from the wound, the main thing is to follow the same rules as in the previous version. You cannot use force, pull or crush the insect too much; you must carry out the procedure as carefully as possible so as not to damage the body or tear it.
It is necessary to grab the bloodsucking as close to the skin as possible in order to hold it by the abdomen and head. Next, use the same technique of twisting out of the wound as in the case of thread.
During the procedure, the tweezers must be held straight, perpendicular to the skin. After removal, disinfect the wound and cover it with adhesive tape. The seized insect should also be placed in a container and submitted to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Twisters
As mentioned earlier, in pharmacies you can purchase special devices that make it possible to carry out the procedure independently, and most importantly, safely. They are available for sale in different versions.
There are special kits that contain twisters of different sizes for removing large and small parasites. The kit also includes a test tube in which the tick is placed.
other methods
There are different situations, and no exception is when the necessary equipment for the procedure is not at hand. Then you can try to remove it with your hands, but this method is quite dangerous.
It will be quite difficult to correctly grab the bloodsucking and calculate the force with which it can be removed without suffocating it. The technique is the same as in previous cases. Hands must be wrapped in a bandage or cloth, which will protect against infection and help hold the tick so that it does not slip out.
Regarding such methods, when the insect is watered with oil, kerosene or other oily substances, such methods are not recommended, since they are the most dangerous.
The fact is that the parasite stops receiving a sufficient amount of air, it experiences stress, and at the same time secretes a large amount of saliva and gastrointestinal products, which contain the virus. In addition, in such a situation it can begin to go deeper into the wound. Even if you manage to pull out an individual, this method significantly increases the risk of infection.
When blood-sucking insects are attached to an arm, leg, or stomach, you can cope with the removal procedure on your own, but in hard-to-reach places you will need help, and it is better if it is a medical facility. After removal, the doctor will give recommendations on next steps.
Situations are possible when, during an independent procedure, a fragment of the parasite remains in the wound. It must be taken out, otherwise inflammation and rotting of the wound will begin. You can use a needle and try to pull the fragment out, as with a splinter, but if it is too deep in the wound, medical attention will be required.
Actions after removal
As already mentioned, the bite itself is quite dangerous for people who suffer from allergic reactions. During an attack, a severe form of allergy may develop, in which swelling of the face, muscle pain, and difficulty breathing appear.
If the body reacts in this way, it is necessary to take an antihistamine. Such drugs include Suprastin, Zyrtec, Claritin. It is necessary to ensure that the victim has normal air access and unfasten the top buttons of his clothes. Be sure to call an ambulance; the patient will be prescribed treatment in the hospital.
Features of vaccination against encephalitis
Protect yourself from tick-borne diseases by getting vaccinated. Only healthy people who have previously been examined by a therapist are allowed to see it. He will inform the patient where exactly he can get vaccinated against tick-borne infections.
Vaccination
Preventive vaccines against encephalitis are represented by the following types of drugs:
- EnceVir;
- Encepur for adults;
- Children's Encepur;
- Cultured viral vaccine, presented in the form of purified dry inactivated concentrate.
Laboratory research on ticks
If you manage to remove a live parasite, you can put it in a jar and place it in the refrigerator for a day. It is advisable to submit it to the laboratory no later than 24 hours later.
Once the parasite has been crushed or torn apart, it can be placed in ice. At the clinic you can find out the addresses of laboratories that accept insects for research.
Dangerous diseases
An infected parasite is capable of transmitting diseases such as encephalitis, Lyme disease, zoonotic infections, all of which have serious consequences and, without timely and proper treatment, can lead to disability and, in rare cases, death.
Tick-borne encephalitis
- The carriers of the virus are ixodid ticks, which receive infection from small animals, rodents, and birds. The infection can also be transmitted to offspring from an infected female. There are known cases when human infections occurred from cow's and goat's milk, from livestock that were attacked by infected individuals.
- Quite often the disease is asymptomatic. The virus may not be transmitted from a blood-sucking person, but the longer it remains on the human body, the greater the likelihood of infection. At a temperature of 80°C, the virus dies, but it withstands low temperatures very well. Statistics show that people become infected more often in May and June, as well as in August and September.
- When the virus enters the human body, it penetrates the central nervous system within several hours. Over the course of 2 days, it penetrates into the brain tissue. If infection occurs through the saliva of a blood-sucking animal, the incubation period is 14-21 days, but if it is eaten through food (milk), it is about a week.
- Only 5% of victims have clear symptoms of infection; in other cases, the disease is asymptomatic. Symptoms are manifested by an increase in body temperature to 40°C, headaches, nausea, diarrhea, weakness, drowsiness, and body aches. With such symptoms, the disease goes through a febrile form, and after 5 days they disappear. This form passes without affecting the central nervous system.
- There are also meningoencephalitic and meningeal forms, which are classified as severe. In this case, the patient experiences drowsiness, apathy, delirium, and hallucinations. Convulsions and epilepsy appear. Without treatment, the meningoencephalitic form can be fatal.
Lyme disease
When the virus enters the human body, it can remain there without manifesting itself in any way for several years. The main sign of infection is the appearance of ring erythema on the skin at the site of the bite.
This redness, which can be 20-50 cm in diameter, has a clear red outline. Symptoms also include fever, weakness, headaches, and apathy. Even if this ring disappears and the person does not experience any signs of illness, be sure to consult a doctor and undergo the appropriate tests.
This virus affects the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, visual organs, muscles and joints. If there is no treatment, the disease leads to disability.
Ehrlichiosis
The main carriers of the disease are deer, but it can also be infected from intermediate carriers, which are horses and dogs. Regarding the incubation period, it is about 3 weeks, the duration of the acute form is from 2 to 3 weeks, in rare cases it lasts up to 8 weeks.
The disease may be completely asymptomatic or, on the contrary, have pronounced symptoms, which include weakness, fever, rapid heartbeat, nausea, and drowsiness. May be fatal.
Relapsing tick-borne typhus
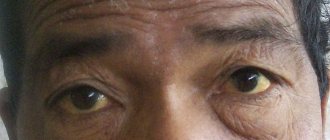
With this disease, a small blister appears at the site of the bite, followed by headache, joint pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting. The bubble turns red, after which a rash appears on the skin. The victim's skin becomes yellow, the liver increases in size, and the proteins also become yellow.
In this case, the symptoms appear several times, the acute form lasts 3-5 days, after which the patient’s condition returns to normal, and then everything repeats. There can be quite a lot of such repetitions, each subsequent one occurring in a milder form.
Coxiellosis
The carriers of this disease are ticks, but the carriers are wild animals and farm animals. 5-30 days after the infection enters the body, symptoms begin to appear, which include decreased appetite, dry cough, increased sweating, increased body temperature, headache, severe weakness, redness of the skin in the upper body and face.
Fluctuations in body temperature are quite common and can occur several times a day. Pains in the muscles and lower back may also appear, and pneumonia may develop. Complications occur only in rare cases. The disease is easy to treat.
Chemicals for home control
Effective extermination of pests in residential areas is possible with the help of highly active chemicals. A powerful effect on ticks repels or kills them, preventing re-invasion.
Bedlam Plus
Bedlam Plus is produced in aerosol form and is intended to combat ticks and their eggs, fleas, beetles, bedbugs and other harmful insects in residential areas. The substance can be used to treat bedding, carpets, upholstery and toys. The required surface is sprayed with an aerosol and then left for a couple of hours. After using Bedlam Plus, you should wash the treated product.
Acaril
Acaril is a component added during washing of textile materials. The product contains a mixture of alcohols, surfactants and tea tree oil in a suspension of methyl salicylate. The purpose of Acaril is to eliminate dust mites and combat allergens. The substance is safe for colored fabrics and produces results when washed in water of any temperature.
All-Rug
Highly concentrated All-Rug shampoo is suitable for treating carpets, upholstered furniture, mattresses and bedding. The product can be added to a washing vacuum cleaner. The main advantages of All-Rug include the following:
- slight foaming;
- anti-mite purpose;
- the ability to clean pile, eliminate insect allergens and prevent the proliferation of pests.
X-mite
X-mite powder is used to kill allergens caused by dust mites, pets and various pests. The optimal frequency of processing bedding, carpets and upholstery is once every 3-4 months.
Allergoff
Allergoff is available in a form designed to spray a surface up to 20 square meters in size. The aerosol ensures the destruction of dust mites at all stages of their spread. After treatment, the effect lasts for six months. Spraying with Allergoff spray must be combined with treatment with an anti-allergenic drug.
Treatment of victims
Treatment directly depends on the disease itself and the stage of development. There are no specific treatments for encephalitis. If there are signs of damage to the central nervous system, the person must be hospitalized. Bed rest is observed, therapy includes the administration of immunoglobulin.
Corticosteroid drugs are also used in treatment; if meningitis is observed, vitamins B and C are administered in increased doses. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed.
For borreliosis (Lyme disease), treatment occurs with the use of antibiotics that suppress the causative agent of the disease. If the disease is accompanied by disorders associated with neuralgia, the patient is hospitalized and treated with blood substitutes, corticosteroids, nootropic drugs and vitamin complexes.
The earlier the diagnosis is made and the correct treatment is used, the easier it is to cope with the virus without complications; severe forms and lack of timely treatment lead to disability and even death.
Where to go?
If you experience: general weakness, malaise, weakness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity in any part of the body, mood disturbance, after receiving a tick bite, you must contact a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital in order to exclude the occurrence of the disease and prevent the development of complications.
At the Yusupov Hospital, you will undergo a comprehensive examination that will identify a possible disease associated with a tick bite and select the necessary antibacterial or immune therapy, as well as offer an effective rehabilitation program.
Complications
Infectious diseases that are transmitted through the bite of a blood-sucking animal can cause very serious complications. The virus that enters the body affects the central nervous system, lungs, cardiovascular system, liver, and joints. This leads to the development of pneumonia, migraines, arthritis, digestive system disorders, surges in blood pressure, hallucinations, and paralysis of the limbs.
When the correct treatment is used at an early stage, a person loses working capacity for 2-3 months, then all functions are restored. If the disease has progressed to a moderate stage, treatment lasts about six months, and in case of a severe form, if there are no complications in the form of paralysis, the recovery period will take up to 3 years.
Preventive actions
The main and most effective preventive measure that helps prevent the disease is vaccination. In regions where there is an increased risk of infection, vaccination is recommended for residents. It is carried out in medical institutions, vaccination is allowed from an early age. Vaccination can be preventive, which allows you to protect yourself from infection throughout the year.
Next, another vaccination is carried out, and subsequent ones after 3 years. There is also emergency vaccination, which is intended for people who are going to visit a dangerous region. It works for a short time.
Do not forget that everyone can independently reduce the risk of a tick attack. To do this, you need to choose the right clothes and inspect them as often as possible for the presence of insects. It is better if it is in light colors.
Pants should be tucked into socks, and a jacket into pants. Choose a sweater that has cuffs and a collar that fit tightly to the body, this will minimize the likelihood of the parasite entering the body.
Avoid shaded areas, thick grass and thickets; for a picnic, stop in sunny open areas. Now there is a huge range of insecticidal products that can be used as protection against blood-sucking insects.
They are applied to clothing and skin, but remember that they have a fairly short duration of action and the protective layer must be regularly renewed. More effective means include acaricides, but they can only be used on clothing; when using, follow the instructions for use.
The earlier the better!
A tick bite is a Russian roulette with health: although the chances of getting sick are not too high, neither you nor the doctors will be able to assess them right away. Before two weeks from the moment of the bite, your tests will not show whether infection has occurred or not, and when they do, it will mean that the disease has already developed. At the same time, encephalitis and borreliosis are extremely serious diseases, fraught with both immediate and long-term consequences for the body. The sooner preventive treatment of borreliosis is started or emergency immunoprophylaxis of tick-borne encephalitis is carried out, the higher the chances of maintaining your health.