Myocardial infarction, a serious disease with high mortality, does not occur spontaneously. It is usually preceded by the development of coronary heart disease, the main cause of which is atherosclerosis.
A pre-infarction condition is an acute insufficiency of blood supply to the heart muscle, not accompanied by the death of myocardial cells. In the medical community, this disease is called unstable angina; in the absence of adequate medical care, it can lead to myocardial infarction.
Let's consider the main reasons for the development of a pre-infarction state, symptoms, features of diagnosis and treatment, and prognosis.
Pathogenesis
The prodromal period, a precursor to the development of myocardial infarction, lasts from several minutes to several days, and various symptoms can occur at different periods separately. The absence of trophism, its deterioration due to impaired blood flow due to narrowing ( stenosis ) or blockage of the coronary vessels lead to ischemia and tissue necrosis, ventricular fibrillation. As a result, acute coronary insufficiency , provoked by a violation of oxidative processes in the myocardium, in addition, there is an excessive accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products, including lactic, pyruvic, carbonic, phosphoric acid, etc.
A heart attack can even begin suddenly, for no apparent reason - exercise or stress. It does not go away even after rest; the patient still experiences compressive pain in the chest. This condition can lead to loss of consciousness and even cardiac arrest.
Features of treatment
Timely, adequate medical care can significantly reduce the risk of developing myocardial infarction. Therefore, when the first signs occur, you need to call a doctor and provide first aid to the person.
It is strictly not recommended to resort to traditional methods of stabilizing the condition. After all, if a heart attack is hidden behind the symptoms of angina, hospitalization should be carried out no later than 6 hours from the onset of pain. Later introduction of some drugs is already useless.
Treatment tactics for pre-infarction conditions depend on the patient’s condition and the likelihood of a heart attack. Most people are advised to take medications (conservative therapy), and if there is a high risk of heart attack, surgery is recommended. After stabilization of the patient’s condition, a diet is prescribed and recommendations are given for lifestyle changes.
First aid
If an angina attack lasts longer than usual, and the pain is more severe, call a doctor immediately. Before the ambulance arrives you need to:
- open the window, balcony;
- sit or lie down so that your head is significantly higher than your body;
- unbutton the collar;
- try not to move;
- take an aspirin tablet;
- put nitroglycerin under your tongue. It is allowed to take up to 3 tablets with an interval of 5-10 minutes;
- no smoking.
Medications
The purpose of drug treatment of unstable angina is:
- decreased oxygen demand of the heart;
- improving the supply of oxygen to the myocardium;
- prevention of possible complications (arrhythmias, myocardial infarction).
To achieve these goals, the patient is prescribed medications that belong to various pharmacological groups.
Antiplatelet drugs
They prevent the formation of new blood clots, help prevent the development of myocardial infarction, and reduce mortality. The most famous representative of the group is aspirin. It has been proven that taking it reduces the likelihood of a heart attack, the risk of death, by almost 50% (4). Another first choice drug is heparin. Its use also significantly reduces the risk of death.
After relative stabilization of the patient’s condition, the drugs ticlopidine or Plavix are prescribed. They are also used for aspirin intolerance as first choice drugs.
Nitrates
They reduce the tension of the myocardial wall, the oxygen demand of the heart, and dilate large and small coronary vessels. Nitrates are considered the best medicines for eliminating angular pain. The first aid drug is nitroglycerin. It is given to relieve the acute phase of the disease. For long-term treatment, other drugs with a prolonged effect are used - isosorbide, nitrosorbide. There must be a break of at least 8 hours/day between the use of nitrates. Otherwise, the body gets used to them and stops responding to the introduction.
Beta blockers
They reduce the frequency and strength of heart contractions and inhibit cardiac conduction. The nature of the heart's work becomes more gentle, it begins to consume less oxygen. The drugs also reduce the tension of the myocardial wall, which promotes blood redistribution. Beta blockers lower blood pressure and prevent platelet aggregation. In the treatment of unstable angina, selective drugs are used: atenolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol, nebivolol.
Calcium channel blockers
Calcium antagonists prevent the mineral from penetrating into the muscle cell. This ensures a decrease in the frequency and strength of heart contractions, and the opening of spasmodic arteries of the heart. As a result, the oxygen demand of heart cells decreases and blood flow improves. Blood pressure decreases with the use of calcium channel blockers. The main representatives are verapamil, diltiazem.
ACE inhibitors (ACEIs)
Helps lower blood pressure and improve blood supply to the myocardium. If ACE inhibitors are prescribed together with nitro drugs, they enhance their effect. The most commonly used drugs are ramipril and perindopril. Taking them helps reduce the likelihood of death, major myocardial infarction, and cardiac arrest by 20%.
Lipid-lowering drugs
Prescribed to reduce the level of bad cholesterol, triglycerides, and increase the concentration of good cholesterol. Most often, people with a pre-heart attack are prescribed statins. The main representatives of the group are atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin. These drugs do not work immediately. A pronounced effect is observed after 30 days. However, their use improves the prognosis, especially long-term.
If lipid levels are poorly normalized during the use of statins, the treatment regimen is supplemented with lipid-lowering drugs of other groups: cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, fibrates.
Surgery
The purpose of surgical intervention in a pre-infarction condition is to restore the patency of the heart vessels. There are two options for the procedure:
Stenting procedure.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting is a complex operation that is performed on an open heart. Using a vessel taken from another part of the patient's body, the surgeon creates a bypass for blood flow, sewing one end above and the other below the narrowing site.
- Stenting is a low-traumatic procedure that does not involve cutting into the chest cavity. The surgeon inserts a catheter with a deflated balloon at the end into a large vessel. Under computer control, he guides the catheter to the area of narrowing. Having reached it, he pumps and deflates the balloon several times. Gradually, the lumen of the vessel expands. To consolidate the result, a stent is delivered to the site of narrowing - a frame that, when expanded, will keep the artery “open”.
Diet, lifestyle changes
Regardless of the treatment method, all patients are prescribed a diet that reduces the likelihood of complications, and a lifestyle review is also recommended.
Proper nutrition involves limiting the intake of salt, cholesterol, and saturated fat. The basis of the diet should be cereals, vegetables, fruits, fish, low-fat dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Eating fast food, red meat, egg yolks, fatty dairy products, and sweets should be avoided.
Our lifestyle largely determines the likelihood of developing angina attacks and other cardiovascular diseases. To reduce the risk it is recommended:
- quit smoking;
- move more, if your health allows, there are no contraindications - play sports;
- exercise moderation in alcohol consumption;
- control stress levels;
- maintain a healthy weight;
- monitor blood pressure;
- treat diabetes mellitus.
All of the above tips are effective for preventing cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, they are recommended for all people, not just those who have experienced an attack of unstable angina.
Causes
The occurrence of a pre-infarction state is facilitated by:
- general disorders of the circulatory system caused by heart failure , which lead to blood stagnation, accumulation of large amounts of carbon dioxide, tissue hypoxia, acidosis, changes in blood pressure , heart rate;
- atherosclerosis of the arteries and other diseases that cause thickening of the intima of the arteries;
- embolism - blockage of blood vessels by gas bubbles or foreign particles - emboli, which are brought with the bloodstream;
- thrombosis - disruption of normal blood flow formed by blood clots;
- arterial spasms - pathological narrowings caused by excessively intense or prolonged muscle contractions;
- arteritis – inflammation of the artery walls due to infections or autoimmune reactions;
- heart injuries - most often blunt, lead to contusion of the myocardial muscles, rupture of the heart chambers and septa, damage to the valves;
- violation of the rheological properties of blood, for example, increased viscosity and aggregation of red blood cells;
- hyperlipoproteinemia - an increase in the concentration of lipids and lipoproteins in the bloodstream, a common cause of problems with the cardiovascular system;
- hypertension leads to constant tension of the vascular walls, which can cause their thickening, impaired elasticity and trophism;
- hypothermia;
- overdose of medications.
Possible causes of pre-infarction condition
What it is
Signs of impending acute myocardial necrosis occur in 50–65% of cases. Scientists who have studied this phenomenon associate this condition with the gradual blocking of the lumen of the coronary vessel, while the heart attack itself represents a complete stop of blood circulation in a certain area. Wherein:
- The general excitability of the body changes, which ultimately leads to spasm of the coronary arteries.
- Atherosclerotic deposits cause contraction of smooth muscle fibers of blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of thrombosis and internal bleeding.
The narrowing of the coronary lumen against the background of spasm leads to necrosis. But it is preceded by an acute attack of angina, which can be seen on the ECG and is accompanied by vegetative manifestations.
Symptoms of pre-infarction condition
Determining the onset of myocardial infarction is not difficult. It is accompanied by severe and sudden pain in the chest, spreading to the left arm and extending to the back and jaw. In addition, a person may experience:
- a surge of nausea;
- lethargy;
- disturbances in concentration;
- feeling of anxiety;
- increased heart rate;
- dizziness.
A pre-infarction condition can also be determined by the appearance of sticky, cold sweat, shortness of breath, weakness, and anxiety. Signs of dysfunction of the heart muscle appear in the form of heaviness in the chest, strong compression or pressure on the heart area.
Symptoms of pre-infarction in women
In women, signs of a pre-infarction condition are atypical and can only be tingling, difficulty breathing and dizziness.
Unusual symptoms also include abdominal pain, but they can be a symptom of other diseases, so additional examinations are necessary before providing medical assistance.
Symptoms of pre-infarction in men
In men, the signs of a pre-infarction state are usually more pronounced - the patient experiences severe pain in the center of the chest and behind the sternum, severe compression, even burning, and lack of air.
Atypical manifestations may be cyanosis or pallor of the skin, drowsiness or, on the contrary, insomnia , swelling of the lower extremities, and a state of euphoria .
Myocardial infarction: clinical recommendations
Pain itself, by acting on the sympathetic nervous system, can significantly increase heart rate, blood pressure (BP), and cardiac function. It is these factors that determine the need to stop a painful attack as quickly as possible. It is advisable to give the patient nitroglycerin under the tongue. This may relieve pain if the patient has not previously received nitroglycerin for this attack. Nitroglycerin can be in tablet or aerosol form. There is no need to resort to its use if systolic blood pressure is below 90 mm Hg.
All over the world, morphine is used to relieve a painful attack, which is administered intravenously in fractional doses from 2 to 5 mg every 5-30 minutes as necessary until complete (if possible) pain relief. The maximum dose is 2-3 mg per 1 kg of patient body weight. Intramuscular administration of morphine should be avoided, since the result in this case is unpredictable. Side effects are extremely rare (mainly hypotension, bradycardia) and are quite easily stopped by elevating the legs, administering atropine, and sometimes plasma replacement fluid.
In elderly people, depression of the respiratory center is uncommon, so morphine should be administered in a reduced (even half) dose and with caution.
The antagonist of morphine is naloxone, which is also administered intravenously, it relieves all side effects, including respiratory depression caused by opiates. The use of other narcotic analgesics, for example promedol and other drugs of this series, is not excluded.
The suggestion that neuroleptanalgesia (a combination of fentanyl and droperidol) has a number of benefits has not been clinically confirmed. Attempts to replace morphine with a combination of non-narcotic analgesics and antipsychotics in this situation are unjustified.
Tests and diagnostics
It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with myocardial infarction, as well as monitoring changes in body temperature, ESR, leukocyte formula, ECG (electrocardiogram) and the level of activity of blood enzymes such as creatine phosphokinase, troponin, lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase .
In addition, pulse oximetry is performed to determine the level of arterial hypoxemia .
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to determine the characteristics of blood supply and heart function.
Coronography is performed if conservative drug therapy is not effective and the patient is indicated for surgical intervention to solve the problems of narrowing of the arteries that bring blood to the heart.
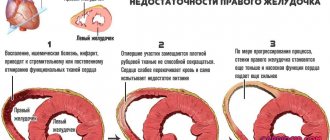
Possible complications
With the right approach to treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Out of 100% of people, 85% recover. In 10% of cases, a heart attack occurs, and in 5%, cardiac death occurs. The medications are effective and give good results - 75% of 100 people got rid of the condition. The rest required surgical treatment.
If a patient has a heart attack, you need to prepare for possible complications:
| Name | Description |
| Cardiogenic shock | It is considered a serious condition. The risk of occurrence increases if the patient has diabetes or a recurrent heart attack. In 20% of cases, the result of shock is death. The main reason is loss of time. Many people do not notice the symptoms, although the condition is treatable. But then it becomes too late |
| Mitral regurgitation | Occurs often, medications or surgery are used |
| Heartbreak | The worst complication of them all. The condition cannot be treated. The complication is especially dangerous for women, because their heart cannot withstand the heavy load or lack of therapy, and a rupture occurs |
| Thromboembolism | There is a risk of blood clots even after surgery, and especially in the first 5 days. For prevention purposes, Heparin is administered. And on the second day they give Warfarin |
| Post-infarction | The body responds with this reaction to cell necrosis. Treatment requires the use of drugs with hormonal composition |
The main sign of pre-heart attack in women is chest pain. Additional symptoms include shortness of breath at rest, tachycardia and others. It is important to recognize a pre-infarction condition and visit a doctor. If the signs appear acutely, you need to call an ambulance. In the absence of disease, pay attention to prevention.
First aid
If a heart attack is suspected, the patient should be seated and calmed down; a tight tie or shirt should be loosened or removed. Next, you should measure the pressure, if it is elevated, then it is advisable to give a nitroglycerin . You can also use aspirin - 300-600 mg in tablets that should be chewed is enough.
In case of loss of consciousness, cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures must be performed. If you are in a public place, perhaps an institution (airport, cafe) has a portable defibrillator, its use greatly increases the chance of survival.
Is it possible to help at home?
You can’t do anything on your own; it’s impossible to distinguish between heart pain and cardiac pathologies without special methods. It is necessary to call an ambulance.
The algorithm before the doctors arrive is as follows:
- Take a Nitroglycerin tablet. If there is no effect, take another one after 10-15 minutes.
- Open the window, window. Provide ventilation in the room.
- Sit down, move less. Do not lie down, your condition may worsen.
- Calm down. Emotional manifestations provoke the release of cortisol and adrenaline. An increase in blood pressure will have an even worse effect on a person’s general condition.
You can't wash your face or eat. Loss of consciousness, vomiting and death from asphyxia are possible. Upon arrival of doctors, tell about your health, briefly and clearly.
You should not refuse offers of hospitalization. This is in the interests of the person himself. It is necessary to prevent the development of a heart attack by all means.
Prevention
The main way to prevent a heart attack is to give up bad habits and follow a diet. It is important to exclude animal fats, fried, smoked, flour products from the diet and add cereals, fruits, vegetables, and seafood.
Prevention of heart attack
Daily moderate morning exercise will also help prevent heart problems, for example, morning exercises or cycling, walking, adjusting the regime of adequate sleep, work and rest.
How does the second stage of prostate adenoma manifest?
Symptoms of benign hyperplasia boil down to certain urinary disorders: frequent urge, pain when urinating, leakage of urine and incomplete emptying of the bladder. These processes are associated with the fact that due to the tumor and the developing muscle spasm, the flow of urine is blocked, and the pressure has an irritating effect on the nerve endings, causing urges. Urinary disorders with second-degree adenoma The severity and nature of symptoms, as well as changes in the prostate gland and other organs of the genitourinary system and the body as a whole may differ at different stages of the development of prostate adenoma. Doctors distinguish 3 stages of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Adenoma illustration If the first stage can take a long time and have mild or even imperceptible symptoms, then in the second stage the patient’s condition worsens due to the continued growth of the adenoma. The second period is different in that the bladder can no longer cope with the load, that is, the muscles cannot contract with the intensity necessary to completely remove urine. Against this background, a certain symptom complex develops.
- The muscle layer becomes thinner and loses its ability to contract. In areas freed from muscles, protrusions form on the walls of the bladder.
- Urine is not completely eliminated. The volume of residual urine can reach 400 ml. Incomplete excretion of urine and other unpleasant symptoms and consequences of adenoma
- General symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and dry mouth often appear. Nausea and dry mouth
- There is a high risk of developing acute urinary retention. This phenomenon represents the inability to drain urine and is accompanied by severe pain. Urinary retention
- Difficulties also arise with the flow of urine into the bladder, which can ultimately lead to kidney complications (renal failure, hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis). Kidney failure and other diseases
- Another consequence of adenoma that develops at the second stage is urolithiasis, inflammation of the pelvic organs (cystitis, urethritis, orchitis, etc.).
Because of this, impurities of pus and blood are observed in the urine. Urolithiasis The structure of the male genitourinary system
To prevent further growth of the tumor, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment.
Don’t hesitate to go to the doctor at the first sign of adenoma
Why do women get sick less often than men?
Although in modern medicine a heart attack is no longer considered a typically “male” disease, men suffer from this disease twice as often as women. This is explained by the fact that a woman's heart beats a little faster than a man's. In addition, the female body produces estrogens, which contribute to the dilation of the heart vessels, which is why blood moves through them with greater intensity. The risk of the disease increases with age when the amount of estrogen decreases.
More than two hundred women around the world die every day from myocardial infarction. You need to know what the first warning signs of a heart attack look like, because the sooner you provide medical assistance, the higher the likelihood of surviving a heart attack.
Consequences for the patient
The further course of coronary heart disease depends on what risk factors for vascular pathology the patient has (age, male gender, hereditary predisposition, smoking, high blood pressure, excess cholesterol in the diet), as well as concomitant diseases.
If timely treatment is started and all causes that can be influenced are eliminated, then long-term stabilization of the condition is possible. An unfavorable prognosis is observed in patients who have:
- myocardial infarction in the past;
- cardiosclerosis;
- age after 55 years;
- multiple disturbances of cardiac blood flow;
- narrowing of the main branch of the left coronary artery;
- severe angina;
- nicotine addiction;
- addiction to alcohol;
- weak reaction to drugs or refusal of treatment.
Etiology
Myocardial infarction is a cessation of nutrition to the heart muscle due to impaired conduction of the coronary arteries. The pre-infarction condition is characterized by narrowing of the arteries supplying the heart muscle. The lumen of the vessels narrows against the background of spasm, blockage with an atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus, and the blood supply to the myocardium deteriorates.
This condition is caused by:
- Stress;
- Nervous fatigue;
- Hypertensive crises;
- Flu and other respiratory infections;
- Overdose of alcoholic beverages;
- Unusual physical overload;
- Heat stroke;
- Overdose of medications;
- Hypothermia;
- Smoking.
Rash on a child’s elbows: photos of acne with explanations of the causes of the rash, why are there pimples on the knees?
Cleanliness of the skin characterizes the internal state of health
Often people immediately pay attention to acne that appears on the face, but minor rashes on the elbows or knees can go unnoticed for a long time
After a while, when the rash begins to itch and cause trouble, the person seeks help from a doctor.
It is important to promptly identify the causes of deterioration of the skin, as this can be caused by serious infectious or fungal diseases
The sooner proper treatment is started, the easier it will be to fight the underlying disease that caused the rash.
General information about pathology
The skin on the elbows and knees has virtually no sebaceous glands, so due to the lack of natural moisture, the skin in these places is very dry.
Lack of special care and non-compliance with hygiene measures over time lead to the formation of microdamages - dry skin areas crack and become “entry gates” for various infections. As a result, a rash, light pimples, itching and even pain appear.
This disease is especially common in warm weather, when the elbows and knees are not protected by clothing and are exposed to direct contact with the environment.
A rash on the elbows of a child or adult can be a manifestation of many unpleasant diseases that must be correctly diagnosed in time
The origin of the rash can be of a different nature (allergic, infectious, viral) - it is important to pay attention to this symptom in a timely manner so as not to trigger the underlying disease
Symptoms of dermatitis on elbows and knees
At the beginning of the disease, the rashes may not bother you, so the person does not pay attention to them. Over time, an unpleasant itching appears, intensifying at night. The skin on the affected areas becomes rough, begins to peel, peel off, and becomes covered with a light film or dried crusts.
The size of the rashes ranges from tiny bubbles to large conglomerates, when several small red dots merge into common shapes.
Causes of rash on elbows and knees
Rashes on the knee-elbow folds can be caused by various factors. The main reasons contributing to the development of the rash:
- Mechanical impact. A sedentary lifestyle, long-term work at the computer and with documents contribute to regular rubbing of the elbows on a hard surface, causing small cracks and the appearance of acne.
- Insect bites (we recommend reading: what remedy to choose for insect bites for children over one year old?). The irritation will disappear on its own when a soothing cream is applied to the affected areas.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Digestive problems can manifest as itching and rashes on the bends of the limbs.
- Pimples on the elbows can be a harbinger of incipient chickenpox (blisters as if filled with liquid), rubella or shingles. Medical attention and treatment is required.
- Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease (we recommend reading: psoriasis in children at the initial stage: symptoms with photos). The rash appears locally on the hands and elbows, the skin peels off and becomes covered with a stratum corneum.
- Dermatitis of various origins. They are characterized by small, dried pimples on the elbows and kneecaps that cause severe itching. They intensify with emotional overstrain and stress.
- Granuloma annulare is most often diagnosed in children under 6 years of age. It occurs for unknown reasons and can go away on its own. White or pink rashes of dense consistency in the form of rings are located on the elbows, feet and the outside of the hands. A photo of granuloma annulare is presented in the article.
- Changes in hormonal levels. Occurs with certain diseases of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands.
- Allergic reactions. The most common cause of rashes, especially in childhood. There are many factors that cause an allergic rash. To identify allergens, you should consult a doctor.
READ ALSO: How is allergic dermatitis treated in children?
Rash on knees and elbows in a child: signs of allergy
Pimples on a child’s knees and elbows are most often a sign of allergies (we recommend reading: pimples on a child’s arms and legs: causes of rashes and ways to eliminate them). The symptoms of allergic reactions are similar to the clinical picture of other dermatological diseases, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Allergies in a child may arise from the introduction of new products into the diet, from washing powders and other household chemicals, pollen from flowering plants, from contact with grass or dust on the street (we recommend reading: how does a child’s allergy to powder manifest itself?).
When a child comes into contact with an allergen, the affected skin areas swell and papules of various sizes and colors appear.
The rashes may become wet and burst, causing a secondary infection. It is forbidden to open the blisters - this leads to the growth of inflamed tissue on the joints. Allergy forms are different, some stages require urgent antihistamine therapy.
Diagnosis and treatment of rashes
A dermatologist diagnoses rashes. The specialist conducts a visual examination of the rash and collects an anamnesis. In some cases, a general blood test may be prescribed.
A number of laboratory tests are carried out: scrapings for the presence of infections and fungal parasites.
It is important to identify incipient chickenpox or rubella in time to prevent further contact with healthy family members. https://www.youtube.com/embed/zbXDaR3-Oqk
READ ALSO: how to recognize chickenpox in a child at an early stage?
If the allergic nature of the rash is identified, a blood test for immunoglobulins may be prescribed, which allows identifying specific allergens.
Until the underlying disease is established, it is recommended to refrain from contact with other people, since the rash may be a sign of a contagious disease (chickenpox, rubella, mycoses).
READ ALSO: What are the photo signs of rubella in children?
ethnoscience
There are quite a few folk methods for getting rid of skin itching and rashes, but you should understand that not a single old recipe can replace a competent consultation with a dermatologist.
Traditional medicine can come to the rescue if the patient has minor rashes on the elbows and knees caused by poor hygiene or excessive dry skin. To moisturize and disinfect, it is effective to wipe the affected areas of the skin with warm olive or linseed oil.
These oils help cope with peeling, dried crusts, and also quickly heal microcracks and wounds.
Aloe juice and chamomile decoction have a bactericidal effect, and an infusion of calendula or string helps eliminate severe itching. It is recommended to soak a cotton swab in decoctions of these herbs and apply it to the affected areas for 10 to 15 minutes. A weeping rash can be dried with hydrogen peroxide, then rinse the wounds in a decoction of St. John's wort.
Preventive recommendations
There are no special preventive measures, but there are simple rules that should be followed:
- maintain body hygiene and promptly moisturize dry areas of the skin;
- avoid mechanical damage to the knees and elbows;
- consume large amounts of vegetables and fruits;
- a course of vitamin therapy is recommended twice a year;
- avoid tactile contact with people suffering from fungal diseases;
- minimize contact with allergens, especially pesticides;
- work with household chemicals (cleaning powders, dishwashing detergents) wearing thick rubber gloves.
To avoid allergies in children, simple measures must be followed. First of all, it is correct to introduce complementary foods to babies and monitor the body’s reaction to the introduction of new foods into the diet of infants. Often babies develop a rash on ready-made cereals and milk formulas. Older children should not overindulge in chocolate, citrus fruits and fast food.
Nursing mothers are advised to follow a diet: avoid large amounts of coffee and chocolate, seafood, concentrated juices, oranges and tangerines. Allergens received by the mother due to poor nutrition may not bother the woman, but are transmitted through breast milk to her baby and cause an atopic rash in him.
Clothes for children are preferably made from natural fabrics. Large manufacturers of household chemicals are developing children's series of antiallergic baby care products: washing powders, shampoos, washing gels. There is no need to wait for the symptoms of allergic dermatitis to appear - it is better to immediately, from birth, use special products from the children's line.
Temporal lobe
The work of this area ensures normal memory, internal speech and mental activity, and hearing in general.
- Epileptic seizures. As is the case with those with lesions of the frontal lobes, they develop suddenly. But they last less time. Otherwise, it is not possible to notice the difference without instrumental techniques. The difference is in the localization of the pathological impulse.
- Lack of hearing. The so-called cortical deafness. The patient completely loses the ability to navigate sounds. This is a temporary phenomenon; treatment as such does not make sense.
- Lack of speech perception. Formally, there is a noise stimulus, but it is impossible to evaluate the logic of the statements, the meaning of them, and even recognize the words.
- Verbal hallucinations of the mental type. So-called pseudohallucinations in outdated terminology. The proverbial voices in my head. Associated with disruption of Wernicke's area.
It is responsible for the production of inner speech. As a result of the anomaly, the signal moves to Broca's center.
He, in turn, identifies external stimuli and perceives them as such, as outside speech. A paradoxical reaction arises.
Memory impairments of various types. Amnesia, failures. The feeling of a repetition of something that once happened (déjà vu).