Dentist-therapist
Spivak
(Therapist) Evgenia Ivanovna
Experience 28 years
Dentist
Make an appointment
Stomatitis is a characteristic inflammation of the oral mucosa. More common in children, this is due to the habit of not washing their hands and “tasting” surrounding objects. It can act as an independent disease or develop against the background of mechanical damage, infections or dental diseases. Manifestations of pathology are different: from small ulcers to large inflammations over the entire surface of the mucosa. Provided that you seek medical help in a timely manner and take a course of medication under the supervision of a doctor, it can be completely cured.
Causes of stomatitis
The list of causes of stomatitis is varied. Provoking factors include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity;
- consequences of chemotherapy;
- mechanical injuries to the gums and oral mucosa, burns from hot food;
- unbalanced diet, hypovitaminosis;
- side effect in the development of cancer;
- consequences of hormonal disorders;
- addiction to nicotine and alcohol;
- infection of the oral mucosa;
- chronic diseases;
- lack of proper oral hygiene;
- long-term use of medications.
Knowing and eliminating the causes of stomatitis will allow you to successfully cope with the disease and reduce the risk of its recurrence.
List of categories of patients at risk
- Children under 7 years old. More than half of cases of stomatitis occur in preschool children due to the lack of the habit of regularly washing their hands.
- Elderly people with diseases of internal organs and loss of several teeth.
- Persons living in unsanitary conditions, as well as those who refuse to observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Smokers, regardless of length of service.
- Persons with reduced immunity after severe illness, chemotherapy or organ transplantation.
- Patients who have undergone a long course of antibiotic treatment.
- Persons with asthma who use inhalers without following hygienic rules for their use.
The frequency of cases of stomatitis is from 5 to 20%, depending on living conditions: less in large cities, more in rural areas where there is no centralized water supply or the water quality is considered unsatisfactory.
Who is at risk
As noted above, stomatitis and its symptoms most often appear in children. Among adults, those with weakened immune systems and hormonal imbalances are more susceptible to the problem. As a rule, those at risk are the elderly (especially those over 60 years of age), pregnant and breastfeeding women, patients with chronic diseases of the body and after chemotherapy, as well as smokers.
This is interesting! Some studies have shown that mucosal inflammation in adults can occur after complex tooth extractions or oral surgery, especially if patients are prescribed antibiotics during rehabilitation.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the reasons that caused the inflammation, infectious and non-infectious diseases are distinguished:
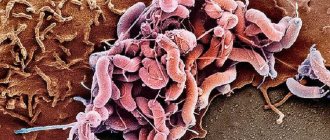
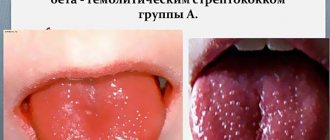
- viral stomatitis - caused by the consequences of an infectious disease or the effects of pathogenic microorganisms on the damaged oral mucosa. It looks like bubbles with transparent contents that gradually become cloudy. Ulcers form at the site of burst blisters;
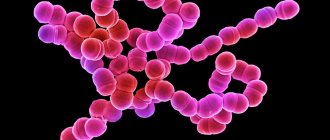
- bacterial – consequences of damage to the body by staphylococci or streptococci. Under favorable conditions, they quickly spread throughout the mucous membrane, on which purulent foci form;
- fungal - characterized by the formation of numerous ulcers with a white coating;
- radiation – the consequences of ionizing radiation in the form of painful erosions and hardening of the mucous membrane;
- chemical – associated with burns of the mucous membrane, after healing of which dense scars form;
- aphthous - one of the popular types of stomatitis, is associated with reduced immunity and the consequences of gastrointestinal diseases. Small ulcers with a diameter of up to 5 mm are painful and quickly grow in size;
- allergic – caused by exposure to external irritating factors, goes away completely without treatment when the allergen is eliminated: foods, medications, incorrectly selected dentures, etc.
Symptoms of stomatitis
The type of stomatitis can often be determined by characteristic signs of the disease associated with the cause of its occurrence. All of the above types of pathology are united by:
- the appearance of characteristic ulcers and areas of inflammation on the oral mucosa;
- the formation of white, yellow or green plaque, under which traces of mucosal erosion are visible;
- redness on the gums;
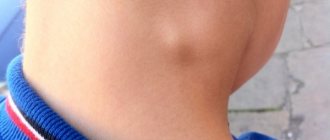
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- unpleasant bloody or putrid taste in the mouth;
- soreness of the affected areas;
- increased salivation.
Signs of stomatitis in adults and children can be more or less pronounced depending on the state of the immune system, compliance with personal hygiene rules and living conditions.
Classification of pathology according to the nature of manifestations and severity of the course
| Type | Peculiarities |
| Catarrhal | The most common type of pathology is when inflammation affects only the surface of the mucosa. It is characterized by swelling and redness of the inflamed areas, their bleeding, pain during eating, and copious salivation. |
| Aphthous | Round ulcers or aphthae appear on the mucous membrane, limited by a red border and often covered with a grayish coating on top. If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic and can recur up to 3-5 times a year. |
| Ulcerative-gangrenous or necrotic | This type is often a consequence of advanced catarrhal form, so the best prevention is attention to the problem at the initial stage. However, there are cases of independent rapid development of this particular type of pathology. The presence of an ulcerative gangrenous form is indicated by the appearance of erosions and ulcers, bleeding and an acute inflammatory process that even affects bone structures. Accompanied by severe pain, putrid odor from the mouth, a sharp deterioration in health, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes. This type of stomatitis is especially pronounced in children. |
Stomatitis in the mouth can manifest itself acutely when all the symptoms are pronounced. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment measures, the disease becomes chronically relapsing, proceeds sluggishly and worsens with accompanying factors (decreased immunity, stress, allergies, injuries).
Possible complications of stomatitis
The requirement to immediately consult a doctor at the first signs of stomatitis is dictated by concern for the health and well-being of the patient. Ignoring this rule may cause:
- damage to the mucous membrane of the entire oral cavity;
- development of infectious diseases of internal organs;
- inflammation of the gums and loss of some teeth;
- digestive problems;
- infection of loved ones through kissing, sharing utensils, etc.;
- diseases of the heart, lungs and blood.
Self-medication can lead to similar consequences. Therefore, if you suspect stomatitis, you should immediately seek help from a therapist or pediatrician.
How the disease is transmitted
The infectivity and mode of transmission of the disease depend on the type of stomatitis. Some types of pathology are not contagious, for example, allergic or traumatic stomatitis, as well as damage to the mucous membrane due to taking medications or wearing dentures. Read more about whether stomatitis is contagious here.
Infectious types of stomatitis of a fungal, viral or bacterial nature can be transmitted to other people. The main method of infection is contact; infection occurs from person to person, as well as through the use of shared utensils or hygiene items (a toothbrush, less often a towel). Some varieties of the disease that have a bacterial etiology can be transmitted by airborne droplets. This is especially often observed with stomatitis against the background of tonsillitis (tonsillitis). In addition, the viral or bacterial form of the disease can be transmitted from mother to child.
Viral stomatitis is extremely contagious. Transmission of the pathogen occurs through contact with a person with pronounced symptoms, for example, through kissing, oral sex, or using shared cutlery.
Diagnosis of the disease
In most cases, an external examination of the patient is sufficient to make a diagnosis. If teeth and gums are affected, a dentist is involved in consultation. If a secondary nature of the disease is suspected, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane, highly specialized doctors can begin working with the patient.
Diagnosis of infectious stomatitis has its own characteristics. Special laboratory tests allow you to determine the type of pathogenic organism that caused the inflammatory process:
- oral swab for testing for fungi and bacteria;
- blood test for the presence of antibodies to pathogens of infectious diseases of internal organs;
- smear or PCR (polymerase chain reaction) blood test to detect and analyze the DNA of viruses.
If the disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a serious deterioration in health, the patient is referred for blood and urine tests. This will identify possible complications or infectious diseases that cause inflammation of the oral mucosa.
Treatment options
When visiting a doctor in the first stages of the disease, treatment of stomatitis at home is symptomatic and lasts about a week. When an infectious cause of the disease is established, the action plan changes:
- a course is prescribed that relieves inflammation and other main symptoms;
- local gels and ointments are prescribed;
- drugs are selected that act on the causative agent of the disease to completely destroy it.
The complex of drugs for the treatment of infectious stomatitis includes antibiotic compounds, painkillers, antiseptic and antihistamine medications. The duration of this course is about 10 days. If the diagnosis establishes the secondary nature of the disease and serious pathologies are identified in the patient’s body, the treatment process may be delayed until the possible provoking factors are completely eliminated.
Additional methods to speed up the recovery process and increase the effectiveness of medications for stomatitis include:
- avoidance of foods that cause irritation to the mucous membranes;
- increasing the volume of fermented milk products in the diet;
- rinsing the mouth with calendula decoctions;
- lubricating ulcers with sea buckthorn oil, aloe juice or petroleum jelly.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. This approach will eliminate possible side effects and promptly adjust the course to increase its effectiveness.
Additional local therapy
Pain relief for stomatitis is only the fight against the symptoms of the disease. Additionally, it is necessary to use products with antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antifungal and immunostimulating properties. Drug therapy is prescribed only after determining the nature of the disease.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
To combat the herpes virus, antiviral agents are prescribed. Dentists actively use Famciclovir, which is used once. If necessary, the dose can be divided into several doses, maintaining an interval of 12 hours. Treatment of herpetic stomatitis should be carried out using Acyclovir. But over the years of use, the herpesvirus has lost sensitivity to this drug.
Treatment of the herpetic form of stomatitis necessarily includes the use of antiseptics. It is recommended to rinse the mouth several times a day with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. To increase immunity, drugs with interferon (Viferon-gel) are used.
Imudon tablets have a good immunostimulating effect. When used in a course, they reduce the frequency of relapses of stomatitis. It is recommended to dissolve 6 tablets per day. The course of treatment and prevention is 2-3 weeks.
Tablets can also eliminate pain; you can read the list of the best tablets on our website.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
When treating aphthous stomatitis, the cause of the disease must be taken into account. Often the disease occurs in the form of an allergic reaction to the medications used. Therefore, for aphthous stomatitis, antihistamines are prescribed. For local treatment of aphthae, antiseptics (Miramistin) and painkillers (Cholisal) are used, which must additionally have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
After the acute process subsides, the dentist prescribes Solcoseryl gel to heal the mucous membrane. Be sure to use immunostimulating therapy. The causative agent of aphthous stomatitis is often staphylococcus, which is found in carious cavities.
If aphthae appears several times a year, it is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity and be sure to cure all dental diseases. Additionally, the doctor must remove hard and soft deposits from the teeth in order to reduce the spread of the infectious focus.
Treatment of Vincent's stomatitis
Vincent's ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis can occur against the background of poor-quality oral care. Long-term smoking, a weakened immune system and frequent viral infections contribute to the development of the disease. To treat the disease, antibiotics must be used: injections of Lincomycin in combination with Metronidazole tablets. It is also possible to use Amoxiclav.
Antiseptic rinses with chlorhexidine are mandatory. Antiseptic treatment of the mucous membrane is carried out daily with Metrogil denta or Cholisal gels. To relieve inflammation and swelling, antihistamines (Tavegil) are prescribed.
Prevention of stomatitis
You can eliminate the risk of inflammation of the mucous membrane and the development of stomatitis by following the following recommendations:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- use antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, strictly in the indicated doses;
- maintain oral hygiene;
- promptly treat diseases of teeth and gums;
- reduce the amount of sweet foods and yeast baked goods;
- choose toothpastes and rinses from leading manufacturers;
- Avoid eating too hot, cold or spicy foods;
- take vitamin complexes and strengthen your immune system.
Additional recommendations based on the patient’s health condition will be provided by the attending physician.
Questions and answers
How to treat stomatitis at home?
Prescribing medications for stomatitis is possible only after examination by a specialist and establishing the causes of the disease. All types of stomatitis are treated at home according to the prescribed course of medications for internal use and local healing agents. The patient is admitted to the hospital only in an emergency, if the examination reveals a serious pathology of the internal organs.
Is stomatitis contagious or not?
The fungal or infectious nature of stomatitis makes the patient a source of spreading the disease to others. If the disease is caused by an allergic reaction, gastrointestinal pathology or mechanical damage to the gums, there is no danger of infecting loved ones. It is possible to indicate the exact cause of the development of the inflammatory process only after examining the patient and studying the test results. Before visiting a doctor, you should limit contact with family and strictly observe personal hygiene rules.