Retinal dystrophy is a severe pathology associated with disturbances in the structure of the retina. The disease is caused by decreased immunity, hereditary predisposition, bad habits, improperly performed ophthalmological operations, etc. The main symptom of dystrophy is decreased vision. A popular treatment method is laser coagulation. Rehabilitation lasts about two weeks, depending on the severity of the disease. Conservative methods, injections, physiotherapy, gymnastics and folk methods are also used in treatment.
Old people are most susceptible to pathology; in general, they need to especially carefully monitor their vision. In this article we will talk about retinal dystrophy, its symptoms, contraindications and treatment methods.
The retina is an important part of the eye
The retina is an important part of the eye Source: ZrenieMed.ru The retina is an important part of the human eye, which is responsible for the organ’s ability to perceive light impulses, as well as for the interaction between the visual system and the brain.
Accordingly, pathological processes occurring in its structures can lead to partial or complete loss of vision. One of the diseases characterized by tissue destruction and dysfunction of the vascular system is called retinal dystrophy.
It entails serious complications, and therefore requires timely diagnosis and competent treatment.
The retina of the eye is the connecting component between the optical components and the visual center of the brain. It is involved in the transformation of light into a visual image. When the retina becomes thinner for some reason, vision begins to decline.
Retinal dystrophy can appear regardless of a person’s age, and it may not manifest itself in any way, but at the same time, irreversible changes occur.
Symptoms
Symptoms, as a rule, do not occur at the onset of the disease, appearing only in the middle and late stages , which makes diagnosis difficult. Among them:
- dark spots, bright flashes, haze before the eyes;
- lack of central and unclear manifestation of lateral vision;
- distortion of the color and shape of perceived images;
- violation of clarity and contrast of images;
- difficulties in visual perception of movement;
- feeling of insufficient illumination.
If one or more signs of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
Retinal dystrophy: what is it?
Source: keymedic.ru Retinal dystrophy is a vision pathology that is caused by irreversible destructive processes in the retina.
This degenerative disease is characterized by slow progression, but is one of the most common causes of vision loss in old age. Retinal dystrophy is most often found in older people. The risk group includes people with myopia, vascular diseases, diabetics and hypertension. This disease can be inherited, so those whose parents had a similar problem are advised to undergo regular examinations.
Most often, pathology is detected in adulthood, and is associated with changes that occur in eye tissue over time.
Factors that provoke the development of the disease can be divided into intraocular and general. The first include eye pathologies, acquired or hereditary - myopia, uveitis, iritis, etc.
External risk factors for retinal dystrophy include:
- systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension), hormonal disorders;
- viral diseases transmitted “on your feet”;
- decreased immunity;
- history of ophthalmological operations, as a result of which the process of scarring began in the tissues;
- unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins in the diet, especially vitamin A;
- nicotine addiction, alcoholism;
- obesity due to metabolic disorders.
The disease is a degenerative transformation that has occurred in the macula of the eye. It is also called “macular degeneration of the retina,” which literally means “yellow spot.” The reason for this color is a special pigment that is found in the cells of the central part of the retina.
Retinal tears
Retinal tears are classified according to their type into perforated, valve and dialysis.
Perforate tears usually occur as a result of lattice and carpal dystrophies, with a gaping hole in the retina. A valvular rupture is a rupture in which a fragment of the retina undergoes vitreoretinal traction, pulling the retina behind itself. When a tear forms, the area of vitreoretinal traction will become the apex of the valve.
A dialysis tear is a linear tear along the dentate line - the place of attachment of the retina to the choroid. In most cases, dialysis ruptures occur due to blunt trauma to the eye.
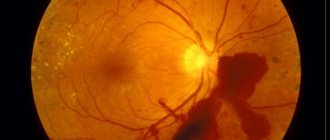
Tears in the fundus are bright red lesions, with a clear outline of various shapes. Beneath them one can discern the pattern of the choroid. Retinal breaks are especially noticeable against the grayish background of the detachment.
Classification of the disease, symptoms in children and adults
Source: wdoctor.ru Depending on the clinical course of the disease and the localization of the pathological process, retinal dystrophy is divided into several types, each of which requires appropriate treatment. There are two main types of retinal dystrophy, which also have their own classification.
- Central
In this form of the disease, the pathological process affects the central area of the eye, mainly the corpus luteum and the vessels that penetrate the eyeball.
- Central chorioretinal
The chorioretinal form of the disease occurs mainly in adulthood, and affects the pigment and inner layer of tissue. It develops as a congenital pathology, as well as due to mechanical damage or infectious diseases of the eye.
The main cause of the disease is a violation of microcirculation in the structures of the retina. CCDS can occur in two forms: non-exudative (dry) and wet (exudative).
In the first case, the disease does not produce symptoms for a long time, after which distortion of contours appears when examining objects, later individual segments disappear from the field of view, and in the final stages, patients have decreased central vision.
The wet form is characterized by a specific deterioration in vision (a person sees as if through a veil of water), spots and flashes appear before the eyes.
- Macular
This form of dystrophy develops due to pathological processes in the macula - the segment of the retina that is responsible for sharpness and visual acuity. The mechanism of development of the disease is the disruption of blood vessels and insufficient supply of oxygen to tissues.
The main risk factor is old age (over 60 years), but the disease also occurs due to gene mutations, family history, hormonal disorders and poor lifestyle.
The clinical course of macular degeneration also has two forms - dry and wet, and the second is considered more dangerous for the patient.
- Peripheral
Unlike central dystrophy, the peripheral form affects tissue on the periphery (at the edges) of the retina and develops most often in people with a family history. In addition, myopia and systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension) are significant risk factors.
The danger of the disease lies in the fact that in the first stages it is asymptomatic, and characteristic signs (flashes and spots before the eyes, blurred vision) appear already when the pathological process is advanced.
Depending on the nature of cell damage and the clinical course of the disease, several forms of peripheral dystrophy are distinguished.
- Lattice dystrophy. Most often it develops in old age or is inherited, with women getting sick less often than men. Upon a detailed examination of the patient's eye, the affected tissues resemble lattice cells. There are no symptoms, sometimes there is a distortion of vision or a decrease in its acuity.
- "Snail trail" The main reason is myopia. The least amount is found in people with farsightedness and ametropia. Foci of the pathological process are presented in the form of characteristic ribbons, reminiscent of a snail's trail. In the final stages, it manifests itself as blurred vision and blurred vision.
- Frost-like form. A hereditary disease that occurs equally in men and women. Small inclusions of a yellow-white hue appear on the retina; in the first stages, frost-like dystrophy occurs hidden.
- "Cobblestone pavement." The pathological process affects distant areas of the retinal periphery, and large lumps of pigment can separate from the tissue. People at risk include people with myopia and those who have reached old age.
- Small cystic dystrophy. This form of the disease develops as a result of mechanical injuries and is characterized by the presence of small cysts on the retina. It produces virtually no symptoms, progresses slowly and does not lead to blindness.
- Pigmentary dystrophy. It is of hereditary origin, the first signs appear in childhood. In the initial stages, there is a narrowing of visual fields and night blindness, and if left untreated, it leads to loss of visual function.
- Retinoschisis. Retinoschisis, or retinal separation, which can be congenital or acquired, and most often develops in people with a family history.
Disease in pregnant women, contraindications
During pregnancy, serious changes occur in a woman’s body: a surge in hormone production, increased blood circulation in all organs, activation of metabolic processes, and surges in blood pressure.
Important
These factors lead to the development of retinal dystrophy in pregnant women who previously suffered from ophthalmological diseases, and the pathology is especially common in expectant mothers with myopia.
The development of retinal dystrophy during pregnancy has a significant impact on the method of delivery. The decision of specialists depends on the age of the mother, general health and the stage of the pathological process, but natural childbirth with this disease is rarely carried out, since the risk of retinal detachment is too great.
A woman is allowed to give birth on her own only in the case of laser coagulation of the retina, which is carried out before the 35th week of pregnancy in the absence of contraindications.
Classification
Each form of such changes has negative characteristics. Ophthalmologists distinguish a large number of types of this disease. They are determined taking into account the reason for the development. Dystrophy is generally divided into primary (hereditary) and secondary (acquired):
- Hereditary. Arises as a result of genetic predisposition. This type includes pigmentary, dotted white dystrophy, Refsum, Best and Stargardt diseases. The first signs are observed in childhood and intensify as the child grows.
- Acquired. Usually occurs in older people. Patients who have suffered eye injuries and certain diseases are at risk. In adulthood, it usually occurs against the background of metabolic disorders in the visual organs. Another reason is the presence of cataracts. This group includes macular degeneration and serous choriopathy.
It should be borne in mind that the type of disease is determined taking into account the location of the lesion. Therefore, the following forms of dystrophy are distinguished:
- Generalized. Damage occurs in central and peripheral areas. Determined by the type of disturbance in the visual organs.
- Central. Affects the macula. It has classic symptoms and a progressive course.
- Peripheral. It affects the passive optical parts of the visual organs. If the pathology extends to the vitreous body and choroid, then the pathology is called chorioretinal dystrophy.
- Spot white. Congenital white spot pathology, which is diagnosed at an early age.
- Pigmented. Doctors were unable to fully study the mechanism of development of this form of dystrophy. Affects both eyes. The first symptoms may appear in childhood.
- Central chorioretinal dystrophy. In ophthalmology it is defined as serous choriopathy. This form of pathology is usually encountered by males. Metabolic processes in the retina are disrupted. Characteristic symptoms are loss of visual fields.
- Age. Occurs in people over 50 years of age. Has dry and wet form. Against the background of such lesions, damage to blood vessels occurs in the central part of the retina. The dry form initially affects one eye and then gradually damages the other. Accompanied by mild symptoms and slow development. Therefore, patients turn to the doctor too late. Due to this, it is almost impossible to restore vision. The wet form is accompanied by pathological growths of blood vessels that are directed to the macula. They collect fluid that ends up on the retinal tissue. This leads to swelling. Against this background, vision distortion occurs. Usually appears against the background of a dry form. This type of pathology can cause complete loss of vision.
Causes
The main causes of retinal dystrophy include:
- Various eye diseases and inflammatory processes (myopia, uveitis).
- Infectious diseases and intoxications.
- Eye injuries due to bruises, blows, etc.
- Genetic predisposition to dystrophy.
- Various systemic diseases (diabetes, hypertension, problems with the thyroid gland and kidneys, atherosclerosis, and so on).
All these reasons, except for genetic predisposition, may not always contribute to the appearance of retinal dystrophy, but they are risk factors. Doctors say that people with excess body weight and bad habits have a high likelihood of developing retinal dystrophy.
Low blood pressure during the second trimester of pregnancy leads to poor circulation and poor nutrition of the retina. Therefore, pregnant women are also at risk.
The causes of retinal dystrophy, first of all, lie in age-related changes that occur in the vascular system enveloping the eyeball - mainly a circulatory disorder, the cause of which, in turn, is vascular sclerosis.
As a result of research, it was revealed that retinal dystrophy is a hereditary disease and if parents had it, then the risk of its occurrence in children is also very high.
Prevention
Simple rules of prevention will help reduce the risk of developing dystrophic changes. Doctors make the following recommendations:
- Avoid excessive strain on the eyes and alternate them with rest.
- Periodically doing eye exercises is especially useful for people who work at the computer for a long time or read.
- Protect your eyes from harmful and dangerous radiation. In sunny weather, be sure to wear safety glasses.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, take vitamins A, E, B. Eat nutritiously, choose a sport that brings pleasure.
- If you are obese, you need to get rid of excess weight.
- You should give up bad habits, alcohol and drugs.
- It is recommended to add active zinc supplements to food.
- Get examined by an ophthalmologist in a timely manner.
If you follow simple rules of prevention, you can avoid the development of severe complications. The key to the health of the whole body is proper nutrition and exercise. If there is a hereditary predisposition, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist more often. This will help avoid the development of irreversible processes.
Symptoms of retinal dystrophy
Sources: pro-zrenie.net Signs of retinal dystrophy appear due to disruptions in color and central vision. The main reason for the manifestation of symptoms of retinal dystrophy is disruptions in color and central vision:
- Visual acuity decreases: here we can mention such an alarming symptom, also associated with the disease, as image distortion, which becomes most obvious when looking at an object representing a straight line, be it a pillar or a tree.
- The appearance of dark spots before the eyes may also indicate the development of a disease such as retinal dystrophy.
- Blurred outlines of objects when viewed with an eye affected by retinal dystrophy is also a symptom of this disease, which refers to a general decrease in visual acuity.
- Color perception is impaired: here we can talk about a change in the color of objects when looking at the affected eye.
Symptoms of dystrophy depend on its type. Thus, peripheral retinal dystrophy can occur without any symptoms for a long time, so it is usually diagnosed completely by accident. The first signs (“floaters” and flashes) appear only when ruptures appear.
With central dystrophy, a person sees straight lines as distorted, and parts of the visual field fall out.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of development, retinal degeneration is accompanied by mild symptoms. Therefore, a person may not pay attention to the presence of suspicious signs. The first symptoms usually appear during the moderate and severe stages of development. The main characteristic clinical manifestations are:
- changes in visual fields;
- decreased visual acuity, impaired color vision;
- increasing the brightness of light when reading and writing;
- the appearance of a distorted picture before the eyes;
- the occurrence of scotomas;
- decreased visual acuity in a dimly lit room;
- the appearance of spots and flashes before the eyes;
- difficult to recognize objects;
- development of metamorphopsia (a person cannot normally perceive the color and size of objects).
If any symptoms are observed, the patient should immediately consult a doctor for a full examination and assessment of the condition of the visual organs. This will help avoid the development of irreversible processes. Lack of treatment can lead to retinal detachment. This complication causes vision loss.
Photo
The photo shows examples of this disease.
Contraindications
With retinal dystrophy, there is a danger that a person will lose vision. To prevent this outcome, laser coagulation is performed, but even when the disease goes away, it is too early to relax.
There are some restrictions after the laser coagulation procedure. The recovery period lasts from one to two weeks, it all depends on the person’s health.
Doctors recommend avoiding sun exposure to your eyes, so it is best to wear sunglasses until your retina strengthens.
Also not recommended:
- watch TV and sit at the computer;
- strain your eyesight with glasses and contact lenses;
- take hot baths, saunas;
- go to the beach.
It is strictly prohibited:
- eat foods with salt,
- drinking alcohol,
- drink plenty of fluids.
Be sure to use eye drops prescribed by your doctor. It is also necessary to avoid any physical activity or sports for a month. You cannot drive a car for the first week after surgery.
People with diabetes should control their blood sugar to a normal level. If you have problems with the vascular system, you need to constantly maintain normal pressure. After surgery, be sure to visit an ophthalmologist once every three months.
Risk factors
When touching on such an issue as retinal dystrophy, one cannot fail to mention what factors contribute to an increased risk and who is more predisposed to this disease than others:
- these are, first of all, people whose age is over 50 years;
- it was found that women are more likely to suffer from this disease than men;
- hereditary factor;
- people with white skin and blue irises;
- persons who have vascular diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- cholesterol problems;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- frequent stress;
- lack of vitamins in food;
- sunburn of the eye;
- environmental problems.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the extent and nature of the lesion. If the doctor has diagnosed the presence of dystrophic changes, then it is impossible to completely cure them. Even modern means in ophthalmology will not be effective. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms and slowing and stopping the progression of the disease. It all depends on the degree of damage and the condition of the retina.
Main methods of treatment: surgical, medicinal, laser. Retinal detachment can be eliminated using laser coagulation. But the result will not always be favorable. Comprehensive treatment will help prevent the development of pathology. If therapy is started in a timely manner, vision can be saved and its function can be improved. The doctor selects treatment individually for each patient.
Is the disease dangerous?
Retinal dystrophy is a common disease that is most often observed in old age and in people who suffer from hereditary ophthalmological pathologies.
It rarely leads to complete blindness, but if left untreated, the patient may lose the ability to do minor work, read, write, and even take care of themselves.
The main danger of the disease lies in the absence of symptoms in the first stages, so those who are at risk need to undergo examinations by specialized specialists twice a year.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
A certain category of people are predisposed to retina diseases. Risk groups include pregnant women, old people suffering from diabetes, and patients with high rates of myopia.
General signs of the disease:
- decreased vision is the main symptom;
- bright light flashes before the eyes;
- disturbance of visual adaptation in the dark - night blindness;
- blurred vision or a feeling of fog before the eyes;
- blindness in one eye;
- pain in the eye or in the area around it.
Often in the initial stages of the disease there are no accompanying symptoms or discomfort in the visual area, therefore, if a person is at risk, it is worth regularly undergoing diagnostics by an ophthalmologist, who will identify the presence of a threat and understand whether the person needs treatment or surgery. If surgery is recommended, do not delay it.
Diagnostics
Source: ya-viju.ru Diagnosing a disease such as retinal dystrophy requires in-depth analysis and careful research and includes the following steps:
- Determination of visual acuity. Examination of vision perimetry, that is, determination of its boundaries.
- Optical coherence tomography, which produces a three-dimensional image of the retina.
- An electrophysiological study that allows you to determine how viable the cells of the retina and optic nerve are.
- Ultrasound. Examination of the intraocular fundus and measurement of intraocular pressure.
To diagnose retinal dystrophy, the following examinations are necessary:
- Visual field examination;
- Study of color perception;
- Visual acuity testing;
- Fundus examination using a Goldmann lens;
- Fluorescein angiography (examination of eye vessels);
- Ultrasound and electrophysiological examination of the eyes;
- tests to determine the state of the body's metabolism.
How is Stargardt disease diagnosed - causes, symptoms and prevention
Stargardt disease begins in childhood and adolescence and often leads to disability. It manifests itself as dystrophic changes in the macular zone, significant deterioration of vision, impaired color perception (merging of red, yellow, green into a single color). Among the causes of the pathology is a mutation of the ABCR gene, a violation of protein production. Early diagnosis gives a high chance of successful treatment. This disease is largely genetically determined, but in the new generation it can be easier, without leading to disability. The pathology is transmitted according to an autosomal recessive type, that is, inheritance of the disease is not always transmitted to another generation and is not related to gender.
To obtain accurate diagnostic data, it is necessary to undergo an electrophysiological examination, visometry, perimetry, optical coherence tomography of the retina, fluorescein angiography (examines the condition of the capillaries and vessels of the retina), as well as a color vision test.
If there are cases of Stargardt disease in the family, it is also advisable to undergo molecular genetic analysis. Moreover, it allows you to detect the disease long before it manifests itself.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy
Source: mgkl.ru It may take a long time to cure retinal dystrophy.
This is quite difficult, and it is not always possible to get a positive result. It will not be possible to restore vision when dystrophy has already worsened. In this case, treatment is aimed at slowing the progression of dystrophy, strengthening the blood vessels and muscles of the eyes, and restoring metabolism in the eye tissues.
Treatment with drugs is based on the use of medications such as:
- Antioxidants;
- Angioprotectors;
- Corticosteroids;
- Vitamin preparations;
- Lutein-containing drugs;
- Vasodilator and vascular wall strengthening drugs.
You need to know that these drugs can only be effective in the early stages of retinal dystrophy. At the beginning of the disease, physical therapy gives good results. It is aimed at strengthening the retina and eye muscles.
The most commonly used physiotherapeutic methods are:
- Electro- and phonophoresis;
- Laser irradiation of blood;
- Ultrasound and microwave therapy;
- Surgical intervention is performed to improve blood circulation in the vessels of the eyes and metabolic processes in the retina.
In the case of wet dystrophy, surgery is needed to remove fluid from the retina. One of the modern methods of treating retinal dystrophy is laser coagulation. It allows you to prevent detachment. When carrying out laser coagulation, damaged areas are cauterized to other areas to a certain depth.
The laser does not touch healthy areas. Unfortunately, laser coagulation cannot restore lost vision, but it can stop further destruction of the retina.
Photodynamic therapy, laser photocoagulation and injections of Anti-VEGF drugs are used in the treatment of such a form of the disease as peripheral choreoretinal retinal dystrophy. In the case of injections, we are talking about a special protein that has a beneficial effect on the macula of the eye and inhibits the development of the disease.
Photodynamic therapy involves the use of substances - photosensitizers, which are administered intravenously and also stop the development of the disease.
This type of therapy is not indicated for every patient, so it is used based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Laser photocoagulation is based on cauterization of diseased vessels: after manipulation, a scar is formed and vision in this place cannot be restored, but this technique also prevents the spread of the disease.
For retinal pigmentary dystrophy, treatment is based more on physiotherapeutic techniques - magnetic stimulation and electrical stimulation of the eye and its tissues.
If an operation called vasoreconstructive (affects the blood supply to the retina) is proposed for retinal dystrophy, it is worth keeping in mind that the effect of its implementation is considered very limited.
Retinal dystrophy during pregnancy, unfortunately, is a well-known phenomenon and ophthalmologists, regardless of the presence of vision complaints, recommend undergoing observation, and 10–14 weeks of pregnancy in this case is the ideal period.
If, nevertheless, retinal dystrophy is detected in a pregnant woman, then in this case peripheral preventive laser coagulation is recommended, which is carried out before the 35th week of pregnancy.
Pregnancy and childbirth in combination with the disease in question is a reason to be vigilant. If the expectant mother is diagnosed with retinal dystrophy, then this disease is an indication to abandon natural childbirth in favor of cesarean section.
Recommendations
With age, the body especially lacks the substances lutein and zeaxanthin, which are necessary for eye health and visual acuity. These substances are not produced in the intestines, so their content must be regularly replenished.
If people over 45 years of age complain of progressive vision loss, they need to follow a diet. In addition to zeaxanthin and lutein, the diet should include vitamin C, tocopherol, selenium and zinc, which nourish, repair and protect eye tissue.
In addition to following a diet, to prevent the development of age-related changes in the retina, it is necessary to take multivitamins. For example, the vitamin and mineral complex “Okuwait Lutein Forte” with lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect the eyes from the negative effects of sunlight, vitamins C, E, zinc and selenium.
It has been proven that this composition prevents the development of age-related changes in the retina of the eye, allowing even older people to enjoy sharp vision.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the type of dystrophy and timely therapy. The congenital form is not completely treatable. Medication can relieve symptoms and improve vision function. They are taken periodically to support the visual system.
A favorable prognosis will only be achieved if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage of development and the necessary measures are taken. Left untreated, it can lead to retinal detachment. This is an irreversible process that cannot be cured. It is important to consider that during pregnancy, immunity decreases and the risk of developing such a pathology increases.
Laser coagulation of the retina
Today, laser coagulation of the retina is performed under local anesthesia. In more than 90% of cases, this operation can be considered successful. As a result of laser coagulation of the retina, partial destruction of the retina protein occurs, which leads to sealing of the affected area.
If the procedure is carried out on time, then the disease will stop progressing. Restrictive laser coagulation of the retina of the eyeball should be performed in specialized medical centers.
Doctors will put a special lens on the patient, which will direct laser beams to the desired layer of the eyeball. Immediately after the operation, physical activity is prohibited.
Despite the fact that ophthalmological research methods are perhaps the most accurate in medicine, determining the true visual acuity of a patient, being a subjective method, often causes significant difficulties.
The latter are aggravated by the fact that in practical work the ophthalmologist may encounter facts of conscious or unconscious distortion of the truth, when the patient simulates a disease that he actually does not have, or aggravates, i.e. exaggerates the severity of the existing disease.
Conscious simulation most often pursues personal gain (obtaining a disability group, exemption from military service, etc.). Unconscious simulation occurs in hysteria and essentially related traumatic neurosis. An expert ophthalmologist placed in the position of investigator and judge should always remember this.
He should try not to miss a single case of simulation, but even more so - not to state simulation when it does not exist.
Forms of age-related macular degeneration
There are several forms of macular degeneration, depending on the type of pathological process and the degree of damage to the retina.
- Dry age-related degeneration.
- Wet.
The dry form of macular degeneration accounts for more than 80% of all cases. Spots appear in the area of the macula, and vision loss progresses quite quickly. The patient ceases to distinguish small details. The development of the disease takes several years. Treatment methods are at the stage of clinical trials; approved drugs and techniques can slow down the progression of the disease, but not cure it.
The wet form of macular degeneration is much less common and is considered more dangerous. Develops even faster than dry. It differs in that in the wet form the growth of new blood vessels begins. Such vessels allow blood and plasma to pass into the space under the retina. Accordingly, the sensitive cells of the retina are more damaged. Symptoms: the appearance of blind spots in the central zone.
Contraindications and complications
The main contraindications to laser coagulation of the retina are associated with eye diseases. The main one is the insufficient transparency of the eyeball, lens and cornea. In addition, the list of restrictions includes a number of rare diseases.
In general, the appointment for surgery depends on the doctor’s examination. There are no other serious restrictions for the procedure.
The operation itself requires high concentration from both the surgeon and the patient, who is forced to sit motionless for a long time. The perseverance of the patient and the professionalism of the doctor largely determine the success of the operation.
Any complications after laser coagulation of the retina associated with the effects of the laser are most often minor and temporary; for example, swelling of the cornea, which goes away within a few days.
In addition to this, in rare cases the following may occur:
- increased intraocular pressure;
- decreased transparency of the vitreous body;
- change in the shape of the iris and lens;
- appearance of visual field defects.
The rests of the LASED COMPETION CONTRICTION GLAZ FORMALLY FOR THE DISTICAL KPAYNE PEDKO, in the purpose of the same, is the gypyd. Minimyy.
What should you not do before and after surgery?
Before the surgical procedure, the patient must:
- avoid intense physical activity, as this is one of the causes of rupture and detachment of the retina;
- avoid traumatic situations;
- wear sunglasses during the day and in bright sunshine;
- Beware of various types of intoxications.
Also, the occurrence of complications can be affected by childbirth in the presence of this pathology. Before giving birth, a woman must undergo laser coagulation.
What not to do after retinal surgery:
- Firstly, the patient should follow all the ophthalmologist’s recommendations. He will tell you what is contraindicated and can cause relapse or complications.
- Secondly, you will have to limit yourself in sports and other heavy activities. Swimming or running, for example, are not prohibited, but lifting weights is strictly contraindicated.
- Thirdly, you should not tilt your head down: tie your shoelaces, sleep on your stomach, or work in your dacha on a plot of land.
- Fourthly, thermal procedures (baths, saunas, solariums) are prohibited.
Even in the absence of complaints, the patient must appear for an appointment with an ophthalmologist after one month.
The patient should also avoid excessive sun exposure and public places in the early postoperative period to avoid infectious diseases. In addition, it is important to take all medications that your doctor prescribes.
They will help the retina recover faster. If you experience any symptoms, such as spots before your eyes, you should go to the hospital immediately.
Possible complications
If recommendations are not followed during the rehabilitation period after surgery, complications may arise.
Most often, inflammation of the conjunctiva occurs. For prevention purposes, ophthalmologists prescribe eye drops. If you don't use them, it won't end well.
It happens that the retina of the eye is exfoliated again. This happens when the cause of the disease is not eliminated, or it is impossible to do so. Sometimes a person does not comply with the restrictions and contributes to poor “soldering” of the retina, for example, on the very first day after the procedure, he engages in physical work or decides to watch TV.
Sometimes the patient develops various visual disturbances. Typically, problems occur immediately after surgery and resolve as swelling decreases.
They are accompanied by the appearance of various spots and points in the field of view. But there are also cases of the development of disorders some time after coagulation due to violations of the regime during the recovery period.
There are cases that doctors call “dry eye syndrome.” This occurs due to a lack of tear fluid. Symptoms include a burning sensation and discomfort that may go away when the person yawns.
Other complications occur rarely and are associated with complication of the disease. The main thing is not to forget that the retina of the eye is a very fragile thing.
Symptoms of peripheral dystrophies
As a rule, most peripheral dystrophies, including the dangerous “lattice” and “snail track”, are completely asymptomatic. In rare cases, a person may notice the appearance of flashes, sparkles, and lightning in the eye. These signs are unfavorable and determine the degree of danger of dystrophy. These symptoms may be harbingers of retinal tears or a sign that breaks have already formed. If a dark “blind” or “curtain” appears in the projection of the field of vision, or thickening of floating “fly spots” before the eyes, you should immediately contact a specialist. These symptoms are signs of retinal detachment and require urgent medical attention.
Treatment with folk remedies
Source: tvoiglazki.ru Treatment of retinal dystrophy with folk remedies involves the following methods: Goat's milk is an excellent remedy against retinal dystrophy.
Milk is mixed with water in equal proportions and dropped into the eyes, one drop at a time, then a dark bandage is placed on the eyes and rest is required for 30 minutes. The duration of the course is a week. This procedure injects strength into the lens and prevents retinal detachment.
A decoction of pine needles, onion peels and rose hips: all components must be crushed and thoroughly mixed in proportions 5:2:2 (1 unit = tablespoon), then the future decoction should be boiled for 10 minutes, filled with a liter of water.
The fire should not be too strong. It is recommended to take one and a half liters daily. Course – 1 month.
Caraway decoction: a tablespoon of caraway seeds is placed in 200 ml of boiling water and heated over low heat for 5 minutes, then a teaspoon of cornflower flowers is added to the decoction and everything is thoroughly mixed and left for 5 minutes. It is recommended to instill 2 drops into the eyes 2 times a day.
Lotions with nettle and lily of the valley - you will need a third of a glass of nettle and lily of the valley leaves (a teaspoon), a glass of water, half a teaspoon of baking soda. Pour lily of the valley and nettle with water and leave for 9 hours away from light, then add soda. Apply 2 times throughout the day as a lotion on the eyes.
The herb harvested in May is recommended for use. An infusion of birch leaves, horsetail, mustard and lingonberries is recommended to be taken freely. Other remedies that can be used to combat eye diseases include garlic infusions, the use of seaweed, and a mixture of honey and cinnamon.
Use of celandine
Celandine against dystrophy is used as follows: a teaspoon of crushed celandine is poured with water in an amount of 100 ml. The resulting mixture must be kept on fire for a couple of seconds and then infused.
The strained mixture should be placed in the refrigerator and used as drops for retinal dystrophy three times a day, 3 drops per eye. The course is 1 month with the same break and resumption of therapy.
Causes
The following factors can cause irreversible changes in the retina:
- Inflammatory lesions of the visual organs.
- Age-related changes.
- Disturbance of local blood supply.
- Past viral infections.
- Arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis.
- Injuries to the eyes or bone walls of the eye sockets.
- Unsuccessful eye surgeries, after which scarring occurred.
- Impaired immune system functions.
- Unbalanced diet, violation of a healthy diet, regular drinking or smoking.
- Chronic heart diseases.