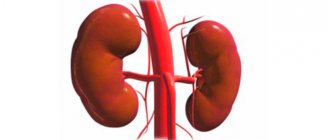
Nephrology is a medical branch that specializes in the study of the normal and pathological functioning of the kidneys and related diseases, as well as developing and implementing methods for diagnosing and eliminating (treating) such diseases. The professional interests of nephrology include the study of not only the kidneys, but also the urethra, ureters and bladder. What does a nephrologist treat?
In this informational article we will look at who a nephrologist is and what he treats.
What does a nephrologist treat?
A nephrologist diagnoses and treats, as well as prevents the following diseases:
- Urolithiasis - the formation of stones from insoluble salts in the bladder, kidneys and ureter;
- Arterial hypertension due to renal pathology - persistently elevated blood pressure is often a symptom of kidney disease.
- Glomerulonephritis is an immune disease that is characterized by inflammation of the renal glomeruli; its symptoms are high blood pressure and swelling;
- Amyloidosis is the excessive formation of the amyloid glycoprotein due to disturbances in protein-carbohydrate metabolism, which in severe cases leads to chronic renal failure (Read also: Causes and symptoms of renal failure);
- Nephritis is an inflammatory disease of the renal pelvis, which affects their vessels, tubules and glomeruli, often develops in children after infectious diseases - tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever.
- Pyelonephritis is an acute or chronic disease of the renal pelvis, most often the cause of its development is the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, in particular E. coli;
- Primary or secondary nephropathy;
- Acute or chronic renal failure;
- Drug-induced damage is the occurrence of renal pathologies in connection with taking medications.
Surgical treatment of kidney diseases is carried out by a urologist; surgical intervention is required for the following pathologies:
- Polycystic kidney disease, cancer neoplasms;
- Formation of large stones in urolithiasis of the kidneys;
- Tuberculous kidney disease
- Abnormal position of the kidneys, violations of their anatomical structure;
- Complicated pyelophritis;
- Nephroptosis.
The symptoms of these diseases are similar to those for which people consult a nephrologist, so additional consultation with a urologist is required to make the correct diagnosis and further treatment.
Difference from a urologist
A nephrologist is a general practitioner who treats diseases affecting the kidneys. This medical specialist specializes in diseases such as glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, stones, cystic formations, as well as various forms of insufficiency.
This doctor monitors the condition of patients after they receive organ transplants. Nephrology is a highly specialized medical field.
A urologist is a surgeon who treats diseases affecting the bladder and urinary tract. This physician treats various diseases affecting the male reproductive system.
All pathologies of the genitourinary system that cannot be cured through surgery do not fall under the competence of a urologist.
Due to the fact that many public hospitals simply do not have a nephrologist, the responsibilities of the urologist are expanded due to the fact that he acquires the functions of treating kidney diseases.
Diseases that can only be corrected through surgery are treated by a urologist, who will act as a surgeon.
Urology, along with nephrology, are one of the most important medical fields that affect the vital organs and systems of the human body.
One of the main differences between a nephrologist and a urologist is that nephrology deals with the treatment and diagnosis of diseases that can be cured using conservative methods.
The range of diseases that fall within the competence of a urology specialist is wider.
Urologists, unlike their nephrologist colleagues, in addition to pharmacological methods to treat patients, can also use surgical techniques that help completely or partially eliminate a person’s problems with the genital organs, urinary tract, or the function of the entire genitourinary system.
When to go to a nephrologist?
With an asymptomatic course, kidney diseases can remain undiagnosed for a long time, which leads to a number of serious complications from the urinary and other body systems. The most vulnerable in this case is the cardiovascular system, which suffers first in case of kidney pathologies.
Therefore, you should be attentive to the condition of the body and if the following symptoms appear, immediately contact a nephrologist:
- Anuria is the absence of urination due to insufficient urine flow into the bladder or its complete absence, which can also occur due to impaired renal function. With anuria, urine is either not excreted from the body or is excreted in an amount of no more than 50 ml per day, which leads to venous stagnation, increased load on the heart and intoxication of the body.
- Oliguria – urine is excreted from the body in insufficient quantities (about 400-500 ml with a norm of 1.5 l), this condition is also characterized by an increased load on the cardiovascular system, as well as an increase in diuresis at night.
- Polyuria - frequent urination with the release of large amounts of urine (2-3 liters per day), can occur due to the consumption of drinks that stimulate urine formation, as well as due to disorders of the endocrine system or chronic renal failure.
- Unilateral or bilateral pain localized in the lower back
- Hematuria or proteinuria is the presence of blood or protein in the urine.
A visit to a nephrologist is also necessary; the patient had previously been diagnosed with the following diseases:
- Renal colic;
- Urinary system infections;
- Acute inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- Chronic or acute renal failure.
High blood pressure can be a symptom of renal pathology, therefore, if there are signs of hypertension, consultation with a nephrologist is necessary.
How is the appointment going?
During the appointment, the nephrologist listens to the patient’s complaints and examines his skin for the presence of swelling and pallor, which accompany many kidney diseases. Tapping of the lumbar region is performed to identify pain in this area. Based on the examination results, the following tests may be needed:
- urine analysis (general, according to Zimnitsky, according to Nechiporenko, Volhard and Reberg-Tareev test);
- Ultrasound;
- angiography;
- biopsy;
- MRI.
After clarification of the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. In the most difficult cases, an operation is needed that can return the patient to a full life.
The cost of an initial appointment with a doctor starts from 1200 rubles. and reaches 16,000 rubles. depending on the diagnostic equipment at the place of consultation or with the possibility of visiting your home.
An appointment with a nephrologist cannot be postponed, since normal kidney function is associated with the functioning of the entire body and is the key to its normal functioning, and sometimes to the patient’s life.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone. Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
When is a child’s nephrologist consultation necessary?
Kidney diseases are often observed in children who have suffered from infectious diseases (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, acute respiratory infections).
Consultation and treatment with a nephrologist is necessary for the following manifestations:
- An increase or decrease in the volume of urine up to 1/3 of the norm excreted per day;
- Changes in the characteristics of urine - color, smell, consistency;
- Edema syndrome - consultation with a specialist is necessary even if slight swelling appears in the eye area;
- The presence of mucus and blood in the urine, cloudy sediment;
- Redness of the external genital organs, pain when urinating;
- Night urination in children over 4 years of age.
What happens at an appointment with a nephrologist?
During a consultation with a nephrologist, the doctor interviews the patient and determines whether he has symptoms of kidney disease. The nephrologist may ask questions about the presence of urinary system diseases among the patient’s relatives in order to identify a hereditary predisposition to renal pathologies. It is also necessary to inform the specialist about the place and nature of the work (to exclude pathologies associated with intoxication of the body), weight and date of birth (nephrons that make up the kidneys are finally formed in the last stages of pregnancy), data on diuresis and blood pressure level.
Pros and cons of the profession
The obvious advantages of being a nephrologist include:
- Narrow specialization - allows you to achieve a high degree of mastery in your chosen profession.
- Possibility of foreign business trips to exchange experiences.
- Application of modern technologies and innovative treatment methods in work.
- If desired, the specialist is provided with rapid career growth.
- Nephrology is a sought-after specialty, so a residency graduate can easily find an open position.
Despite a significant number of advantages, the profession of a nephrologist also has a number of disadvantages, including:
- High degree of responsibility both at the diagnostic stage and during the treatment of the patient.
- Participation in and management of complex, multi-hour operations.
- Kidney diseases are often detected in the terminal stage, when even a qualified nephrologist is unable to help the patient.
- High stress levels.
- Long and extremely difficult specialty training.
Tests prescribed by a nephrologist
- Tests that determine the level of creatinine, urea, calcium and phosphate, blood and urine tests for electrolytes;
- Blood test to determine the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation;
- C-reactive protein test.
Additionally, the following instrumental studies may be needed:
- X-ray examination of the kidneys - angiography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal organs;
- Radionuclide examination – scintography;
- CT scan;
- Kidney tissue biopsy.
Treatment of kidney diseases by a nephrologist has two main directions:
- Nephroprotective treatment is a universal option that allows you to restore kidney function in any possible pathologies;
- Specific treatment – therapy is aimed at treating a specific disease.
Diagnosis of kidney pathologies
After a conversation with the patient, the nephrologist refers for examination. It is important to listen to the doctor’s recommendations, undergo all tests, and do an ultrasound of the kidneys.
At the appointment, the doctor tells patients the rules for preparing for blood donation, urine collection, ultrasound examination, biopsy, and other types of research. Only if you follow the recommendations will the test result be accurate.
Diagnostic methods:
- general urine analysis;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- analysis according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky;
- Rehberg's test.
Additional research:
- angiography;
- kidney tissue biopsy;
- ultrasound examination of bean-shaped organs;
- excretory urography;
- kidney scintigraphy;
- conducting MRI and natural filters.
Preparing to see a nephrologist
- Diagnosis by a nephrologist is carried out on an empty stomach; you must abstain from food for 12 hours before visiting a specialist;
- 12 hours before visiting a nephrologist, it is also prohibited to drink alcohol and smoke;
- The day before administration, liquid is limited to a minimum amount;
- It is recommended not to take any medications for 24 hours unless it threatens your health. If the course of the drug cannot be interrupted, you must inform your doctor about this.