General information
A condition called thrombocytopenia is characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood to less than 150 x 109/L. As a result, the patient experiences increased bleeding and difficulty stopping the bleeding . Thrombocytopenia (ICD-10 code - D69.6 Thrombocytopenia, unspecified) may accompany hematological diseases. However, an independent disease is also diagnosed - idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ICD-10 code - D69.3), as well as an autoimmune form of the disease.
Speaking about thrombocytopenia - what kind of disease it is, it should be noted that it develops as a result of a disruption in the production of platelets or too active destruction of them. The autoimmune form of the disease is most often diagnosed. This condition can also develop against the background of a number of diseases: herpes , hepatitis , HIV, infectious mononucleosis , influenza .
It can also be provoked by some exogenous factors. What thrombocytopenia is, the causes and treatment of this disease are described in detail in this article.
Appearance and formation of platelets
Plate-shaped blood components are formed in the bone fluid from megakaryocytes - giant bone marrow cells, inside of which there is cytoplasm. During maturation, microparticles called platelets detach from megakaryocytes and later enter the bloodstream. The formation and growth of megakaryocytes is controlled by a special hormone of protein origin - thrombopoietin. It is formed in the liver, kidney tissue and muscles. Then it penetrates into the red bone marrow with the blood flow and provides the blood process for the formation of platelets and megakaryocytes. At the same time, thrombopoietin production is inhibited. This helps to balance these microorganisms and maintain their number at a normal level.
Platelets in the blood
Main tasks of platelets
The blood component performs two functions in the human body:
- Stopping bleeding, hemostasis. When the structure of an artery or blood vessel is damaged, platelets are immediately released. Then serotonin is produced - a substance that spasms blood vessels. Platelet processes, connecting with the wall of the damaged vessel, form a barrier that inhibits bleeding. Within a few minutes the hemorrhage stops.
- Supplying blood vessels with nutrients. When destroyed, activated platelets contribute to the growth factor that nourishes the walls of the damaged vessel or artery. The described action helps speed up the recovery process.
Platelets are vital blood cells, without which stopping bleeding and healing wounds is impossible.
Pathogenesis
Platelets are blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow. They live in the body for a little more than a week, after which they disintegrate in the spleen and liver. The main functions of these cells in the body are to prevent the development of bleeding. The cells stick together and a blood clot forms, blocking the wounded vessel. In addition, they determine the synthesis of growth factors that affect tissue repair processes. Platelet levels may fluctuate depending on certain factors. However, such fluctuations are physiological and temporary. Normally, the level of these cells is 150 thousand per microliter (150 x 109/l). If the platelet count decreases, we are talking about thrombocytopenia.
Currently, the pathogenesis of this disease has not been sufficiently studied.
The mechanism of development of the disease may be associated with the following factors:
- impaired platelet production by the bone marrow;
- disruption of their distribution in the vascular bed;
- platelet deficiency and increased destruction.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura develops due to an autoimmune reaction that is directed against one’s own platelets. This immune reaction is a complex cyclic process in which B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, macrophages , NK cells, and cytokines participate. Antibodies to platelets are not always detected in the blood.
In children, the development of ITP often occurs after acute respiratory viral infections. When the platelet count falls below 10 x 109/L, the bleeding period prolongs.
How does thrombocytopenia manifest?
Destructive processes
Under normal conditions, platelets remain in the peripheral blood after eight days, performing standard functions. At the end of this period, their structure and structuring changes. As a result, microelements are absorbed and destroyed by the spleen, an internal organ that is involved in eliminating blood elements with an altered structure from the circulation.
Spleen in the human body
Classification
The disease is divided according to several characteristics. Taking into account the origin, it is determined:
- Primary thrombocytopenia - development is associated with a violation of hematopoietic processes, the production of antibodies in the body that destroy platelets.
- Secondary thrombocytopenia develops against the background of other diseases. The secondary form of the disease can also be the result of serious poisoning, radiation, or alcoholism.
The types of thrombocytopenia are determined by:
- Immune thrombocytopenia - this condition develops if the immune system begins to perceive platelets as foreign agents. As a result, immune thrombocytopenia leads to the destruction of platelets by the body's immune system.
- Essential thrombocytopenia - this form of the disease most often affects older people, after 50 years. The essential form often develops after surgical operations, as well as against the background of chronic diseases of internal organs and iron deficiency.
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is most often diagnosed in children. The disease is associated with blood clotting disorders.
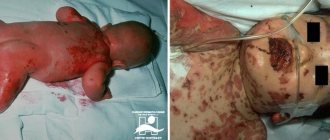
- Thrombocytopenia in newborns can accompany congenital pathological conditions, and also develop as a secondary disease during asphyxia during childbirth, infection of the child, etc.
Taking into account the severity of the disease, it is determined:
- Easy . The platelet level is the lower limit of normal (30-50 x 109/l), symptoms of pathology do not appear. Sometimes nosebleeds occur. As a rule, this condition is determined by chance, during preventive tests. In this case, no treatment is required; the doctor monitors the patient’s condition.
- Average. The platelet level is reduced (20-50 x 109/l). There are hemorrhages under the skin, even with minor blows noticeable hematomas occur, and frequent nosebleeds are a concern. Small rashes may appear on the body. Treatment of the condition is carried out if there is a threat of internal bleeding.
- Heavy. The platelet level is very low, sometimes critical (less than 20 x 109/l). Extensive internal bleeding and multiple skin rashes develop. Treatment is mandatory and the patient should be hospitalized.
Based on the nature of the disorders, the following forms of thrombocytopenia are distinguished:
- isoimmune;
- transimmune;
- heteroimmune;
- autoimmune.
The nature of the flow determines:
- acute (up to six months);
- chronic:
- with rare relapses;
- continuously relapsing.
Stages of the disease
The brightness and obviousness of the symptoms of pathology depends on the decrease in platelets in the body. A classification based on severity has been developed. At the initial stage, periodic nosebleeds, prolonged and heavy periods in women, bruises from minor blows, and skin damage are noticeable. The initial stage of the disease is often detected by chance, during a comprehensive examination or diagnosis of another concomitant disease.
With the second, moderate degree of development of the pathology, tiny hemorrhages are observed throughout the body in the form of dots. This process is observed on the body, internal organs, and in the human oral cavity. In the severe, advanced stage, abundant bleeding occurs into the internal organs and brain tissue. In case of illness, the doctor prescribes drug therapy.
Causes of thrombocytopenia
The reasons for the decrease in platelet levels in children and adults are due to the fact that they are being destroyed too actively, or an insufficient number of them is formed in the body.
The following conditions can lead to platelet destruction:
- idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- other autoimmune diseases - lupus erythematosus , rheumatoid arthritis ;
- previous surgical operations ( heart bypass surgery );
- side effects of certain medications;
- preeclampsia in pregnant women.
The causes of thrombocytopenia in adults, leading to decreased platelet production, may be the following:
- viral diseases - hepatitis C , chickenpox , HIV , mononucleosis , etc.;
- oncological diseases – leukemia , lymphoma ;
- bone marrow irradiation;
- chemotherapy;
- alcoholism;
- deficiency of folic acid , vitamin B12 .
Disease prevention
The possibility of using preventive measures depends on the cause of the pathology. It is impossible to avoid hereditary disease or age-related changes. The following recommendations will help avoid thrombocytopenia and improve physical condition during illness:
- Alcohol interferes with the formation of platelets, so drinking alcohol should be kept to a minimum.
- Avoid contact with toxic, chemical and radiation substances.
- Do not take medications that lead to a decrease in platelet concentration. It is also better not to take medications that increase the risk of bleeding.
- Get vaccinated against viruses that can lead to the development of pathology.
Following the above tips will reduce the risk of the disease, relieve symptoms and prevent relapse in those who have recovered.
Symptoms
Thrombocytopenia in adults is manifested by a number of symptoms that depend on the severity of the disease. Signs may be as follows:
- the appearance of spontaneous hemorrhages in the mucous membranes and under the skin;
- nausea, dizziness ;
- prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction;
- increasing the period of bleeding cessation;
- spontaneous appearance of hematomas in different parts of the body;
- severe drowsiness , loss of strength;
- increased nosebleeds;
- very heavy periods.
Speaking about what thrombocytopenia is in adults, it should be noted that the results of a blood test for thrombocytopenia show from 0 to 50 per 10 in 9 platelets / l.
Initial thrombocytopenia in adults
The chronic form of idiopathic purpura occurs mainly in women between twenty and forty years of age. This pathology is unspecified thrombocytopenia. The female population gets sick twice as often as the male population. Pathology has a slow progression. The external stimulus cannot be determined. In some individual cases, there is a connection with chronic tonsillitis, contact with substances that have a chemical basis.
Over a long period of time, the pathology takes a subclinical form and is discovered unexpectedly during the examination of another disease. Then a hemorrhagic process slowly forms, expressed by the appearance of hematomas on the body, differing in shape and shade. There is bleeding when coughing, vomiting, urinating, and diarrhea. Hematomas occur most often on the abdomen, arms and legs, at the point of recent injection punctures. Bruising on the face, conjunctiva, lips, mucous tissue signals the development of a serious pathology.
During the final, last stage, anemia occurs, bleeding into the eyes and brain. Blood drops in the oral cavity and on mucous tissues can warn of this phenomenon. The unexpected retreat of the disease in adults occurs as an exception to the rule. The pathology requires the supervision of a doctor who is prescribed therapeutic treatment for thrombocytopenia.
Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy
Gestational pathology during pregnancy is rare. According to statistics, 7% of women experience the disease in the third trimester of pregnancy. The form of the disease is not pronounced, so there are no visible clinical manifestations and symptoms. The disease occurs without hemorrhagic syndrome. The process of the occurrence of pathology in this case has not been fully studied. Autoimmune thrombocytopenia in pregnant women is dangerous because antibodies can penetrate the body of the unborn child, destroying platelets in it.
This leads to the development of pathologies in newborns and bleeding. But more often the disease reveals a favorable prognosis for the woman and the baby. A dangerous outcome occurs with a sudden outbreak of a jump in blood pressure that occurs during late toxicosis. There is a sharp decrease in platelets and the risk of bleeding increases, and a transimmune pathology develops in the child. During this period, inpatient medical supervision is necessary, and emergency care may be required.
Tests and diagnostics
The main test to determine thrombocytopenia is a clinical blood test that determines platelet levels.
If, based on the test results, the patient is diagnosed with congenital thrombocytopenia , a bone marrow examination is performed. megakaryocytes is determined . If they are absent, this indicates a disruption in the process of platelet formation, if they were present - we are talking about the deposition of platelets in the spleen or their peripheral destruction.
To determine the causes of the development of pathology, the doctor may prescribe the following studies:
- antibody tests;
- genetic tests;
- Ultrasound;
- electrocardiogram;
- endoscopic examination;
- radiography.
Diagnosis of the disease
Hematology, a medical science, studies blood diseases. To identify it, you need to take a blood test for laboratory testing to see the number of cells and components it contains. After this, a comprehensive diagnosis of the body is carried out in order to exclude the recurrence of thrombocytopenia. The pathology may turn out to be false, so it should be examined carefully. Causal diseases that are accompanied by a decrease in platelet concentration have pronounced symptoms, so it will not be difficult for an experienced doctor to identify them. This is a reduction in platelets in liver cirrhosis, leukemia, malignant tumors and other diseases.
In some cases, they are content with a thorough history taking. But more often a complex analysis is carried out, a bone tissue puncture is taken, an immunological test is taken for further scrupulous research in the laboratory. Before diagnosing autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, it is based on the following criteria:
- A decrease in platelet concentration in the absence of other pathologies during a blood test.
- Absence of clinical blood pathologies in close relatives.
- The presence of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow exceeds the permissible norm.
- Lack of diagnosis of additional, concomitant diseases.
- Identification of antibodies with antiplatelet properties.
- The effectiveness of corticosteroid therapy.
The diagnosis must be made by a doctor specializing in this area, based on the examinations performed.
Tests prescribed by the doctor
For each type of thrombocytopenia, a clinical blood test is prescribed for clinical examination and calculation of the content of its components, as well as a morphological analysis of platelets. The level of blood clotting is examined. These actions determine the degree of the disease and the further course of treatment and additional examinations. If, as a result of the tests performed, there are no characteristic symptoms, then a bone marrow puncture is performed to examine the nature of the stem cells and the presence of antibodies; platelet aggregation is observed.
After establishing an accurate diagnosis of stage 1 thrombocytopenia, an abdominal ultrasound is performed to examine the condition and health of the internal organs. X-rays, biopsies and tomography are also done to exclude serious damage to the body. If, as a result of the examinations carried out, a secondary form of the disease was discovered, then the algorithm for subsequent actions depends on which disease is diagnosed as causative. Additional tests and examinations of the body are prescribed to identify pathology.
So, suspecting a blood cancer, there is a reduced concentration of platelets, muscle weakness, and rapid fatigue. There is a noticeable thickening and increase in the size of the lymph nodes, the formation of purulent wounds, and frequent colds. The doctor prescribes a bone marrow puncture test, as well as lymph nodes. The puncture is subjected to detailed microscopic examination in order to identify the type and stage of development of oncology, the prevalence of metastases in the body.
To confirm the diagnosis of oncology, additional examinations of internal organs are prescribed to exclude the spread of metastases. Abdominal ultrasound, radiography, tomography, biopsy and other methods are performed. In some cases, tests are taken to detect HIV and AIDS infections. The method of examining the patient is prescribed by the attending physician, based on the symptoms of the disease, the general condition of the patient, his age and gender.
Treatment with folk remedies
If the treatment of thrombocytopenia is carried out according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, then after consultation with a specialist, you can try to improve the general condition of the body using folk remedies. However, it is important to understand that treatment of thrombocytopenia with folk remedies should under no circumstances replace therapy prescribed by a doctor.
You can use the following traditional methods:
- Verbena infusion. Pour 5 g of verbena into a glass of boiling water. Leave for half an hour. Drink a glass every day for a month.
- Sesame oil. Every day you should consume 10 g of oil, adding it to a salad or consuming it separately from food.
- Stinging nettle. Pour 10 g of dry raw material into a glass of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes. Drink 20 ml 3 times a day.
- Burnet decoction. An effective remedy for stopping bleeding. 2 tbsp. l. pour the product into a glass of water and boil for 15 minutes. After 3 hours, strain, drink 20 minutes before meals, 3 tbsp. l.
- Herbal collection. Mix 30 g of yarrow flowers and shepherd's purse. 1 tbsp. l. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over this mixture and leave for several hours. Drink half a glass three times a day before meals.
- Rose hip decoction. Pour 50 g of rose hips into 0.5 liters of water and cook for 5 minutes. Pour into a thermos and leave overnight. Drink instead of tea, adding honey.
- Viburnum bark. 2 tbsp. l. dry raw materials, pour 300 ml of water, cook for half an hour. Strain and add water to get the original volume. Drink 4 times a day, 2 tbsp. l.
- Dried fruits. It is necessary to chop 200 g of dried apricots, figs, raisins, and prunes. Add 200 g of honey and the juice of 2 lemons to the mixture. Place the mixture in small jars and store them in the refrigerator. In the morning, take 1 tbsp. l. facilities.
- Beetroot juice. Mix fresh beet juice with equal amounts of cucumber and carrot juice. Take a glass of this remedy in the morning, then have breakfast an hour later.
Anemia and leukemia
Blood cells are similar in functionality to other cells of the human body, so they can also become malignant. In most cases, pathological transformation affects leukocytes, provoking one of the most severe blood diseases - leukemia. Low hemoglobin in leukemia is recognized by doctors only as an indirect cause of the disease, but the main provoking factors have not yet been established.
Important: the acute form of leukemia is characterized by a rapid and unsystematic accumulation of unripe white blood cells in the bone marrow structures, and healthy cells are replaced by tumor cells.
As a result, the bone marrow loses the ability to create healthy cells and a deficiency of platelets responsible for blood clotting appears, leukocytes and red blood cells degenerate. To diagnose anemia, leukocytes do not necessarily have to deviate quantitatively and qualitatively from the norm.
In children
When discussing the treatment and causes of thrombocytopenia in children, it should be noted that this condition can be congenital, accompanying pathologies in newborns. Thrombocytopenia may also be a secondary disease. The reasons for this are related to infection of the child, premature birth or asphyxia during childbirth.
The causes of thrombocytopenia in children depend on the form of the disease.
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura develops with a frequency of 3-5 cases per 100 thousand children. Most often diagnosed in school-age children. Most often it manifests itself in children who have recently suffered a viral disease - mumps , measles , chickenpox , rubella , etc.
- Secondary thrombocytopenia can develop against the background of certain diseases ( hepatitis , cytomegalovirus infection ), taking a number of medications ( Heparin , Abciximab , etc.).
In order to recognize the disease in a child in time, parents should pay attention to the characteristic manifestations of the disease. In this condition, bleeding develops - pinpoint hemorrhages appear on the skin, frequent nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and gastrointestinal bleeding are disturbing. It is important to understand that internal bleeding can threaten the baby's life.
If the diagnosis has been confirmed through research, it is important to properly treat thrombocytopenia in children. His regimen is prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment is prescribed if the platelet count is less than 20-30 thousand per microliter. But most often, the doctor is guided by the presence of pronounced clinical manifestations before prescribing a treatment regimen. The specialist may prescribe corticosteroids ( Prednisolone , Dexamethasone ). In severe cases, cytostatics ( Vincristine , Vinblastine ) and immunosuppressants ( Azathioprine , Cyclosporine ) are prescribed. In rare cases, the spleen is removed.
But most often, the platelet count in children becomes normal over time on its own, without treatment. According to statistics, in 60% of children the condition returns to normal after a month and a half, in 80% of children - after 6 months.
But in any case, over a certain period it is necessary to visit a doctor and conduct control blood tests.
In addition, parents must adhere to some important rules to protect their baby:
- It is important that the child does not engage in activities that could cause injury. He should not engage in traumatic sports.
- You should choose your toothbrush carefully - it should be soft.
- In some cases, it is advisable to take laxatives to avoid intestinal trauma.
- Do not use medications that increase bleeding ( Aspirin ).
- Provide hospitalization of the child in case of bleeding, in the presence of severe hemorrhages in the mucous membranes and skin.
Parents should be aware that the most serious complication of thrombocytopenia is cerebral hemorrhage. It develops if the platelet count is 10-20 thousand per microliter. Symptoms that should be alarming are a sharp bursting headache , convulsions , vomiting, and facial asymmetry. If such signs occur, you should immediately call an ambulance. However, such complications rarely develop.
Consequences and complications
The main manifestations of thrombocytopenia are hemorrhages and bleeding. Depending on their location and intensity, various complications can develop, sometimes life-threatening.
The most serious complications of thrombocytopenia are:
- Brain hemorrhage. It is a relatively rare, but the most dangerous manifestation of thrombocytopenia. It can occur spontaneously or with head injuries. The occurrence of this condition is usually preceded by other symptoms of the disease (hemorrhages in the oral mucosa and facial skin, nosebleeds). Manifestations depend on the location of the hemorrhage and the volume of blood shed. The prognosis is poor - approximately a quarter of cases are fatal.
- Retinal hemorrhage. It is one of the most dangerous manifestations of thrombocytopenia and is characterized by the saturation of the retina with blood released from damaged capillaries. The first sign of a retinal hemorrhage is a deterioration in visual acuity, after which a sensation of a spot in the eye may appear. This condition requires urgent qualified medical care, as it can lead to complete and irreversible loss of vision.
- Posthemorrhagic anemia. Most often develops with heavy bleeding in the gastrointestinal system. It is not always possible to diagnose them immediately, and due to increased capillary fragility and a reduced platelet count, bleeding can continue for several hours and often recurs (repeats). Clinically, anemia is manifested by pallor of the skin, general weakness, dizziness, and death can occur if more than 2 liters of blood are lost.
Werlhof's disease Hemolytic anemia Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke Aplastic anemia Cytomegalovirus Endocarditis
Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy
Pregnant women may experience a decrease in platelet counts and hemocoagulation changes. Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy can be a consequence of both physiological and pathological processes. Normally, in most expectant mothers, the platelet count decreases by 10% compared to normal levels. The most significant decrease in platelets during pregnancy is observed in the last trimester.
If severe thrombocytopenia develops, this is manifested by a loss of strength and the formation of hematomas on the skin and mucous membranes.
Specific conditions associated with pregnancy are:
- Gestational thrombocytopenia - the platelet count may decrease to 43x109/L. Develops at the end of the second to the beginning of the third trimester. It is a physiological condition that does not complicate pregnancy.
- Thrombocytopenia in a hypertensive state – these conditions include preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. These conditions require treatment, as they threaten the normal course of pregnancy.
To prevent complications, a pregnant woman should regularly take blood tests, eat right and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Normal platelet count
For normal blood clotting, it must contain a certain number of blood platelets. The unit of measurement is one thousand in 1 microliter.
- On average, the norm is 150-400 Chl . The limits of normal indicators depend on gender, age, physiological state, and calculation methods.
- For men, 200-400 Chl ,
- For women – 150-320 Chl . During menstruation, their number can decrease by 50%, then quickly recover. A slight decrease in platelets below normal in pregnant women is not considered a pathology, but the lower limit should not be less than 100 Chl.
Norms for children
| Child's age | Platelet rate |
| newborn | 100-420 thousand units/µl |
| 2 weeks – 1 year | 150-350 thousand units/µl |
| 1-5 years | 180-380 thousand units/µl |
| 5-7 years | 180-450 thousand units/µl |
Diet
Diet for essential thrombocythemia
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 3 weeks
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles per week
People who have a low platelet count in their blood should follow some recommendations when shaping their diet.
- You need to eat meals in small portions, doing this at least 5 times a day.
- The diet should contain protein foods that are easily digestible (liver, poultry, fish).
- It is important to get proteins from plant foods, consuming legumes, nuts, and mushrooms.
- It is recommended to include more fresh vegetables and fruits in the menu. It is better to choose seasonal fruits and steam, boil, or bake vegetables.
- Low-fat dairy products should also be included in your diet every day.
- It is recommended to cook porridge in water from whole grains - buckwheat, rice, wheat.
- It is better to choose bread with bran.
- You should drink weak tea, dried fruit compote, berry fruit drinks, cocoa, and fresh juices.
- You can make an omelet from quail eggs.
Low hemoglobin and white blood cells
Share the article on social networks:
Any of the subgroups of leukocytes is produced and matures until it enters the blood in the bone marrow structures. Damage to an organ or a change in its functionality under the influence of chronic diseases, including anemia, leads to a change in the percentage of leukocytes in the blood.
Important: anemia is one of the main reasons affecting bone marrow function. However, intoxication, inflammation, infectious invasions, chemotherapy, and taking immunostimulating drugs also lead to changes in the level of leukocytes.
Decreased platelets associated with immunity
Immune thrombocytopenia includes such forms as:
- Isoimmune or alloimmune - can be neonatal or occur as a result of blood transfusion that is incompatible by group affiliation;
- Hapten or heteroimmune (hapten is part of an antigen), resulting from the entry of a foreign antigen (viruses, drugs) into the body;
- Autoimmune thrombocytopenia is the most common and frequently encountered. A breakdown in the immune system, the nature of which, as a rule, is not established, leads to the fact that the immune system ceases to recognize its own healthy platelet and mistakes it for a “stranger,” which in turn reacts by producing antibodies against itself.
Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura (AITP) is the most common form of immune thrombocytopenia. It most often affects young women (20-30 years old).
Hemorrhagic diathesis in AITP
A drop in platelet levels that accompanies another disease and is part of its symptom complex is called secondary thrombocytopenia. As a symptomatic, thrombocytopenia is observed in various pathologies:
- Collagenosis (systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma, dermatomyositis);
- Acute and chronic leukemia (myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia);
- Chronic hepatitis and kidney diseases.
However, AITP, which is called essential or idiopathic thrombocytopenia (Werlhof's disease), occurs much more often as an independent isolated disease.
This form is called idiopathic due to the fact that the cause of its occurrence remains unclear. With this pathology, platelets live not 7 days on average, but 2-3-4 hours, despite the fact that the bone marrow initially continues to produce all cells normally. However, a constant deficiency of blood cells forces the body to react and increase platelet production several times, which negatively affects the maturation of megakaryocytes.
In pregnant women, essential thrombocytopenia has a fairly favorable course, but an increase in the frequency of miscarriages is still observed. Treatment of thrombocytopenia in such a case is carried out by administering prednisolone 5-7 days before birth. The issue of obstetrics is decided on an individual basis, but more often they resort to surgery (caesarean section).
The therapeutic effect of corticosteroids is not necessarily used during pregnancy; they are also used in other cases. In addition, a positive effect was observed from intravenous administration of immunoglobulin, which reduces the rate of phagocytosis. However, with repeated relapses of the disease, preference is often given to splenectomy (removal of the spleen).
What drugs are used to treat thrombocytopenia?
- delagil - 1 tablet per day for 2 months under the control of the number of leukocytes and the ophthalmological picture,
- cyclosporine A - at a dose of 2.5-5 mg/kg body weight per day,
- azathioprine - 1-4 mc/kg body weight per day,
- vincristine - 1-2 mg intravenously once a week,
- novoseven - at a dose of 90 mg/kg body weight.
Thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy treatment
Prompt treatment of thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy is important, as a low platelet count reduces the ability of blood to clot. For this purpose, the drug “Erythrophosphatide”, obtained from human red blood cells, is widely used. This remedy increases platelet levels, thereby increasing blood viscosity. The drug is injected into the muscle at a dose of 150 mg once over 4-5 days. The course of treatment is at least 15 injections.
With the help of the drug "Revolade" the synthesis of platelets is also stimulated. It must be taken in an individually selected dosage by a doctor. When using it, many side effects may occur, such as vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth and back pain. The drug "Dexamethasone" is indicated after chemotherapy not only to suppress vomiting and nausea, but also to increase platelets.
Diagnostic examination
To begin with, if leukopenia and/or thrombocytopenia is suspected, it is necessary to do a laboratory test of a complete blood count to calculate the number of all types of cells in the blood. However, with the help of this study it will only be possible to determine the number of platelets; with leukocytes it will be more difficult. Since in a number of diseases the number of leukocytes remains normal, but the level of the most numerous group of leukocyte cells - neutrophils - decreases sharply. Therefore, when diagnosing the disease, an absolute count of neutrophils, not leukocytes, is necessary. Then, in order to establish the cause and mechanism of development of the disease, a diagnosis should be made:
- determination of blood clotting time;
- puncture of the red brain;
- genetic research;
- ultrasonography;
- perform liver tests;
- examine the level of vitamin B12 in the body;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Having received a conclusion about the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient, the hematologist will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary correct treatment for the patient. Which should ease the patient’s internal well-being within a few days.
Low platelets during pregnancy
There is thrombocytopenia typical of pregnancy , which is associated with toxicosis of pregnancy or preeclampsia (high blood pressure, fluid retention and edema, protein in the urine), which goes under the name HELLP syndrome (H=hemolysis, E=elevated, L=liver enzimes, L= low, P=platelets). In some cases, HELLP syndrome in combination with preeclampsia causes such problems that the pregnant woman requires hospitalization.
In the case of a pregnant woman who suffers from thrombocytopenia, an assessment by a team of hematologist, gynecologist and possibly an immunologist is required. If the mother's platelets fall below 50,000 cells per milliliter of blood, a caesarean section is necessary, preventing any risk of bleeding.
Methods for correcting platelet levels
A low platelet level is not a separate disease; it is a sign of some abnormality occurring in the body. The attending physician who has identified this pathology will definitely prescribe a full examination of the man’s body, after which he will make a diagnosis and prescribe a comprehensive treatment.
Every person can be at risk, for example, due to infection with an infectious disease. This process can be prevented by constantly strengthening the immune system, exercising and proper nutrition.
Basic tips:
- Food should be varied and include all types of fish, red meat and rich meat broths, sausages, pates, liver, eggs, cheese, vegetable salads, greens, buckwheat and oatmeal, nuts and berries, rosehip juice and green varieties of apples.
- Juices, fresh juices and a vitamin-mineral complex have a positive effect on blood composition.
- You cannot drink alcohol, consume marinades, pickles and spices.
- You need to adjust your sleep and rest, and relax at sea at least once a year.
- Stimulate the body with cardio exercises.
- Stop taking anticoagulant medications.
- If a dangerous form of thrombocytopenia is identified, glucocorticoid hormones and therapy to correct immunity are prescribed.
- Anti-Rhesus D serum and donor platelet transfusion are used.
- Plasmapheresis is used because blood plasma contains antibodies, an insufficient amount of which causes immune deficiency. This is effective in the development of an autoimmune process in the body.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - t
| Treatment of thyrotoxicosis |
| Treatment of toxicoderma |
| Treatment of toxoplasmosis |
| Treatment of tracheitis |
| Treatment of trematodosis |
| Treatment of trichinosis |
| Treatment of trichomoniasis |
| Treatment of pulmonary embolism |
| Treatment of skin tuberculosis |
| Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis |
| Treatment of liver tuberculosis |
| Treatment of genital tuberculosis |
| Treatment of kidney tuberculosis |
| Treatment of splenic tuberculosis |
| Treatment of tularemia |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.