MCV (mean corpuscular volume) is one of the erythrocyte indices that shows the average volume of erythrocytes. This indicator can characterize the entire population of red blood cells in the blood. The calculated measure denotes the average volume occupied by one red blood cell. The value of this index is calculated by the formula: hematocrit as a percentage, multiplied by 10 and divided by the total number of red blood cells in the blood. Most laboratories measure MCV in cubic microns (µm2) or femtoliters (fl).
The MCV index determines the average volume of red blood cells
Changes in the erythrocyte composition of blood are one of the main laboratory criteria in the diagnosis of anemia, therefore, calculation of the average volume of erythrocytes in combination with other indicators of a clinical blood test is used for differential diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of anemia and diseases of the hematopoietic system, and determination of water-electrolyte balance disorders.
MCV in a blood test is calculated automatically - using a hematology analyzer, which determines the average volume of all measured red blood cells.
Normal values
The average volume of red blood cells normally depends on several parameters, namely: the gender and age category of the person. The units of measurement for this value are femtoliters (fl) or cubic micrometers (µm^3).
| Age | Norm (fl) |
| First week of life | 88-126 |
| 1 month | 88-124 |
| 2 months | 77-115 |
| 3-6 months | 77-108 |
| 1-5 years | 73-85 |
| 5-10 years | 75-87 |
| 10-15 years | 76-95 |
| Girls (15-18 years old) | 78-98 |
| Boys (15-18 years old) | 79-95 |
| Women (18-45 years old) | 81-100 |
| Men (18-45 years old) | 80-99 |
| Adults from 45 to 65 years old | 81-101 |
| Older women | 81-102 |
| Older men | 81-103 |
It is very important to consider that in a child under the age of 10 years, such an index may fluctuate slightly in any direction, which is considered quite normal. Most often, the parameter stabilizes and coincides with the above values by the age of 15.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
The average volume of red blood cells in children or adults may fluctuate up or down, which in any case indicates the occurrence of some pathological process.
For example, when the mean red blood cell volume is elevated, a person may be diagnosed with one of the following:
- severe poisoning from chemicals or poor-quality food;
- thyroid dysfunction and other pathologies of the endocrine system;
- deficiency of iodine or iron in the body;
- reticulocytosis;
- liver pathologies, in particular hepatitis and cirrhosis;
- cancer of the bone marrow;
- celiac disease;
- DiGuglielmo's disease;
- hypothyroidism;
- hyperglycemia;
- infection or inflammation in the pancreas;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- chronic liver failure.
If mcv is elevated, then this does not always indicate the course of the disease, for example, among the less harmless sources are:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- long-term addiction to bad habits;
- specific working conditions, for example, under which a person is forced to constantly come into contact with toxins;
- hormonal imbalance that develops during menstruation or pregnancy.
If a general clinical blood test shows that the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, this may indicate:
- various types of anemia;
- formation of malignant neoplasms;
- heavy metal intoxication;
- thalassemia;
- leukemia;
- heavy blood loss;
- metastasis of malignant tumors;
- porphyria;
- autoimmune diseases.
Also, the indicator can be reduced due to abuse of the following medications:
- "Isoniazid";
- "Colchicine";
- "Metformin";
- "Phenacetin";
- "Trimethoprim";
- "Methotrexate";
- "Pyrimethamine";
- "Triamterene";
- "Glutethimide";
- mefenamic acid;
- estrogens;
- oral contraceptives;
- nitrofurans;
- anticonvulsants;
- aminosalicylic acid.
The drug Isoniazid
In some situations, the average volume of erythrocytes mcv remains within the normal range, but a person may experience:
- normocytic anemia;
- hemoglobinopathy;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- hypogonadism;
- hypopituitarism;
- hypoadrenalism;
- hypothyroidism;
- chronic infectious processes;
- uremia.
Correlation of MCV with other erythrocyte indices
MCV values correlate with other erythrocyte indices:
- MCH - it is measured in picograms (pg) and denotes the average content of red blood pigment (hemoglobin - Hb) in a red blood cell, this index has a correlative relationship with MCHC (average concentration of Hb in Er) and with MCV - an indicator indicating the average volume of red cells;
- MCHC - its value is expressed in grams per deciliter (g/dl), this index characterizes the average concentration of Hb in the red blood cell, it correlates with MCH (average Hb content in Er) and with MCV, that is, with the index described in this work .
These indicators are also calculated by an automatic hematology analyzing system, although all this can be done manually if you first determine the number of red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin level (HB) and hematocrit (Ht). And all this is done in the analyzer... Thus:
- MCH = [Hb, (g/dl) x 10] /
- MCHC = [Hb, (g/dL) x 100] /
It is obvious that erythrocyte indices have correlative relationships with each other, however, the MCH and MCHC indices are not as often used to determine the type of anemia as the average volume of erythrocytes, although, it should be noted, an increased level of MCH is observed in hyperchromic anemia (megaloblastic and accompanying cirrhosis of the liver). A reduced value of the indicator (MSI) is observed in hypochromic iron deficiency conditions and malignant tumor processes.
MSHC is usually reduced in hypochromic anemia (sideroblastic anemia, IDA), as well as thalassemia.
In addition, this erythrocyte index (meaning MCV) is often used as a supplement to another indicator characterizing the state of red blood cells - RDW or the degree of anisocytosis of erythrocytes. Together they help to make a differential diagnosis of microcytic anemias.
Display all posts with the tag:
Analyzes
Go to section:
Blood diseases, tests, lymphatic system
Recommendations to SosudInfo readers are given by professional doctors with higher education and specialized work experience.
One of the leading authors of the site will answer your question.
Symptoms
Since the average volume of red blood cells in a child or an adult can decrease and increase, any deviation will have characteristic external manifestations. However, they can go completely unnoticed by a person or be masked by the symptoms of the underlying pathology.
If the volume is increased, this may be indicated by:
- excessive pallor of the skin and lips;
- frequent occurrence of pain in the abdominal area;
- increased heart rate;
- yellowness of the skin of varying degrees of severity;
- aversion to food;
- severe weakness and fatigue.
When the average red blood cell volume is low, a person may complain of:
- constant drowsiness;
- significant decrease in performance;
- cold sweat;
- cold skin;
- decreased blood tone;
- lethargy and slowness of movements;
- fainting state;
- increased heart rate;
- emotional insufficiency.
Such external manifestations should be an impetus for immediately seeking qualified help. It is worth noting that in children some symptoms may be much more pronounced than in adults.
Significance in analysis
Let's look at why it is so important for clinicians, especially considering the fact that MCV is present in every transcript of a blood test performed in an automatic hematology analyzer. To answer this question, let’s dive a little into the physiology of hematopoiesis, as well as the processes of respiration and circulation.
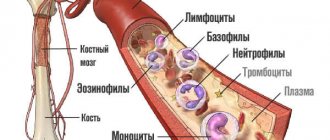
Hematopoiesis
In the process of hematopoiesis, young precursor cells are formed from erythroblasts - reticulocytes, which mature into full-fledged red blood cells and enter the bloodstream, where the hemoglobin included in their composition performs its functions of transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide, and also maintains the buffer capacity of the blood. As is already known, folic acid (vitamin B9) and cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) are necessary for the formation of red blood cells of normal size and volume. If these components are lacking, then megaloblastic anemia may develop, which is characterized by the presence in the blood of immature red blood cells of increased volume - erythrocyte normoblasts and reticulocytes. There are also a number of diseases that lead to macrocytosis of erythrocytes and are characterized by an increase in MCV in the CBC results of more than 100 fL.
The other extreme is erythrocyte microcytosis, where many small cells with an MCV volume of less than 80 fL circulate in the blood. The reason in this case is not a violation of hematopoiesis, but a violation of hemoglobin synthesis or the lack of building material for its synthesis - most often it is iron deficiency.
Breathing and circulation
The significance of determining the blood MCV indicator for clinicians is to identify problems with the addition of oxygen in the alveoli of the lungs, its transportation to tissues and the deterioration of the rheological properties of blood due to an increase in the volume of red blood cells. All this can lead to hypoxia, shortness of breath, decreased saturation, deterioration of tissue respiration and an increased risk of thrombosis.
Diagnostics
The volume of red blood cells is assessed during a general clinical analysis of the main biological fluid of the human body. For such a study, venous or capillary blood may be needed.
As for preparation for the analysis, it is limited to refusing to eat on the day of visiting the medical facility. Otherwise, the results will be false, which may require repeat blood donation.
In situations where the analysis showed that mcv is low or above normal, the provocateur of such changes should be identified. This will require a comprehensive examination of the body, which is individual in nature.
Primary diagnostic measures, common to all, are:
- familiarization with the medical history;
- collection and analysis of life or family history;
- assessment of the condition of the skin;
- measurement of blood tone and heart rate values;
- a detailed survey of the patient so that the clinician obtains a complete picture regarding the course of a particular disorder.
In addition, the following may be prescribed:
- specific laboratory tests;
- a wide range of instrumental procedures;
- consultations with specialists from various fields of medicine.
Treatment
The normal average volume of red blood cells can be restored only after the underlying disorder has been eliminated. In some cases, for correction it is enough:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- reconsider food preferences;
- Do not take medications for no apparent reason or without a doctor’s prescription.
In other situations, you should completely get rid of the underlying disorder, which can be done with the help of:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet therapy;
- the use of non-traditional treatment methods;
- surgical intervention.
Treatment tactics are selected individually for each person in accordance with the mechanism of development of a violation of the average volume of red blood cells.
How is the MCV blood test performed?
The determination of the erythrocyte index is performed as part of a general blood test, but can also be prescribed as a separate study.
The MCV index value is calculated using the formula: hematocrit as a percentage, multiplied by 10 and divided by the total number of red blood cells in the blood.
Blood is drawn on an empty stomach, after an overnight period of fasting of at least eight, and preferably ten to twelve hours. On the eve of the analysis, it is recommended to refrain from excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress and to exclude physiotherapeutic procedures.
MCV in a blood test is calculated automatically - using a hematology analyzer, which determines the average volume of all measured red blood cells. The manual calculation method, in which the laboratory assistant himself counts the cells and makes calculations using a formula, is rarely used.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Prevention and prognosis
To ensure that women, men and children do not have problems with an increase or decrease in the average volume of red blood cells, it is necessary to adhere to the following simple preventive rules:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- balanced diet;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the clinician;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- use of personal protective equipment when working with toxins, chemicals and poisons;
- annual complete examination at the clinic with visits to all doctors.
The prognosis is dictated by the pathological provocateur that provoked any deviation from the norm. Patients should not forget that, in addition to the above consequences, each basic pathology can lead to the development of its own complications.
Decrease in the values of the average erythrocyte volume parameter
The presence of small and underdeveloped blood cells with an impaired color index in the body can cause hypochromic anemia, in which the MCV index is significantly reduced.
Patients who have an increased, decreased average volume of red blood cells experience fatigue, increased absent-mindedness and irritability, general weakness, problems with remembering even the simplest things and with concentrating. These manifestations are a signal of disturbances occurring in the body and require immediate medical attention. A decrease in the volume of red blood cells in the blood can occur for several reasons:
- Disturbances of metabolic processes, especially disturbances of water-salt metabolism. The balance of ions in the blood cells changes, so the fluid contained in the cells leaks out, causing the MCV to decrease;
- Massive burns;
- Disturbances in the formation of hemoglobin molecules or their rapid destruction. In medical institutions, a diagnosis of hemoglobinopathy is made; this disease is transmitted at the genetic level;
- Violation of the synthesis of blood cells, as a result of which their quality component changes. Red blood cells are smaller and subject to deformation, which gives a reduced MCV parameter in the analysis results;
- Severe dehydration;
- Damage to the human body by lead ions;
- Malignant tumors;
- Taking medications that disrupt polypeptide bonds.
Both in the case of an increased parameter of the average volume of erythrocytes, and in cases of a decrease, in no case should this deviation from the norm be left without attention. It is necessary to identify the causes of pathologies and prescribe effective treatment with specialists, monitoring after a certain time whether it has had a positive effect.
Thus, if symptoms similar in description to those presented in the article are detected in patients, the person should immediately seek help from specialists
It is important to remember that pathologies affecting blood cells are among the most dangerous and require immediate treatment. Ignoring symptoms in people themselves and their loved ones will not solve the problem, but will only contribute to its aggravation
The norm for the average volume of red blood cells contained in the blood is the range of 70-110 femtoliters, in all other cases there will be either an increase in the parameter or a decrease in it, which is accompanied by general symptoms of fatigue, tiredness, irritability and a general deterioration in well-being. To solve problems, it is first necessary to identify the causes of deviations from the norm, and then choose adequate treatment, agreed with a specialist.