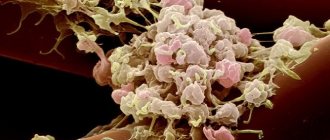
Platelets (PLT) are blood cells that participate in the process of blood clotting and prevent blood loss when blood vessels are damaged. The indicator determines the number of platelets per unit volume of blood. Their excess causes thrombosis, and their deficiency can lead to blood loss.
Platelets are blood cells whose main function is to form the primary plug that closes the site of vessel damage.
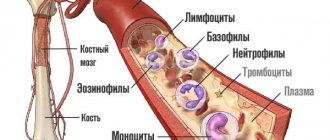
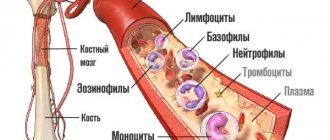
Platelets are formed from the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes (giant cells of the red bone marrow). They are oval or round plates, the size of which does not exceed 4 microns. These cells have no nuclei. PLTs have a lifespan of about seven days and are then utilized in the spleen and liver cells.
Receptors consisting of glycoprotein complexes are located on the cell membrane. They enable them to become active and form pseudopodia, with the help of which platelets communicate with each other and are fixed to the walls of blood vessels in the place where damage occurs.
If the cause of a decrease in platelet levels is infectious or oncological diseases, then, first of all, the underlying disease is treated.
By sticking to fibrin threads, they provoke the release of the thrombostenin protein, which leads to twisting and compaction of the threads. Platelets take part in processes such as:
- formation of a primary blood clot that closes the damage and stops bleeding from small vessels;
- vasoconstriction;
- dissolution of a blood clot;
- immune processes.
The role of platelets in the body
If we talk about the functions of these formed cells, they can be represented by the following list:
- Creation of a primary plug that prevents blood from leaving the body. This process takes place in several stages. It all starts with adhesion, that is, attachment to a damaged vessel.
Then aggregation is observed. The clumping of platelets, the creation of the actual plug itself. Fibrinogen takes an active part in the process. A special protein that ensures the connection of platelets.
- Regeneration of damaged tissues. As it turned out recently, the plates are also capable of producing special substances that increase the intensity of cell division in place. Thus, normal tissue restoration is accelerated. This is another powerful feature.
- Nutrition of the vascular wall. A close task. The point is to restore normal blood circulation at the local level. This happens due to the release of special substances.
PLT in a blood test: what is it, norm and deviations
Platelets (PLT) are blood cells that participate in the process of blood clotting and prevent blood loss when blood vessels are damaged. The indicator determines the number of platelets per unit volume of blood. Their excess causes thrombosis, and their deficiency can lead to blood loss.
Platelets are formed from the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes (giant cells of the red bone marrow). They are oval or round plates, the size of which does not exceed 4 microns. These cells have no nuclei. PLTs have a lifespan of about seven days and are then utilized in the spleen and liver cells.
Receptors consisting of glycoprotein complexes are located on the cell membrane. They enable them to become active and form pseudopodia, with the help of which platelets communicate with each other and are fixed to the walls of blood vessels in the place where damage occurs.
If the cause of a decrease in platelet levels is infectious or oncological diseases, then, first of all, the underlying disease is treated.
By sticking to fibrin threads, they provoke the release of the thrombostenin protein, which leads to twisting and compaction of the threads. Platelets take part in processes such as:
- formation of a primary blood clot that closes the damage and stops bleeding from small vessels;
- vasoconstriction;
- dissolution of a blood clot;
- immune processes.
Tables of norms by age
The abbreviation PLT (short for platelets) in a general blood test refers to platelets.
The rate of red plates, regardless of gender, is highest in the first days after birth and steadily decreases with age.
Among women
| Age | Indicator in thousands U/μl |
| Up to 17 | 160-382 |
| 17-25 | 170-380 |
| 26-36 | 175-400 |
| 37-60 | 170-350 |
| 60 years and older | 175-310 |
The PLT norm in women is in the range of 160-400 thousand units/μl of blood and may vary slightly during one age interval, deviating from the presented calculations.
In men
| Age (years) | Norm in thousands of units per µl |
| Up to 17 | 175-380 |
| 17-25 | 175-390 |
| 26-36 | 185-400 |
| 37-60 | 190-395 |
| 60+ | 175-370 |
In children
| Age | PLT level thousand units/µl |
| Newborns | 180-490 |
| First month | 185-400 |
| Up to a year | 180-400 |
| 1-2 years | 155-390 |
| 2-3 years | 160-385 |
| 3-10 years | 160-380 |
During pregnancy
| Trimester | Normal value (thousand units/μl) |
| I | 170-340 |
| II | 155-321 |
| III | 145-310 |
The PLT norm in a blood test is a dynamic level, we are talking about ranges from 145 to 490 thousand units/μl of blood. Natural factors can also affect the results: physical activity, stress, habits. Also past illnesses. This needs to be taken into account.
How to prepare for the PLT study
In order to determine the level of platelets, it is necessary to take a general blood test. The material is collected in the morning, on an empty stomach. In order for the indicator to be reliable, the day before the analysis it is necessary to stop drinking alcohol and reduce physical and emotional stress.
To determine the level of PLT, you need to take a general blood test
Blood for analysis is taken from a finger (in rare cases, from a vein). 8 hours before the procedure you should avoid eating and drinking coffee and tea.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in platelet concentration or PLT is associated with pathologies of the excretory, hematopoietic or digestive systems. Other problems are also possible.
Let's try to summarize the list of pathological processes.
Inflammatory conditions
Multiple in character and properties. We are talking about a variety of disorders. This can include infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Particularly common are:
- Respiratory problems.
- Respiratory system lesions.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Autoimmune disorders of the heart, myocardium.
- Crohn's disease.
And others. There are actually dozens of options. Just look at the ICD classifier to get an idea of the number of possible diseases.
Symptoms depend on the specific pathological process. If we talk about a general clinic, there will always be the following symptoms:
- Uncomfortable sensations.
- Increased body temperature. Systematic or rare. Indicators are also determined by the disease.
- Weakness, nausea, drowsiness.
For the rest, you need to start from a specific diagnosis. Therapists and rheumatologists treat pathological processes.
Correction includes the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiviral agents. If there is an autoimmune process, glucocorticoids cannot be avoided. If they are ineffective, immunosuppressants are prescribed.
The list of medications, as well as treatment regimens, is determined by the doctor. PLT values will return to normal on their own as soon as the underlying disease is treated.
Sepsis
It stands apart from other pathological processes. We are talking about generalized inflammation. All body systems are involved. The disorder is always infectious in nature. It is provoked by a variety of agents.
The condition is accompanied by several typical symptoms.
Among them:
- Pain of unclear localization.
- Serious increase in body temperature.
- Impaired consciousness. If nothing is done, the patient will very quickly go into shock and die.
Sepsis is a deadly disorder. The concentration of platelets in this pathological process increases rapidly. This is due to the body's attempts to compensate for the disorder.
Treatment is carried out strictly in intensive care. Loading doses of antibiotics are prescribed. Hardware methods of blood purification. The goal is to return the patient to an adequate state.
The primary disorder is then treated. The one that provoked the development of generalized inflammation.
Oncological processes
Simply put, cancer. Benign tumors do not cause an increase in PLT concentration. Localization doesn't matter much. However, the process is especially aggressive during the degeneration of bone marrow cells. Which is quite understandable: this is where the formed elements of blood are produced and mature.
For cancer, especially advanced cancer, a typical group of symptoms is:
- Increased body temperature. Up to 37-38 degrees. The condition is stable, because the body is poisoned by the decay products of neoplasia.
- Weakness, drowsiness. Loss of performance.
- Loss of body weight. The person is not getting better. This is due to the increased need of altered tissues for nutrition.
The clinic is also focal. Depends on the type and location of the formation. Its size.
The therapy is carried out by oncologists. The goal is to remove the tumor. It is excised surgically. Chemotherapy and radiation treatment are provided as needed.
An increased concentration of PLT means that the cancer continues to develop. Based on the dynamics of the indicator, it is quite possible to talk about the progress of the process.
Consequences of surgical interventions
This includes almost any surgical treatment that affects the spleen. This organ acts as a kind of storage facility for blood cells.
If damage occurs, platelets (among others) are released into the bloodstream, PLT in the blood is increased steadily, although there is a temporary increase in the indicator.
Then, after a few weeks, everything returns to normal. It is possible that the process of change will end many times faster.
A pathological condition is also observed with injuries to the spleen. For example, its increase and further rupture. Deposited reserves of blood cells circulate throughout the body and are recorded using objective laboratory methods.
There is no need for correction as such. After surgery, you just need to wait. After some time, everything will recover on its own. If we talk about injuries, surgical treatment is necessary. Splenectomy.
Anemia
Most often, this reason for an increase in platelet count is observed in younger patients. From approximately 3 to 12-15 years. Although changes are also possible in adults.
Elevated PLT indicates anemia due to insufficient iron intake or absorption. This is a classic case. Other options are also possible: megaloblastic forms, congenital pathological conditions.
The clinical picture, especially in the early stages, is atypical or completely absent.
Typical symptoms include:
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Increased sweating.
- Decreased performance.
- Nausea.
- Brittle hair and nails.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Decreased exercise tolerance.
- Perversion of taste preferences.
Bleeding is possible despite a formally high platelet count. They do not perform their function sufficiently, although there are many of them.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a hematology specialist. Therapy involves external administration of a deficient substance. Whether it's iron or vitamins.
If the problem is in the absorption of a beneficial compound, the cause must be treated. Gastritis, inflammation of the digestive tract.
Blood levels of PLT will remain high until the anemia resolves. Therapy may take more than one month. As a help, a diet is prescribed. Balanced, fortified diet.
Read more about the causes and treatment methods of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) here.
Colitis
Isolated inflammatory process. We are talking about intestinal damage. Thin or thick, that's a different question. The point is different.
The disease is accompanied by bleeding. Even if not so noticeable at first glance. The body is forced to produce more formed cells to replace those that are eliminated, this leads to an increase in the concentration of PLT. Until the condition is stabilized, the disorder will not stop.
Colitis is accompanied by typical manifestations, so it is difficult not to notice it.
Among the clinical signs of the disorder:
- Stomach ache. Intense, cramping.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Weakness.
- Diarrhea. Including interspersed with mucus, blood, pus.
- Disorders of normal digestion.
- Increased body temperature.
Treatment rests on the shoulders of a gastroenterologist. The goal is to stop the inflammatory process. It almost always has an infectious origin.
Antibiotics and drugs are prescribed to restore microflora and protect it. Therapy requires several weeks.
During this entire time, be sure to adhere to a gentle diet. The diet is developed individually or a standard treatment table is used for patients with colitis.
Blood clotting disorders
The platelet concentration may change if coagulation (blood clotting) occurs directly within the vessel itself. This is the so-called DIC syndrome.
The disease is associated with profound fundamental changes in the body. In this case, a paradoxical situation is observed.
On the one hand, platelets stick together and die, breaking down on their own. On the other hand, the body produces them in inadequately high concentrations, which is why an abnormally high level of PLT is recorded.
The condition does not have any specific symptoms. However, it causes a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Among the clinical manifestations:
- The appearance of hematomas and bruises on the body for no apparent reason.
- Thrombosis. They are more likely to be considered complications. The formation of clots can lead to tissue necrosis. The condition is often urgent and requires hospitalization and intensive treatment.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a hematologist. As a rule, this is not a quick matter. Up to several months of close correction is required.
The problem is solved with the help of anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. The prognosis is mostly favorable.
Genetic abnormalities
In some cases, the reason lies deeper than it seems at first glance. The pathological process may well be congenital.
In this case, the bone marrow works too intensively. Produces many shaped cells. And not necessarily only platelets. Complex disorders also occur.
Diseases are caused by mutations and are established before birth. If nothing is done, life-threatening complications are likely.
There are no symptoms as such. Thrombosis is possible. The abundance of red plates makes the blood thicker, this is a serious risk factor.
Treatment as such makes no sense. At least radical ways. All that remains is symptomatic correction. The problem is that the violation is encoded at a genetic, deep level. There's nothing you can do about it.
As for methods that will alleviate the condition, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are prescribed. They help prevent thrombosis and serious complications.
An increase in indicators indicates in favor of diseases.
Types of thrombocytosis
The phenomenon of increased PLT cells compared to the norm, which is 200 - 400 * 109 / l in adults, is called thrombocytosis. When platelets are elevated to 700 - 900 * 109/l, this means that thrombocytosis in the blood is moderate, and if the PLT level is much higher than normal and more than 900 * 109/l, then this indicates a high level of thrombocytosis.
An increase in the PLT of a population can be:
- absolute – an increase in the number of blood platelets;
- relative - a decrease in plasma volume caused by dehydration of the body.
Loss of fluid from blood plasma during relative thrombocytosis may occur due to:
- prolonged vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- common burns;
- reducing the daily volume of fluid consumed.
Dehydration is dangerous due to the risk of blood thickening and blood clots. Absolute thrombocytosis poses no less danger to human health.
With absolute thrombocytosis, the reasons for the increase in blood platelets can be:
- primary - arise as a result of the active production of megakaryocytes, which are the source of young platelets;
- secondary - develop as a concomitant phenomenon with various diseases.
The increase may be physiological in nature and does not pose a danger to the body. Such temporary increases in PLT cell indicators, sometimes quite significant, include an increase in test results after physical activity, emotional overstrain in response to the release of adrenaline.
Reasons for the decline
This condition occurs no less often. Among the development factors.
Hepatitis
Inflammatory liver damage. Accompanied by acute dysfunction of the organ. In the chronic phase it is not so dangerous.
Among the symptoms:
- Pain in the right side of the abdomen.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Change in color of stool.
- Diarrhea, constipation.
- Digestive disorders.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- Increased body temperature (not always).
The disease is progressing. Not at the same speed, but steadily. If nothing is done, necrotic changes will begin.
The condition is corrected under the supervision of a hepatologist. When such a narrow specialist is not available, a gastroenterologist is involved. The goal is to slow down, and ideally stop, change altogether. Protective drugs are prescribed.
Be sure to prescribe a gentle diet low in animal fat. If hepatitis is of infectious origin, you cannot do without special antiviral medications.
The prognosis for systematic treatment is positive, PLT concentration will recover quickly.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Necrotic process. Characterized by the death of organ tissue. In the acute phase, days and even hours count. It is necessary to transport the patient to the hospital. Then carry out urgent correction.
The clinical picture corresponds to that of hepatitis, only more severe. Problems begin with the nervous system and hematopoietic structures.
Among the manifestations:
- Pain in the right side.
- Impaired consciousness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Decline in cognitive level and intellectual abilities.
- Discoloration of stool.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Bleeding.
- The formation of spider veins on the body.
Chronic forms allow more time for treatment. Therapy consists of using protectors. We must do everything we can to stop the progression of the disease.
At the initial and middle stages of the pathological process, there is a chance of a liver transplant. The operation can only be successful during these periods.
In the decompensated stage, transplantation will make little sense. Bleeding begins and surgery is no longer possible. The disease is serious and must be dealt with quickly.
PLT decreases because cells die and new ones are not produced in sufficient quantities.
Thyroid disorders
Pathologies in which too much hormones T3 and T4 are synthesized. The lifespan of platelets in this case is significantly reduced. Hematopoiesis slows down. This is the reason for the deficiency of red PLT plates.
Pathology is treated under the supervision of an endocrinologist. The task is not quick, it takes several months. Iodine preparations are prescribed, as well as a diet low in this element.
Radiation sickness
As such, it inhibits the normal functioning of the bone marrow. This just ends with insufficiently rapid platelet maturation.
Attention:
The same is possible with a systematic, but weak influence of radiation. For example, when performing X-rays, CT scans too often.
If platelets are elevated in an adult, what does this mean?
At present, the definitive causes of such failures in the hematopoietic system have not been established. It is believed that increased megakaryocyte formation occurs due to mutations in the V617F gene.
Consider the main causes of reactive thrombocytosis:
- malignant neoplasms of the digestive, genitourinary or respiratory systems. Tumor cells produce substances that enhance the process of platelet formation;
- infectious infections of bacterial etiology. Thrombocytosis is rare in fungal or viral infections;
- damage to large bones, such as the femur or humerus;
- extensive surgery;
- splenectomy. Part of the platelets that should be deposited in the spleen enters directly into the bloodstream;
- dehydration;
- myeloproliferative pathologies;
- significant physical stress;
- bleeding in acute or chronic form. The acute form occurs abruptly against the background of mechanical trauma or surgery, the chronic form lasts for a long time, accompanies ulcers and oncopathologies of the digestive organs. The result is a decrease in the amount of iron ions in the blood against the background of an increased level of platelets. The mechanism of the phenomenon remains unclear;
- inflammation of organs and tissues, such as the walls of blood vessels, the large intestine, or joints. During inflammation, a specific substance is produced - thrombopoietin, which has a direct effect on the division of megakaryocytes, stimulating this process;
- taking synthetic analogues of hormones that are secreted by the adrenal glands, as well as chemotherapy drugs.
After the patient recovers, the criterion in question returns to within acceptable limits.
Read further: All the most important information about platelets in a blood test and their count according to Fonio
Additional examinations
Ancillary measures are aimed at establishing the origin of the pathology.
Among the techniques:
- Oral interview with the patient.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract.
- MRI as needed.
- Blood and urine tests: general, biochemical. For hormones.
- Coagulogram.
This is a basic diagnostic checklist. Based on its results, specialized examinations are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
Treatment
Regarding symptomatic correction:
With elevated platelets
It is necessary to eliminate the primary cause of the pathological process. These are the diseases that were described earlier. There is no need to fight the platelets themselves. The task is to remove the primary factor. It is better to address this question to a specialized specialist.
Symptomatic correction is to prevent the formation of blood clots. Anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents are prescribed.
At low
The same. Etiotropic treatment is necessary. Fighting the primary cause.
Prevention
Preventive measures are extremely simple. It is enough to follow simple recommendations:
- Regularly undergo inspections. Every six months or a little less often.
- Eat well. To prevent the development of anemia and deficiency diseases.
- Treat pathologies of any profile in a timely manner. Even an old source of infection can present an unpleasant surprise.
- Eliminate alcohol from your life.
- Do not self-medicate.
PLT stands for platelet, which means platelets in English. The indicator is informative, but it needs to be clarified by other methods. This way you can quickly detect health problems.