Heart rate (HR) is an important indicator that allows doctors to determine the health status of the unborn child.
You can hear the fetal heartbeat already 1 month after conception, but at this stage it is impossible to count the number of beats without special equipment. Heart rate differs at different stages of pregnancy. Accordingly, heart rate norms are determined by week.
Heart rate measurement methods:
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination). The most common way to evaluate the size of the fetus, gestational age, condition of the placenta, etc. Using ultrasound, they listen to heart sounds, examine the structure of the heart, and identify anomalies;
- auscultation. Involves listening to the heartbeat using a stethoscope. Determines the approximate heart rate, clarity of tones and presentation of the baby. Even a person without medical education can use the device, but it is effective only from the 3rd trimester. In some cases, auscultation is not possible. For example, if a pregnant woman is overweight, has a small or large amount of amniotic fluid;
- Cardiography (CTG). An informative method that allows you to determine the baby’s heartbeat, oxygen starvation and take timely measures. The CTG device is equipped with sensors for uterine contractions and fetal movements. They record the activity of the uterus and examine the waking and sleeping phases of the embryo. The first CTG is performed after 32 weeks. The second is immediately before childbirth. In rare cases, CTG is performed throughout pregnancy according to indications;
- echocardiography. It is carried out in the 2-3 trimester if heart defects are suspected in the fetus. EchoCG is an ultrasound examination that studies the structural features of the baby and blood flow.
Prescribed for different periods
Formation of the fetal heart by week
The fetus needs autonomous blood circulation, so first of all its cardiovascular system is formed. Already at the 3rd week, an ultrasound will show the rudiments of the organ, and after 5 weeks, that is, by the 8th week of the embryo’s life, the heart will be formed.
In the 3rd week, the heart looks like a hollow tube, which will soon begin to beat.
By the 4th week, the tube begins to bend, and on the 5th week the first septum appears - and now the mother can hear the baby’s heartbeat for the first time.
By the 6th week, the interventricular septum is formed, followed by the interatrial septum.
By the 8th week, the fetal heart is formed, like that of an adult.
The difference is that the fetus does not breathe on its own - blood comes to it from the mother. And this will happen until the baby is born and takes his first breath - only then his blood circulation will be divided into 2 circles - large and small. Then the oval window will also close - the hole through which blood flows from one atrium to another while the baby is in the mother’s stomach.
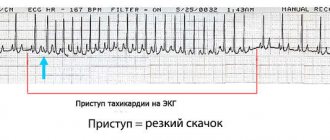
How does tachycardia manifest?
Symptoms of the disease are similar to those in adults:
- Chest pain;
- Increased heart rate;
- Periodic loss of consciousness;
- Dizziness;
- Shortness of breath;
- Constant increase in temperature;
- Drowsiness and lethargy;
- Nausea;
- Excessive pallor.
If problems arise in infants, they become more moody, restless, sleep worse and eat less. Of course, diagnosing the disease in infants is especially difficult, because the symptoms can indicate completely different things. For example, asthma.
When do you start tracking your heart rate?
The baby’s heartbeat during pregnancy is monitored as part of routine screenings:
- In the 1st trimester - from the 11th to the 13th week;
- In the 2nd trimester - from the 18th to the 20th week. At this stage, developmental disorders are identified;
- In the 3rd trimester - from the 28th to the 35th week, when the heart and the arteries that are connected to it are assessed.
On an individual basis, an extensive diagnosis of the baby’s heart is necessary. For example, if there is a suspicion of a heart defect, with an enlarged cervical fold in the early stages, with disturbances in the child’s heartbeat during pregnancy, or with abnormal development of other organs.
Particular attention is paid to expectant mothers with heart disease, diabetes and those who have suffered infectious diseases during pregnancy or are taking anticonvulsant therapy.
Increasing acetone
A rapid deterioration in the child's condition can be caused by acetonemic intoxication. In this case, a rapid heartbeat appears in a child of 5 years or another age. You can also determine the pathological condition of the baby by some other signs. We will list the main ones in this article, since the disease is very dangerous, you should know exactly about its signs in order to recognize it in time and immediately seek qualified medical help.
An increase in the level of acetone in the body in a minor can be determined by the following symptoms:
- Cardiopalmus.
- Abdominal pain in the form of cramps.
- Severe and sharp vomiting, repeated many times.
- Weakness, nausea, pale skin.
- Pungent odor of acetone in urine, vomit and on breath.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Increased body temperature.
- Retardation of movements, convulsions, photophobia, loss of consciousness.
If a child has acetone in his urine, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. During the treatment period, alkaline drinking, a special diet, and restoration of normal glucose levels in the child’s body are recommended.
Baby's heart rate by week
Depending on the trimester and phase of activity of the fetus, its heart pulsates at different frequencies. Gynecologists focus on the following indicators of the baby’s heartbeat in the womb:
- 4th - 6th weeks - in the early stages, heart rate is 80 - 85 beats per minute;
- 6th week - from 100 to 135 beats;
- 7th week - 115 - 130;
- 8th week - no higher than 170;
- 9th - 10th weeks - from 170 to 190;
- from 11th to the birth of the baby - an average of 150 beats.
The baby's heartbeat during pregnancy, starting from the 2nd trimester, becomes stable. A pulse of 140 - 160 beats per minute is considered normal. But any fluctuations in one direction or another indicate a serious condition of the fetus, for example hypoxia. In the 3rd trimester, the baby's heartbeat in the abdomen may fluctuate, but not by more than 10 units (+/-).
Pathological physiology
The supply of nerves to the heart in a child occurs primarily through the vagus nerve and sympathetic ganglion. Afferent fibers that are connected to the sympathetic ganglia are responsible for transmitting pain sensations. At the same time, people usually do not notice a rapid heartbeat, paying little attention to this condition. Some patients may complain of blocked ears or noise in the head already in childhood. This is a serious reason to consult a specialist to find out what is the cause of this problem.
First of all, if a child has a rapid heartbeat, you should be wary of tachycardia. This is a painful condition during which the heart rate increases noticeably. This disease is associated with the conductivity of electrical signals, which deteriorates for one reason or another. In some cases, tachycardia is congenital. Then it can be diagnosed during pregnancy.
Methods for monitoring fetal heart rate
Monitoring a child’s heartbeat during pregnancy allows you to assess his well-being and development, identify risks in time and, if possible, correct them.
In each trimester, gynecologists use different methods to assess the baby's heartbeat. Also, modern technologies allow expectant mothers to listen to the hearts of their babies at home.
Listening to the baby's heartbeat in the clinic
Gynecologists use the following methods:
- Ultrasound examination, or ultrasound. The most popular method that allows you to calculate your heart rate in the early stages. Using the device, the structure of the heart is assessed, abnormalities in development are identified, and sounds are listened to. There are 2 types of examination: vaginal (the sensor is placed in the woman’s vagina) and abdominal (the sensor is moved along the patient’s abdomen). The woman is lying on her back at this time. The procedure takes up to 20 minutes;
- Auscultation with a stethoscope. The device allows you to determine the approximate frequency and clarity of the baby’s heartbeat and his presentation. Diagnostics is informative only in the 3rd trimester. If the pregnant woman has polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, or is overweight, this assessment method is not suitable. The procedure goes like this: the woman empties her bowels and bladder in advance, lies down on the couch and bends her knees. The doctor determines the position of the fetus and the listening point, then applies the wide side of the stethoscope to the patient’s abdomen and the narrow side to his ear;
- Cardiotocography, or CTG. Used from the 32nd week. In addition to the baby’s heartbeat during pregnancy, the device evaluates the movement of the fetus and determines oxygen starvation. This allows you to immediately take measures to improve the baby’s condition. The first CTG is performed at the 32nd week, the second - before birth. In this case, the frequency of uterine contractions, fetal activity and sleep phases are monitored. If necessary, diagnostics are carried out more often. The procedure is carried out as follows: the woman lies on her side or half-sitting, and a sensor is attached to her stomach. During the procedure, the heartbeat is audible to the naked ear. It lasts 40 minutes.
If heart defects are suspected, echocardiography, or echocardiography, is performed. Ultrasound examination allows us to study the structure of the heart and blood flow. Informative in the 2nd - 3rd trimester. The procedure takes 25 - 40 minutes. The woman is asked to lie on her back, her stomach is lubricated with gel and a sensor is attached. If the procedure is prescribed in the early stages, the sensor can be inserted vaginally.
Devices for assessing heart rate at home
If you are overly worried about your baby's condition and constantly think about his well-being, purchase a portable device to measure the baby's heartbeat during pregnancy. Manufacturers offer several options:
- Portable fetal doppler. You can listen to your baby’s heart at any time and make sure everything is okay with him. Or react instantly if something goes wrong. The device can be used from 12 weeks; models with particularly sensitive sensors can be used from the 10th week.
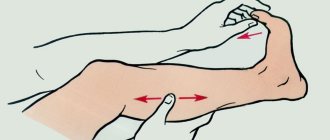
- Stethoscope. At 18 - 20 weeks, you can listen to the baby's heartbeat using this simple but informative device. The best time to listen is before bed or 1 - 2 hours after eating. Don’t be alarmed if you don’t hear your baby right away—move the stethoscope over your belly in different directions. Give preference to devices from well-known manufacturers.
In later stages of pregnancy, you can download a mobile application. Some versions even allow you to make an audio recording of your baby's heartbeat during pregnancy.
First aid
If a child has an attack of tachycardia, you should immediately call an ambulance. Until the doctors arrive, there are several ways to alleviate the baby’s condition.
Free his neck and chest from tight clothing, provide the patient with a sufficient flow of fresh air, and place a damp cloth or handkerchief on his forehead.
Deviations from the norm: when to sound the alarm¹
If your baby's heart beats 1 - 2 units slower or faster than normal, there is no reason to worry. You should sound the alarm if the fluctuations are too significant, the child’s heartbeat has sharply increased/decreased, or the condition is persistent.
Decreased heart rate, or bradycardia
There are many reasons for a decrease in heart rate. Only doctors will identify the true cause of bradycardia in a particular fetus. Here are possible reasons for a baby's heart rate to decrease during pregnancy:
- Mom's unhealthy lifestyle. The fetus suffers greatly if the mother smokes and drinks alcohol during pregnancy, does not walk in the fresh air, or does not move;
- Mother's health status. Vitamin deficiency, anemia, pulmonary and infectious diseases, heart defects, cardiovascular diseases can cause pathologies in the fetus;
- Psychological state of a woman. The expectant mother should not be nervous, because stress has a detrimental effect on the development and health of the child.
Heart rate may decrease due to taking medications, Rh-conflict, multiple pregnancy, severe toxicosis, premature placental abruption, oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios, or when the umbilical cord is entangled. All these conditions need to be either excluded or confirmed and urgent action taken.
If the pulse is non-monotonic and rhythmic, bradycardia does not threaten the baby’s life - it is enough to correct it with drugs.
If persistent bradycardia is diagnosed, it almost always indicates a pathological condition of the fetus: hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, or congenital pacemaker pathology.
Increased heart rate, or tachycardia
If the pulse reaches 170 - 200 beats per minute, the child’s heart rate is said to be increasing. This condition is caused by the same reasons as bradycardia. The child is simply trying to cope with the situation differently.
In addition to the reasons listed above, tachycardia is caused by severe bleeding, cardiovascular pathologies, endocrine diseases and dehydration against the background of toxicosis in the mother.
An increased heart rate of a child does not directly threaten his life, but the reasons that caused it can lead to serious consequences. Timely drug therapy can correct the condition. If it worsens and cannot be corrected, the woman is offered to induce labor early.
Persistent tachycardia with a heart rate above 180 beats per minute is dangerous for the fetus. It can lead to heart failure, dropsy, or fetal death in the womb.
Monotonous heartbeat of a child
Depending on the phase of activity, the baby’s heart beats at different frequencies. If he is sleeping, the pulse slows down and becomes more monotonous; if he wakes up and moves, the pulse quickens and becomes spasmodic. These “slides” are clearly visible on CTG: every movement of the fetus leads to an increase in heart rate. The indicators do not change if the fetus is deeply asleep. In this case, they try to wake him up: they ask his mother to take a walk, stroke his belly, and eat something sweet. But if these attempts do not lead to anything, and the baby continues to sleep, this is a very alarming sign, since it may indicate severe hypoxia.
Irregular heart rhythm, or arrhythmia
This condition is characterized by irregular and irregular contractions or changes in heart rate in the form of tachycardia or bradycardia.
If the heart rate is above 180 or below 100 beats per minute for a long time, this is a dangerous condition for the baby.
Irrhythmic contractions are a sign of pathology of pacemakers and pathways.
Arrhythmia appears against the background of structural defects, ischemia, electrolyte imbalance, inflammatory processes, and acute viral infections.
Pathological conditions
A rapid heartbeat in a child may occur against the background of pathological conditions. These include:
- myocarditis (cardiopathy);
- Congenital heart defect;
- dehydration;
- anemia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- pheochromocytoma - tumors of the adrenal glands;
- obesity.
Here are the main causes of heart palpitations in children. In a newborn baby, external irritants, for example, swaddling or examination by a doctor, as well as various pathological processes, can provoke a rapid heartbeat. These are anemia, perinatal encephalopathy, respiratory or heart failure, low blood sugar, congenital malformations or acute asphyxia. This is why a child can experience heart palpitations even in infancy.
Determining gender by heartbeat
Previously, when there were no hardware diagnostic methods, gynecologists determined the gender by the child’s heartbeat. Modern doctors and mothers trust ultrasound examination more, which can almost accurately determine the sex of the unborn baby already in the 15th - 16th week. However, there are still gynecologists who use the predecessor method in practice.
According to the approach, girls and boys' hearts beat at different frequencies. For boys it is slower and more clear - from 130 to 150 beats, for girls it is faster and more subdued - from 150 to 170 beats.
However, this technique does not take into account the dependence of the pulse on the phase of activity and the position of the baby, the formation of his cardiovascular system, the condition of the mother, as well as differences in the baby’s heartbeat from week to week. All these factors affect heart rate, so they must be taken into account. Therefore, the method of determining sex by heartbeat cannot be considered reliable.
If you want to find out who will be born in your family, wait until the second scheduled screening - in most cases, at this time the ultrasound doctor can already clarify.
Sources:¹https://journals.lww.com/clinicalobgyn/Fulltext/2020/09000/Physiology_of_Fetal_Heart_Rate_Monitoring.18.aspx
Useful video about some research methods during pregnancy
| Week of pregnancy | Fetal heart rate by week | Determination methods |
| 5 | 90-110 | — |
| 6-7 | 100-130 | Ultrasound diagnostics |
| 8-9 | 130-150 | |
| 10-11 | 130-160 | |
| 12-13 | 140-170 | |
| 14-15 | 140-180 | |
| 16-17 | 140-170 | |
| 18-19 | 130-170 | |
| 20-21 | 140-170 | |
| 22-23 | 130-160 | Cardiotocography, ultrasound |
| 24-40 | 120-160 | Ultrasound diagnostics, CTG Listening with a stethoscope (heartbeat can be heard from 27-28 weeks of pregnancy) |