The formed elements of blood represent a wide variety of specific structures of the body responsible for certain functions. In more detail, we are talking about a number of cytological units.
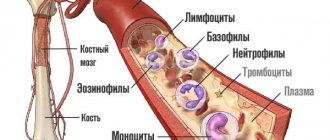
In total there are three large groups:
- Leukocytes. White blood cells. Responsible for the normal immune response. They act as a kind of protectors of the body. They work as a defensive force. There are several more subtypes of these cytological structures, but that’s a completely different conversation.
- Platelets. Red blood platelets. Perform several important functions. The key, if described superficially, is to quickly close the wound areas. They form a special plug that prevents blood from leaking out. There are other tasks, but they are secondary.
- Red blood cells. Red blood cells (RBC). They ensure normal gas exchange due to the fact that they are able to attach and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Without them there can be no normal life.
If the red blood cells in the blood are elevated, this may indicate infectious and inflammatory processes, disorders of the bone marrow, endocrine disorders, oncology and other diseases, that is, it is basically a sign of a pathological process. But not always.
We need to look into this in more detail.
Etiology
An increased content of red blood cells in the blood is defined as when the level of red blood cells is very different from the permissible values. It is worth noting that the norm depends on factors such as a person’s gender and age category.
| Age | Normal (10^12 cells per liter of blood) |
| Newborns | 3.6-6.6 |
| 1 month | 3-5.4 |
| 2-4 months | 2.7-4.9 |
| 5 months-2 years | 3.4-5.2 |
| From 3 to 6 years | 3.9-5.3 |
| From 7 to 12 years | 4-5.2 |
| Boys | 4.5-5.3 |
| Girls | 4.1-5.1 |
| Men | 3.9-5.5 |
| Women | 3.5-4.7 |
As mentioned above, the increase in red blood cells is influenced by the course of a limited range of diseases, which include:
- disruption of the functioning of the respiratory system;
- congenital or acquired heart defects;
- Pickwick's syndrome;
- erythremia;
- chronic leukemia;
- various acute infectious diseases;
- oncological processes;
- Aerz's disease;
- diseases leading to increased blood viscosity;
- pulmonary failure;
- vascular pathologies;
- any type of anemia;
- problems in the functioning of the bone marrow;
- malignant hypertension;
- extensive burns;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastritis or ulcers;
- diabetes.
However, the high content of red blood cells in the body is not always a consequence of one of the pathological processes described above. Physiological reasons are presented:
- drinking large amounts of chlorinated water or sugary carbonated drinks;
- living in mountainous areas with thin air;
- frequent mental or physical fatigue;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- emotional instability;
- poor nutrition, which is why a person does not receive enough vitamins;
- professional sports;
- food poisoning, which often results in profuse vomiting and diarrhea;
- long-term addiction to smoking cigarettes, and this factor can be attributed even to infants (passive smoking).
It is very important to remember that elevated red blood cells in the blood can be inherited from parents.
Structure and functions of red blood cells
The role of red blood cells in the blood
Red blood cells are round, biconcave red blood cells that contain hemoglobin, fats and protein. This composition provides basic and additional functions of the cell. The main purpose of red blood cells is oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange. The hemoglobin contained in the cell allows oxygen to be transported from the lungs to all tissues and carbon dioxide to be introduced from them.
Additional purpose of red blood cells:
- deliver nutrients (vitamins, amino acids and glucose) necessary for normal cell functioning;
- protect cells from the effects of radicals and toxins (they destroy cells and interfere with their normal functioning) and promote their removal from the body;
- help maintain immunity;
- regulate metabolic processes and maintain acid-base balance;
- maintain blood viscosity and participate in the formation of clots (a function necessary when a vessel is injured, to prevent loss of large amounts of blood);
- maintain the elasticity and strength of blood vessels.
Red blood cells are necessary for the normal functioning of the body, as they maintain balance in all metabolic processes. A change in their concentration in the blood leads to a malfunction of all organs. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, and after 4 months they are destroyed in the spleen and liver.
Symptoms
When the distribution width of red blood cells is increased, some clinical manifestations may be expressed. However, they are nonspecific, which is why they cannot indicate the course of this particular disorder with 100% accuracy.
The main symptoms are:
- redness of the skin, especially on the face;
- slight but rather unpleasant skin itching;
- increase in blood tone indicators;
- nasal hemorrhages;
- hepatosplenomegaly;
- decreased visual acuity;
- periodic dizziness;
- attacks of severe headache;
- decreased ability to work;
- lethargy and weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- muscle and joint pain;
- dyspnea;
- tinnitus.
Such symptoms of elevated red blood cells in women, men and children will be complemented by clinical manifestations that are most characteristic of a particular pathological etiological factor.
How to reduce
Reducing the number of red blood cells is carried out using blood thinning drugs. For this purpose, medications are used, which can be divided into 2 groups:
Anticoagulants
. Coagulation is the process of blood clotting, which occurs with the help of the protein fibrin (fibrinogen). Anticoagulants reduce fibrin in the blood plasma, and they can act both immediately after administration (heparin) and gradually, some time after the start of therapy (Warfarin, Phenilin).
Antiplatelet agents
. The drugs act on platelets - blood cells that form blood clots when sticking to each other. Antiplatelet agents prevent platelet aggregation and promote blood thinning (Aspirin, Ipaton, Integrilin).
Erythrocytosis can be caused by serious pathological reasons, therefore, if red blood cells are elevated in a blood test, then it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the circulatory, cardiovascular, hormonal and excretory systems.
Diagnostics
The level of red blood cells in the blood is determined during a general clinical study of the main biological fluid of the human body. For such laboratory diagnostics, both capillary and venous biological material may be needed.
It must be taken into account that patients should prepare for such an analysis, namely, completely stop eating food at least 4 hours before such a procedure. If a person does not do this, then most likely the results will be interpreted incorrectly by the hematologist, which may require repeat blood donation.
However, the data obtained during this method of diagnosis cannot show which particular pathology or physiological factor was the impetus for the development of such a disorder. In order for a doctor to find the root cause, a person needs to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Primary diagnostics, common to all, combines:
- examination by the clinician of the medical history;
- collection and analysis of life or family history to identify the influence of physiological sources or genetic predisposition;
- palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity - this is how hepatosplenomegaly is detected;
- measurement of blood tone and heart rate values;
- a detailed survey of the patient - this will enable the doctor to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, which sometimes accurately indicates the provoking disease.
In addition, patients may be prescribed:
- specific laboratory tests;
- instrumental procedures, including endoscopic;
- consultations with specialists from various fields of medicine.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes, which are used for high levels of red blood cells, help thin the blood, lower blood pressure, normalize heart rate and prevent the formation of blood clots.
Dill seeds
. The plant is actively used for diseases of the cardiovascular system, including reducing the level of red blood cells and normalizing blood pressure. Dill seeds contain flavonoids, essential oils and amino acids.
To prepare the product, dried dill seeds (100 grams) must be ground into powder using a coffee grinder and stored in a closed container in a dark place. You need to consume dill seed powder twice a day, one teaspoon, dissolving in your mouth for five minutes, and drinking water. The course of treatment is two months.
Herbal collection
. For the medicinal infusion you will need: bitter wormwood, fireweed tea and mint infusion. The composition of medicinal herbs used for infusion includes organic acids (ascorbic, malic, succinic, aspartic, glutamic), essential oils and amino acids. An infusion of herbs helps reduce blood viscosity and normalize elevated red blood cells.
To prepare, you need to take 1 teaspoon of chopped herbs and pour a liter of boiling water. After 40 minutes, the liquid should be filtered and taken half a glass before meals three times a day for three weeks.
Treatment
What to do if red blood cells are elevated
If during the diagnosis it is confirmed that a person’s red blood cells are elevated, then treatment of the underlying pathology begins first. Treatment tactics are selected individually and can be:
- conservative;
- surgical – operations are performed open or laparoscopically;
- complex.
However, regardless of the sources of the increase in red blood cells in the blood of men, women or children, the level of red blood cells can be normalized with the help of:
- taking medications - very often this is limited to the use of vitamin-mineral complexes;
- transfusion of red blood cells;
- adherence to a therapeutic diet;
- use of alternative methods of therapy.
In such situations, the following products are required for daily consumption:
- dietary meats;
- seafood;
- hot red pepper;
- fermented milk products;
- legumes;
- raw vegetables;
- cottage cheese;
- garlic and tomatoes;
- melon and citrus fruits;
- cherries and sweet cherries;
- bell pepper;
- green tea and other blood thinning products.
A complete list of approved food components can only be provided by the attending physician.
After the approval of the clinician, it is allowed to prepare decoctions and infusions at home, based on:
- bitter wormwood;
- sweet clover;
- dandelion roots;
- shepherd's purse;
- horsetail;
- mistletoe;
- dried cranberries.
These are just the basic rules of treatment - the treatment regimen is drawn up individually for each person.
Selected reasons for women
Basically the same as in general. But there are some additional points. For example.
Menstrual cycle
A temporary and slight increase in the concentration of red blood cells is possible. Not necessarily, but it does happen. This cannot be called a pathological process. You don't need to do anything. Everything will return to normal on its own.
Pregnancy
The same applies to the gestational period. Especially often, an increase in the concentration of erythrocytes is observed at the initial stage and at the very end of the natural process. No special treatment is required.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent an adult or child from having problems with elevated red blood cells, you need to follow several simple preventive rules, including:
- lifelong cessation of bad habits;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- constant strengthening of the immune system;
- drinking only purified water;
- avoiding physical, emotional and mental fatigue;
- taking medications strictly as prescribed by the clinician;
- eating quality foods.
It is also very important to conduct a full examination of the body in the clinic several times a year, undergoing the necessary laboratory and instrumental procedures and visiting all specialists. This will make it possible to identify any of the pathological sources early.
As for the prognosis, the increased content of red blood cells does not pose a threat to human life. However, we should not forget about the danger of the sources of this condition - each provoking disease has a number of its own complications.
External symptoms of pathology
Erythrocytosis is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which intensify with a further increase in the indicator. Signs of pathology have external and internal manifestations.
External changes:
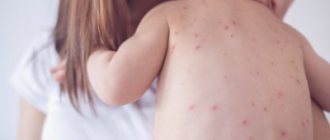
- the skin takes on a red tint, especially on the face and limbs. With a sharp increase, a blush appears on the cheeks. The tongue and oral mucous membranes also become redder;
- with severe thickening of the blood (due to a large number of red blood cells), its passage through small capillaries worsens, which is accompanied by blue discoloration of the extremities;
- sudden nosebleeds, without provoking factors;
- the appearance of blood while brushing your teeth;
- rapid fatigue, decreased performance and memory impairment are noticeable. The patient also constantly feels sleepy. This change is also caused by the thickness of the blood. More energy is spent pumping it throughout the body;
- the patient is often in a tearful mood accompanied by apathy and depression;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath and causeless cough;
- chronic runny nose due to swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- With cuts or abrasions, viscous and bright red blood appears. This is due to the fact that a greater presence of red blood cells (red cells) colors the blood more red, and their increased number thickens the blood;
- the appearance of scratching on the skin due to itching after taking water procedures;
- deterioration of the condition of hair, nail plates, as well as increased dryness of the skin;
- the presence of minor bruises and bruises without receiving blows;
- fog and confusion, possibly fainting;
- disruption of the functioning of the digestive system, which is accompanied by deterioration of appetite, nausea with vomiting, and loose stools. As a result, weight is significantly reduced.
If a person has 2 or more of the listed symptoms, and also has, or has recently had, provoking causes of an increase in red blood cells, then it is necessary to contact a specialist to diagnose and eliminate the pathology. The disease is dangerous due to the development of serious complications (discussed below) and death.
What test do you need to take?
To find out the level of red blood cells, you need to take a routine clinical blood test. Biomaterial for research is taken from a finger. Test results are usually ready the next day.
This study does not require special preparation. To ensure accurate test results, it is recommended to follow these rules:
- It is advisable to take the analysis on an empty stomach. If it is difficult for the patient to abstain from food, then a light breakfast is allowed. It is not recommended to eat fatty, high-calorie and carbohydrate foods before the test.
- Smoking should be avoided 2 hours before the test. Exposure to nicotine may interfere with test results.
- The day before the test you must not drink alcohol.
- It is important to avoid physical activity on the eve of the test. Strenuous training and sports can distort red blood cell counts.
When examining biomaterial in the laboratory, not only the content of red blood cells is determined, but also the level of leukocytes, platelets, hemoglobin and ESR. During the diagnosis, the doctor evaluates all the analysis data as a whole.
Possible consequences
Delayed treatment or ignoring symptoms can lead to malfunction of all organs. Thick blood disrupts oxygen delivery, wears out blood vessels, and enlarges the liver and spleen. The functioning of the heart and brain is disrupted. Without proper treatment, erythrocytosis can be fatal.
An increase in red blood cells is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of most diseases. Changes in skin color, unexplained bruising and shortness of breath should be a reason to contact your doctor and have your blood examined. In adults, increased pathology is possible due to nicotine and alcohol addiction.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Drug therapy
As already mentioned, erythrocytosis is not an independent pathology. There are no special medications to lower red blood cell counts. Therefore, it is necessary to cure the disease that caused erythrocytosis. After recovery or remission, blood counts return to normal.
To prevent blood clots, patients are prescribed blood thinning medications: