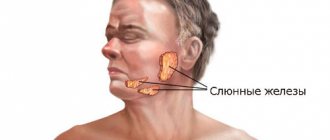
Adenoids in children are an enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsil, which leads to a narrowing of the airways and the development of a number of symptoms. In addition to adenoids, there are also other synonyms for this pathology. Parents may come across words such as: adenoid vegetations, hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, hyperplasia of the pharyngeal tonsil. Adenoiditis is inflammation of the adenoids in a child. The pharyngeal tonsil is a collection of lymphatic tissue. Lymphatic tissue consists of cells that destroy microorganisms. Its function is also to produce antibodies (which also protects against germs). In addition to the pharyngeal tonsil, there are also palatine tonsils and other smaller collections of lymphatic tissue. Together they create a single lymphoid pharyngeal ring. It also has another name - the Pirogov-Waldeyer ring. Thus, the Waldeyer ring performs a very important function - it is a protective barrier for the body.
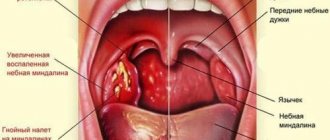
The pharyngeal tonsil is located in such a way that it is difficult for parents to see it during a routine examination of the throat. Upon examination, you can see the back wall of the pharynx and pharynx with a tongue, and the pharyngeal tonsil is located at the top of the throat behind the indicated small tongue.
Functions of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
A pathologically enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil is called “adenoids”
Adenoids in the nose are not a separate neoplasm, such as polyps, but a consequence of excessive growth of tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. This is an unpaired amygdala, which performs an important protective function. The nasopharyngeal tonsil consists of lymphoid tissue, and it is its proliferation that leads to the formation of adenoids.
In the nasopharyngeal tonsil, immune cells are formed and mature, as well as antibodies to fight viruses and infections. Amygdala hypertrophy is a childhood disease, which is explained by the peculiarity of the functioning of the children's immune system.
Adults almost never encounter this problem, except in rare cases when the disease was not cured in childhood. In general, adenoids are treated with conservative methods, but in severe cases their removal is advisable.
Amygdala hypertrophy is a peculiar response of the body to a weak immune system in children. With age, the size of the tonsil decreases, so most children successfully “outgrow” the adenoids.
Symptoms of adenoids in the nose
Symptom of adenoids
is a violation of nasal breathing (when a child sleeps with his mouth open at night), headaches, hearing loss, chronic apathy of the child, after sleep he gets up tired.
The lower part of the mouth droops due to a constant open mouth; over time, the shape of the face may change; there is even a name “adenoid face” or “external adenoidism”. At school, such children are teased by their peers, which traumatizes the child. Such children have few friends; for this reason, in most cases they withdraw into themselves. This can greatly influence the patient’s future life in terms of the formation of his character and mental characteristics. If you suspect symptoms of adenoids in a child, immediately seek help from a specialist, because eliminating these manifestations at the initial stage is much easier than fighting the disease when the time to start treatment is delayed, and the child develops deficiencies of which he will be ashamed.
Young children with adenoids find it more difficult to speak; in older children, their voice changes and becomes less sonorous. Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract may occur, anemia may begin to develop, sometimes urinary incontinence at night, coughing attacks at night, and asthmatic attacks may occur. With acute adenoid, the temperature can rise to 39 °C and higher, and a burning sensation appears in the nasopharynx.
Such children suffer from dysfunction of the nervous system. Due to reflex neurosis, some may have enuresis - urinary incontinence. At school, children study poorly, become inattentive, and are not assiduous at their desks. Patients have a constant runny nose that cannot be treated conservatively, the use of various medications does not give any positive results, the nose does not breathe as required.
Symptoms of adenoids also include an incomprehensible sharp cough at night, incomprehensible pain in the ears and congestion, the nose cannot breathe, and it is painful to touch the lymph nodes. In young children, this disease worsens and lasts for about one week.
Chronic adenoiditis appears due to the fact that you often suffer from respiratory diseases. For a chronic disease, the course of the disease is characterized by the following signs: a person begins to vomit after eating, mucus along with pus flows down the back walls and causes a sudden cough, inflammation gradually grows to the throat and nose, it becomes difficult to breathe and swallow. To identify such a disease, X-rays and rhinoscopy are used.
The symptoms of adenoids in adults are almost identical:
- A person suffers from constant nasal congestion.
- There is copious mucus discharge from the nose.
- If you open your mouth and look at the back wall of the pharynx, you can often see draining nasal contents, represented by serous exudate. This irritates the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and provokes a lingering cough.
- Heavy nasal discharge irritates the skin in the vestibule of the nose and upper lip. It is constantly red, thickens, and may become cracked.
- During sleep, a person snores and breathes through his mouth, as nasal breathing is difficult. This affects the quality of night's rest: first of all, it becomes restless. During sleep, attacks of suffocation are possible, since the root of the tongue can sink (with mouth breathing in a horizontal position).
- If the adenoids grow to the third degree, this contributes to a change in voice. He becomes nasal.
- As the lymphoid tissue increases in size, it begins to block the auditory tubes. This negatively affects hearing acuity.
- The combination of symptoms such as poor quality sleep and hearing loss makes a person absent-minded.
- The patient begins to suffer from colds more often, as local immunity weakens, the air is not cleared of dust and germs, and is not warmed up enough. The most common diseases that develop against the background of adenoids: bronchitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis.
- Periodically, the enlarged adenoid tissue becomes inflamed. At this time, the patient will experience symptoms such as: increased body temperature, general weakness, and an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes.
- If the disease is ignored for a long time, this leads to characteristic changes in appearance. The lower jaw of a person lengthens, becomes narrow, and the bite changes. In medicine, there is even such a thing as “adenoid face.” One glance at a patient is enough for a doctor to understand his problem.
- Frequent headaches and decreased mental performance are constant companions of enlarged adenoids. The fact is that difficult nasal breathing does not allow the brain to get enough oxygen. This negatively affects a person’s ability to work as a whole.
- Some patients with adenoids experience disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system: loss of appetite, episodes of vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Thus, in 23.3% of patients, intestinal dysbiosis is detected, which is confirmed by bacteriological research methods.
- Otitis media (acute and chronic) are also constant companions of the adenoids. Their formation is based on the overlap of the pharyngeal mouth of the auditory tube by lymphoid tissue. In the future, this can lead to the development of hearing loss.
Causes of adenoid development
The main reason for the appearance of adenoids in the nose in children is a weak immune system. Hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue is designed to improve the protective function of the tonsil and increase the number of immune cells. However, with an increase in the size of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the process of breathing through the nose worsens, since the organ covers part of the vomer, as a result of which local immunity is further weakened. The result is diseases of the ENT organs associated with impaired nasal breathing.
Causes and predisposing factors to the development of adenoids:
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent ARVI;
- allergic reactions;
- too dry air;
- “childhood” infectious diseases – chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- weakened immunity.
One of the most common reasons is genetic predisposition. It has been proven that children of parents who experienced adenoids in childhood are more susceptible to this disease.
A predisposing factor is a decrease in general immunity. This may be due to various reasons - from long-term use of antibiotics to chronic diseases. Also one of the reasons is the presence of a focus of infection in the body, for example, in the case of chronic tonsillitis.
One of the factors that indirectly affects the development of adenoids is the air that the child breathes is too dry or polluted. This is explained by the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil acts as a kind of filter, purifying all the air entering through the nose. If it fails to cope with its functions, the process of proliferation of lymphoid tissue begins and adenoids form.
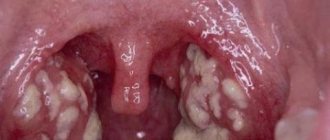
Hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
Unfortunately, in children, adenoids are often accompanied by another disease - hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils). In this case, breathing becomes difficult not only through the nose, but also through the mouth. The palatine tonsils, like the nasopharyngeal tonsils, protect the baby from pathogenic microorganisms, but they do this much more actively. Therefore, their removal is a more significant loss for the body. Without them, the child is at greater risk of bronchopulmonary diseases.
Inflamed tonsils pose a much greater danger than possible colds. They are a source of chronic streptococcal infection, which, periodically exacerbating, provokes the development of fever and sore throat. The latter, in turn, can cause complications on the kidneys and heart. So in the case of a “double set” of illness, it may be wiser to undergo surgery rather than expose the child’s health to serious risk.
In conclusion, I would like to note that enlarged tonsils are a very delicate issue. Here a lot depends on the competence of the doctor and the sanity of the parents. The decision about treatment should be made by a competent specialist. Not grandmothers who “raised you healthy and will take care of your grandchildren,” not friends who had “exactly the same situation,” and certainly not numerous forums with virtual mothers.
The doctor has a thorough knowledge of the problem and experience. Believe me, he will fight to the last to bring the tonsils “to life” without a scalpel. But if treatment does not help, and the adenoids continue to undermine the child’s health, then surgical intervention should not be postponed.
Adenoid grades
As the adenoids grow, they gradually block the vomer, and it becomes more and more difficult to breathe through the nose.
The severity of the disease and symptoms of the pathology depend on the extent of the disease. There are three in total:
- Grade 1 adenoids are the mildest form of the disease. The nasopharyngeal tonsil is slightly enlarged, the vomer is blocked by less than ⅓. Nasal breathing deteriorates slightly, but a decrease in immunity is observed. The problem with this grade is that the disease progresses without treatment.
- Grade 2 adenoids in the nose are a disease of moderate severity. The opener is blocked by more than ⅓, but less than ⅔. Nasal breathing is complicated, but perhaps the disease makes itself felt by decreased immunity, night snoring and frequent acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis or otitis media.
- Grade 3 adenoids in the nose are the most severe stage of the disease. The vomer is blocked by almost 90% (sometimes more), breathing through the nose is impossible. A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is that the child breathes only through the mouth. The disease is difficult to treat; removal of the adenoids in the nose is often prescribed.
For effective treatment of adenoids in the nose, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor and diagnose the proliferation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil.
Classification of adenoids and adenoiditis
Growing with pathology, the pharyngeal tonsil closes certain anatomical formations - the vomer and choanae. They are not visible during normal examination. The classification of adenoids is based on the degree of enlargement and the degree of overlap of these anatomical structures. So, there are three degrees of adenoid vegetations:
- First degree - the tonsil closes the upper part of these formations.
- Second degree - the tonsil covers half of the anatomical structures.
- Third degree - the amygdala completely covers these formations.
For adenoiditis (inflammation of the tonsil) there is another classification based on the duration of this pathology:
- Acute adenoiditis is a disease lasting up to 5 days.
- Subacute adenoiditis is a disease lasting 10-15 days.
- Chronic adenoiditis is diagnosed if the duration of the pathology exceeds 1 month. The chronic process has a remission stage and an exacerbation stage.
Symptoms of the disease
Adenoids are a childhood disease that in 95% of cases goes away with age. Typically, tonsil volume loss begins during adolescence. However, in some cases the problem remains in adults.
Symptoms of adenoids in the nose in adults and children are as follows:
- difficult breathing through the nose;
- night snoring;
- sleep apnea (with grade 3 adenoids);
- prostration;
- nasal voice;
- frequent otitis and chronic rhinitis;
- hearing loss;
- frequent headaches.
For nasal adenoids in adults, symptoms include difficult nasal breathing and night snoring. All signs and symptoms of adenoids in the nose are generally the same for adults and children, however, in childhood there is a general decrease in immunity and frequent acute respiratory viral infections.
Important! The main problem of adenoids is complications on the nose and ears. Therefore, any cold or acute respiratory viral infection ends in otitis media or sinusitis.
Quite often, the diagnosis of adenoids in the nose in adults is carried out accidentally, for example, if a person complains of snoring at night. This is explained by the fact that the disease is more typical for young children. Adenoids in an adult can be suspected if there is a chronic runny nose and an increased tendency to otitis media, since these two diseases are typical signs of adenoids.
What do adenoids look like in the nose?
It is impossible to find out on your own what exactly the adenoids in the nose look like, but you can see the proliferation of lymphoid tissue with the help of a special examination. This is due to the fact that the nasopharyngeal tonsil is located deep in the nasopharynx and can only be seen through the nose using a special device.
In general, what exactly the adenoids in a child’s nose look like can be determined using endoscopy. This is an examination during which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the nasopharynx. With the help of such an examination, the doctor will not only diagnose the extent of the adenoids, but will also show the parents a picture of the growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, because the image during endoscopy is displayed on the monitor. The screen will show pink lymphoid tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil extending beyond the nasopharynx and overlying part of the vomer.
Rehabilitation period
In adults, treatment goes well if they follow the doctor's recommendations. Within 10 days after the intervention:
- do not eat hot, salty, spicy, smoked, or solid foods;
- do not get into stressful situations;
- use vasoconstrictor medications;
- limit physical activity;
- do not contact people with influenza and ARVI;
- refuse to take hot baths, visit baths and saunas;
- do not use drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid (they thin the blood and can cause bleeding).
It is possible to treat adenoids with homeopathy, medications, herbs, or surgery. Before using any remedies (including folk remedies), you should consult a doctor. The treatment regimen should be drawn up taking into account the course of the disease, the patient’s condition, existing contraindications, etc. Otherwise, the desired effect may not be achieved and the pathology may progress.
Adenoids in adults, the symptoms and treatment of which are described in detail by doctors, often become enlarged and inflamed. The outcome of therapy depends on the qualifications of the doctor and how carefully the patient follows the specialist’s recommendations.
Why are adenoids dangerous?
Due to constant mouth breathing, the child’s body does not receive enough oxygen.
It is necessary to treat adenoids in the nose in a timely manner, otherwise complications cannot be avoided. The danger is not the proliferation of lymphoid tissue itself, but the diseases associated with it. Among the complications:
- chronic otitis;
- chronic sinusitis (sinusitis);
- hearing impairment;
- the appearance of speech defects;
- hypoxia;
- stopping breathing during sleep.
Chronic otitis is a sluggish inflammatory process in the middle ear. It is dangerous due to perforation of the eardrum and hearing loss. Otitis media does not lead to deafness, but a person with a chronic form hears about 20% worse than healthy people.
Chronic sinusitis, in particular sinusitis, is another common complication of adenoids. The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the nasal sinuses and requires complex treatment.
Note! Quite often, otitis media and sinusitis “go hand in hand” with grade 2 and 3 adenoids.
Another common complication is the appearance of speech defects. Since the child cannot breathe through his nose, he does not pronounce some sounds. Also, if nasal breathing is impaired, a noticeable nasal voice is observed.
Hypoxia, or oxygen starvation of tissues, is a complication of grade 3 adenoids. This is due to the fact that when breathing through the mouth, the body lacks oxygen. As a result, metabolic processes deteriorate, sleep quality decreases, and cognitive functions suffer. This is especially noticeable in children of primary school age who have problems concentrating in class due to the fact that the brain does not have enough oxygen.
The most dangerous complication is sleep apnea. This disorder manifests itself as a short-term cessation of breathing during sleep. In severe cases, there is a risk of complete respiratory arrest.
What complications may arise?
The most common complication is bleeding that occurs when hypertrophied tissue is incompletely removed. You can stop the bleeding using a posterior tamponade (a tampon is placed on the wound and removed after 2 days).
A cause for concern should be an increase in temperature to +38°C or higher, indicating the presence of inflammatory processes. When an infection is introduced into the body, the development of cervical lymphadenitis, otitis, pneumonia, diphtheria and even sepsis is possible.
Trauma to the mucous membrane during surgery can lead to narrowing and deformation of the nasopharynx and disruption of its functions. It is also possible to develop atrophic epipharyngitis - an inflammatory process accompanied by thinning of the mucous membrane, dry mouth, unpleasant odor and pain when swallowing.
Diagnostics
Before you figure out how to treat adenoids in the nose, you should find out the degree of proliferation of lymphoid tissue. To do this, you need to contact an otolaryngologist and undergo an examination.
First, the doctor will simply examine the patient. Rhinoscopy is performed - a small metal funnel is inserted into the nose, allowing you to visually examine the nasopharynx. To obtain a more detailed picture, endoscopic examination, radiography or CT of the nasopharynx is used.
Additionally, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed to identify a chronic inflammatory process.
Komarovsky’s opinion on adenoids in a child
Dr. Komarovsky's school has gained popularity among parents due to its information activities, which help parents decide whether it is worth removing the adenoids, or whether it is necessary to continue conservative treatment of the child.
According to E. O. Komarovsky, enlargement of adenoids occurs in almost all children from time to time. But not everyone’s adenoiditis reaches the point where the child cannot do without surgery.
To prevent adenoiditis, Dr. Komarovsky suggests creating conditions for the child in which viral and bacterial infections will occur more easily, that is, increasing immunity. At the same time, limit the entry of microbes into the child’s body. Great importance is attached to air quality in the treatment of adenoiditis. Regular humidification and ventilation of the premises is required.
How to treat adenoids?
Treatment of adenoids in the nose begins with the second stage. For a mild form of the disease (grade 1), only symptomatic therapy is used if the adenoids make themselves felt by otitis media or sinusitis. But adenoids in the nose of the third degree or stage are most often treated surgically. The final choice of treatment method depends on the accompanying symptoms and the presence of complications. Treatment of adenoids is prescribed only by an otolaryngologist and on an individual basis.
Conservative therapy
Dosage: drops should be taken in the morning, afternoon and evening (the number of drops is selected by the doctor based on the patient’s age)
Conservative therapy refers to drug treatment and physical therapy. It is most effective for grade 1 and 2 adenoids. If the disease was detected at stage 1 and treatment was started on time, in most cases it is possible to stop the process of tonsil hypertrophy and reduce the risk of complications.
Drug therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms and includes:
- nasal rinse;
- using nasal drops;
- taking antibiotics (for inflammation);
- strengthening the immune system.
Adenoids in children's nose require complex treatment. First you need to restore nasal breathing. For this purpose, a number of drugs are used in drops - vasoconstrictor, antiseptic, antibacterial or immunostimulating drugs.
If the disease is complicated by acute otitis media or bacterial sinusitis, antibiotics are prescribed. Most often, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used, which are effective against staphylococci and streptococci - the causative agents of otitis media and sinusitis in children. For inflammation of the middle ear, antibacterial drops are additionally needed.
After a course of treatment aimed at eliminating the disease caused by adenoids in the nose, the attending physician can select immunostimulants, since to prevent exacerbation it is necessary to strengthen the general immune system.
Important! There are no drugs, tablets or drops that can shrink existing adenoids.
Physiotherapy is used to restore the function of the nasopharyngeal tonsil and disinfect the source of infection. The most commonly used is UV irradiation.
For chronic runny nose, professional nasal rinsing is indicated - the “cuckoo” procedure. At home, sea water is used for rinsing (Humer, Aquamaris sprays). To reduce swelling of the nasopharynx, allergy pills are often prescribed.
Surgery
The method of removal depends on many nuances and is prescribed only after all examinations and diagnostic measures have been carried out.
Adenoid removal is prescribed for children if conservative therapy is ineffective. Indications for surgery may include apnea and frequent exacerbations of diseases associated with adenoids. For example, if a child suffers from otitis media more than 4 times a year, a decision may be made to remove the nasopharyngeal tonsil.
Adenoids in adults are diagnosed very rarely and must be removed. The fact is that the immunity of an adult, unlike a child, does not suffer much due to the absence of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, so it is easier to remove the cause of all health problems than to regularly treat otitis media or sinusitis.
The operation to remove adenoids is performed under general or local anesthesia. The method of removing nasal adenoids in children is selected according to the recommendations of the pediatrician. Today, clinics offer many minimally invasive operations with minimal risks of complications, for example, endoscopic resection and laser removal of adenoids.
The operation allows you to cure adenoids in the nose permanently. The rehabilitation period lasts about a week; in the first days you feel a general malaise due to the postoperative wound, but it quickly passes.
Treatment of acute adenoiditis with folk remedies
Thanks to traditional medicine methods, swelling is reduced, but they are recommended to be combined with conservative treatment. The most popular folk remedies include the following:
- Mix mint, St. John's wort and oak bark in equal proportions. Take 1 tbsp. l. mixture and boil in 200 ml of water. Cool, filter and instill 3-4 drops into each nostril 3 times a day.
- Grind a Kalanchoe or aloe leaf, squeeze out the juice and instill 2 drops 4-5 times a day.
- 1 tbsp. l. Dry lingonberry leaves are poured into 0.5 liters of water, brought to a boil, cooled and filtered. Used to rinse the nose or taken orally.
- Take horsetail, chamomile, marigold inflorescences and 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour and filter. Use the resulting infusion to rinse your nose and gargle.
In addition, to boost immunity, you can drink fresh carrot juice, cranberry juice, or oregano infusion. Dried fruit compotes and freshly squeezed fruit juices are of great benefit.
What happens after adenoid removal?
The patient’s nose remains virtually unchanged after removal of the adenoids, but in the first 10-14 days there remains a wound in the nasopharynx, which recovers fairly quickly. Already on the second day, after the postoperative swelling subsides, the person will feel relief and will be able to breathe through the nose. The swelling of the nasopharynx finally disappears after a maximum of two weeks, and by this time the ability to breathe through the nose is completely restored. Around the same time, snoring and sleep apnea disappear, the person breathes normally during sleep, and gets better sleep. After removal of the adenoids, the feeling of chronic fatigue associated with lack of oxygen disappears.
Although relief is immediate, adenoid removal is not always necessary. In mild forms of hypertrophy, it is possible to normalize the process of nasal breathing and improve the quality of life using conservative methods. There is no need to rush to remove the adenoids, since the nasopharyngeal tonsil performs an important function. At the same time, if conservative therapy does not help, it is better to remove the adenoids as early as possible to avoid possible complications.
Related Articles
Adenoids grade 3: causes, symptoms, conservative and surgical treatment
Adenoids 2 degrees: symptoms and treatment methods
Inflammation of the adenoids in a child: how adenoiditis manifests itself and how to treat it
Where are the adenoids located, what do they look like and why do they grow?
Tonsil hyperplasia: causes and treatment of pathological proliferation of tonsils
Consequences of adenoids in children: complications, indications for surgery
Complications and consequences
Adenoids are dangerous not only because they can worsen the patient’s quality of life, but also because they cause health complications.
Among them are:
- The formation of chronic pathologies of the respiratory system, in particular, rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis.
- Against the background of adenoids, patients often develop chronic otitis media. In the future, the source of infection can lead to serious hearing impairment and even hearing loss.
- Enlarged adenoids are a source of chronic infection in the body, which negatively affects the overall health. The risk of developing rheumatism, myocarditis and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system increases.
- The body's resistance will gradually decrease.
A person with adenoids will suffer from frequent headaches and decreased performance. He is plagued by paroxysmal coughing, and the likelihood of developing neuroses and chronic fatigue increases due to poor quality night rest. Therefore, you should not delay treatment of adenoids.