Quite a controversial opinion arises regarding the use of antibiotics. However, in the context of the constant development and progression of viruses, the varieties of which are becoming more numerous every year, the need for their use is fully justified.
Often, when infectious diseases occur in patients, pediatricians choose Amoxiclav 125. This drug has long proven itself, especially for the treatment of inflammatory processes in children.
Composition of the finished suspension
| 5ml ready suspension | |
| Amoxicillin (trihydrate) | 125 mg |
| Clavulanic acid (as potassium salt) | 31.25 mg |
Amoxicillin is the active substance included in Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg. It is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic with activity against many gram-positive/gram-negative microorganisms. Amoxicillin is susceptible to destruction by beta-lactamases; its activity does not extend to microorganisms that produce this enzyme.
Clavulanic acid is the second active substance included in Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg. It is a beta-lactamase inhibitor, structurally related to penicillins, and has the ability to inactivate a wide range of beta-lactamases found in microorganisms resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins. Clavulanic acid is sufficiently effective against plasmid beta-lactamases, which cause bacterial resistance, but is not effective against type I chromosomal beta-lactamases, which are not inhibited by clavulanic acid.
Excipients Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg:
- lemon acid;
- sodium citrate anhydrous;
- sodium carboxymethylcellulose microcrystalline cellulose;
- xanthan gum;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- silicon dioxide;
- strawberry flavoring;
- sodium benzoate (E 211);
- sodium saccharin;
- mannitol (E 421).
Pharmacodynamics
The powder for preparing the suspension is a beta-lactam antibiotic that inhibits penicillin-binding proteins of an integral structural component of the bacterial cell wall (peptidoglycan). Under the influence of this drug, the cell membrane loses its strength, which subsequently leads to lysis and death of microorganisms. The spectrum of activity of Amoxicillin does not apply to resistant bacteria that produce beta-lactamases.
Clavulanic acid, a beta-lactam related to penicillins, can inhibit some beta-lactamases, broadening the spectrum of activity and preventing drug inactivation.
Amoxiclav has antibacterial activity against the following microorganisms:
Gram-positive anaerobes (Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococcus, streptococcus pyogenes, other species of the genus Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, clostridia, peptococci);
Gram-negative anaerobes (Coli bacterium, bacteria of the genus Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Moraxella catharalis, Bordetella, Salmonella, Shigella, Vibrio cholerae).
Due to the fact that some strains of the above bacteria produce beta-lactamase, this makes them insensitive to Amoxicillin monotherapy.
pharmachologic effect
The presence of clavulanic acid in the Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension protects amoxicillin from destruction by enzymes - beta-lactamases, which allows expanding the antibacterial spectrum of amoxicillin.
The following microorganisms are sensitive to the combination of amoxicillin + clavulanic acid:
- Gram-positive aerobes: Streptococcus agalactiae (1, 2), Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus anthracis, Nocardia asteroids, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pyogenes (1, 2), methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp., Staphylococcus saprophyticus, other beta -hemolytic streptococci Streptococcus spp. (12);
- Gram-positive anaerobes: Clostridium spp., Peptostreptococcus magnus, Peptostreptococcus spp., Peptococcus niger, Peptostreptococcus micros;
- gram-negative aerobes: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Haemophilus influenzael, Vibrio cholerae, Pasteurella multocida, Moraxella catarrhalisl (Branhamella catarrhalis), Helicobacter pylori, Bordetella pertussis;
- Gram-negative anaerobes: Porphyromonas spp., Capnocytophaga spp., Prevotella spp., Eikenella corrodens, Bacteroides spp. (including Bacteroides fragilis), Fusobacterium spp., Fusobacterium nucleatum;
- Other: Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae, Treponema pallidum, Borrelia burgdorferi.
For the following microorganisms, acquired resistance to the drug Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg is likely:
- Gram-negative aerobes: Proteus spp. (including Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis), Escherichia coli (1), Salmonella spp., Klebsiella spp. (including Klebsiella pneumoniae (1) and Klebsiella oxytoca), Shigella spp.;
- Gram-positive aerobes: Enterococcus faecium, Streptococcus pneumonia (1, 2), Corynebacterium spp., Streptococcus spp. groups
The following microorganisms are naturally resistant to the action of amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid:
- Gram-negative aerobes: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Pseudomonas spp., Enterobacter spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, Legionella pneumophila, Hafnia alvei, Citrobacter freundii, Serratia spp., Providencia spp., Morganella morganii, Acinetobacter spp.;
- Other: Mycoplasma spp., Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia spp., Coxiella burnetii, Chlamydia pneumoniae.
Notes:
1) For these bacteria, clinical studies have established the effectiveness of using Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg.
2) Strains of these types of microorganisms do not produce beta-lactamases and are sensitive to amoxicillin, and therefore, presumably, to the combination of amoxicillin + clavulanic acid.
Indications
Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension is intended for the treatment of bacterial infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
- acute bacterial sinusitis;
- acute otitis media;
- exacerbation of chronic bronchitis has been confirmed;
- community-acquired pneumonia;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- infections of the skin, soft tissues, animal bites;
- infections of bones and joints (osteomyelitis).
The presence of clavulanic acid in the Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension protects amoxicillin from destruction by β-lactamases and expands the spectrum of its antibacterial action to include microorganisms that are usually resistant to other penicillins and cephalosporins.
When is it appointed?
Used for young patients of any age when they have a bacterial infection in the upper respiratory tract. For example, when coughing.
In addition, the medicine is prescribed in the following cases:
- for tonsillitis and pharyngitis;
- with the development of a retropharyngeal abscess;
- with the development of acute otitis and bronchitis;
- for various forms of sinusitis and sore throat;
- with the development of an inflammatory process in the lungs;
- if there is an infection in the urinary tract;
- when lesions appear on the skin and soft tissues;
- with the development of infection in bones and connective tissue;
- in the presence of lesions in the oral cavity.
Remember that, despite its wide range of applications, you should not use the antibiotic yourself. The drug only helps get rid of a bacterial infection; if a viral disease develops, then the use of this antibiotic will not give the desired result. Moreover, if a person develops a fungal infection, the drug will not only not give the desired result, but can even cause harm.
Dosage
To reduce possible side effects from the digestive tract, Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension should be taken with or before meals. Before use, check the integrity of the cap, shake the bottle so that the powder separates from the walls, add drinking water in two portions (first 2/3 of the bottle, then up to the circular mark on the bottle), shaking the bottle. Shake well before each use.
The dosage of Amoxiclav suspension 125 mg + 31.25 mg for children is determined individually, taking into account age, body weight, kidney function, and severity of infection.
Newborns and children up to 3 months
Single doses of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg for the treatment of infections in children under 3 months:
| Body weight (kg) | 2,0 | 2,2 | 2,4 | 2,6 | 2,8 | 3,0 | 3,2 | 3,4 | 3,6 | 3,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 4,4 | 4,6 | 4,8 |
| Amoxiclav 156ml (2 times a day) | 1,2 | 1,3 | 1,4 | 1,6 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 2,0 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,6 | 2,8 | 2,9 |
Children over 3 months
- from 20 mg/kg for mild to moderate infections;
- up to 40 mg/kg for severe cases and lower respiratory tract infections, otitis media, sinusitis every 8 hours.
Dosage for the treatment of mild to moderate infections in children over 3 months of age:
| Body weight, kg | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| Suspension 156.25 ml (3 times a day) | 1,3 | 1,6 | 1,9 | 2,1 | 2,4 | 2,7 | 2,9 | 3,2 | 3,5 | 3,7 | 4,0 | 4,3 | 4,5 | 4,8 | 5,1 | 5,3 | 5,6 | 5,9 |
| Body weight, kg | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | |
| Suspension 156.25 ml (3 times a day) | 6,1 | 6,4 | 6,7 | 6,9 | 7,2 | 7,5 | 7,7 | 8,0 | 8,3 | 8,5 | 8,8 | 9,1 | 9,3 | 9,6 | 9,9 | 10,1 | 10,4 |
Single doses for the treatment of severe infections in children over 3 months of age:
| Body weight, kg | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| Suspension 156.25 ml (3 times a day) | 2,7 | 3,2 | 3,7 | 4,3 | 4,8 | 5,3 | 5,9 | 6,4 | 6,9 | 7,5 | 8,0 | 8,5 | 9,1 | 9,6 | 10,1 | 10,7 | 11,2 | 11,7 |
| Body weight, kg | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | |
| Suspension 156.25 ml (3 times a day) | 12,3 | 12,8 | 13,3 | 13,9 | 14,4 | 14,9 | 15,5 | 16,0 | 16,5 | 17,1 | 17,6 | 18,1 | 18,7 | 19,2 | 19,7 | 20,3 | 20,8 |
Dosing with a spoon Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg / 5 ml (in the absence of a dosage pipette):
| Body weight, kg | Age | Mild to moderate course | Severe course |
| 5-10 | 3-12 months | 3 × 2.5 ml (½ spoon) | 3 × 3.75 ml |
| 10-12 | 1-2 years | 3 × 3.75 ml | 3 × 6.25 ml |
| 12-15 | 2-4 years | 3 × 5 ml (1 spoon) | 3 × 7.5 ml (1½ spoons) |
| 15-20 | 4-6 years | 3 × 6.25 ml | 3 × 9.5 ml |
| 20-30 | 6-10 years | 3 × 8.75 ml | — |
| 30-40 | 10-12 years | — | — |
| ≥40 | ≥12 years | Amoxiclav tablets are used | |
Preparation of solutions for intravenous injections
Dissolve the contents of the Amoxiclav bottle with water for injection 600 mg (500 mg + 100 mg) - 10 ml of water for injection. The drug should be administered intravenously slowly (3‒4 minutes).
Amoxiclav for injection should be administered within 20 minutes after preparing solutions for intravenous administration.
Amoxiclav is administered intravenously after diluting 600 mg (500 mg + 100 mg) with 50 ml of infusion solution. Duration of infusion is 30-40 minutes.
| Period of stability | ||
| at 25°C | at 5°C | |
| Water for injections | 4h | 8h |
| Sodium chloride solution 0.9% for intravenous infusion | 4h | 8h |
| Lactated Ringer's solution for intravenous infusion | 3h | |
| Calcium chloride and sodium chloride solution for intravenous infusion | 3h | |
The drug solution cannot be mixed with solutions of dextrose, dextran or sodium bicarbonate. Only clear solutions should be used. Prepared solutions should not be frozen.
Possible side effects
In children, the described side effects are extremely rare. Liquid Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg is well tolerated by children, sometimes children experience stomach upset or skin reactions that go away after stopping the antibiotic.
From the digestive system:
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- rarely - stomach pain, liver dysfunction, increased activity of liver enzymes (ALT or AST);
- cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, pseudomembranous colitis.
Allergic reactions:
- itching, urticaria, erythematous rash;
- rarely - exudative erythema multiforme, angioedema, anaphylactic shock, allergic vasculitis;
- rarely - exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
From the hematopoietic system, lymphatic system:
- rarely - reversible leukopenia (including neutropenia), thrombocytopenia;
- very rarely - hemolytic anemia, reversible increase in prothrombin time (when used together with anticoagulants), eosinophilia, pancytopenia.
From the nervous system:
- dizziness, headache;
- very rarely - convulsions (may occur in patients with impaired renal function when taking high doses of Amoxiclav), hyperactivity, anxiety, insomnia.
From the urinary system:
- very rarely - interstitial nephritis, crystalluria.
Other:
- rarely - development of superinfection, candidiasis.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of Amoxiclav:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- Impaired liver function and/or cholestatic jaundice caused by taking the drug (history);
- Lymphocytic leukemia;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- Severe liver and kidney failure;
- Pseudomembranous colitis (history);
- Breastfeeding period.
Certificates of Conformity and Analysis
Drug interactions
The simultaneous use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg and probenecid is not recommended. Probenecid reduces renal tubular secretion of amoxicillin.
The use of allopurinol during treatment with amoxicillin may increase the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Like all antibiotics, Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension for children can affect intestinal flora.
The medicine should not be used together with bacteriostatic chemotherapeutic agents/antibiotics (chloramphenicol, macrolides, tetracyclines or sulfonamides).
The simultaneous use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg and methotrexate may increase the toxicity of the latter (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, formation of skin ulcers).
With simultaneous use of a combination of amoxicillin with clavulanic acid and mycophenolate mofetil, a decrease in the concentration of the active metabolite MPA in the blood plasma was reported by approximately 50%.
Comments (2)
Olga
10/08/2016 at 23:22 |
Augmentin is a really excellent drug, I’ve seen it from my own experience. I am a mother of three children and amoxiclav is my lifesaver; I have treated both ears and sore throat with it more than once. He has been helping us out for 10 years now.Answer
Ilya
08/22/2017 at 10:47 am |
if you don’t get carried away with antibiotics, then amoxiclav can be used to treat serious illnesses - in my case, it helped a lot with prostatitis, and I didn’t drink anything extra, I just went on Smartprost. I think this is because for trifles like a sore throat, I never take antibiotics; I use local remedies. And now, since childhood, everyone has been stuffed with these antibiotics.
Answer
Features of use
Before starting therapy with Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension, it is necessary to accurately determine the presence of hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins or other allergens.
Serious and sometimes even fatal cases of hypersensitivity (anaphylactic reactions) have been observed in patients during penicillin therapy. These reactions are reliable in individuals with similar reactions to penicillin. If allergic reactions occur, treatment with Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension should be stopped.
If the infection is proven to be due to microorganisms sensitive to amoxicillin, the possibility of switching from the amoxicillin/clavulanic acid combination to amoxicillin should be considered according to official recommendations.
This dosage form Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg should not be used when there is a high risk of pathogen resistance to β-lactams, and is not used for the treatment of pneumonia caused by penicillin-resistant strains of S. pneumoniae.
Children with impaired kidney function or those receiving high doses of the drug may experience seizures.
Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg should not be prescribed if infectious mononucleosis is suspected, since cases of morbilliform rashes have been observed with the use of amoxicillin for this pathology.
Long-term use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg can cause excessive growth of insensitive microflora with the development of pseudomembranous colitis of varying severity. In the presence of severe persistent diarrhea after the use of antimicrobial agents, it is important to ensure that it is not associated with this pathology. Drugs that suppress peristalsis are contraindicated. If colitis occurs, treatment should be stopped immediately and consult a doctor.
With long-term use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg, as well as other broad-spectrum antibiotics, superinfection with resistant bacteria and fungi (Pseudomonas spp, Candida albicans) may occur, which requires discontinuation of therapy and the use of other drugs.
During long-term therapy, it is recommended to periodically assess the functions of organs and organ systems, including renal, hepatic and hematopoietic functions.
Overdose
There are no reports of life-threatening side effects due to an overdose of Amoxiclav®. Symptoms of overdose include gastrointestinal disorders (abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting) and water and electrolyte imbalance. There have been reports of crystalluria caused by amoxicillin, which, in some cases, led to the development of renal failure.
Convulsions may develop in patients with renal failure or in patients receiving high doses of the drug.
In case of overdose, the patient should be under medical supervision and treatment should be symptomatic.
In case of overdose of the drug, gastric lavage and taking adsorbents (activated carbon) are recommended.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are eliminated by hemodialysis.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg may be associated with an increased risk of developing necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns. The use of Amoxiclav suspension should be avoided during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, unless the benefit of using the antibiotic outweighs the potential risk.
Both active ingredients are excreted in milk, but there is no information regarding the effect of clavulanic acid on the nursing infant. Accordingly, the baby may develop diarrhea or a fungal infection of the mucous membranes, so breastfeeding should be stopped.
The use of Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension during breastfeeding is possible only after a careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio.
"Amoxiclav": instructions for use for children
Babies and young children are usually prescribed an antibiotic in the form of a suspension. Is it possible to somehow dilute the already prepared drug? After all, children often refuse to take medicine.
It is allowed to mix the medication with food. It is important that it is not hot. For babies, you can dilute the drug with breast milk or formula. Juices are allowed. But you need to dilute the already prepared syrup. It is unacceptable to mix the bulk antibiotic substance with anything other than water.
Analogs
The analogues contain a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Preparations with one of the components do not have a wide spectrum of action Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg. An absolute analogue is Augmentin, but the price of the suspension for children is lower.
Cheap analogues with the same active ingredient:
- Amoxicillin;
- Amosin;
Substitutes with a similar effect, but a different active ingredient:
- Azithromycin;
- Flemoxin Solutab;
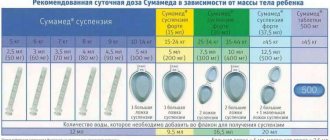
- Sumamed;
- Suprax;
Pharmacokinetics
Both active substances are well absorbed, regardless of food intake. The maximum concentration in plasma is reached one hour after taking the drug (Cmax for amoxicillin - 3-12 μg/ml, Cmax for clavulanic acid - 2 μg/ml.
The components of Amoxiclav are well distributed in pleural, parietal, synovial fluids, bronchial secretions, secretions of the nasal sinuses, saliva, as well as in body tissues (lungs, tonsils, middle ear, ovaries, uterus, liver, prostate gland, muscle tissue, gall bladder ). The drug is not able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (with non-inflamed meninges). Penetrates the placental barrier and is excreted in trace concentrations in breast milk. It binds poorly to plasma proteins, amoxicillin trihydrate disintegrates partially, clavulanic acid completely.
The drug is excreted by the kidneys almost unchanged. Small amounts are excreted by the lungs and through the intestines. The half-life is 1-1.5 hours.
Amoxicillin is excreted by the kidneys almost unchanged by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration. Small amounts may be excreted through the intestines and lungs. T1/2 of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid is 1-1.5 hours. In case of severe renal failure, it increases for amoxicillin to 7.5 hours, for clavulanic acid - up to 4.5 hours. Both components are removed during hemodialysis.
Prices
Dear readers, the price list for Amoxiclav 125 mg + 31.25 mg suspension is updated on our website once a day, which is why the prices indicated in it may differ from the real ones. Hope for your understanding.
| Drug name | Price for 1 unit, rub. | Price per package, rub. | Link |
| Amoxiclav® powder for the preparation of suspension for oral administration 125 mg + 31.25 mg/5 ml, 1 pc. | |||
| 110 | 110.00 | Buy | |
| 123 | 123.00 | Buy | |
| 130 | 130.00 | Buy | |
| 125 | 125.00 | Buy | |
| 120.91 | 120.91 | Buy | |
| Amoxiclav® powder for the preparation of suspension for oral administration 125 mg + 31.25 mg/5 ml, 1 pc. | |||
| 130 | 130.00 | Buy | |
| 125 | 125.00 | Buy | |
| 116 | 116.00 | Buy |