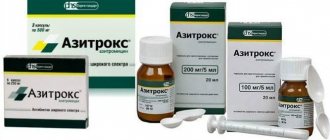
Azitrox is a new generation drug from the group of antibiotics. The product destroys a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms and at the same time (when compared with other medications from this group) Azitrox contains a small list of contraindications and complications.
In this regard, the drug is popular for treating children. When prescribing an antibiotic, it is important to strictly adhere to the rules specified in the instructions. For ease of dosing and use of the medication, Azitrox is prescribed in pediatrics in the form of a suspension.
Release form
The pharmacological agent "Azitrox" is produced in several forms, but the most convenient for children is the powder from which a medicinal suspension is prepared. It is presented in two main versions, differing only in the dosage of the active element. The 15.9 gram powder is placed in a tinted glass bottle that can hold 50 ml of liquid. The cardboard package contains one bottle with a pipette, as well as a measuring spoon and instructions with the rules for using and taking the medicine.
The powder has the form of white crystals or granules (may have a yellow or creamy tint), and the medicine made from it (after adding water) is a homogeneous yellowish-white or creamy-white suspension, with a fruity odor.
The composition of the Azitrox suspension for children is indicated in the instructions for use. Let's take a closer look at it.
Composition of the drug
The main active ingredient of the Azitrox suspension is azithromycin (in the form of dihydrate). A medicinal product with a dosage of 100 mg per 5 ml of this substance contains 400 mg, and in bottles of 200 mg per 5 ml - 800 mg of azithromycin.
The pleasant sweet taste, due to which the finished suspension resembles syrup, is provided to the medicine by the sucrose present in its composition. Additionally, the preparation contains sodium carbonate, hyprolose and xanthan gum. The pleasant aroma of the suspension is due to the presence of vanilla, cherry and banana flavors in it.
Pharmacological properties
Azithromycin (the main active element) is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action, and represents a subgroup of macrolide antibacterial substances - azalides. By binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, the drug inhibits peptide translocase at the translation stage, suppresses protein production, and slows down the reproduction and development of pathogenic bacteria. The Azitrox suspension has a bacteriostatic effect on extra- and intracellular pathogens, and in high concentrations has a bactericidal effect.
Pathological microflora, in relation to which the active element of the drug exhibits functionality: aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Streptococcus spp. (A, B, C, G), Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-sensitive); aerobic gram-negative microbes: Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Pasteurella multocida, Moraxella catarrhalis, Legionella pneumophila, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae; other anaerobic microorganisms: Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp., Porphyromonas spp., Prevotella spp., as well as Borrelia burgdorferi, Chlamydia (trachomatis, psittaci, pneumoniae), Mycoplasma (hominis, pneumonia). Microorganisms that can develop resistance to azithromycin are gram-positive aerobes. Pathogenic microorganisms initially resistant to the effects of the Azitrox suspension: aerobic gram-positive, including methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Bacteroides fragilis. After taking the suspension, the maximum level of its main substance in the blood is observed after approximately 2-3 hours. The medication is able to penetrate the body's cell membranes and tissue barriers. When the last dosage is taken, the concentration of the pharmacological drug remains for another 5-7 days after completion of therapeutic measures.
Pharmacodynamics
The main element of the antibiotic enters the body and begins to affect pathogenic microflora. It penetrates bacterial cells and slows down the process of protein synthesis in them. As a result, the bacteria stop growing and gradually die, since protein is necessary for their life.
Also, due to protein deficiency, bacteria lose their ability to reproduce. As a result (but only if you follow the rules for taking the suspension and complete the full course of treatment), the drug completely destroys pathogenic microflora that are sensitive to this antibiotic.
Thanks to the action described above, the antibiotic has the following effects on the body:
- in the area affected by bacterial activity, the development of the inflammatory process ceases. As a result, the temperature and swelling of the affected tissues decreases;
- due to the death of bacteria, intoxication of the body stops (bacteria release toxins during their life processes). Intoxication also causes an increase in temperature and a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
After eliminating the bacteria, the child’s immunity is gradually restored. It should be borne in mind that an antibiotic can destroy not only pathogenic microflora, but also beneficial microorganisms, so abuse of the drug can lead to a deterioration in well-being.
It is important that the exact list of antibiotic-sensitive bacteria is listed in the instructions for the drug.
Indications for use
Taking the medicinal suspension "Azitrox" for children is recommended in the following cases:
- sore throat, otitis media, sinusitis and other infections localized in the upper respiratory tract and ENT organs;
- early stages of Lyme disease;
- bronchitis, pneumonia in children;
- inflammatory pathologies of the urinary tract, provoked by microbes sensitive to this antibacterial drug;
- erysipelas, dermatoses and other skin infectious pathologies.
Contraindications
According to the instructions for use, Azitrox suspension for children is contraindicated if they are intolerant to macrolide antibiotics or additional components of this drug. In addition, it is recommended to avoid using the medication in the following cases:
- severe impairment of liver function;
- kidney dysfunction;
- sucrose deficiency;
- fructose intolerance;
- treatment with ergotamine and dihydroergotamine;
- glucose-galactose malabsorption.
With caution, experts prescribe the drug to children with diabetes mellitus, with moderate liver dysfunction in a child, as well as if the patient is prone to arrhythmias and myasthenia gravis.
The instructions for use of the Azitrox suspension for children also contain information about side effects.
special instructions
The high concentration of azithromycin and the properties of this substance allow the use of Azitrox for short-term courses. The long-term and effective effect of the drug is due to the ability of the active element to remain in the child’s body for eight hours. Antibiotics have some peculiarities in their use. These nuances must be taken into account. Otherwise, the effectiveness of therapy may be impaired.
Special instructions are the following recommendations:
- children can only be given Azitrox in the form of a suspension (capsules are intended for adult patients);
- Azitrox should be taken one hour before meals or two hours after eating;
- Do not take the drug simultaneously with drugs from the alkaloid group;
- Azitrox increases the effect of Warfarin;
- carrying out a course of treatment with Ergotamine or Dihydroergotamine is a contraindication for taking Azitrox;
- after treatment with an antibiotic, it is necessary to carry out restorative therapy of the intestinal microflora (Linex, Smecta or other drugs);
- if a child has a tendency to arrhythmia, antibiotics are taken under the supervision of a specialist and only if there are serious indications;
- the combination of an antibiotic with Disopyramide, Lovastatin and Rifabutin is strictly prohibited;
- When using the drug simultaneously with Cyclosporine, the toxic effect on the body increases.
Side effects
A child’s body, more often than an adult, reacts negatively to taking antibacterial medications, for example, the drug Azitrox. Therefore, children with this treatment often experience pathological symptoms such as dizziness, poor appetite, paresthesia, headache, impaired taste perception, nausea, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, itching, weakness.
More rarely, the following side effects of the drug "Azitrox" for children are observed:
- decrease in the number of lymphocytes and eosinophils in the blood;
- sleep disorders – drowsiness, insomnia;
- excessive nervous excitement;
- dyspepsia (vomiting, nausea);
- bowel dysfunction (most often diarrhea);
- hepatitis;
- allergic reactions, up to Quincke's edema;
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes.
In extremely rare cases, the drug can cause pathological phenomena such as thrombocytopenia, anemia, fainting, anxious or aggressive behavior, deafness, convulsions, cardiac arrhythmia, decreased blood pressure, colitis and others.
The dosage of the suspension for children "Azitrox" should be looked at in the instructions for use.
Overdose
Azitrox is a suspension for children; it cannot be taken longer than the indicated course or with an increase in dosage.
Ignoring these recommendations may cause the development of the following deviations:
- severe nausea, possible vomiting;
- diarrhea (or lack of bowel movement). The antibiotic has a detrimental effect on the intestinal microflora, as a result the organ ceases to function normally;
- deterioration or loss of hearing;
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin due to impaired liver function;
- manifestation of nervousness, aggression;
- irregular heartbeat, may be accompanied by blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle;
- severe dizziness and disorientation;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- voluntary muscle contractions in the limbs;
- If a child is allergic, then there is a high probability of developing Quincke's edema.
If the overdose occurs once, then it is necessary to rinse the child’s stomach in the near future and give sorbents. If the child is under 3 years old or the poisoning occurred due to long-term use of the drug, then the victim must be examined in a hospital, followed by symptomatic treatment.
Dosage regimen
In accordance with the instructions for use for the Azitrox suspension, the dosage of the medication is determined in each case individually, since for the calculation it is necessary to know the baby’s body weight. The number of kilograms should be multiplied by 10 mg - this is how the volume of a single dosage of a pharmacological agent is obtained.
For children weighing less than 10 kg, a dosage of 100 mg of the active element in a bottle is used.
Approximate dosages of the drug according to the child’s weight:
- 5 kg - 2.5 ml of suspension;
- 10-14 kg 0 5 ml;
- more than 15 kg - use bottles with a higher concentration of the active substance.
Therapy for Lyme disease should begin with an increased dosage of the drug. On the first day of treatment, the child is given a suspension at the rate of 20 mg per kg of weight. Subsequently, it should be gradually reduced to 10 mg per 1 kg.
The duration of therapy for infectious lesions of soft tissues or respiratory tracts is usually 3 days. When treating Lyme disease - 5 days.
What else can you learn from the instructions for the Azitrox suspension?
Directions for use and doses
Take orally, 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals, 1 time per day.
To prepare the suspension, add 9.5 ml of water (distilled or boiled and cooled) to the bottle with the powder. Measure the water using the dosing pipette included with the bottle. Shake the contents of the bottle thoroughly until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. The actual volume of the prepared suspension will be 20 ml.
The suspension must be shaken before each use. To dispense the finished suspension, use a dosing pipette or measuring spoon. Immediately after taking the suspension, you need to drink a few sips of water to rinse and swallow the drug remaining in the mouth. After use, a measuring spoon or pipette, which is previously disassembled, washed with running water, dried and stored with the drug.
The dosage and duration of use are determined by the attending physician depending on the disease and the age/weight of the patient.
Drug interactions
According to the instructions for use, this pharmacological agent is often prescribed as part of complex therapy. There are certain recommendations regarding drug interactions:
- Ethanol, antacid substances and food slow down the absorption of the active component of this antibiotic.
- There is no interaction between azithromycin and drugs such as terfenadine, theophylline, carbamazepine, triazolam, and digoxin.
- The Azitrox suspension significantly increases the toxicity of the drugs Cycloserine, Methylprednisolone, Felodipine, as well as indirect anticoagulants.
- When the active substance is combined with digoxin, the blood level of the latter medication increases.
- When Azitrox is combined with warfarin, the anticoagulant effect increases, so it is very important to monitor the prothrombin time.
- Lincosamides significantly reduce the effectiveness of azithromycin, while chloramphenicol and tetracycline, on the contrary, increase it.
- In combination with the substances ergotamine and dihydroergotamine, the toxic effect of the latter drugs on the body increases.
- When combined with triazolam, its pharmacological effect increases and clearance decreases.
- The therapeutic effect of dihydroergotamine and ergot alkaloids is enhanced.
- An absolute contraindication is to combine the antibiotic Azitrox with heparin.
The instructions for use for the Azitrox suspension for children do not list analogues.
Reviews
Reviews about this pharmacological drug on medical websites are mostly positive. Azitrox suspension for children is in great demand, since antibiotics are prescribed to children quite often. Parents note that children really like this medication, which is due to its pleasant smell and taste; it is easy to give it to the child and convenient to dose.
As for the effectiveness of this drug, according to information from reviews, the antibiotic helps very well in acute inflammatory diseases. It is prescribed for complications of flu or colds, for example, bronchitis in a child, pneumonia, and various skin infectious diseases.
In most cases, this medication was well tolerated by children, but reviews note that some patients experienced stool problems in the form of acute diarrhea. Dyspeptic symptoms were also observed in the form of slight nausea, regurgitation in breastfed children, etc.
Experts do not recommend self-medication, and if necessary, it is best to show the child to a doctor and get the appropriate prescription, since the drug may be contraindicated for him.
We reviewed the instructions for use of Azitrox for children.
Analogues of the drug
Analogs of the drug also belong to the group of macrolides. A replacement may be prescribed according to indications. There are twenty-five drugs in total that are similar in composition to the drug Azitrox, but not all have the suspended form.
The most famous analogue of Azitrox is the drug Sumamed. Next come medications such as Z-Factor, Sumamecin, Sumaklid, etc.