Composition of the drug
The main active ingredient in the medicine is metamizole sodium or analgin, which is more familiar to people.
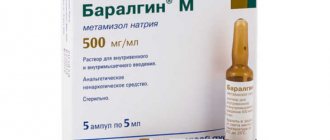
1 Baralgin ampoule contains up to 2.5 grams of sodium metamizole, up to 0.5 grams per tablet, and up to 1 gram per suppository.
Years earlier, Baralgin was registered in Russia, which contained three main components. These are: analgin, pitofenone and fenpiverinium bromide.
But in 2009, Baralgin M, produced by Aventis Pharma (India), began to spread. And it contains only one active substance - analgin.
Analogs
Baralgin analogues can be divided into two groups. The first category includes drugs that are structural substitutes for the drug. The second group includes medications with a similar therapeutic effect.
- The first group of analogues: Analgin and Analgin Ultra Optalgin; Metamizole sodium; Spazdolzin (the drug is intended for children).
- The second group of analogues: Aprofen; Buscopan; Dibazol; Diclonac; Drataverine; No Shpa and No Shpa Forte; Spasmonet; Spasmalgon; Unispaz.
Other drugs should only be taken after studying the relevant information.
Indications for use
This drug is prescribed when pain or spasms occur. This:
- headache or toothache;
- radiculitis, arthritis or osteochondrosis;
- renal colic;
- disorders in the pelvis;
- diseases of a neuralgic nature;
- for pain in the urinary tract;
- fever;
- pain in the postoperative period;
- heat.
Reviews from doctors
Anna Viktorovna, nephrologist, Tver: “The drug has a strong effect and quickly relieves pain.
The downside of the medication is a large list of side effects, including oliguria.” Denis Andreevich, chief physician, Moscow: “I recommend tablets for relieving acute pain. It is preferable to use for rare episodes of pain, as well as colic.”
Yuri Petrovich, surgeon, Arkhangelsk: “I use it in practice in injection form. An effective remedy after surgical interventions.”
Contraindications for use
To avoid side effects from Baralgin, you need to carefully study what contraindications exist for taking the drug:
- allergy to medication components;
- hepatic porphyria;
- disorders of the kidneys or liver;
- deficiency of glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase;
- tachycardia;
- glaucoma;
- asthma;
- rhinitis or urticaria that appears when taking paracetomol, ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc.;
- gastric obstruction;
- problems with hematopoiesis;
- 1st and 3rd trimester of pregnancy (2 with caution);
- alcohol;
- individual intolerance to preservatives or dyes.
special instructions
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no negative effect on psychomotor reactions.
Pregnancy and lactation
Baralgin is strictly contraindicated for use in the first and last trimester of pregnancy. At other times, it is also recommended to refrain from taking the drug (only a doctor can make an exception based on the individual clinical picture of the woman’s health condition). Breastfeeding is one of the absolute contraindications to the use of the drug.
Use in childhood
It is not recommended to use the drug for children in the first months of life. For babies from the first year, minimal dosages are used.
For impaired renal function
The drug is prescribed to eliminate renal colic. If you have other kidney pathologies, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
For liver dysfunction
Contraindications for taking Baralgin are hepatic porphyria in the acute stage and liver failure.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
A prescription is required.
Side effects from Baralgin
When using the drug, unpleasant symptoms may occur:
- dysfunction of the cardiac system;
- anuria;
- allergic reactions (urticaria, anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema);
- proteinuria;
- interstitial nephritis;
- decrease in pressure;
- agranulocytosis;
- bleeding;
- constipation;
- visual impairment;
- confusion;
- inflammation at the injection site;
- stomatitis;
- vaginitis;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- convulsions;
- erythema;
- decreased sweating.
Indications and contraindications
The main indication for using the drug is acute pain . This symptom is characteristic of many diseases. Baralgin is administered:
- for fractures;
- osteochondrosis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- sciatica;
- renal colic.
In the form of injections, the drug can only be used in a hospital setting. In rare cases, the medicine is used to lower a very high fever. Baralgin is not prescribed as the main therapeutic drug.
You should stop using the drug if there are the following contraindications:
- individual intolerance to components;
- problems with bone marrow functioning;
- bronchial asthma;
- acute renal porphyria;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- pathologies in the liver and kidneys;
- bleeding disorders;
- age up to 12 months.
Improper use of the drug can lead to serious consequences. Self-administration of medication into a vein or muscle is prohibited. Before prescribing Baralgin, the doctor must make sure there are no contraindications.
Instructions for use of the drug "Baralgin"
"Baralgin" is used as injections in 2 ways: intramuscularly or intravenously. In the first case, 2 to 5 ml are administered at a time. If the pain does not go away, then after 7-8 hours the procedure can be repeated. But you cannot administer more than 10 ml in 24 hours. In the second case, the dose should not exceed 2 ml per day.
To avoid side effects from Baralgin injections, the correct dosage should be observed. The solution must be administered very slowly and, preferably, under the supervision of a physician. Rapid administration of the medication may cause shock or low blood pressure. For children over 3 months old, the injection is given intramuscularly. The instructions for use for Baralgina tablets say that you can take 1 or 2 tablets at a time. You should not take more than 6 tablets per day.
Important! Dosage for children under 15 years of age is prescribed only by a doctor.
Storage conditions
Baralgin should be stored in a dry, dark place, away from children's access to the drug. Storage temperature – up to 25˚C.
Shelf life – 4 years.
Baralgin M is available with a prescription.
Tab. Baralgini 500 mg Dtd N (the number of tablets is indicated) S. 1 tablet. for pain.
Sol. Baralgini 5ml Dtd N (the number of ampoules is indicated) S. 5 ml for pain.
The manufacturer recommends storing ampoules and tablets away from light, maintaining a temperature range of 8-28 degrees.
Indications for the use of Baralgin analogues
The list of direct or indirect analogues of Baralgin includes drugs whose active substance is almost completely identical to that included in the drug in question:
- "Maxigan." The drug is prescribed for severe pain, renal colic, and spasms. And also for treating symptoms of neuralgia, relieving pain in the postoperative period, reducing fever. It is allowed to take tablets no more than 2-3 times a day, 1-2 tablets after meals. The daily injection dose is up to 4 ml per 24 hours.
- "Zologan." The medicine is recommended for use for pain, spasms, neuralgia, and pelvic diseases. The tablets are taken in the same doses as the previous drugs.
- "Spazmalgon." It is used to relieve pain, relieve spasms from the smooth muscles of internal organs, reduce body temperature, reduce painful symptoms in the joints or after surgery. Tablets are prescribed 1-2 pieces 2-3 times in 24 hours, no more than 5 days.
- "Analgin." Take to relieve pain of various etiologies (injuries, toothache, burns, headache, neuralgia, menalgia, etc.) and fever. Take 0.5 g 2-3 times per 24 hours.
- "Trigan." It is used for hepatic, intestinal or renal colic and algodismenorrhea. Single injection dose 20 mg. If a second injection is necessary, an interval of 6 hours should be observed between them.
- "Optalgin". Indications for use: pain of any nature, rheumatism, inflammatory processes, lichen, tumors, pancreatitis, pneumothorax, peritonitis, insect bites, urological diseases, thrombosis of great vessels. Orally 1-2 tablets at a time, but not more than 4 times a day. Or a solution of 25-50 drops, no more than 4 times a day.
Pharmacological group
The drug Baralgin is an antispasmodic and analgesic with a combined composition. The combination of various active components of the drug mutually enhances each other's therapeutic effectiveness.
Metamizole sodium acts as the main element of the composition of the drug Baralgin. The substance is a derivative of pyrazolone. It has a pronounced analgesic effect, reduces the severity of inflammatory processes and has a significant antipyretic effect by lowering body temperature.
Pitophenone hydrochloride has a direct relaxant effect on smooth muscles. It has a papaverine-like effect. The substance eliminates spasms and prevents their secondary manifestation.
Fenpiverinium bromide has an m-anticholinergic effect. The substance suppresses nerve impulses, reduces the tone of smooth muscles of blood vessels and organs and improves blood circulation in tissues.
While taking Baralgin, the following side effects may occur:
- proteinuria;
- a sharp and significant decrease in blood pressure;
- leukopenia;
- anaphylactic shock (extremely rare);
- oliguria;
- thrombocytopenia;
- Quincke's edema;
- interstitial nephritis;
- agranulocytosis;
- rash on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, conjunctiva or skin;
- bronchospasm.
Under a trade name that contains the word Baralgin, only one drug is registered in Russia - “Baralgin M”, containing a single active substance. This is metamizole sodium, otherwise analgin, a derivative of 5-pyrazolone. Baralgin M is classified as an NSAID with weak anti-inflammatory activity, non-selectively blocking cyclooxygenase enzymes and inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins.
Until 2009, there was a medicine called “Baralgin”, the composition of which included 3 active ingredients. In addition to metamizole, these are the myotropic antispasmodic pitofenone and the m-anticholinergic fenpiverinium bromide. Combinations of these active compounds led to a wider range of uses of the drug.
Why was Baralgin prescribed: in addition to the therapeutic effect of metamizole sodium, it could also be used to relax the smooth muscles of internal organs and vascular walls, relieve spastic pain, strengthen spasmodic muscle fibers of blood vessels, improve blood flow, incl. brain, and to lower blood pressure.
At the moment, pharmacy chains do not sell the combination drug.
- analgesic – weakens or completely relieves pain of low or moderate intensity by inhibiting the conduction of pain impulses, increasing the threshold of excitability and reducing the sensitivity of receptors to the action of various pain stimuli;
- antipyretic – reduces pathologically elevated temperature without affecting the normal value. The effect is achieved by the inhibitory effect of Baralgin, which reduces the flow of impulses from thermal receptors to the nuclei of the hypothalamus, which are responsible for thermoregulation. Due to the suppression of the activity of nerve cells of the posterior hypothalamus, heat generation decreases, peripheral vasoconstriction is eliminated, heat transfer increases and, accordingly, body temperature returns to normal;
- antispasmodic - eliminates spasms caused by strong contraction of the muscles of the walls of the internal organ, mainly the ureters, renal pelvis, bladder wall of the urinary cavity and biliary tract;
- anti-inflammatory – reduces the severity of inflammation. The effect is minor.
The active substance is a non-narcotic drug and is a pyrazolone derivative. The drug has antipyretic, analgesic and mild anti-inflammatory effects. According to the main mechanism of action, the drug is similar to other non-narcotic analgesics.
Interaction of Baralgin with other drugs
There are a number of medications that are contraindicated to be taken simultaneously with Baralgin.
- "Phenylbutazone" and drugs based on barbituric acid. They significantly weaken the effect of Baralgin.
- Allopurinol, oral contraceptives, TCAs (tricyclic antidepressants). Causes liver dysfunction.
- Phenothiazine derivatives. Taking it together with Baralgin will cause hyperthermia.
- "Sarcolysine" or "Thiamazole". There is a high risk of a decrease in leukocytes in the blood, that is, leukopenia.
- Myelotoxic drugs. By mixing with their “Baralgin”, you can increase the hepatotoxicity of the medication.
- Alcohol. The toxic effect is greatly enhanced.
- Tranquilizers, histamine H2 blockers, sedatives, propranolol or codeine increase the analgesic effect.
Drug overdose
If an overdose of the drug "Baralgin" occurs, then the following may occur: nausea, dry mouth, drowsiness, lethargy, increased blood pressure, abdominal pain, disturbances of consciousness, convulsions.
In this case, it is necessary to do a gastric lavage as quickly as possible and drink activated carbon (3-4 pieces). Then immediately call emergency services.
In the hospital, with the help of hemodialysis and forced diuresis, the drug will be removed from the body.
While taking the medication, it is necessary to frequently monitor the condition of the peripheral blood, as well as monitor the condition of the liver.
Features of using the medicine
You need to know some rules for taking the drug. Doctors give useful advice that will make the therapy successful and without complications:
- In some patients, Baralgin can cause anaphylactic shock. In this case, you must immediately go to the hospital. To eliminate the syndrome, doctors will prescribe adrenaline or antihistamines;
- Baralgin should be prescribed with great caution if a person has a congenital allergy to other drugs. It is necessary to start with a small dose and, if there are no side effects, gradually increase it;
- During therapy, the patient may experience agranulocytosis. It does not depend on a large or small dose and is difficult to predict. That is why the patient should often see the doctor and talk about all the symptoms daily;
- If a person has hematological diseases, he needs to take Baralgin only as a last resort. In this case, the doctor must monitor blood counts during treatment;
- For diseases of the kidneys and liver, an individual dose must be prescribed;
- Baralgin should be prescribed with caution for digestive diseases. Frequent use of the drug can cause severe intoxication. It is necessary for the doctor to constantly monitor the patient's health status and adjust the dose;
- It is necessary to carefully administer more than 2 ml of Baralgin solution if the patient has problems with blood pressure. Otherwise, if administered quickly, the pressure may drop sharply.
Follow all these recommendations and visit your doctor more often. Then the risk of complications will be reduced and the therapy will be successful.
Injections "Baralgin M"
Baralgin M injections have an analgesic and antipyretic effect. This non-narcotic analgesic belongs to the pyrazolones group. It is used to eliminate any pain that does not respond to other drugs.
Side effects of Baralgin M are manifested in the appearance of:
- phlebitis;
- Quincke's edema;
- rash;
- bronchospasm;
- arrhythmias;
- decrease in pressure;
- anphylactoid manifestation;
- Lyell's or Stevens-Johnson syndrome (very rare).
Prohibited for use if available:
- bronchial asthma;
- sensitivity to metamizole sodium;
- agranulocytosis that occurs while taking medications from the pyrazolidine group;
- impaired renal or liver function;
- 1st and 3rd trimester of pregnancy;
- allergic reactions when taking paracetamol, indomethacin, salicylates;
- dysfunction of the bone marrow;
- hemodynamic disorders.
According to the instructions for using Baralgin M injections, when injecting the solution intravenously, it is necessary to take a lying position due to a possible sharp drop in pressure. The injection is administered very slowly, 1 ml in 60 seconds and another 1 ml in the second minute, if such a dose is required.
Infusing the solution too quickly may cause the patient to go into shock.
If erosion in the oral cavity, fever, chills, or neutropenia suddenly appears, you should immediately stop taking the medication and call an ambulance.
People with kidney disease and heart failure should be careful with the drug. And also while driving a vehicle.
Mechanism of action
Pharmacodynamics are determined by the effects of metamizole sodium:
- The chemical compound has the ability to reduce pain sensitivity and lower body temperature during fever.
- Blocks a group of cyclooxygenase enzymes, slows down the synthesis of prostaglandins. Raises the sensitivity threshold of pain receptors, reduces the transmission of pain impulses.
- Improves heat transfer.
- The anti-inflammatory effect is insignificant, because the medicine does not have a strong effect on water-salt metabolism.
The medicine has an antipyretic effect.
The medicine acts as a pain reliever. It has an antipyretic effect and a relaxing effect on smooth muscle spasms.
Pharmacokinetics
Metamizole sodium is characterized by good absorption into the mucous membranes of the digestive tract. It is completely converted into metabolites and is absent in the bloodstream in unchanged form. It is excreted from the body by the kidneys within 3 hours. The period increases against the background of pathological conditions of the liver.