pharmachologic effect
Glucocorticosteroid for local use.
Has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects.
Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators, increases the production of lipomodulin - an inhibitor of phospholipase A, reduces the release of arachidonic acid, and inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins. Prevents the marginal accumulation of neutrophils, reducing the formation of inflammatory exudate and the production of lymphokines, inhibits the migration of macrophages, which leads to a slowdown in the processes of infiltration and granulation.
Increases the number of active β-adrenergic receptors, neutralizes their desensitization, restores the patient's response to bronchodilators, allowing them to be used less frequently.
Under the influence of beclomethasone, the number of mast cells in the bronchial mucosa decreases, the swelling of the epithelium and the secretion of mucus by the bronchial glands decreases. Causes relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles, reduces their hyperreactivity and improves external respiration function.
Does not have mineralocorticoid activity.
In therapeutic doses it does not cause side effects characteristic of systemic corticosteroids.
The therapeutic effect usually develops after 5-7 days of course use of beclomethasone.
Beclomethasone price, where to buy
The price of Beclomethasone averages 300-400 rubles per bottle of 200 mcg.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
ZdravCity
- Beclomethasone-aeronative aerosol for in.
dosage 100 mcg/dose 200 doses Nativa LLC/JSC Pharmstandard-Leksredstva RUB 272 order - Beclomethasone-aeronativ aer. d/ing. dosage 50 mcg/dose 200 doses No. 1 (balloon with dosing spray nozzle) Nativa LLC/Pharmstandard-Leksredstva OJSC
RUB 258 order
- Beclomethasone Azr. d/ing dosage 100 mcg/dose 200 doses balloon with dosage. nozzle JSC Binnopharm
RUR 326 order
Directions for use and doses
Inhalation.
- Bronchial asthma
Adults and children aged 12 years and older. Beclomethasone aeronate is used regularly (even in the absence of symptoms of the disease), the dose of beclomethasone dipropionate is selected taking into account the severity of bronchial asthma and the clinical effect in each specific case. The daily dose is divided into several doses.
Recommended initial doses of the drug:
mild bronchial asthma - 200–600 mcg/day;
moderate bronchial asthma - 600–1000 mcg/day;
severe bronchial asthma - 1000–2000 mcg/day.
Children aged 4 to 12 years. Up to 400 mcg/day in several doses.
Depending on the patient's individual response, the dose of the drug can be increased until a clinical effect appears or reduced to the minimum effective dose.
When switching to a high dose of inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate in many patients receiving systemic corticosteroids, it is possible to reduce their dose or discontinue them completely.
- COPD
The maximum recommended dose of Beclomethasone-aeronativ for COPD is 2000 mcg/day.
If you accidentally miss an inhalation, the next dose must be taken at the scheduled time in accordance with the treatment regimen.
Administration can be carried out using special dispensers (spacers), which improve the distribution of the drug in the lungs and reduce the risk of side effects.
Beclomethasone, 100 mcg/dose, 200 doses, metered inhalation aerosol, 1 pc.
Before prescribing inhaled drugs, it is necessary to instruct the patient on the rules for their use, ensuring the most complete delivery of the drug to the desired areas of the lungs. The development of oral candidiasis is most likely in patients with high levels of precipitating antibodies in the blood against the Candida fungus, which indicates a previous fungal infection. After inhalation, you should rinse your mouth and throat with water. To treat candidiasis, topical antifungal drugs can be used while continuing Beclomethasone therapy.
If patients take GCS orally, then Beclomethasone is prescribed while taking the previous dose of GCS, and the patients should be in a relatively stable condition. After about 1–2 weeks, the daily dose of oral corticosteroids begins to be gradually reduced. The dose reduction scheme depends on the duration of previous therapy and the size of the initial dose of GCS. Regular use of inhaled corticosteroids allows, in most cases, to cancel oral corticosteroids (patients who need to take no more than 15 mg of prednisolone can be completely transferred to inhaled therapy). However, in the first months after the transition, the patient's condition should be carefully monitored until his pituitary-adrenal system has recovered sufficiently to ensure an adequate response to stressful situations (for example, injury, surgery or infection).
When transferring patients from taking systemic corticosteroids to inhalation therapy, allergic reactions (for example, allergic rhinitis, eczema) that were previously suppressed by systemic drugs may occur.
Patients with reduced function of the adrenal cortex who are transferred to inhalation treatment should have a supply of GCS and always carry a warning card with them, which should indicate that in stressful situations they need additional systemic administration of GCS (after eliminating the stressful situation, the dose of GCS can be repeated reduce). A sudden and progressive worsening of asthma symptoms is a potentially dangerous condition, often life-threatening for the patient, and requires an increase in the dose of GCS. An indirect indicator of the ineffectiveness of therapy is the more frequent use of short-acting β2-agonists than before.
Beclomethasone dipropionate for inhalation is not intended for the relief of attacks, but for regular daily use. Short-acting β2-adrenergic agonists (for example, salbutamol) are used to relieve attacks. In case of severe exacerbation of bronchial asthma or insufficient effectiveness of the therapy, the dose of inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate should be increased and, if necessary, a systemic corticosteroid and an antibiotic should be prescribed if the infection develops.
If paradoxical bronchospasm develops, you should immediately stop using Beclomethasone, assess the patient's condition, conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe therapy with other drugs. With long-term use of any inhaled corticosteroids, especially in high doses, systemic effects may be observed (see “Side effects”), but the likelihood of their development is much lower than when taking corticosteroids orally. Therefore, it is especially important that when a therapeutic effect is achieved, the dose of inhaled corticosteroids is reduced to the minimum effective dose that controls the course of the disease. At a dose of 1500 mcg/day, the drug does not cause significant suppression of adrenal function in most patients. Due to possible adrenal insufficiency, special care should be taken and regular monitoring of adrenal function indicators when transferring patients taking oral corticosteroids to treatment with beclomethasone.
It is recommended to regularly monitor the growth dynamics of children receiving inhaled corticosteroids for a long time.
Administration can be carried out using special dispensers (spacers), which improve the distribution of the drug in the lungs and reduce the risk of side effects.
Abrupt withdrawal of Beclomethasone aerosol is not recommended.
It is necessary to protect the eyes from contact with the drug. By washing after inhalation you can prevent damage to the skin of the eyelids and nose.
The Beclomethasone canister should not be pierced, disassembled or thrown into fire, even if it is empty. Like most other inhalation aerosol products, Beclomethasone may be less effective at low temperatures. When cooling the cylinder, it is recommended to remove the inhaler nozzle from it and warm it with your hands for a few minutes.
Information about the possible effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
No data.
special instructions
Beclomethasone is not intended for the relief of acute asthmatic attacks. It should also not be used for severe asthma attacks requiring intensive care. The recommended route of administration for the dosage form used should be strictly followed.
Beclomethasone should be used with extreme caution and under close medical supervision in patients with adrenal insufficiency.
The transfer of patients who constantly take GCS orally to inhaled forms can be done only if their condition is stable.
If there is a possibility of developing paradoxical bronchospasm, bronchodilators (for example, salbutamol) are inhaled 10-15 minutes before the administration of beclomethasone.
With the development of candidiasis of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract, local antifungal therapy is indicated without stopping treatment with beclomethasone. Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, if appropriate therapy is prescribed, are not a contraindication for treatment with beclomethasone.
Use of the drug Beclomethasone
Inhalation use Adults (including elderly patients) and children over 12 years of age with mild asthma (forced expiratory volume (FEV) or peak expiratory flow (PEF) - more than 80%, daily variation in PEF indicators - less than 20%) - 200 each –600 mcg/day for 2 inhalations; for moderate asthma (FEV or PEF - 60-80%, daily variation in PEF - 20-30%) - 600-1000 mcg/day for 2-4 inhalations; Severe BA (FEV or PEF - 60%, daily variation in PEF - 30%) - 1000-2000 mcg/day for 2-4 inhalations. The maximum daily dose of the drug in adults should not exceed 1 mg, in very severe cases - 1.5–2 mg/day in 3–4 doses. Children aged 6 to 12 years are prescribed an initial dose of 50–100 mcg 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 400 mcg. The daily dose is divided into 2–4 doses. The maximum daily dose of the drug in children should not exceed 500 mcg. After each inhalation, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with water. Beclomethasone dipropionate, containing 250 mcg per dose, is not intended for use in pediatrics. Intranasal use The recommended dose for adults and children over 12 years of age is 200 mcg (2 inhalations, with the first inhalation directed to the upper and the second to the lower part of the nasal passage) 2 times a day in each nasal passage or 100 mcg in each nasal passage stroke 3–4 times a day; the maximum daily dose is 1000 mcg. Children aged 6–12 years: 42–50 mcg in each nasal passage 3–4 times a day. The total daily dose is 252–400 mcg, the maximum is 500 mcg.
general information
The Latin name of the drug is Beklometazon. Available in the form of a metered dose inhaler containing an aerosol. The aluminum canister contains 200 doses. The aerosol is supplied by pressing the bottom of the inhaler.
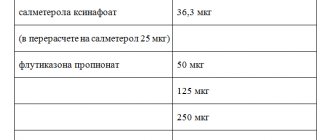
The active component is beclomethasone dipropionate. The share in the composition of the drug is 0.050 mg, 0.100 mg, 0.250 mg. Refers to glucocorticosteroids. When it enters the respiratory tract through inhalation, it acts locally and is localized in pathological areas. A small amount of active substances penetrates into the systemic circulation. Thanks to this effect, the likelihood of developing adverse events is reduced.
Main indications for use: bronchial asthma – moderate, severe form; COPD as maintenance therapy. Beclomethasone inhaler is prescribed by a specialist for adults and children. Treatment is carried out under control. The medication has a number of contraindications and can cause side effects.
Beclomethasone for inhalation via nebulizer
There is no drug in the form of a solution with an identical name. To carry out breathing procedures through a compressor device, buy Clenil UVD. Produced in Ukraine. Sold in glass bottles. Each contains 2 ml of medication. The active ingredient is beclometazone with a concentration of 800 mcg. The main indication for use is bronchial asthma.
Standard scheme
| Age | Clenil (ml) per procedure | Frequency of procedures per day (times) |
| Adults | 2 | 1-2 |
| Children from 6 years old | 1 |
Additionally, there is no need to dilute the medication with saline solution. Used undiluted. For a nebulizer, Beclomethasone solution is stored for no more than 8 hours. The contents of the ampoule or half are poured into the inhaler chamber. In the second case, the bottle is closed with a cap and placed in the refrigerator. You need to use it before the end of the day or in the morning if you had to open the nebula in the evening.
Beclomethasone inhalation solution is inhaled through a mouthpiece. You need to breathe slowly, deeply. Frequent breathing causes dizziness, weakness, and increased heart rate. The duration of the procedure for children is 10 minutes, for adults – 15.
Contraindications to the use of Beclomethasone
According to the instructions, Beclomethasone is contraindicated for diseases such as:
- acute bronchospasm, bronchitis of non-asthmatic origin;
- hemorrhagic diathesis and frequent nosebleeds;
- herpetic eye damage, systemic infectious diseases, including acute respiratory infections and pulmonary tuberculosis.
The drug is not prescribed to children under 6 years of age, as well as to women in the first trimester of pregnancy. In the second and third trimesters, as well as during lactation, treatment with Beclomethasone is allowed, but as prescribed by a doctor and when comparing feasibility and risks.
The drug in the form of a spray is carefully prescribed to people with various deformities of the nasal septum, hypothyroidism, amebiasis, severe renal failure, and glaucoma.
In limited doses, Beclomethasone is indicated for persons who have suffered a myocardial infarction and nasal trauma, as well as for those who have undergone surgical interventions in the nasal cavity.
Side effects of Beclomethasone
Beclomethasone spray, like powder, can cause unwanted reactions from the body:
- Cough, sneezing, dysphonia, bronchospasm (in rare cases), eosinophilic pneumonia;
- Candidomycosis of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract;
- Headache, dizziness, cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, leukocytosis, eosinopenia - with long-term treatment with Beclomethasone in large doses;
- Allergic reactions;
- Rhinitis, nosebleeds, atrophy of the mucous membrane, perforation of the nasal septum - with intranasal use;
- Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system - with a single overdose of more than 1 mg.