Pharmacological properties of the drug Betasalik
Pharmacodynamics . A drug that has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic, keratolytic, antimicrobial effects. Betamethasone dipropionate inhibits the release of interleukins IL-1 and IL-2, interferon gamma, inflammatory mediators, reduces the metabolism of arachidonic acid, and induces the formation of lipocortins, which have anti-edematous activity. Salicylic acid promotes better penetration of betamethasone dipropionate into the deep structures of the skin and has a keratolytic and antimicrobial effect. Pharmacokinetics. Systemic resorption of betamethasone after external use is 12–14%. Metabolized in the liver. Metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine, a small part - in bile.
Betasalik ointment - how to use it
Indications for the use of ointment may include the following conditions:
- Neurodermatitis;
- Psoriasis;
- Lichen planus;
- Acute or chronic types of eczema;
- Dyshidrosis;
- Ichthyosis;
- Seborrhea;
- Chronic atopic dermatitis.
Neurodermatitis
Psoriasis
Ringworm red
Eczema
Dyshidrosis
Ichthyosis
Seborrhea
dermatitis
Contraindications to treatment with ointment:
- Tuberculosis;
- Syphilis disease;
- Fungal infections;
- Primary viral infections.
The instructions do not encourage the use of Betasalik if acne appears, a post-vaccination reaction occurs, or if there is special sensitivity to some of the substances in the drug.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Betasalik
If skin irritation or hypersensitivity is noted during use of the drug, treatment should be discontinued. In case of infection, appropriate therapy must be prescribed. Side effects that occur with the use of systemic corticosteroids, including inhibition of adrenal cortex function, may occur with excessive and prolonged use of corticosteroids, especially in pediatric practice. Systemic absorption of local corticosteroids and salicylic acid increases when applied to large areas of skin, as well as when using occlusive dressings. Avoid applying salicylic acid to open wounds or broken skin. Caution must also be observed during prolonged use, especially when treating children. If skin irritation develops, including excessive dryness, you should stop using the drug. The drug is not used in ophthalmology. It is necessary to avoid getting the drug into the eyes and mucous membranes. During pregnancy and breastfeeding. The safety of using local corticosteroids during pregnancy has not been proven, therefore, the prescription of this group of drugs during pregnancy is possible only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. During pregnancy, drugs in this group should not be used in high doses or for a long time. It has not been established whether local use of GCS through systemic absorption can lead to their appearance in breast milk. The decision to stop breastfeeding or use the drug should be made taking into account the need for the drug for the mother. Children. Children more often experience signs of suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system and the appearance of external corticosteroid effects under the influence of local corticosteroids than in adult patients. This is due to higher absorption of the drug in children and a higher ratio of skin surface area to body weight. Children receiving treatment with topical corticosteroids may experience depression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, insufficient weight gain, and increased intracranial pressure. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children: low plasma cortisol levels and lack of response to ACTH stimulation. Increased intracranial pressure is manifested by protrusion of the crown, headache, and bilateral swelling of the optic discs. The ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or working with other mechanisms has not been studied.
Betasalik: composition, indications, dosage, side effects
This pharmaceutical product refers to a combination of corticosteroids and keratolytic drugs that are intended for use in dermatology.
In particular, betamethasone is a synthetic fluorinated adrenocorticosteroid that is applied topically.
This substance has high glucocorticosteroid activity, and at the same time, minimal mineralocorticoid effect. Produces anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antipruritic, antiproliferative and vasoconstrictor effects.
It is a synthetic analogue of prednisolone. Like all corticosteroids, it helps reduce the release, formation, and activity of chemical elements that mediate the inflammatory process. These include kinins, histamines, lysosomal enzymes, and prostaglandins.
It has the property of inhibiting cell migration into the cell, to the site of damage, causing a decrease in vasodilation and increased permeability of veins, arteries and capillaries at the site of damage. As a consequence of this vasoconstrictor effect, extravasation is reduced and the likelihood of edema is reduced.
Thanks to corticosteroids, the entry of macrophages and certain types of T-lymphocytes (sensitized) into target cells is limited.
Salicylic acid, which is also part of the drug, has a keratolytic effect (if applied topically). As a result, corticosteroids are able to penetrate the skin more easily.
Composition and release form
The main active drugs are betamethasone and salicylic acid.
Auxiliary components are: mineral oil, white soft paraffin.
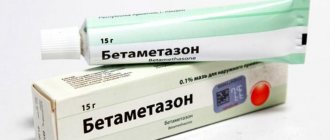
Available in the form of an ointment, packaged in tubes of 15 grams each. 1 gram of the drug contains 0.64 mg of betamethasone (in the form of dipropionate) and 30 mg of salicylic acid.
Indications
The drug is intended to reduce the symptoms of the inflammatory process in such dermatoses that are sensitive to treatment with local corticosteroids, such as:
– eczema (acute, chronic);
– contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, solar dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, radiation dermatitis, intertriginous dermatitis;
– neurodermatitis, lichen planus;
– psoriasis, ichthyosis;
– seborrhea of the scalp.
Particularly effective for weeping diseases and oily skin.
Contraindications
This drug should not be used if the patient has previously experienced hypersensitivity (allergy) to one of the components that make up the drug - both main and auxiliary.
Also contraindicated for:
– rosacea, molluscum contagiosum;
– ophthalmological diseases;
– post-vaccination reactions, viral infections (herpes, herpes zoster, chickenpox);
– skin manifestations of syphilis, skin tuberculosis;
– other bacterial and fungal skin infections.
In pediatrics it can be used from 2 years of age.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Not used to treat pregnant women in the first trimester.
Breastfeeding should be suspended during treatment with this drug.
Directions for use and doses
This drug is used by applying it in an even layer twice a day to the affected areas of the skin.
In mild cases, it is enough to apply the drug once a day.
If there are signs of improvement, it is necessary to reduce the amount of the applied drug.
Make sure that the drug does not get into your eyes! In case of contact with eyes, rinse with water.
The duration of treatment is determined individually by the attending physician, but not more than 10 days (for children over 2 years old - no more than 5 days).
Do not cover the affected area of skin with an occlusive dressing containing this drug.
Overdose
An overdose of corticosteroids can cause:
– inhibition of pituitary-adrenal function;
– secondary insufficiency of the adrenal glands;
– manifestation of symptoms of hypercortisolism, including Cushing's syndrome.
An overdose of salicylic acid can cause:
– nausea, vomiting;
– pallor of the skin;
– increased fatigue;
– hearing impairment.
Symptomatic treatment, increased diuresis, and gradual withdrawal of the drug are recommended.
Side effects
The most commonly observed side effects are:
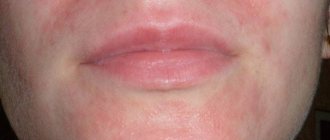
– rash, increased sensitivity, hyperpigmentation;
– skin irritation, erythema, itching;
– dry skin, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acne-like rash;
– hypopigmentation, acne, rosacea-like dermatitis, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis;
– skin maceration, skin atrophy (when wearing occlusive dressings);
– peeling of the skin, telangiectasia, prickly heat;
– stretch marks, protrusion of blood vessels on the face, with prolonged use of local corticosteroids on this area of the skin;
– insufficiency of the adrenal glands.
Overdose of the drug Betasalik
Symptoms: excessive or prolonged use of local corticosteroids can lead to inhibition of the function of the pituitary-adrenal system, which can cause the development of secondary adrenal insufficiency and the appearance of symptoms of hypercortisolism, including Cushing's disease. Excessive or prolonged use of topical medications containing salicylic acid may cause symptoms of salicylicism. Treatment: Appropriate symptomatic treatment is indicated. Acute symptoms of hypercortisolism are usually reversible. If necessary, correction of water and electrolyte disturbances is indicated. In case of chronic toxic effects, gradual withdrawal of GCS is recommended. Treatment of salicylicism is symptomatic. Measures are taken to more quickly remove salicylates from the body. Sodium bicarbonate is used orally to alkalize urine and increase diuresis.
Belosalik ointment: method of application and dosage:
The drug is intended for external use.
A small amount of ointment is evenly distributed over the surface of the skin, lightly rubbing. The frequency of use is 2 times a day; in mild cases, a single use is sufficient.
The duration of a continuous course of treatment is usually limited to 3-4 weeks. If a longer course of therapy is necessary, it is recommended to use the drug less frequently, for example, every other day. When treating chronic diseases, treatment should be continued for some time after the disappearance of all symptoms, under the supervision of a doctor, to avoid relapse of the disease.
Repeated courses of therapy are possible throughout the year.
Indications
According to the instructions for use, Betasalik ointment is used in the presence of the following diseases:
- A chronic disease, dermatosis, which mainly affects the skin.
- A chronic skin lesion of the allergic type, which occurs with exacerbations.
- Acute or chronic inflammatory disease of the skin surface, which is characterized by a variety of rashes, burning, irritation and a tendency to relapse).
- Chronic dermatosis, the characteristic and only element of which is a papule.
- A disease of the skin, manifested by focal redness and peeling.
- Dyshidrosis (skin disease that is localized mainly on the hands and feet).
- Ichthyosis (a genetically determined skin disease characterized by excessive keratinization with deformation).
- Seborrhea of the scalp.
- An inflammatory lesion of the skin surface that occurs with periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Adverse reactions
Application of Betasalik can provoke the following negative manifestations:
- Infectious lesion of the middle and deep parts of the hair follicle, leading to its purulent inflammation.
- Increased local or general appearance of dark and thick hair on any surface of the body.
- Acne (a disease in which the pores of the skin become clogged).
- Hypopigmentation (loss of natural skin color, appearance of light spots, or an unusually light color throughout the body).
- An inflammatory lesion of the skin that occurs at the site of direct contact with the allergen.
Side effects when using the drug with occlusive dressings provoke the following reactions:
- Maceration (physiological or pathological process of wet loosening, impregnation and swelling of the epidermis).
- Skin irritation that occurs as a result of increased sweating with a simultaneous decrease in sweat evaporation.
- Irreversible damage to the skin, which is characterized by a decrease in its volume, as well as qualitative deformation of its tissue, especially elastic fibers.
- Stretch marks are a peculiar lesion of the skin in the form of narrow wavy stripes of different widths, which range in color from white to purple.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
- Vasodilation.
Contraindications
Use is contraindicated for skin tuberculosis, skin manifestations of syphilis, chicken pox, viral skin infections, skin post-vaccination reactions. Do not use this drug on open wounds, trophic ulcers due to chronic venous insufficiency, rosacea, acne vulgaris, bacterial, viral and fungal skin diseases, perioral dermatitis, skin tumors (skin cancer, atheroma, nevus, melanoma, epithelioma, hemangioma, sarcoma, xanthoma).
The drug should not be used if there is increased individual sensitivity to its components.