Antibiotic therapy has changed the essence of the fight against dangerous infectious diseases. Previously, doctors did not have methods of influencing pathogenic pathogens, and all efforts were aimed at maintaining the general condition of the patient.
After the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming, it became possible to destroy microorganisms that previously provoked the development of epidemics that took the lives of thousands and millions of people. And cephalosporins in tablets play a very important role in this successful fight.
The group of cephalosporins are drugs that have a very important practical role in the inpatient and outpatient treatment of bacterial pathologies. Statistics show that this group of antibiotics is most often prescribed in domestic hospitals. This is due to the large list of pathologies for which it is used, low overall toxicity, and a wide spectrum of action.
Also, over decades of use, cephalosporins have received a good evidence base and good experience in prescription. New studies are regularly conducted that confirm the effectiveness of these medications.
Pharmacological features of the drug
Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. They have a common chemical structure, which determines their general pharmacological properties. Cephalosporins have a bactericidal effect.
The mechanism of action of the drugs is as follows: antibiotic compounds act on the components of the cell wall, and in this way disrupt their integrity.
As a result, there is a massive death of pathogenic pathogens.
The pharmacological characteristics of drugs determine the features of their use. Most cephalosporins are poorly absorbed from the digestive tract, so most are available in the form of ampoules for intravenous or intramuscular use. They also pass well through the blood-brain barrier, especially with inflammation of the meningeal membranes.
Cephalosporin antibiotics are distributed fairly evenly in the patient's body. The highest concentrations of drugs are observed in bile, urine, respiratory epithelium and digestive tract. The therapeutic concentration is maintained for 5-6 hours after taking the medication.
When administered orally, cephalosporin antibiotics pass through hepatic metabolism. These bacterial preparations are excreted from the body mainly unchanged by the kidneys. Therefore, if the function of this organ is impaired, the accumulation of antibiotics in the patient’s body is observed. The spectrum of action of cephalosporins is quite wide, especially in recent generations. Most drugs act on:
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- Neisseria;
- enterobacterial infection;
- Klebsiella;
- Moraxella;
- E. coli;
- shigella;
- salmonella.
5th generation drugs
Means that belong to the 5th generation contribute to the provision of a bactericidal effect, destroying the walls of pathogens. Active against microorganisms that demonstrate resistance to 3rd generation cephalosporins and drugs from the aminoglycoside group.
5th generation cephalosporins are presented on the pharmaceutical market in the form of drugs based on the following substances:
- Ceftobiprole medocaril is a medicine under the trade name Zinforo. Used in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, as well as complicated infections of the skin and soft tissues. Most often, patients complained of adverse reactions in the form of diarrhea, headache, nausea, and itching. Adverse reactions are mild in nature; their development should be reported to your doctor. Particular care is required in the treatment of patients with a history of seizures;
- Ceftobiprole is the trade name of Zeftera. Available in powder form for the preparation of solution for infusion. Indications for use are complicated infections of the skin and appendages, as well as infection of the diabetic foot without concomitant osteomyelitis. Before use, the powder is dissolved in glucose solution, water for injection or saline. The product should not be used in the treatment of patients under 18 years of age.
5th generation agents are active against Staphylococcus aureus, demonstrating a broader spectrum of pharmacological activity than previous generations of cephalosporins.
Classification of cephalosporins
Currently, there are five generations of cephalosporins. They differ in some characteristics. The first representatives of this group of medications have a more effective effect on gram-positive bacteria.
Also, the latest cephalosporin drugs act on a large number of microbes and penetrate the blood-brain barrier better.
An important problem is the development of antibiotic resistance to the first generations, which have already been used for many decades. This situation leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of the drugs used.
Cephalosporins are divided into the following generations:
- first - cephalexin, cefazolin;
- second - cefuroxime, cefuroxime;
- third - ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefotaxime;
- fourth - cefepime, cefpirome;
- fifth - ceftobiprole, ceftaroline, ceftolozane.
Story
Zalman Vaksman - one of the fathers of antibiotics Antibiotics are substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin that inhibit the growth of living cells. The term was coined by Z. Waksman, an American microbiologist who received the Nobel Prize in 1952 for the discovery of streptomycin. The term “antibios” itself was coined by L. Pasteur and carried a certain meaning - “life against life.” The first antibiotic was penicillin , isolated from the fungus Penicillum notatum. Observations of the relationship between the culture of streptococcus and fungus were begun by Fleming in a London hospital in the 20s of the last century. However, his speech at the Second International Congress of Microbiologists did not make an impression on the public (perhaps due to the fact that he was not a very skilled speaker). The further history of the study of penicillin is connected with the names of the members of the “Oxford Group” - Howard Florey and Ernst Chain. Chain was involved in isolating penicillin, and Flory was testing it on animals. The first trial of penicillin took place in 1941 on a London policeman dying of sepsis. Scientists managed to improve his condition, but the supply of the drug was too small, and the patient died.
The same Petri dish with a culture of Staphylococcus sp., in which Alexander Fleming, upon returning from vacation, discovered the mold Penicillium notatum instead of bacterial colonies. 1928 In 1945, Fleming, Chain and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize. Penicillin, optimally combining high antibacterial activity and safety for humans, is still used successfully. gramicidin was isolated in 1939 , streptomycin in chlortetracycline in 1945 chloramphenicol in 1947 , and by 1950 more than 100 antibiotics had been described. Over time, it became clear that existing antibiotics were not active enough against microorganisms: this was the reason for the start of chemical research and the creation of semi-synthetic antibiotics. Since then, various groups of antibacterial agents have been discovered. Thus, in Russia today about 30 groups of antibiotics are used. Among them, there are drugs with antibacterial, antiparasitic, antifungal and antitumor effects. The postulates of antibiotic therapy were also formed. The basic rules of antibacterial therapy can be formulated as follows:
1. Identify the causative agent of the disease;
2. Determine the drugs to which the pathogen is most sensitive;
3. For an unknown pathogen, use either a drug with a broad spectrum of action, or a combination of two drugs, the total spectrum of which includes probable pathogens;
4. Treatment should be started as early as possible;
5. Doses of drugs must be sufficient to provide concentrations in cells and tissues that prevent reproduction ( bacteriostatic ) or destroy bacteria ( bactericidal );
6. The duration of treatment must be sufficient; a decrease in body temperature and weakening of other symptoms are not grounds for stopping treatment;
7. The choice of rational routes of drug administration plays a significant role, given that some of them are not completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier , etc.;
8. The combined use of antibacterial agents must be justified, since if the combination is incorrect, the total activity may be weakened and their toxic effects may be cumulative.
Let us consider the antibacterial drugs themselves from the point of view of the nature, spectrum and mechanism of their action.
Antibiotics act directly on the etiological factor, and by the nature of their action they are bacteriostatic and bactericidal:
- Bacteriostatic drugs inhibit the growth and reproduction of microorganisms. They do not cause their death. It is assumed that the immune defense mechanisms are able to independently cope with the destruction and elimination of microbes. Bacteriostatic drugs include macrolides, clindamycin, streptogramins, chloramphenicol, tetracyclines;
- Bactericidal drugs lead to the death of microorganisms, and the body only needs to ensure their elimination. These include beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, glycopeptides and others (trimethoprim, metronidazole, rifampicin, etc.).
How are microorganisms neutralized? There are several mechanisms of action of antibiotics:
- Violation of cell wall synthesis by inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesis (penicillin, cephalosporin, monobactams), the formation of dimers and their transfer to growing peptidoglycan chains (vancomycin), chitin synthesis (nikkomycin). Antibiotics acting according to this mechanism have a bactericidal nature of action; they do not act on resting cells and L-forms (devoid of a cell wall) of bacteria;
- Impaired functioning of membranes due to disruption of their integrity, formation of ion channels, binding of ions into lipid-soluble complexes and disruption of their transport (nystatin, gramicidins, polymyxins);
- Suppression of nucleic acid synthesis : DNA (streptomycin, griseofulvin, rifampicin, rifamycin, vancomycin) and RNA (bruneomycin, rubomycin, olivomycin);
- Violation of protein synthesis by the cell (tetracyclines, macrolides);
- Violation of the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines (azaserine, sarcomycin);
- Inhibition of the respiratory chain (antimycins, oligomycins).
For ease of use, it is customary to classify antibiotics according to their spectrum of antimicrobial action:
- Acting predominantly on gram-positive microflora: biosynthetic penicillins, oxacillin, first generation macrolides, lincomycin, rifampicin, rifamycin, ristomycin, vancomycin;
- Acting predominantly on gram-negative microflora: polymyxin;
- Broad spectrum of action: semisynthetic penicillins (except oxacillin), cephalosporins, second generation macrolides, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides;
- Antifungal antibiotics: nystatin, levorin, amphotericin B, mycoheptin, griseofulvin, etc.;
- Antitumor antibiotics: olivomycin, rubomycin, etc.
The value of antibiotics as medicines is undoubtedly very high. The discovery of these drugs has made it possible to get rid of many previously fatal infections. But microorganisms quickly adapt to changing environmental conditions, including acquiring resistance to antibiotics.
There are several “basic” mechanisms of resistance:
1.
Changing
the target of an action ;
2. Enzymatic inactivation of an antimicrobial drug;
3. Active removal of the antimicrobial drug from the microbial cell ( efflux );
4. Violation of the permeability of the microbial cell to the antimicrobial drug;
5. Formation of metabolic “shunts”.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria is undoubtedly dangerous both for the person from whom they are isolated and for many other people. Increased resistance leads to worsening of the course of infectious diseases, increased mortality, and increased healthcare costs.
Let's look at the most popular classes of antibiotics:
Rules for the use of antibacterial drugs
Antibiotics are potent drugs that have a systemic effect on the body. Therefore, antibacterial drugs should not be used independently without consulting a doctor. It is very difficult for a patient to choose the optimal treatment option for the disease for himself and his relatives. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics also more often leads to the development of side effects and a decrease in the effect of the drug.
During therapy, you must follow a few simple rules of administration. The course of treatment usually lasts at least 3 days.
It is not recommended for the patient to independently cancel or refuse therapy after the first signs of improvement in general condition.
This very often leads to recurrence of the pathology.
Antibiotics must be used at the same time of day. This allows you to maintain a good concentration of the drug in the peripheral blood, which gives an optimal therapeutic effect.
If you miss a dose of an antibiotic, you should not panic, but take the missed dose of cephalosporin as quickly as possible. In the future, therapy should be continued as usual.
When using antibiotics, it is important to monitor the development of side effects, which should be reported to your doctor as soon as possible. Only he is able to competently assess their severity and make a decision on suspending or continuing cephalosporin therapy.
1st generation drugs
The use of these drugs helps to provide a narrow spectrum of antibacterial action.
Cefazolin is one of the most popular drugs that helps to act against streptococci, staphylococci, and gonococci. After parenteral administration it penetrates into the affected area. A stable concentration of the active substance is achieved if the medicine is administered three times over 24 hours.
Indications for use of the drug are: the effects of streptococci, staphylococci on soft tissues, joints, bones, skin.
It should be taken into account: Cefazolin was previously widely used to treat a large number of infectious pathologies. However, after more modern 3-4 generation medications appeared, Cefazolin is no longer used in the treatment of intra-abdominal infections.
How to correctly prescribe cephalosporins in tablets
Before prescribing cephalosporins, the doctor must make sure of the bacterial etiology of the patient's disease. This is very important, since antibacterial drugs do not act on viral or fungal flora, and in such cases they can even harm the patient. To this end, the doctor must conduct a complete examination of the patient, which usually begins with a complete medical history. The patient or his relatives (if his condition is serious) must talk about how, when and after what the first symptoms of the pathology appeared.
Information is also usually collected about the presence of a similar disease in close relatives and friends, about possible contact with patients, as well as about concomitant disorders of other organs and systems. The next step is a thorough examination of the affected areas, skin or mucous membranes, palpation, percussion and auscultation of the heart, lungs and abdomen. Do not be surprised by questions about urination frequency, changes in stool and appetite.
After this, a series of laboratory and instrumental studies are usually carried out. A number of changes in them with a high degree of probability may indicate the bacterial etiology of the pathological process.
First of all, we are talking about changes in the general blood test - leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in the number of neutrophils (as well as their immature forms) and an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
With an infection in the genitourinary system, leukocytes and various bacteria are often found in a general urine test.
The most accurate research method is considered to be bacteriological. It allows not only to accurately isolate the causative agent of the pathology, but also to study its sensitivity to certain antibiotics. This makes this test the reference test for all diseases of infectious origin.
In this case, blood, a smear from the back of the throat, urine, sputum, biopsy or any other biological media in which a microorganism may be located can be used as research material.
The most significant drawback of the bacteriological research method is the long time it takes to perform it in conditions where the doctor needs to make a decision on the choice of treatment tactics immediately. Therefore, this test has the greatest practical value in situations where the initial treatment was not effective enough. It allows you to change the drug used in treatment.
Modern international and national recommendations play a very important role in determining the indications for prescribing cephalosporins, which clearly regulate the situations in which they need to be used.
The effectiveness of prescribed antibiotic therapy is assessed 48-72 hours after the first dose of the drug.
For this purpose, laboratory tests are repeated and the dynamics of the patient’s clinical symptoms are also looked at. If it is positive, the doctor continues treatment with the original drug. If there is no improvement, there is a need to switch to second-line or reserve antibacterial agents.
The role of cephalosporins in tablets in treatment
Cephalosporins in clinical practice are used mainly in injection form. However, this significantly reduces their ability to prescribe in outpatient practice, since not all patients can correctly dilute and administer the antibacterial drug.
This also determines the role of tablet forms of cephalosporins. They are often used as initial antibiotic therapy for pathologies that do not require hospitalization, if the patient’s condition is satisfactory and there are no decompensated diseases of other organs.
They also play an important role in step therapy. It consists of two stages. In the first stage, cephalosporin is used in injection form in order to eliminate the pathological process as quickly and effectively as possible. To consolidate the result of treatment and complete the course of therapy, the same drug is prescribed to the patient in tablet form for several days after discharge from the hospital.
This strategy allows you to reduce the number of days the patient spends in the hospital.
Today in pharmacies it is possible to find only drugs of the first three generations of cephalosporins in tablets or suspensions:
- first - cephalexin;
- the second - cefuroxime;
- third - cefixime.
Drug interactions
When using 3rd generation cephalosporins while drinking alcohol, there is a high risk of developing a disulfiram-like effect. This deviation is similar to the state of the body during ethyl alcohol poisoning. Against this background, the patient develops an aversion to alcohol. The effect persists for several days after discontinuation of cephalosporins. The danger is the possible development of hypoprothrombinemia - an increased tendency to bleed. Interaction of cephalosporins with drugs:
- simultaneous use of antacids reduces the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy;
- combination with loop diuretics is not allowed due to the risk of nephrotoxic effect;
- combination with thrombolytics, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents is also not recommended due to the increased likelihood of intestinal bleeding.
Indications for the use of cephalosporins in tablets
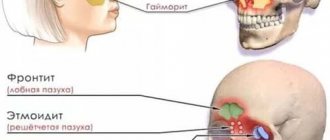
Cephalosporins are used to treat bacterial pathologies in systems where they accumulate during their metabolism and create a therapeutic concentration sufficient to kill microbes. First of all, we are talking about diseases of the respiratory, genitourinary systems and ENT organs. They are also used for inflammation of the biliary tract and some pathologies of the digestive system.
According to the instructions for use, there is a list of pathologies for which the prescription of cephalosporins is justified. They are used for:
- pneumonia;
- bronchitis;
- tracheitis;
- laryngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- sinusitis;
- otitis media;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- prostatitis;
- bacterial inflammation of the uterus and its appendages;
- prevention of complications during surgical procedures or interventions.
How to take cephalosporins tablets
The duration of treatment with cephalosporins is at least 5 days. Usually the tablets are taken 2 times a day to ensure the required concentration of the drug. The tablet should be taken with a sufficient amount of water.
It is not recommended to use other drinks (soda, dairy products, tea, coffee) for this purpose, since they can change the pharmacological properties of the drug.
Drinking alcohol during the course of treatment is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to the development of acute hepatosis and impaired liver function.
- Groups of antibiotics - their descriptions and classification;
- See here - antibiotics for pyelonephritis;
- Antibiotics without penicillin - brief characteristics: https://med-antibiotiks.com/sovety/antibiotiki-ne-soderzhashhie-penicillina-v-svoem-sostave/.
Carbapenems
General structure of carbapenems They belong to β-lactam antibiotics; compared to penicillins and cephalosporins, they are more resistant to the action of β-lactamases. These include impineme and meropenem . The mechanism of action is similar to that of penicillins and cephalosporins. They have a wider spectrum of activity, acting on many Gr+ and Gr– bacteria. Staphylococci, streptococci, including pneumococci, gonococci, meningococci, bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family, spore-forming and non-spore-forming anaerobes are sensitive to them. Indications: 1. Severe infections of the lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, intra-abdominal, pelvic organs, skin and soft tissues, sepsis caused by multiresistant and mixed microflora; 2. Endocarditis, infections of bones and joints - only impinema; 3. Meningitis - only meropenem. Frequent side effects: allergic, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, from the central nervous system - dizziness, tremor, convulsions. Allergic reactions are cross-reactions with all carbapenems, and in 50% of patients also with penicillins. Cannot be used with other β-lactam antibiotics due to their antagonism.
Side effects when using cephalosporins
Cephalosporins are classic drugs of the beta-lactam group, so they are characterized by the presence of fairly frequent allergic reactions of varying severity. The development of urticaria, dermatoses, angioedema and even anaphylactic shock in patients has been described.
Allergy to all beta-lactams is cross-linked, therefore, if there are hypersensitivity reactions to any of the drugs from a number of penicillins, carbapenems, monobactams, prescribing cephalosporins is strictly contraindicated.
Another dangerous condition is pseudomembranous colitis, which sometimes develops due to uncontrolled proliferation of clostridial infection. In most cases, it has a mild course, manifests itself only in stool disorders, and is not even diagnosed. But in some cases, the pathological process follows an unfavorable scenario and is complicated by perforations, intestinal bleeding and sepsis.
The most common side effect of cephalosporins is transient digestive disorders.
They are manifested by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain or flatulence. These symptoms disappear quickly after discontinuation of the drug.
Sometimes there are increases in liver enzymes or toxic effects on the renal tubules. Additionally, the addition of superinfection or fungal pathology (mainly candidiasis) against the background of antibiotic therapy is described. There have been isolated cases of negative effects on the central nervous system, which were manifested by epileptic seizures, convulsions and emotional lability.
Top 10 drugs from the pharmacy
4th generation cephalosporins (the list of drugs allows you to choose the most suitable drug for each patient) can be found on pharmacy shelves in large quantities. There are several medications that are used most often.
Cefepime
The first medicine of the 4th generation of cephalosporins. It contains the active component of the same name and is available in the form of a white lyophilisate for the preparation of a solution, packaged in transparent glass bottles. The drug has pronounced antimicrobial properties; 1 bottle costs approximately 100 rubles. You can purchase it with a prescription.
Cefepime - 4th generation cephalosporin
The drug is administered intravenously and intramuscularly after preliminary dissolution in 0.9% physiological solution in an amount of 5 ml (for intramuscular administration) or 10-20 ml (for intravenous administration). The daily dosage for the patient is selected individually and is no more than 2 g per day. Treatment lasts up to 10 days.
The drug is contraindicated in case of intolerance to its components, as well as under the age of 2 months. During the treatment period, it is better to stop breastfeeding. The most common side effects when using the medicine are skin rash, itching, and lacrimation. Some patients experience the development of dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain.
In case of an overdose of the drug, there is a worsening of all adverse reactions, as well as the development of Quincke's edema, accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat and difficulty breathing.
Maxipim
The drug is in the form of a lyophilisate for the preparation of a solution that contains cefepime as an active component. The drug has pronounced antimicrobial properties and is prescribed for acute advanced pathologies of the respiratory system, meningitis in children and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
The dosage of the medication is selected individually. Adults are prescribed 1 to 2 g of the drug per day for 10-12 days. Children whose body weight does not exceed 40 kg are prescribed a dose based on weight. There are 50 mg of medication per 1 kg of body weight. This means that 1 bottle with a dose of 1 g is per 20 kg.
The duration of the course for a child is also no more than 12 days. The drug is administered intramuscularly after preliminary dissolution with 5 ml of Novocaine or saline solution.
It is allowed to administer the drug intravenously after dissolving in 20 ml of sodium chloride. But the introduction should be slow. It is worth remembering that the daily dose is usually divided into 2 times, which facilitates the absorption of the medication. The drug is not prescribed if you are allergic to its components, or if the child is under 2 months of age.
If adverse reactions develop, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Attacks of vomiting.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- Rash and itching of the skin.
- Loose stools.
- Weakness.
With an overdose of the drug, all symptoms are aggravated. It is possible to develop acute urticaria, accompanied by allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, unbearable itching and other manifestations. The price of a bottle of the product is approximately 400 rubles. Prescription from pharmacies.
Maxicef
4th generation cephalosporins are available in the form of a lyophilisate for the preparation of a solution. The list of the most popular drugs includes Maxicef, which is also available in powder form and contains cefepime as an active ingredient.
Prescribed for various inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, lungs, and membranes of the brain, when other remedies do not bring the expected result.
The product helps stop the proliferation of microorganisms, destroy them and prevent complications due to the ability to penetrate microbial membranes. The drug is administered intramuscularly and intravenously. In the first case, it is allowed to dissolve in 5 ml of sodium chloride or Lidocaine, Novocaine. The second requires the addition of 20 ml of sodium chloride and a very slow introduction.
The dosage is selected individually, taking into account the degree of neglect of the condition. Adults are prescribed 1 to 2 g of the drug, children – 50 mg per 1 kg of weight. The daily dose is divided into 2 administrations. The course of therapy lasts up to 12 days.
The drug is contraindicated in cases of intolerance to its components, as well as in children under 2 months of age, and in patients with severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver. Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain and skin rash.
An overdose provokes a deterioration of the condition, the development of respiratory failure and signs of encephalopathy. You can buy the medicine at the pharmacy with a prescription for 350-500 rubles.
Cefomax
A product based on cefepime, produced in powder form for the preparation of a solution. At the pharmacy the medicine costs about 150 rubles. per bottle, can be purchased with a doctor's prescription. The medication has pronounced anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, helps destroy many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria due to the rapid destruction of their shell.
The drug is prescribed to adults and children intravenously and intramuscularly for the following pathologies:
- Infected skin diseases.
- Blood pathologies of infectious origin.
- Inflammatory joint diseases.
- Advanced damage to the kidneys and lungs.
Dosage for adults is from 500 mg to 2 g, divided into 2 times. Children from 2 months are prescribed the medicine in an amount of 50 mg per 1 kg of weight. The duration of treatment for children and adults should not exceed 10 days. The drug is administered intramuscularly to adult patients and children over 12 years of age, after dissolving the powder in 4-5 ml of lidocaine or sodium chloride 0.9%.
It is administered intravenously to all patients, dissolving the powder in 20 ml of sodium chloride. Be sure to administer the medicine slowly.
The drug is contraindicated in end-stage renal and liver failure, in patients under 2 months of age. During pregnancy and lactation, the drug is prescribed according to strict indications.
Side effects include weakness, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting. When an excessive dose is administered, an overdose develops, accompanied by convulsions, signs of encephalopathy and acute allergic manifestations.
Chain
4th generation cephalosporins (the list of drugs increases every year) includes such a medicine as Tsepim. It is available for purchase by prescription and costs approximately 200-300 rubles. The product is available in powder form for preparing a solution. The solution is administered intramuscularly and intravenously slowly.
The drug is prescribed for advanced forms of pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and sepsis. It is indicated for infectious lesions of the skin, joints, and lungs. Prescribed for adults and children from 2 months.
The daily intake for a child is calculated individually and is 50 mg per 1 kg of weight. Adults are prescribed from 1 to 4 g of the drug, depending on the severity of the condition.
The daily dose is always divided into 2 or 3 administrations. Before use, add 0.9% sodium chloride to the bottle with powder.
The duration of antibiotic therapy is 5-10 days. The drug is not prescribed for allergies to its composition, severe liver damage, or for patients under 2 months of age.
Negative reactions occur rarely and are accompanied by dyspeptic disorders and headaches. With an overdose, they get worse, convulsions and impaired consciousness occur.
Ladef
A product based on cefepime, produced in powder form in bottles. It has pronounced properties, helps fight advanced forms of pneumonia, sepsis, and pyelonephritis.
Prescribed for infectious lesions of the skin and long-term non-healing wounds. Helps quickly destroy pathogens. Prevents the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby tissues and organs.
For patients from 2 months of age, the dosage is selected at the rate of 50 mg of the drug per 1 kg of weight. Adults are prescribed from 1 to 3 g. The daily norm is divided into 2-3 times. The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously for 10 days.
The product is not used during pregnancy and lactation, under the age of 2 months. It is not prescribed for allergies to components or for severe pathologies of the digestive tract.
When used, negative reactions are possible in the form of weakness, dizziness, loss of appetite. If an increased dose is administered, the symptoms worsen, and the risk of death as a result of suffocation due to Quincke's edema increases.
The drug is sold by prescription, its price starts from 200 rubles. per bottle.
Movisar
Powder for preparing a solution based on cefipime. Available at pharmacies, but sold with a doctor's prescription. The price is approximately 300-500 rubles.
The drug is prescribed for many pathological conditions:
- Peritonitis.
- Biliary tract infections.
- Cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Infectious skin lesions.
- Advanced form of bronchitis and pneumonia.
The dosage for adults is 1 g 2 times a day. For children, the dose is determined taking into account their weight; 50 g of medication per 1 kg is administered 2-3 times during the day at equal intervals. The duration of the therapeutic course is 7-10 days.
The drug is injected only into a muscle or vein after preliminary addition of sodium chloride. The drug is not prescribed for end-stage renal and liver failure, during lactation and pregnancy. The drug is also contraindicated for children under 2 months of age.
If the instructions are violated, the development of adverse reactions in the form of vomiting, headache, weakness and sleep disturbances is noted. In case of an overdose, signs of urticaria appear, as well as convulsions and impaired consciousness.
Efipim
4th generation cephalosporins (the list of drugs today allows you to choose an option with a lower cost) are always used according to a strict regimen, which ensures the effectiveness of therapy. For example, the drug Efipim, available in the form of lyophilisate, has antimicrobial, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects due to proper use.
The product costs approximately 400 rubles. per bottle, sold by prescription and prescribed for pneumonia, neutropenic fever, urinary tract infections, meningitis in children and adults. Do not use the medicine if you are allergic to its components.
The daily dosage for a child is determined as 50 mg per 1 kg of weight, divided into 2-3 times and administered during the day. Adults are prescribed from 1 to 4 g of the drug, depending on the degree of neglect of the condition. Treatment lasts up to 10 days. Before administration, the product must be diluted with physiological solution in the required quantity.
Side effects when using the medication are rare; they usually manifest themselves in the form of rashes and itchy skin. With an overdose, the itching intensifies and the rash spreads over large areas.
Cefpir
One of the few 4th generation antibiotics, which contains not cefipime as an active component, but the substance cefpirome, is available in powder form. It has pronounced properties that help cope with even advanced inflammatory pathologies of tissues and internal organs.
Prescribed for infections of the skin, biliary and urinary tract, and digestive tract. Not used in case of allergy to the active component, for the treatment of pregnant women. Nursing women and small children.
As a rule, the medicine is prescribed to adults in a dosage of 1 g 2 times a day. The drug is administered intravenously, sometimes intramuscularly. Before administration, be sure to add saline solution in the required amount. The course of therapy lasts from 8 to 12 days. The drug can provoke negative reactions such as headache, nausea, and discomfort in the abdominal area. Often the drug leads to flatulence and diarrhea.
In case of overdose, all symptoms worsen. The drug is available in pharmacies with a prescription and costs approximately 200-300 rubles.
Cefanorm
Another remedy based on cefpirome. It has pronounced properties, destroys gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms that provoke inflammation of soft tissues and internal organs.
The product is available in the form of a lyophilisate to obtain a solution and is prescribed for the following conditions:
- Cystitis, pyelitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis.
- Sepsis.
- Pleural empyema, lung abscess.
- Pneumonia and advanced form of bronchitis.
As a rule, the medicine is prescribed to adults intravenously after preliminary dilution of the powder in saline solution. 1 g is administered 2 times per day with equal intervals between manipulations.
The drug is not prescribed to small children, pregnant and lactating women, as well as patients who suffer from hypersensitivity to the components of the composition. Adverse reactions to the drug manifest themselves in the form of weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and lack of appetite.
With prolonged administration of an increased dose of medication, convulsions, fainting, and a decrease in blood pressure may occur. The drug is expensive, the price is approximately 1000-1200 rubles. You can buy it at a pharmacy with a doctor's prescription.
4th generation cephalosporins are effective and relatively safe medications that allow you to fight various advanced diseases. The list of these drugs is quite long, which allows everyone to choose a medicine taking into account price and other features.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Contraindications for use
The main contraindication to taking oral cephalosporins is the presence of an allergy to any of the beta-lactam antibiotics. Before the first use of the drug, a test for the presence of hypersensitivity must be carried out.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing these antibacterial drugs in patients with impaired renal function, since this condition can lead to the accumulation of the antibiotic in the patient's body. In such cases, the doctor must individually calculate the dose based on the glomerular filtration rate.
Cephalosporins are classified as low-toxic drugs that are approved for use in young children, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
Oral use of these drugs can lead to the development of exacerbations of chronic inflammatory processes of the digestive system (colitis, enteritis). Therefore, for these pathologies, it is recommended to give preference to parenteral forms of antibiotics.
2nd generation drugs
2nd generation drugs are characterized by increased activity against gram-negative pathogens. 2nd generation cephalosporins for parenteral administration based on cefuroxime (Kimacef, Zinacef) are active against:
- gram-negative pathogens, Proteus, Klebsiella;
- infections caused by streptococci and staphylococci.
Cefuroxime, a substance from the second group of cephalosporins, is not active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Morganella, Providence and most anaerobic microorganisms.
After parenteral administration, it penetrates into most organs and tissues, including the blood-brain barrier. This makes it possible to use the drug in the treatment of inflammatory pathologies of the lining of the brain.
Indications for the use of this group of funds are:
- exacerbation of sinusitis and otitis media;
- chronic form of bronchitis in the acute phase, development of community-acquired pneumonia;
- treatment of postoperative conditions;
- infection of the skin, joints, bones.
The dosage for children and adults is selected individually, depending on the indications for use.
Drugs of this group are not recommended for use in the treatment of meningitis due to the greater effectiveness of drugs that are part of the third generation.
2nd generation drugs for internal use
Medicines for internal use include:
- tablets and granules for preparing Zinnat suspension;
- Ceklor suspension - this drug can be taken by a child; the suspension has a pleasant taste. It is not recommended to use Ceclor during the treatment of exacerbation of otitis media. The drug is also available in the form of tablets, capsules and dry syrup.
Oral cephalosporins can be used regardless of food intake; the active component is excreted by the kidneys.