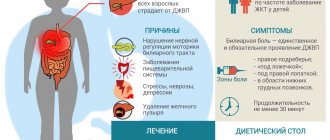
Biliary dyskinesia is a condition that manifests itself as pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen or biliary colic. In this case, there is no deformation of the bile ducts, biliary sludge (“sand” in the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis. That is, it is virtually impossible to detect any anomalies in the gallbladder and biliary tract.
In modern medical literature, the term “biliary dyskinesia” is used less and less. It was replaced by the concept of “functional disorders of the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi.” However, in everyday practice such a disease is still described.
Biliary dyskinesia is a fairly common disorder, occurring on average in 20% of women and 8% of men1. Over the age of 60, this condition occurs on average in 25% of the population.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease can vary depending on what form the pathology has: hyperkinetic or hypokinetic.
The following symptoms are characteristic of hyperkinetic pathology:
- sharp pain in the right side when walking and exercising;
- burning sensation in the stomach after stress and eating sweets;
- loose stools;
- nausea, vomiting with bile;
- white coating on the surface of the tongue;
- apathy, fatigue, symptoms of chronic fatigue;
- impaired appetite or its complete absence;
- headache.
Biliary colic may appear, accompanied by rapid heartbeat, panic attacks, numbness of the arms and legs, as well as pain under the right rib.
Hypokinetic pathology is characterized by symptoms:
- weight loss;
- constipation is chronic;
- appetite is impaired;
- the intensity of the gallbladder decreases, heaviness appears in the right side.
In the advanced stage, bile retention in the bile ducts is possible. It is accompanied by itching of the skin, staining them and the whites of the eyes yellow.
Signs typical of both types of disease:
- increased irritability;
- increased sweating;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowish coating on the tongue;
- bloating;
- bad breath;
- decreased sexual desire in representatives of the stronger sex;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- loss of appetite.
Diagnosis
A variety of methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Ultrasound helps determine the degree of emptying of the gallbladder, its shape and congenital developmental anomalies.
- General blood analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- X-ray studies (cholecystography; infusion cholecystography; cholangiography).
Doctors also prescribe laboratory tests:
- duodenal intubation;
- study of bile composition;
- examination of bile for the presence of parasites;
- biochemical study of bile portions “B” and “C”;
Causes
More often, JVP is diagnosed in young women and children aged three years and older.
Lingering in the bladder and ducts, the bile begins to thicken. This leads to the formation of stones and disruption of bile characteristics.
Due to problems with bile secretion, the breakdown of fats worsens, metabolism is disrupted, difficulties with digestion appear, etc.
In order to prevent the disease from developing and starting to progress, you need to know the prerequisites that contribute to its development:
- irregular and incorrect meals;
- excessive consumption of unhealthy food;
- frequent stressful situations;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- various allergies;
- endocrine diseases;
- intestinal infections;
- dysbacteriosis;
- menopause;
- the existence of parasites in the body;
- pancreatitis and any other abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract;
- VSD symptoms;
- heredity;
- various respiratory tract infections.
Conducted research in this area has shown that, for the most part, directly stressful situations lead to JVP. This is explained by the fact that a nervous disorder causes compression of the bile ducts and bladder.
A large amount of bile enters the duodenum and pancreas, and pancreatic fluid is blocked.
In the future, this liquid can corrode the pancreas and cause the formation of pancreatitis and diabetes. The progression of the disease to dermatitis, cholecystitis, and cholelithiasis is not excluded.
Mechanism of bile formation
The secretion of bile from the gallbladder is regulated by the following neurohumoral factors:
- The visceral nervous system (ANS) regulates the functionality of many organs. When the vagus nerve is activated, the gallbladder contracts and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes. When the functionality of the ANS is impaired, this process is disrupted.
- Gut hormones are produced by the digestive organs during meals. Cholecystokinin provokes contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi.
- Neuropeptides are a type of protein molecules that are produced in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system and have the properties of hormones. They prevent contraction of the gallbladder.
These factors interact with each other and provoke contraction of the gallbladder muscles during eating and an increase in pressure in it. As a result, the Lütkens sphincter relaxes, and the liver secretion enters the bladder duct. Then it enters the common bile duct, and then through the sphincter of Oddi into the duodenum. When a disease occurs, this mechanism is disrupted.
Under the influence of bile, pepsin in the duodenum loses its properties. In addition, liver secretion provokes the breakdown and absorption of fats, improves jejunal motility, increases appetite, and activates the production of mucus and intestinal hormones.
Types of biliary dyskinesia
The main signs of biliary tract activity are motor role and muscle activity. Based on the nature of the disorder, there are 4 types of disease:
- Hypotonic – reduced sphincter activity;
- Hypertensive – increased activity;
- Hypokinetic – slow decrease in bile;
- Hyperkinetic – rapid decrease in bile.
In medical practice, a double classification is used, but for patients it is enough to know the last two types.
Dyskinesia in children
The disease can occur in children due to improper formation of the body structure. These include overlap of the gallbladder or the discovery of a wall in it. In addition, doubled or abnormal placement of the bile ducts occurs.
In adolescents, the catalyst for the onset of the disease can be excessive emotional stress. These include workload at school, family scandals, moving to another city and subsequent new acquaintances at school.
Other causes of dyskinesia in children include:
- trauma at birth;
- previous hepatitis A (Botkin's disease), salmonellosis;
- allergies of various etiologies;
- neuroses;
- VSD;
- sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis;
- diathesis in neuro-arthritic form.
The development of such a disease in children is quite dangerous, since it threatens to impair the absorption of the required number of substances beneficial to the body. Their intake is especially important for a growing body.
Parents should monitor their child's behavior. If he develops irritability, becomes withdrawn, gets tired faster than usual, or cries for no apparent reason, then it would be a good idea to visit a pediatric gastroenterologist to rule out dyskinesia.
Even if after the examination it turns out that there is no disease, you should not relax. With such psychological data, the child is at risk; this moment needs to be controlled in order to avoid the development of pathology.
Particular attention should be paid to the child’s daily routine and diet.
Additional symptoms that may indicate the development of the disease:
- itchy skin that appears for an unknown reason;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- the occurrence of painful sensations in the right hypochondrium after eating fatty and fried foods.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment, which should be used in combination with other techniques, also has a good effect. In particular, diadynometry is used, which implies a therapeutic effect on the area of the right hypochondrium with electric current of various frequencies. Electrophoresis is also used, which involves the effect of a direct electric current on the body and drugs administered with its help into the liver area.
Acupuncture or acupuncture is a treatment method in which the body is affected by inserting special needles into specific points on the body. Massage, especially acupressure, has a good therapeutic effect. That is, by influencing certain places on the body, the gallbladder is affected. Many experts recommend hirudotherapy, that is, treatment with leeches affecting biologically active points - projections of the nerve endings of the corresponding organs.
Drug treatment
Prescribed in courses, it is aimed at preventing the localization of pain. Also helps for preventive purposes.
The doctor will tell you how to treat biliary dyskinesia based on the type of dyskinesia.
General Tips
One of the main reasons for the development of the disease is disorders in the nervous system. Therefore, the first stage of getting rid of the disease should begin with restoring the psychological background. Only after this can the main treatment of biliary tract activity problems begin.
Traditional therapy
Drug therapy for biliary dyskinesia is often supplemented with folk remedies.
In the case of treating a disease in children, traditional medicine may become the only method.
Based on the form of the disease, various herbs are used.
For hypertonic form, decoctions are made from the following plants:
- chamomile;
- motherwort;
- dill;
- mint;
- valerian;
- licorice.
For the hypotonic form, the following are used:
- nettle;
- chamomile;
- rose hip;
- St. John's wort;
- immortelle;
- oregano
Mineral waters have a good effect: Essentuki at numbers 17, 4 and 20, Narzan.
Auxiliary methods for treating the bile ducts include:
- Physiotherapy. Microwave methods, dynamic currents, and electrophoresis are used.
- Acupuncture.
- Acupressure massage.
- Use of leeches in therapy.
- Rest in gastroenterological sanatoriums. Mineral waters are used in treatment.
What examination do you need to undergo?
The basis of primary diagnosis in cases of suspected hypokinetic type VHD is laboratory testing of blood and urine. Laboratory signs of impaired bile formation and excretion will be increased bilirubin, liver enzymes, bile acids and cholesterol. Indirect signs are also an increase in the concentration of copper and urobilinogen, a product of bilirubin reduction under the influence of intestinal bacteria. Simultaneously with a biochemical blood test, patients are prescribed a lipidogram - a blood test for the content of lipoproteins of various densities and cholesterol.
Normal blood count values
Among the instrumental diagnostic methods for suspected GIVP, as well as for determining the motor function of the gallbladder and ducts, the following are used:
- cholecystography (can be performed using oral or intravenous medications);
- radiography;
- duodenal intubation (used for diagnostic and treatment purposes);
- radioisotope study of the liver, which allows assessing the functioning of the biliary tract;
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder, liver and bile ducts.
Duodenal sounding
If, based on the results of a study of motor function, a hypokinetic type of dyskinesia is determined in a patient, he will be prescribed appropriate treatment: diet therapy, correction of vegetative status and drug restoration of biliary function.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug treatment for biliary dyskinesia are three groups of drugs: cholekinetics, choleretics and cholespasmolytics. To choose the right medicine, you need to understand what these drugs are and what they are needed for.
Discuss taking medications with your doctor
Table 2. Drugs for the treatment of ADHD
| Pharmacological group | How do they work? | Drugs |
| Cholespasmolytics | They reduce the tone of the gallbladder and facilitate the excretion of bile into the small intestine. |
|
| Cholekinetics | Stimulate contraction of the gallbladder and reduce pressure in the organs of the hepatobiliary system. |
|
| Choleretics | Increase the concentration of bile acids in bile. The composition may include plant components, animal bile, and synthetic components. |
|
Cholespasmolytics are not used for hypotension of the gallbladder, since drugs in this group can lead to complete atony of the walls of the organ and stagnation of bile. Cholekinetics and choleretics (both types of drugs are classified as choleretic drugs) should be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor after carrying out a full range of diagnostic measures. An approximate dosage regimen for these medications is listed below.
- Flamin . A herbal preparation containing flavonoids of sandy immortelle. A special dosage form is produced for children - granules for preparing a sweet suspension. Take 50 to 100 mg 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
"Flamin"
- Holenzim . Combined preparation of animal origin. Contains bile and dried powder of the pancreas and small intestinal mucosa. Teenagers can take Cholenzym starting at age 12. The dosage is 1-3 tablets per day.
"Holenzym"
- Holosas . The drug is in the form of syrup. Contains rosehip extract, which has a choleretic effect and a hepatoprotective effect. Take 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. The dosage for children is ½ the daily dosage for adults.
"Holosas"
- Allohol . A combined preparation containing bile, activated carbon and plant extracts (garlic powder and nettle leaf extract). You need to take the tablets 3-4 times a day for four weeks. Dosage per dose – 1-2 tablets.
"Allohol"
- Berberine . The drug is used not only for the treatment of hypokinetic type VSD, but also for complex treatment of diseases of the hepatobiliary system (including the sphincter of Oddi). The daily dosage is 15-30 mg. It must be divided into 3 doses.
Berberine
To increase tone, the patient can be prescribed herbal stimulating drugs, for example, tincture of lemongrass or eleutherococcus. Standard drug therapy can be combined with the use of traditional medicine recipes. The most effective way to restore gallbladder motility is to ingest olive oil. You need to take it warm, 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
It is important to take medications as prescribed by your doctor and not stop treatment yourself.
Important! Any drugs with a choleretic effect should not be taken for cholelithiasis and obstructive jaundice. Persons with these pathologies should undergo treatment under the constant supervision of a specialist.
Correction of vegetative status
To eliminate autonomic disorders, which may be one of the factors in the development of gallbladder hypotension, the patient needs to change his lifestyle and give up bad habits. Almost 80% of patients with autonomic dysfunction have tobacco or alcohol addiction (including the initial stage of alcoholism), therefore the most important stage of complex treatment is quitting smoking and drinking alcohol. To normalize the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, you also need to walk a lot, move enough, and avoid stressful situations.
You should give up bad habits
If you are very stressed or tired, you should use relaxation techniques or relaxation methods available at home. General methods for correcting vegetative status are:
- Aromatherapy. Allows you to relieve fatigue, improve your mood and cope with stress.
- Warm baths with salt. Relieves muscle tension and increases the overall tone of the body.
- Foot baths with essential oils. Helps fight fatigue. You can add bergamot, rose, fir or lavender oil to the bath.
- Herbal teas. Relieves tension and has a mild sedative effect. For autonomic disorders, you can use chamomile, oregano or sage. It is best to drink them 1-2 hours before bedtime.
- Assistive therapy. As auxiliary methods, the patient can be offered sanatorium-resort treatment, including treatment with mineral waters using blind duodenal sounding techniques, mud therapy, and massage. Of the physiotherapeutic procedures, electrophoresis and treatment with low-intensity ultrasonic waves are the most effective.
Long-acting tenoten is not only a modern, but also the safest way to protect yourself from stress and keep your nervous system under control.
If there is no effect from home methods, you can use medications with minimal toxic load on the liver (Tenoten, Persen, Novopassit, Valerian medicinal extract, Motherwort tincture). Phenobarbital-based drugs have a stronger effect: Corvalol or Valocordin (Valoserdin).
Important! If there are serious indications, the patient may be prescribed medications from the neurotropic group. Such medications contain psychoactive substances and are dispensed from pharmacies with a prescription from the attending physician.
Treatment prognosis
If you have a strong enough desire to overcome the disease and follow all the doctor’s recommendations, your condition should improve within a few weeks.
The peculiarity of this disease is that it largely depends on the psyche and resistance to stress, as well as proper nutrition.
In many ways, success in treatment can be achieved by normalizing the regimen, allocating time for rest, and balancing the diet.
Modern remedies, when prescribed correctly, will give quick and excellent results and allow you to return to your normal rhythm of life.
Diet for jvp
Since poor nutrition is one of the causes of the disease, you should adhere to a special diet.
Special nutrition aims to ensure soft functioning of the liver, better waste of bile, balanced functioning of the bile ducts, liver and other digestive organs.
A prerequisite is a balanced intake of food. The daily menu should include sufficient proteins and carbohydrates, and the fat content should be limited.
The main principles of nutrition for JVP:
- Mode.
Therapeutic nutrition is frequent (up to six times a day) and in small portions. It is necessary to exclude the possibility of overeating; eating food should be organized at the same time.
This approach will allow you to adjust the gallbladder to normal production of bile; its release into the intestines occurs strictly at the prescribed time.
As a result, the outflow of bile is normalized, food is better digested and absorbed. Small portions taken frequently prevent bile from remaining in the bladder for a long time. Spasms of the bladder and excretory tract do not occur. The person does not experience pain.
- Cooking method.
Dishes must be prepared by boiling or baking. It is permissible to stew food. Fried food is prohibited, since during frying, polyunsaturated fatty acids are destroyed and toxic substances are formed. This leads to an increased load on the bile ducts and bladder, as well as the gastric mucosa.
- Temperature.
Avoid eating cold foods, as they can cause contractions of the bile ducts. You shouldn't eat very hot foods either. Moderate warm temperatures will be sufficient.
- Salt and spices.
Their consumption needs to be reduced. In case of excess, fluid is retained, and this in turn leads to the concentration of mucus and complicates its exit from the bladder.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
You need to drink about three liters of liquid per day. This amount will help thin the bile, prevent the formation of stones and help remove toxins.
- Alcohol.
Complications and possible consequences of biliary dyskinesia
People do not always seek qualified help at the first symptoms of pain.
Usually you start taking painkillers on your own, which can only make the situation worse.
Possible manifestations of dyskinesia:
- Weight loss that occurs due to impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestines.
- Chronic cholecystitis (with an inflamed gallbladder for more than six months).
- Cholangitis (inflamed bile ducts).
- Gallstone disease (formation of stones in the bile ducts and bladder).
- Chronic pancreatitis (with an inflamed pancreas for more than six months).
- Gastritis.
- UC.
- Duodenitis (inflamed mucous membrane in the duodenum).
- Atopic dermatitis in children (skin allergies). Occurs when poorly digested food and harmful substances are absorbed.
Diagnostics
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor sends the patient for an instrumental examination:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. It is carried out in 2 stages. The first time, the study is carried out on an empty stomach to determine echo signs of inflammation, deformations and stones in the bile ducts. The patient is then asked to eat a fatty product, and an hour later a repeat examination is performed to assess the rate of bile movement. In this way, the form of dyskinesia is determined - hypermotor or hypomotor.
- Duodenal sounding. A probe is inserted into the duodenum and a portion of bile is taken. The rate of bile excretion determines the form of the disease.
- Cholecystography. May be oral or intravenous. The patient takes a contrast agent orally, or it is injected into him intravenously, after which an X-ray is taken. In this way, the rate of bile evacuation is assessed and the form of the disease is established.
- FGDS. It is carried out to identify pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract that could provoke dyskinesia.
To confirm the diagnosis and identify concomitant diseases, laboratory tests are carried out:
- general clinical tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- fecal analysis for helminths;
- lipidogram.
Based on the results of the examination, laboratory tests and instrumental studies, the diagnosis of ADHD is confirmed or refuted.
The photo shows preparation for duodenal intubation
Prevention of biliary dyskinesia
Having recovered from a disease, you need to make every effort to prevent its reappearance. To do this, you should adhere to a number of rules:
- Complete rest and sleep.
You need to sleep at least eight hours. This will not only save you from relapse of the pathology, but will also relieve you from many other ailments.
- Compliance with the regime.
You need to go to bed no later than eleven o'clock in the evening. This is the optimal time, taking into account the fact that in the morning a person needs to get up early for work.
- Alternation of types of work.
You should not overwork yourself while doing physical or mental work. Give your body a break. Constant overwork can cause the development of not only JVP, but also much more serious complications.
- Walks in the open air.
It is worth setting aside time for such walks several times a week. This will strengthen the body and serve as a preventive measure for many diseases.
- Complete nutrition.
Include cereal products, boiled lean meat, and plant foods in your daily diet.
- Eliminate stressful situations.
Do not allow traumatic moments to arise, as they can become a catalyst for the re-development of the disease.