Composition of Caffetina
of paracetamol , 210 mg of propyphenazone , 50 mg of caffeine and 10 mg of codeine sesquihydrate phosphate as active substances .
As excipients, Caffetin contains 6.3 mg of glyceryl dibehenate , 21.1 mg of calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate , 14.5 mg of sodium carboxymethyl starch , 2.5 mg of colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, 9.6 mg of croscarmellose sodium, 13.5 mg magnesium stearate, 1.5 mg sodium lauryl sulfate, 12.5 mg povidone and 28.5 mg microcellulose.
Interactions with other medicinal drugs and other types of interactions
With Zagalom, caution must be exercised when using NSAIDs in combination with other medications that may increase the risk of sclero-intestinal ulcers, scutum-intestinal bleeding or impairment of function. rock
Ibuprofen (as well as other NSAIDs) should not be combined with:
acetylsalicylic acid
, the fragments may increase the risk of adverse reactions if acetylsalicylic acid (dose no more than 75 mg per dose) is prescribed by the doctor.
Experimental data suggest that, when ingested for one hour, ibuprofen may interfere with the antiplatelet effect of low-dose aspirin. However, the generality of these data and the lack of clarity in extrapolating ex vivo
to the clinical picture do not allow for the development of clear conclusions regarding the systematic administration of ibuprofen. However, with unsystematic administration of ibuprofen, such clinically significant effects are considered unlikely;
Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
), including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Due to the uniqueness of one-hour stagnation of two or more NPZDs, this may increase the risk of side effects.
Be careful when using ibuprofen in combination with:
antihypertensive (ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists) and sechoginous methods:
NSAIDs may alter the therapeutic effect of these drugs. In some patients with impaired narcotic function (for example, in patients during the winter or especially in the summer with impaired nirofunction), immediate treatment with an ACE inhibitor or an antagonist The use of angiotensin II and drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase may lead to further impairment of the function of drugs, including the possible gostra nirkov insufficiency, which seems to have a negative character. Monitor interactions in patients by administering coxib simultaneously with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II antagonists. However, such combinations should be used with caution, especially for summer age patients. If necessary, follow-up with adequate hydration of the patient and the need to monitor the function of the muscles at the beginning of combination therapy, as well as at regular intervals stu nadali. Diuretics may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity from NSAIDs;
anticoagulants:
NSAIDs may increase the clinical effect of anticoagulants such as warfarin;
antiplatelet agents and selective inhibitors of serotonin secretion:
movement rhizik and intestinal hemorrhage;
corticosteroids:
Possible dislocation of the rhizicus, intestinal tract infection or bleeding;
ethanol:
advances the risk of the appearance of intestinal bleeding;
cardiac glycosides:
NSAIDs may precipitate heart failure, alter glomerular filtration rate, and increase the level of glycosides in blood plasma;
cyclosporine:
increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
mifepristone:
Do not take NSAIDs earlier, or 8 - 12 days after taking mifepristone, as NSAIDs may alter the effectiveness of mifepristone;
tacrolimus:
there may be an increase in the risk of nephrotoxicity with one-hour administration of NSAIDs with tacrolimus;
Let's fly:
There is evidence of a potential increase in blood plasma levels;
methotrexate:
There is a significant increase in blood plasma levels similar to methotrexate;
phenytoin:
its concentration in the blood plasma and, consequently, toxicity are evolving;
zidovudine:
increased risk of hematological toxicity with one-hour administration of NSAIDs and zidovudine. There is evidence of an increased risk of hemarthrosis and hematomas in HIV-infected patients who suffer from hemophilia and who simultaneously take zidovudine with ibuprofen;
quinolone antibiotics:
The data, taken from the investigation on animals, indicate that NPZD can push for risks in court related to quinolone antibiotics. The immediate use of NSAIDs and quinolone antibiotics may increase the risk of prosecution;
probenecid and sulfinpirazone:
Wait an hour to take ibuprofen. The uricosuric effect of these functions decreases with intensive treatment with ibuprofen;
aminoglycosides
: with one-hour stagnation, they can promote their nephritis and ototoxic effect.
Drugs of the sulfonyl derivative and phenytoin group:
more powerful effect.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Caffetin is a combination drug, its effect is determined by the action of the components that make up the drug:
- paracetamol in the composition is responsible for the antipyretic and analgesic effect of the drug.
- Caffeine is responsible for the stimulation of the psychomotor centers of the brain , the presence of an analeptic effect , an increase in the effect of analgesics , a decrease in drowsiness and fatigue, an increase in mental and physical performance, an increase in heart rate , and an increase in blood pressure in the presence of arterial hypotension . In addition, caffeine can improve the absorption of the remaining active ingredients of the drug.
- The action of codeine is due to its antitussive effect , which occurs due to the suppression of the excitability of cough center . Codeine also has an analgesic effect by stimulating opiate receptors located in different parts of the central nervous system and in peripheral tissues of the body. This stimulates the antinociceptive system and changes the emotional perception of pain.
- Propyphenazone relieves pain and has an antipyretic effect . The analgesic effect is achieved in 30–60 minutes, and the duration of the effect is 4–8 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Paracetamol is absorbed very quickly. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved 0.5–2 hours after taking the drug. Has the property of penetrating the blood-brain barrier. Metabolism occurs in the liver in three main ways: by conjugation with glucuronides, conjugation with sulfates, or by oxidation through the action of microsomal liver enzymes . In case of oxidation, toxic intermediate metabolites are formed. These metabolites are then conjugated with glutathione .
If the body is deficient in glutathione , such metabolites can cause damage and death of liver cells. The half-life is 1-4 hours. It is excreted from the body through the kidneys in the form of metabolic substances, most of them in the form of conjugates.
Caffeine is well absorbed, with absorption occurring throughout all parts of the intestine. The maximum concentration in blood plasma occurs 50–75 minutes after taking the drug orally. Caffeine is characterized by rapid distribution throughout all organs and tissues of the body; it can cross the blood-brain barrier and the placenta . More than 90% of caffeine is metabolized in the liver. The half-life is 3.9–5.3 hours. Excretion from the body is carried out due to the work of the kidneys.
Codeine is also rapidly absorbed. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached after 2–4 hours. Metabolism occurs in the liver - active metabolites are formed. Excretion from the body is carried out by the kidneys, and is also excreted with bile. The half-life is 2.5–4 hours.
Propyphenazone is very quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in blood plasma occurs approximately 0.5–0.6 hours after administration. Metabolism occurs in the liver. It is eliminated from the body by excretion in urine or bile. The half-life is 2.1–2.4 hours.
Pharmacological properties
The drug Caffetin belongs to the group of combined drugs. Its properties are determined by the action of the active components present in the composition.
Paracetamol helps relieve pain and reduce fever. The mechanism of its action is associated with inhibition of the inflammatory process. The substance affects the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus.
Like paracetamol, propyphenazone is characterized by antipyretic properties and an analgesic effect.
The formula of the drug includes a component that has a psychostimulating effect - caffeine. The substance relieves drowsiness, tones, eliminates the feeling of fatigue, activates mental activity, promotes an increase in blood pressure in the presence of hypotension, and increases performance.
The tablets also include codeine, which has a central antitussive effect; it inhibits the cough center. The analgesic effect of the active component is the result of stimulation of opioid receptors.
After oral administration, all components of the drug are well and quickly absorbed. Caffeine is absorbed 100% and easily penetrates all tissues of the body. It has been proven to promote better absorption of other elements.
The active compounds of the tablets are metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The combination of paracetamol and propyphenazone increases the elimination time; this phenomenon allows you to reduce the number of daily pills taken.
Contraindications
Contraindications may be if the patient has:
- hypersensitivity;
- liver or kidney failure ;
- leukopenia;
- hematopoietic disorders;
- anxiety disorders ( agoraphobia , panic disorder );
- organic diseases of the cardiovascular system (including acute myocardial infarction , atherosclerosis , angina ), arrhythmia , arterial hypertension ;
- glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency ;
- sleep disorders;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- under 18 years of age.
Caution should be exercised when:
- acute abdominal pain, with an unknown cause of this pain;
- attack of bronchial asthma ;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- convulsions;
- drug dependence (including when it is mentioned in the anamnesis);
- alcoholism;
- increased excitability;
- benign hyperbilirubinemia (for example, Gilbert's syndrome );
- viral hepatitis;
- glaucoma;
- in old age.
If the patient has the diseases or conditions listed above, consultation with a doctor is required.
Indications for use
The use of the drug Caffetin is intended for the relief of moderate pain of various etiologies:
- tooth damage accompanied by pain;
- migraine;
- headache;
- periodic pain in women;
- local pain along the nerve;
- condition after injury;
- hyperthermia caused by influenza or other acute respiratory viral infections;
- joint pain;
- muscle pain.
In addition, the drug is used to eliminate the symptoms of a cold or flu (if the patient has a dry cough, rhinitis, headache and muscle pain, sore throat, fever).
Side effects
Caffetin tablets can have side effects on some body systems:
- Nervous system and sensory organs: excitability increases, tremors , anxiety, and insomnia may occur.
- Cardiovascular system: increased heart rate, increased blood pressure .
- peptic ulcer disease may worsen , the activity of liver transaminases , nausea and vomiting may occur.
- urticaria , itching, facial swelling, bronchospasm , laryngeal edema, laryngospasm or angioedema are relatively rare .
- Hematopoietic system: rarely, anemia, thrombocytopenia, methemoglobinemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis may develop .
If the patient experiences any of the possible side effects listed above too severely, or if any other side effects occur, they should be reported to their doctor.
Overdose
Each active substance included in the drug can cause specific symptoms.
- Paracetamol : the first 24 hours after taking the drug - the skin turns pale, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain ; metabolic acidosis develops . Symptoms associated with liver dysfunction may appear 12–48 hours after taking the drug.
- Caffeine : a state of anxiety may occur, tremors , headaches, confusion, and extrasystole .
- Codeine : the appearance of cold sticky sweat, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, decreased blood pressure , signs of nervousness, fatigue, development of bradycardia , severe weakness, slow difficulty breathing, hypothermia , anxiety , miosis , convulsions.
In case of overdose, the stomach is washed, activated charcoal , cardiac activity and blood pressure , and maintenance therapy is carried out. Naloxone, is administered intravenously . SH-group donors and precursors for the synthesis of the substance glutathione are also administered - Methionine for a period of time about 8-9 hours after administration and acetylcysteine - for 8 hours.
If you suspect poisoning, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Contraindicated
Increased sensitivity to ibuprofen or other components of the drug.
Hypersensitivity reactions (for example, asthma, allergic rhinitis, angioedema, or urticaria), which were previously avoided after taking ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) or other nonsteroidal Common anti-inflammatory agents (NPS).
Viral disease of the vulva and duodenum/bleeding in the past or relapses in history (two or more clear episodes of acute viral disease or bleeding).
Intestinal hemorrhage or perforation, associated with congestion of NSAIDs, in the anamnesis.
Severe heart failure (IV functional class according to the criteria of the New York Heart Association (NYHA)), severely impaired liver function or anything.
Cerebrovascular or other bleeding; destruction of hematopoiesis or throatiness of blood.
More active intestinal ignition.
The remaining trimester of gestation.
Interaction
Caffeine
- combined use of caffeine with barbiturates and anticonvulsants can lead to increased metabolism and increased clearance of caffeine;
- use simultaneously with Cimetidine, oral contraceptive drugs, Disulfiram, Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin reduces the metabolism of caffeine produced in the liver;
- the strength of the effect of narcotic and sleeping pills decreases;
- the combined use of caffeine and beta-blockers can lead to a mutual decrease in therapeutic effects;
- combination with adrenergic bronchodilators causes additional stimulation of the central nervous system;
- absorption of ergotamine ;
- the combination of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and large doses of caffeine can cause dangerous cardiac arrhythmias or a significant increase in blood pressure ;
- the effect of caffeine may reduce the clearance of theophylline and some other xanthines .
Codeine
- simultaneous use of codeine with ethanol, muscle relaxants , as well as with drugs that depress the central nervous system, can lead to increased sedation, suppression of the respiratory center and depression of the central nervous system;
- combination with drugs with anticholinergic activity , antidiarrheal drugs increases the risk of constipation;
- of Metoclopramide is reduced .
Paracetamol
- taking with inducers of microsomal oxidation , which occurs in the liver (that is, with anticonvulsants, barbiturates, Rifampicin, Phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants ), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increases the production of hydroxylated active metabolic products, and this can lead to the development of severe intoxication even with relatively small overdose;
- simultaneous use of high doses of paracetamol can lead to an increase in the effect of indirect anticoagulants (these include derivatives of Dicumarin );
- of uricosuric drugs is reduced ;
- myelotoxic drugs enhance possible manifestations of the hematotoxic effect of the drug;
- of chloramphenicol by 5 times ;
- Metoclopramide may speed up the absorption of paracetamol.
Features of good stagnation
Side effects associated with ibuprofen can be reduced by maintaining the minimum effective dose required to relieve symptoms for a short period of time.
In particular, in the summer, beware of an increased incidence of adverse reactions to NSAIDs, especially bowel bleeding and perforation, which can be fatal.
Infusion into the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems
Patients with a history of arterial hypertension and/or heart failure should be treated with care (consultation with a physician is required), after treatment with ibuprofen, as well as In other NSAIDs, episodes of congestion, arterial hypertension, and swelling have been reported.
Clinical studies and epidemiological data indicate that ibuprofen ingestion, especially at high doses (2400 mg per dose), and that trival ingestion may lead to a slight increase in the risk of developing to arterial thrombotic complications (for example, myocardial infarction or stroke). Overall, epidemiological data do not indicate that low doses of ibuprofen (for example, ≤ 1200 mg per dose) can lead to the development of arterial thrombotic complications before the risk of progression. Patients with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, congestive heart failure (II - III functional class according to the NYHA classification), diagnosed with ischemic heart disease, will get sick Baths of peripheral arteries and/or cerebrovascular diseases may be prescribed by the doctor only after cerebral analysis. Slide is unique in high doses (2400 mg per dose). Patients with significant risk factors for cardiovascular complications (such as arterial hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetic diabetes, chicken) should be treated with NPZD, especially if high doses are necessary. zi (2400 mg per dose), a trace after renal obscuration.
Vpliv na organi dikhannya.
Bronchospasm may occur in patients who suffer from bronchial asthma or allergic diseases or a history of illness.
Other oil refineries.
The difference between one-hour administration of ibuprofen and other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, increases the risk of adverse reactions.
Systemic red bloodworm and systemic illness of healthy tissue.
Use ibuprofen with caution in case of manifestations of systemic red bloodworm and systemic diseases of the affected tissue
through movement of the rhizic the development of aseptic meningitis.
Episodes of aseptic meningitis have been reported when taking ibuprofen. Although this effect is more pronounced in patients with systemic worms and other diseases of the tissue, such episodes have also been reported in some patients who do not suffer from chronic diseases illness, therefore it is necessary to take care of the patient’s medical care.
Float on the nirki/stove.
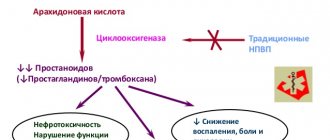
Long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to a dose-dependent decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins and provoke the development of nitric deficiency. A high risk of this reaction is in patients with impaired liver function, cardiac damage, impaired liver function, and patients taking diuretics that suppress prostaglandins. can lead to a blockage of the core and further impairment of the function of the eyes. Such patients should be treated with the lowest possible dose of ibuprofen and their function should be monitored regularly. In the event of a rainy season, it is necessary to ensure sufficient living conditions. There is a significant risk of nicotine deficiency in children (age 6 years old) and children born in winter.
Regular use of analgesics, especially a combination of various analgesics, can lead to a high level of analgesics with the risk of analgesic deficiency (analgesic nephropathy). The greatest risk of this reaction is observed in patients with frail age, patients with narcotic deficiency, heart failure and liver failure, as well as in those who are withdrawing from therapy uretics or ACE inhibitors. After initiating NPZD therapy, you should be able to turn around to the position that you need to take care of before bathing.
Like other NSAIDs, ibuprofen may cause slight increases in early liver function tests, as well as increases in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (AL). T). In the case of sutonic displacement of these indicators, the liquid has a trace of pripinit.
When taking ibuprofen, it is necessary to regularly check liver function indicators, liver function, and hematological function/blood picture.
Impact on fertility in women.
There is evidence that medications that inhibit the synthesis of cyclooxygenase/prostaglandins can cause a decrease in reproductive function in women as a result of the ovulation process. Given the appearance of a werewolf during the celebration. Long-term stagnation (a dose of 2400 mg over a period of time, as well as a three-day bath for 10 days) and Buprofen can impair a woman’s fertility and is not recommended for women who are susceptible to pregnancy. Women who have difficulty with pregnancy or are under stress due to infertility should take this drug.
Floods into the scolio-intestinal tract.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with caution to patients with a history of illnesses of the intestinal tract (virulent colitis, Crohn's disease), as it is possible that these illnesses may become severely ill. With the treatment of various NSAIDs, there were reports of swelling, bleeding or perforation of the gut-intestinal tract (CTT), which can lead to death, at any stage of treatment, regardless of the presence of pre-malignant symptoms or evidence of severe disorders in the side of the CT in the anamnesis.
The risk of intestinal hemorrhage, perforation, and virulence increases with increasing doses of NSAIDs in patients with a history of virulent disease, especially characterized by bleeding or perforation, and in cents of the summer century. These patients should begin treatment with minimal doses. Caution is necessary for patients who are receiving concomitant therapy with drugs that may increase the risk of viral infections or bleeding, for example, congestion of internal corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective inhibitors of serotonin secretion or antiplatelet agents, such as acetylsalicylic acid. If necessary, carry out combined therapy with protective drugs (for example, misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors), especially for patients who require a three-dose infusion of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid.
Patients who have suffered from scutulo-intestinal disorders, especially patients of summer age, may report some non-essential abdominal symptoms (especially bleeding from the grass tract), looking at the ear.
Trying to use any pain-relieving medicines to relieve headaches can devastate the whole body. In such situations, you should go to the doctor and give treatment. Let us look at the prevalence of headaches due to the use of medications in patients who suffer from frequent or constant headaches, regardless of (or through) regular use of medications for headaches.
In case of scutulo-intestinal bleeding or symptoms in patients who are taking off ibuprofen, the liquid should be carefully applied.
On the side of the skin and under the skin.
Even rarely, aphids with NSAIDs can cause severe forms of skin reactions that can lead to death, such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necritis. h. The greatest risk for the development of such reactions in patients occurs at the beginning of the course of treatment; in most cases, the culprit reaction is avoided during the first month of treatment. Take Ibuprofen at the first signs of skin rash, pathological changes in the mucous membranes or any other signs of hypersensitivity.
In cases of varicella, chickenpox can cause severe infections on the sides of the skin and soft tissues. At this time, it is not possible to turn off the infusion of the NPZZ for the development of these infections; it is recommended that you stop using the medicinal product Caffetin® Ice in cases of chickenpox.
Tablets containing barvniki (E 110 and E 124), which can cause an allergic reaction.
Tablets to dissolve glucose. Patients with rare seizure disorders containing glucose-galactose should not take this medication.
Tablets containing soya lecithin. Patients with an allergy to peanuts or soy are not to blame for this medicinal benefit.
Suspension during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Medicine's remedy for menstrual pain.
During the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, ibuprofen treatment begins to wear off. Ibuprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Inhibition of the synthesis of prostaglandins can negatively affect the gestation and/or development of the embryo/fetus. Epidemiological data indicate increased risk of heart disease and gastroschisis after administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in the early stages of pregnancy. The absolute risk of cardiovascular diseases increased from less than 1% to approximately 1.5%. It is important that the risk progresses with increasing doses and severity of therapy.
In animals, the use of inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis led to increased pre-implantation pre-implantation complications and embryonic/fetal mortality. In addition, an increased frequency of various developments, including those on the side of the cardiovascular system, was reported in animals that suppressed inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis during the period of organogenesis.
NSAIDs should not be taken during the first two trimesters of pregnancy or during pregnancy, as long as the potential risk for the patient does not outweigh the potential risk for the fetus. If a woman starts taking ibuprofen when she is about to get sick, or during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, take the smallest possible dose for the shortest period of time.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, when any inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis are stagnant, the following risk may occur:
- for the fetus: cardiac-legenian toxicity (pre-closing of the arterial ducts of the fetus with pulmonary hypertension); impairment of nitric function, which can progress to nicoric deficiency, which is accompanied by oligohydramnios;
- for mothers and newborns, due to vomiting: possible increased bleeding, antiplatelet effect, which can develop at very low doses; suppression of the uterus very quickly, which should be done before trimming or increasing the density of the canopies.
In some studies, ibuprofen was found in very low concentrations in mother's milk, so it is unlikely that it could have a negative impact on the inconvenience of breastfeeding.
This is due to the fluidity of the reaction during treatment with vehicles or other mechanisms.
It doesn’t pour in, the mind is stagnant with recommendations for dosages and the need for treatment. Patients who experience dizziness, drowsiness, disorientation, or blurred vision when taking NSAIDs should be advised to use vehicles or robots with machinery.
special instructions
Before consulting a doctor, you should not take the drug for more than 5 days. In case of long-term (longer than 1 week) use, it is necessary to monitor the peripheral blood picture and monitor the functional state of the liver.
At the time the drug is used, it is necessary to stop drinking ethanol (as this increases the risk of developing hepatotoxicity).
In laboratory studies, the indicators obtained from the quantitative determination of sugar, as well as uric acid in the blood plasma, are distorted.
The use of the drug can lead to changes in the results of doping control tests in athletes, and also interfere with the diagnosis of acute abdominal pain syndrome .
Instructions for use
Caffetin must be taken orally, washing down the tablet with the required amount of purified water - 100 ml. It is prohibited to take the medicine with other drinks.
The drug is not intended for self-medication, and can be used in therapy only on the recommendation of the attending physician, who will prescribe the required dosage, as well as describe the dosage regimen and duration of the therapeutic course.
Adult patients and adolescents over 16 years of age – 1 tablet three times a day. As prescribed by the doctor, you can take 2 tablets three times a day. Children over 12 years of age are recommended to take Caffetin 1 tablet three times a day. Children from 7 years of age – half a tablet, 1 to 4 times a day. The duration of drug therapy is from 3 to 7 days.
With prolonged drug treatment, it is necessary to control blood flow in the peripheral parts of the system, as well as monitor liver enzyme levels.
When treating with Caffetin, you should avoid drinking alcohol, because ethyl alcohol increases the risk of side effects. Also, during therapy, you should avoid caffeine-containing drinks, because their consumption can provoke a caffeine overdose.
Caffetine price, where to buy
You can buy Caffetin in Moscow at almost any pharmacy. The price of Caffetin (pack of 12 tablets) is approximately 115 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Caffetin Light tablets 12 pcs. Alkaloid AO
134 rub. order - Caffetin Cold tablets p.p.o. 10 pcs. Alkaloid AO
206 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Caffetin Light (tab. No. 12) Alkaloida
113 RUR order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Caffetin Lady 200 mg No. 10 tablets Alkoloid AD-Skop є, Republic of Macedonia
98 UAH.order
Analogs
Analogs by ATX code: Rinza, Rinzasip, Sedalgin-neo, Migrenol, Toff Plus.
Drugs with a similar mechanism of action (4th level ATC code match): Combispasm, Maxicold, Theraflu, Antigrippin, Maxicold Rhino, Fervex, Antiflu Kids, Antiflu, Solpadeine, Flukoldex, Pentaflucin, Saridon, Grippostad, Novalgin, Coldrex, Acetaminophen, Efferalgan , Cefekon D, Calpol, Panadol, Paracetamol, Tylenol.
Do not decide to change the drug on your own; consult your doctor.