Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Mig 400 tablets contain ibuprofen , which is an analgesic with antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties. It indiscriminately inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 , as well as prostaglandin .
The analgesic properties of the drug are most pronounced in cases of inflammatory pain. The analgesic effect is not of the narcotic type.
After taking the tablets orally, the medicine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum plasma concentration of the active ingredient is reached approximately 120 minutes after taking tablets at a dosage of 400 mg.
99% bound to plasma The active component is slowly distributed in the synovial fluid . It is biotransformed in the liver through carboxylation and hydroxylation of the isobutyl group. Pharmacologically inactive metabolites .
Plasma half-life is 2-3 hours. in the form of metabolites and their conjugates . A small part of the drug is excreted unchanged in urine and bile.
Pharmacological action of Mig 400
Ibuprofen, which is part of mig 400, as the main active ingredient, is a derivative of propionic acid. It has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Its mechanism of action is based on a non-selective blockade of COX-1 and 2 and inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis.
Ibuprofen exhibits antiplatelet activity.
Its analgesic effect is more pronounced in pain caused by inflammation.
The analgesic activity of ibuprofen is a narcotic type.
Indications for use
The drug is indicated for use for:
- headache;
- toothache;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- fever due to colds and flu ;
- migraine;
- neuralgia;
- menstrual pain.
If you need to find out why Mig 400 tablets will help in each specific case, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Contraindications
This product is prohibited for use when:
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- hemophilia and other bleeding ;
- pregnancy;
- under 12 years of age;
- breastfeeding;
- history of a negative reaction to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs ;
- aspirin asthma;
- bleeding;
- deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ;
- diseases of the optic nerve.
The medicine should be used with caution in the elderly, as well as in cases of arterial hypertension , liver or kidney failure , hyperbilirubinemia , gastritis , colitis , heart failure , liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension , nephrotic syndrome , gastric and duodenal ulcers (including a history ), enteritis , blood diseases.
Side effects
Like all non-steroidal drugs, Imet can have a negative effect on various systems of the human body, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- Abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, bloating, stomach and intestinal ulcers;
- Headaches;
- Edema, decreased diuresis, damage to liver tissue, necrosis of the renal papillae;
- Hematopoietic disorders;
- Severe allergic reactions, in particular rash with blisters and redness, asthma attacks;
- Decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, edema and tachycardia.
Side effects
The use of Mig 400 can lead to the following adverse reactions:
- Gastrointestinal tract: vomiting, pain in the abdomen, loss of appetite , nausea, flatulence , heartburn , diarrhea , constipation ;
- sensory organs: dry or irritated eyes, decreased hearing, toxic damage to the optic nerve, ringing or noise in the ears, blurred or double vision, swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- CVS: heart failure , high blood pressure , tachycardia ;
- allergies : rash, Quincke's edema , dyspnea , anaphylactic shock , erythema multiforme , eosinophilia , itching , anaphylactoid reactions , bronchospasm , fever , Lyell's syndrome , rhinitis ;
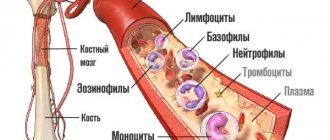
- changes in laboratory parameters: increased serum creatinine concentration , increased bleeding time, decreased hemoglobin , decreased creatinine clearance liver transaminase activity serum glucose , decreased hematocrit ;
- respiratory organs: shortness of breath , bronchospasm ;
- CNS: insomnia , headache , nervousness, psychomotor agitation , depression , hallucinations , dizziness , anxiety, irritability, drowsiness , impaired consciousness ;
- urinary system: allergic nephritis , acute renal failure , cystitis , nephrotic syndrome , polyuria ;
- hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenic purpura , anemia , leukopenia , thrombocytopenia , agranulocytosis .
In rare cases, ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, pain in the mouth, aphthous stomatitis , hepatitis , irritation or dryness of the oral mucosa, ulceration of the gum mucosa, pancreatitis , and aseptic meningitis .
With prolonged use of the drug in high doses, the likelihood of ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, visual impairment, and bleeding increases.
Instructions for use Mig 400 (Method and dosage)
The medicine is used internally. For those who take Mig 400 tablets, the instructions for use indicate that dosages are set individually depending on the indications.
Usually start taking the medicine with 200 mg every day 3-4 times. If necessary, the dosage can be increased to 400 mg, which are taken 3 times a day. When the therapeutic effect is achieved, the daily dosage is reduced to 600-800 mg.
The instructions for use of Mig 400 advise that this product should not be taken for more than a week or in higher dosages without consulting a specialist.
In case of , heart or liver dysfunction, the dose is reduced.
Overdose
When using the drug in doses above normal, abdominal pain , vomiting, drowsiness , headaches, metabolic acidosis , acute renal failure , bradycardia , atrial fibrillation , nausea, lethargy, depression , tinnitus, coma , marked decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia , respiratory arrest are possible. .
If less than 60 minutes have passed since the overdose, gastric lavage . In addition, alkaline drinking, taking Activated Carbon , and forced diuresis . Treatment is symptomatic.
MIG® for children
The simultaneous use of MIG® for children with other NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 blockers, is not recommended.
The risk of side effects can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible period of time.
Cases of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcerative lesions or perforation with a fatal outcome have been reported during the use of any drug from the NSAID group, regardless of the presence or absence of previous symptoms or whether the patient has a history of serious gastrointestinal diseases.
Patients should be informed of the need to immediately report to the doctor any symptoms (especially bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract) that appear while using the drug. If vomiting blood, blood in the stool, or tarry stools occurs, stop using the drug and immediately seek medical help.
Caution should be exercised when using ibuprofen simultaneously with drugs that increase the risk of gastrointestinal complications (including bleeding), such as glucocorticosteroids or anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (warfarin, acetylsalicylic acid) (see section Interactions with other drugs).
To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the minimum effective dose should be used for the shortest period of time.
To prevent the development of NSAID gastropathy, simultaneous use with prostaglandin E drugs (for example, misoprostol) is recommended.
In case of long-term use of ibuprofen, monitoring of peripheral blood parameters and the functional state of the liver and kidneys is necessary.
When symptoms of gastropathy appear, a thorough examination is indicated, including esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a blood test to determine hemoglobin and hematocrit, and a stool test for occult blood.
Before starting use in patients with arterial hypertension and/or heart failure, caution should be exercised and consult a doctor, since in this category of patients the use of NSAIDs can lead to fluid retention, edema and increased blood pressure.
Long-term use of any painkillers to relieve headaches can lead to its aggravation. In such a situation (or if there is suspicion of its development), it is necessary to stop using painkillers and seek medical help. The diagnosis of headache associated with excessive use of painkillers should be suspected in patients who often or daily suffer from headaches despite/or as a result of regular use of painkillers.
Frequent, habitual use of painkillers (especially their combinations) can lead to kidney damage with the risk of developing renal failure (analgesic nephropathy).
There is evidence of rare cases of severe skin reactions (such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) with the use of NSAIDs. At the first manifestations of a skin rash, damage to the mucous membranes or other signs of an allergic reaction, the use of MIG® for children should be stopped immediately.
In very rare cases, severe soft tissue skin infections and complications may occur during chickenpox infection. The use of MIG® for children with chickenpox should be avoided.
Like other NSAIDs, ibuprofen may reduce the diagnostic value of symptoms such as fever and inflammation, and thereby affect the diagnosis of the disease. Patients suffering from allergic diseases and/or chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases have an increased risk of allergic reactions when using ibuprofen. Allergic reactions can manifest themselves in the form of attacks of bronchial asthma, Quincke's edema or urticaria. In very rare cases, severe hypersensitivity reactions (eg anaphylactic shock) have been observed. If the first signs of a hypersensitivity reaction appear, the use of MIG® for children should be discontinued and consult a doctor.
Caution should be exercised when using MIG® for children in patients with bleeding disorders, because ibuprofen inhibits platelet aggregation. If it is necessary to determine the concentration of 17-ketosteroids in the blood plasma, use of the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the study.
During the treatment period, drinking alcohol is not recommended.
MIG® for children contains maltitol, therefore its use in patients with hereditary fructose intolerance is contraindicated.
MIG® for children can be used in children with diabetes mellitus, since the drug does not contain glucose.
Does not contain dyes.
This drug contains sodium in an amount of 3.7 mg/ml, which should be taken into account for patients who are on a diet with limited salt intake.
Interaction
When taking Mig 400, the effect of Furosemide and thiazide diuretics , which can be caused by sodium retention due to inhibition of prostaglandin .
In addition, the active ingredient of the drug may enhance the effect of oral anticoagulants . Taking them together is not advisable.
Ibuprofen also reduces the antiplatelet effect of acetylsalicylic acid and reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs.
Mig 400 should be used with caution in combination with NSAIDs and corticosteroids , as this can lead to adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract.
The drug also provokes an increase in the level of Methotrexate in the blood plasma .
In HIV-infected patients with hemophilia, the combination of ibuprofen with zidovudine increases the risk of hemarthrosis .
Combination with Tacrolimus increases the likelihood of nephrotoxicity due to inhibition of prostaglandin .
Under the influence of the drug Mig 400, the hypoglycemic properties of oral hypoglycemic drugs and Insulin are enhanced. Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
special instructions
In order to prevent the development of NSAID gastropathy, this drug is combined with misoprostol.
If gastropathy occurs, an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, stool test for occult blood and a blood test are performed.
For patients with infectious diseases, ibuprofen is prescribed with caution.
While taking Mig 400, ethanol intake is not recommended.
If visual impairment occurs, it is necessary to discontinue the drug and be examined by an ophthalmologist.
Side effects of Mig 400 can be reduced by taking the drug in the minimum effective dose.