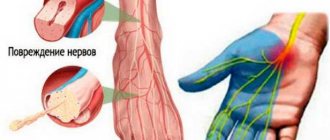
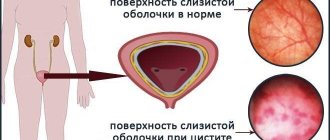
If the kidneys are inflamed, their functions are impaired to varying degrees depending on the type, cause and depth of the pathological process. This disease is known as nephritis. While the acute form can cause only temporary dysfunction, the chronic course of the disease is fraught with irreversible damage to organ tissue - scarring. And this, in turn, slowly leads to a life-threatening condition - kidney failure.
What is jade
Nephritis is a general term that includes a group of inflammatory diseases of different structures of the kidney. The structures are understood as the so-called renal glomeruli and tubules, interstitial tissue. Types of nephritis differ in the origin and development of pathology.
The kidneys are a paired organ that filters water and waste from the blood and produces urine. The kidneys are located on opposite sides in the lumbar region under the ribs.
The kidney consists of thousands of structural units - nephrons. This unit is a glomerular filter and a system of tubules for the reabsorption of useful elements.
It is in the nephron that substances are separated into waste, which is then excreted in the urine, and useful elements, which are reabsorbed.
The concept of nephritis includes inflammation of the kidney tubules and adjacent tissues, which leads to damage to the organ. The kidneys stop filtering the blood properly, and harmful substances accumulate in the body, seriously affecting human health. Long-term nephritis can result in kidney failure.
Blood pressure, the volume of circulating blood and the level of salts in the body also depend on the quality of kidney function.
Prevention
Proper nutrition will help protect your kidneys and other organs from developing diseases.
The main measures to prevent the development of nephritis are increasing immunity, timely elimination of infectious foci (sore throat, caries, etc.), treatment of glomerulonephritis. Respiratory diseases cannot be caused.
It is important not to succumb to stress, to avoid overwork and hypothermia. It is recommended to give up bad habits, proper nutrition, exercise and regular preventive medical examinations of all organs and systems.
Types of diseases and their features
Jade is classified according to its origin:
- primary - occurs as a separate disease,
- secondary - due to the presence of an underlying disease associated with metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis) or systemic damage to connective tissue (vasculitis, rheumatism).
Nephritis is classified as acute or chronic. In the first case, eliminating the cause of inflammation leads to recovery. In chronic nephritis, progressive kidney damage persists at various levels.
Inflammation can occur in one or both kidneys at once. Depending on this, one-sided and two-sided nephritis are distinguished.
According to statistics, the disease is more often bilateral with simultaneous damage to both kidneys.
There are several types of nephritis, which are rather separate diseases due to the reason that caused them and clinical manifestations:
- Interstitial nephritis is an inflammation of the tubular apparatus of the nephrons of a non-bacterial nature. This species is characterized by a pathological process in the interstitial tissue, its swelling, but the negative effect does not extend to the calyces and pelvis, and there are no destructive changes in the tissue.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue, usually due to a bacterial infection. In most cases, it begins in the bladder and then migrates up the ureters to the kidneys.
- Glomerulonephritis is a type of autoimmune nephritis when the focus of inflammation is in the glomeruli. Each kidney has millions of capillaries. Glomeruli are tiny clusters of capillaries that transport blood and act as filtering units. Damaged and inflamed glomeruli cannot perform this job correctly.
- Nephritis in systemic diseases is secondary kidney damage as a result of diseases such as:
- lupus erythematosus (lupus nephritis),
- scleroderma,
- rheumatism, etc.
- Hereditary - a genetically determined disease with damage to interstitial tissue, and then glomeruli. Sometimes it causes damage to vision and hearing. It does not appear immediately after birth, but after a while, when intermediate metabolic products, remaining in the body, begin to have a toxic effect. Up to 10 years of age, it is poorly diagnosed, since the only sign is changes in urine analysis. This type of disease is metabolic in nature. It is more severe in males.
- Embolic purulent is a limited inflammation of the kidney with purulent foci (up to 5 mm), caused primarily by the entry of pyogenic microbes into the blood and lymph flow, and from there into the kidneys. Causes scarring of kidney tissue.
- Radiation nephritis - occurs with prolonged ionizing radiation and manifests itself in the form of tubular degeneration followed by their atrophy.
- Toxic - caused by chronic intoxication as a result of exposure to external factors (medicines, chemicals).
To classify the current disease as a specific type, one should study how much the excretory function of the kidneys has decreased, what pathological processes occur in their tissues and the degree of their prevalence.
Classification and causes of nephritis
With different types of nephritis, different parts of the kidney are affected - the glomeruli, tubules or interstitial tissues of the organ.
Classification:
- glomerulonephritis (glomerular nephritis) – inflammation of the glomeruli (kidney glomeruli);
- pyelonephritis – affects the pyelocaliceal system;
- interstitial (tubulointerstitial) nephritis is a pathology of the tubules and surrounding tissue.
The origin of diseases is varied. Possible factors for the occurrence of nephritis:
- infectious diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- congenital pathologies;
- other reasons (injuries, allergies, vaccinations, insect bites, etc.).
It is known that such kidney disease can be caused by radiation exposure or severe poisoning.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerular nephritis, or glomerulonephritis, is an immuno-allergic inflammatory pathology that affects the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Primary glomerulonephritis occurs due to a violation of the morphology of the kidneys. Secondary – due to infections, drug addiction or cancer.
The disease can be acute or chronic, with repeated exacerbations and periods of rest. A subacute (malignant) form is distinguished separately.
Causes:
- Infectious diseases caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus most often lead to glomerulonephritis.
- Diseases caused by pneumococcus, staphylococcus, hepatitis C virus. Glomerulonephritis can appear 1-3 weeks after the flu or respiratory tract infections (sore throat, laryngitis).
- Allergies, insect bites, trauma, sun exposure, food or drug intolerance.
During an infection, the immune system produces antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms. Antibody complexes act on the vessels of the glomerulus, which becomes inflamed during nephritis.
Pyelonephritis
This is a kidney disease in which the destructive process affects the pyelocaliceal structure of the organ.
The cause of this nephritis in most people is E. coli. Other microorganisms that cause the disease include Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus vulgaris. Less than 5% of cases are gram-positive staphylococci and enterococci.
Organs become infected:
- ascending route - from the lower urinary tract or genital organs;
- hematogenously - due to acute inflammation outside the genitourinary system (mastitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.).
Pyelonephritis in the acute stage can lead to renal failure.
Interstitial
Interstitial nephritis of the kidneys is characterized by a destructive-inflammatory process of connective tissue.
You can get sick due to taking antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Other factors include previous infections (sore throat, diphtheria), poisoning, burns, and injuries.
Medicines that can provoke the disease:
- antibiotics (Penicillin, Tetracycline, Ciprofloxacin);
- antiviral drugs (Acyclovir);
- most non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics (Furosemide, Triamterene);
- antihypertensives (Amlodipine, Captopril).
The risk of nephritis has been identified in people taking herbal medicines based on Chinese herbs. Plants containing aristolochic acid are unfavorable.
Characterized by polyuria, weakness, and a tendency to form kidney stones. Hypertension is expressed in 30-45% of patients.
Treatment involves discontinuation of the drug that caused the malaise, vitamin complexes, antihistamines and anti-sclerotic medications.
Purulent
Pyelonephritis can occur with severe and dangerous complications, in purulent forms. These include apostematous nephritis, carbuncle, and kidney abscess.
Complications with the occurrence of purulent processes can be a consequence of uncontrolled use of antibiotics. The immune system forms antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms. As a result, the classical treatment regimen for pyelonephritis becomes insufficiently effective. The inflammatory process gets out of control, flowing into suppuration of the kidneys.
Ray
Radiation nephritis is inflammation of the kidneys due to radiation. The disease occurs both after strong single radiation exposure and with prolonged exposure to small doses. The kidneys are most sensitive to the effects of radioactive radiation.
This type of nephritis can develop both during irradiation of the lumbar region directly and against the background of general radiation sickness. The renal glomeruli and tubular system are subject to dystrophic changes.
The clinical picture of the disease is changes in the composition of urine, hypertension, anemia, swelling. Treatment is similar to that of interstitial nephritis caused by other causes.
Toxic
This variety occurs under the influence of toxic chemicals. These include lead, mercury, nitrogen-containing compounds, cyanides, insecticides, etc. Toxic nephritis is typical for workers who directly deal with pesticides, polymers, and synthetic rubber.
The second factor is biological poisoning - poisonous mushrooms, snake and insect bites, poor quality food, as well as alcoholism.
Due to severe damage from toxic substances, kidney failure can be fatal.
Lupus
This is the name for kidney damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This is a disease of unknown etiology that provokes immune complex inflammation of the connective tissue of organs.
Suspected factors for lupus nephritis:
- genetic predisposition;
- increased estrogen levels;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- past infectious diseases.
The external manifestations of SLE are red rashes on the skin. But it is possible to reliably detect the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus only by the results of a blood test.
Treatment depends on the form of the disease and ranges from hormone therapy to kidney transplantation.
Congenital
Hereditary nephritis is classified as a genetically determined type of glomerulopathology. A child is diagnosed with a disorder in the morphology of the renal glomeruli. This disease is often accompanied by hearing loss and blindness.
The first symptoms of kidney damage become visible between the ages of 3 and 10 years. Hematuria (blood in the urine) may spontaneously appear and disappear in a child. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of renal tissue is prescribed.
There are no effective treatments for hereditary nephritis. The child is prescribed a gentle regimen, limited physical activity, and a diet.
Primary and secondary
Types of kidney nephritis include primary and secondary. Primary nephritis has no previous disease. Secondary may be a consequence of autoimmune diseases, allergies, infections. The cause is diabetes, oncology or alcoholism.
Diffuse and focal
All types of nephritis can be divided into diffuse or focal. With the diffuse nature of the disease, the systemic immunoinflammatory process affects the entire tissue of the damaged organ. In focal cases, the lesion is localized in certain areas (foci) of the kidney.
Acute and chronic
An acute form of nephritis can occur in any of the types of this disease. This term refers to a rapidly developing inflammatory process. Characterized by high fever and severe pain.
A chronic disease accompanies a person for a long time, alternating stages of exacerbation and remission. Treatment is reduced to reducing the frequency of exacerbations and increasing periods of remission.
Reasons for the development of nephritis
Among the causes of kidney inflammation are the following:
- hereditary predisposition - in families the disease can occur from generation to generation, which confirms a genetic connection,
- infections such as HIV and hepatitis B or C are also often accompanied by nephritis,
- diseases of the immune system - six out of ten patients with lupus develop lupus nephritis,
- long-term use of antibiotics, painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and diuretics.
In some cases, the cause of the disease remains unclear.
Diagnosis of nephritis
Diagnosis of nephritis includes the following examination methods:
- General urine analysis;
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys;
- X-ray examination (X-ray);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Kidney tissue biopsy (if necessary);
- In case of kidney inflammation, the analysis usually shows proteinuria, hypoproteinemia and hyperlipidemia.
Risk factors
Risk factors for developing nephritis include:
- high blood pressure,
- diabetes,
- obesity,
- heart diseases,
- age over 60 years,
- hypothermia,
- gynecological diseases,
- kidney injuries,
- recent surgeries on the urinary tract,
- oncological diseases in the body.
Acute nephritis can occur in people of any age and gender. Chronic usually appears in late childhood or adolescence with hereditary metabolic diseases.
Nephritis is very rare in children under 5 years of age.
A child is more at risk of glomerulonephritis if he has:
- a systemic autoimmune disease such as lupus,
- polyarteritis nodosa,
- Wegener's granulomatosis is an autoimmune nodular inflammation of the walls of blood vessels,
- Henoch-Schönlein disease - vasculitis, or immunopathological inflammation of blood vessels,
- Alport syndrome is a hereditary non-immune glomerulopathy characterized by decreased liver function, blood in the urine, and sometimes deafness,
- streptococcal infection.
Risks and complications from nephritis
If the disease is not treated and the symptoms of nephritis are not addressed, then over time the pathology will lead to the following complications:
- Problems with the cardiovascular system. And this will lead to an early heart attack or stroke.
- Kidney failure. Which will definitely result in intoxication of the whole body with protein breakdown products, excess salts, etc. As a result, this condition can result in coma.
- Extensive swelling of the entire body. The result is cerebral edema.
- In addition, a patient with nephritis in an already chronic form may develop atherosclerosis.
Advice: monitor your health and respond to alarming symptoms in a timely manner. This will help you live a long and happy life.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations will depend on the type of nephritis that a person suffers from, as well as on whether the process is acute or chronic. The most common symptoms of all types of acute nephritis are:
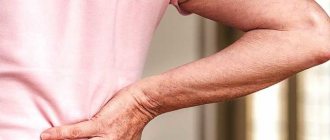
- pain in the pelvis, lower back or abdominal area,
- pain or burning sensation when urinating,
- frequent need to empty the bladder,
- decrease/increase in daily urine volume,
- visually noticeable changes in urine (turbidity, darkening),
- blood or pus in the urine
- swelling of the body, usually the face and upper torso,
- weight gain (due to edema),
- pallor, dryness and flaking of the skin,
- vomit,
- weakness and decreased performance,
- elevated temperature,
- high blood pressure.
In the early stages, symptoms may appear inactive, but there are a number of obvious signs indicating problems with the kidneys. Such manifestations require immediate contact with a nephrologist:
- changes in urinary habits
- swelling anywhere in the body, but especially in the upper half,
- change in urine color
- foamy urine - bubbles and foam arise from excess protein in urine, a symptom indicates pathology if present regularly,
- blood in urine.
The chronic form of nephritis can develop over several years without any symptoms. Sometimes there is a slow development of manifestations similar to the acute form. An underlying inflammatory process, such as in glomerulonephritis, can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys and lead to kidney failure.
A history of acute nephritis significantly increases the risk of a chronic course of the disease in the future.
Symptoms of nephritis in children
Symptoms of nephritis may manifest differently in each child. To summarize, we can identify the following signs of the disease:
- dark brown urine (due to blood and protein),
- decreased amount of urine,
- lack of energy or weakness (fatigue),
- labored breathing,
- headache,
- high blood pressure,
- convulsions,
- rash, especially in the buttocks and legs,
- weight loss,
- pain in the joints and throat,
- pale skin,
- accumulation of fluid in tissues (edema).
Symptoms of nephritis in children may masquerade as other conditions or diseases. Therefore, if several of these signs are present, the child should be seen by a doctor immediately.
Video: how to suspect you have a chronic form of nephritis
Causes
As mentioned above, the disease for reasons of development can be primary or secondary. In the first case, nephritis is formed as a result of primary renal diseases. The primary form accounts for about 80% of all clinical cases of morbidity.
The secondary form of nephritis develops against the background of existing pathological processes in the body.
Causative agents of nephritis:
- gonococcus;
- streptococcus;
- Pneumococcus;
- meningococcus
The main causes of nephritis:
- autoimmune diseases;
- nephropathy during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- amyloid dystrophy;
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- cancer;
- diseases of infectious nature;
- some diseases of the female reproductive system;
- thrombosis;
- urticarial rashes;
- long-term use of certain groups of synthetic medications;
- intoxication of the body with poisons or heavy metals.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a nephrologist or urologist. The doctor studies the patient’s medical record, asks for complaints, and conducts a physical examination, which includes the Pasternatsky test - tapping in the lumbar region at the level of the kidneys. If the patient experiences obvious discomfort or pain, this is a sign that the kidneys are inflamed.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory tests include:
- general urinalysis - the presence of hidden blood in the form of red blood cells in the urine, as well as the presence of protein indicate renal dysfunction and inflammation,
- bacterial culture of sediment - normally urine should be sterile, but if bacteria are present in significant quantities, this indicates an infection in the urinary system,
- biochemical blood test for urea nitrogen - if the indicator is elevated (from 16-20 mmol/l), this indicates an active inflammatory process in the kidneys or a violation of water-salt metabolism,
- a test for the level of creatinine in the blood is the final product of protein metabolism, which is formed in the liver and excreted by the kidneys; a significant excess of the indicators indicates problems in the functioning of the kidneys, including chronic renal failure.
Normal levels of creatinine in the blood: women - 53-97 µmol/l, men - 62-115 µmol/l, for infants under 1 year - 18-35 µmol/l, children under 15 years - 27-62 µmol/l.
Instrumental studies
Instrumental methods of examining the patient are important for diagnosis:
- Ultrasound examination is intended to establish a general picture of the condition of the kidneys, their size, contour, presence or absence of edema, stones, sand.
- Computed tomography can be performed with or without a contrast agent, which is previously injected into the patient’s vein. The study allows you to study in detail the structure of the organ in a three-dimensional image, as well as adjacent tissues of the urinary system. The method allows you to determine the functional state of the kidneys, including their vessels, nutrition through the bloodstream.
As for acute nephritis, a kidney biopsy is one of the best ways to diagnose the disease. Such an analysis is not always indicated, but only in the case of a controversial diagnosis or ineffective previously prescribed treatment. A biopsy involves taking samples of kidney tissue for microscopic analysis using a long needle that is inserted directly through the patient's skin.
Preventive measures against nephritis
In order not to encounter renal pathology of any kind, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, always dress and put on shoes only according to the weather
. To avoid encountering renal pathology of any kind, you must adhere to these simple rules:
- Avoid hypothermia, always dress and put on shoes appropriate for the weather.
- If you work at a chemical plant, undergo a medical examination on time and regularly.
- Follow the drinking regime and diet of a healthy person (excluding carcinogens, introducing a large amount of fresh herbs, vegetables, fruits and dairy products into the diet).
- Follow the rules and principles of intimate hygiene.
- Be selective about sexual intercourse with mandatory protection with condoms.
- Quit alcohol and smoking, or at least reduce bad habits to a minimum.
- Avoid excessive exercise and sports injuries.
- And the most important thing is not to suffer viral infections on your feet and fully treat them.
Treatment options
Nephritis is a serious kidney disease that requires constant monitoring by a nephrologist. Treatment options depend on the type of nephritis and its cause, as well as the symptoms, age and general condition of the patient. The goal of therapy is to slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
Treatment of some types of nephritis, such as interstitial or toxic, may require addressing the underlying cause of the disease. If it is a specific medicine, then the doctor will be forced to select an alternative drug.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is usually long-term and takes from 20 days to one and a half months. To treat bacterial or purulent nephritis, as well as infection associated with inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets or intravenously. The following groups of antibacterial drugs are used:
- cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, Cedex, Zinnat),
- aminopenicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoxin),
- fluoroquinolones - (Tsiprolet, Nolitsin, Flexid),
- aminoglycosides - (Gentamicin, Amikacin).
Sometimes the treatment regimen involves a combination of antibacterial drugs with uroseptics of plant origin, such as:
- Canephron,
- Cyston,
- Phytolysin,
- Urolesan.
If the disease is accompanied by severe pain symptoms, then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed to relieve it:
- Ibuprofen,
- Indomethacin,
- Diclofenac.
Poor kidney function negatively affects the balance of electrolytes in the body, such as magnesium, sodium, potassium, due to which the necessary chemical reactions occur in the human body. If the level of electrolytes exceeds the norm, the doctor prescribes diuretics (Furosemide, Diuver, Veroshpiron) to remove excess minerals, as well as excess fluid in the urine and reduce swelling. If a lack of electrolytes is detected, supplements of these elements in tablets are indicated, for example, potassium, magnesium or phosphorus preparations.
Poor kidney function is also a cause of high blood pressure, which can be controlled with hypertension medications, including:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, such as: Captopril,
- Lisinopril,
- Perindopril,
- Losartan,
If nephritis is caused by an autoimmune disease, then corticosteroids (Prednisolone) are used in treatment - they reduce the immune response.
Acute nephritis is characterized by a state of general increasing intoxication, since the efficiency of the kidneys is greatly reduced, and they cannot cope with the disposal of waste and toxic substances. This situation is dangerous due to complications in the functioning of other vital organs, in particular the liver. To prevent secondary damage to organs, intravenous administration of anti-intoxication solutions in the form of droppers is used. These include drugs:
- native plasma,
- sodium chloride,
- glucose solution 5%,
- Reamberin.
To eliminate intoxication, enterosorbents are also used, for example, Enterosgel.
Photo gallery: drugs used in the treatment of nephritis
Canephron N is a herbal preparation with diuretic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects.
Ibuprofen is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug that relieves pain due to nephritis
Cefotaxime is a broad-spectrum antibiotic necessary in cases of bacterial nephritis.
Captopril helps manage high blood pressure due to nephritis
Prednisolone is a hormonal drug that helps suppress inflammation in the kidneys
Other treatments
Another method of reducing inflammation and purifying the blood of toxic components and antibodies due to improper functioning of the immune system is therapeutic plasmapheresis. This is the process of collecting a portion of blood for the subsequent separation of formed elements (red blood cells, white blood cells) from its liquid part, called plasma, and replacing it with intravenous fluids or donor plasma, which does not contain antibodies. The formed elements with renewed plasma are then returned back to the bloodstream.
If the patient’s condition, despite the medication measures taken, worsens and kidney failure develops, he will need to undergo a lifelong blood purification procedure - hemodialysis, or an “artificial kidney”.
Dialysis is a machine that filters toxic waste as well as excess fluid from the blood. It is this job that the kidneys do in the body in healthy people.
Hemodialysis is performed in a specialized medical center or hospital. First, a small operation is performed on the person, during which a special type of access is formed on the patient’s arm, called an arteriovenous fistula, or shunt, which is an artery and vein connected together. Less commonly, an external (intravenous) catheter is inserted. The patient is then connected to a hemodialysis machine. Blood is pumped through a tube into a machine to filter waste and additional fluid. The purified blood goes back into the patient's body through another tube.
Hemodialysis is usually performed several times a week. Each session lasts from 4 to 5 hours. During the procedure, adults can read, watch movies, children can play any static games.
Traditional methods
In addition to drug treatment for nephritis, various herbs are used, which help more effectively fight kidney inflammation. Homemade medicines have mild anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and diuretic effects. Despite the availability and ease of use of herbal remedies, using them without consulting a doctor is strictly contraindicated.
Bearberry infusion is used for chronic nephritis. To prepare it you need:
- Brew a tablespoon of herb with a glass of boiling water.
- Infuse the medicine for half an hour.
- Take one tablespoon of infusion five times a day.
The second way to use bearberry for nephritis is to prepare a decoction:
- Add a tablespoon of bearberry to 500 ml of cold water.
- Cook until a third of the liquid has evaporated.
- Strain the resulting medicine and divide it into three equal parts to take in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Bearberry can be combined with lingonberry leaves. A decoction is prepared from these components:
- Pour two tablespoons of bearberry and the same amount of lingonberry leaves into 2 liters of cold water.
- Evaporate the resulting mixture over low heat.
- When about half of the original volume remains, you should cool and strain the medicine.
- Take 150–200 ml 3 times a day.
As a preventive measure, as well as for the treatment of kidneys, vegetable juices with antibacterial and diuretic effects are used:
- potato,
- beetroot,
- radish juice
Drink 100 ml of natural freshly squeezed juices three times a day before meals.
Nettle decoction is very effective as a diuretic and anti-inflammatory agent. It is prepared like this:
- You need to take 1 tbsp. spoon of dry nettle per 250 ml of boiling water.
- Cook in a water bath for 10 minutes.
- Cool, strain and take 125 ml before meals 2-3 times a day.
Black elderberry has an excellent diuretic and disinfectant effect:
- Pour 250 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of black elderberry flowers or fruits.
- Leave for 30 minutes, strain.
- Take 125 ml three times a day before meals.
Photo gallery: components of folk recipes for the treatment of jade
Bearberry is widely used to treat diseases of the kidneys, bladder and the entire genitourinary system.
Lingonberry acts as a natural antiseptic
Nettle decoction improves metabolism in the kidneys
Black elderberry is a natural diuretic and antiseptic.
Beetroot juice is an excellent prevention of nephritis
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods can be used as auxiliary methods for chronic nephritis:
- UHF therapy is a therapeutic effect of an electric field (output power from 15 to 80 watts) through special metal plates in an insulating shell, which are placed in the area of the diseased organ. The UHF electric field has an anti-inflammatory effect, stimulates metabolic processes and tissue regeneration, and acts as an analgesic and antispasmodic.
- Balneotherapeutic procedures - pine, oxygen and general carbon dioxide baths activate metabolism in damaged tissues, improve lymph and blood circulation.
- Drinking low-mineralized waters is used to correct ion exchange in the kidneys (Naftusya, Essentuki No. 20, etc.). The specific name of the water and its dosage are prescribed by the doctor.
Diet food
General rules of dietary nutrition for nephritis involve the patient switching to a low level of consumption:
- sodium (salt),
- potassium,
- squirrel,
- fats,
- phosphorus.
The patient is prescribed a predominantly plant-based and dairy-based high-vitamin diet.
Thus, it is recommended to drink only vegetable juice during the first few days of the disease. This will help cleanse the urinary tract and remove toxins from the blood. After the period of eating vegetable juices, you must follow a fruit diet for about 4-5 more days. Then alternate dairy products and fruits for another week or so.
Finally, the patient can gradually switch to a vegetarian diet for up to several months until the nephritis is completely cured or goes into remission. It is useful to eat foods such as:
- carrot,
- cucumber,
- celery,
- oranges,
- pineapples,
- grape,
- peaches,
- apples,
- goat milk,
- nuts.
You can add more variety to your daily meals by adding bananas, avocados, papaya, asparagus and parsley. These products do not burden the kidneys and help to subside the inflammatory process in them.
Tobacco and alcohol are on the prohibited list for patients with nephritis.
Foods that a patient with nephritis should strictly avoid:
- White bread,
- caffeine,
- spicy, fatty and fried foods,
- salted cucumbers,
- sauces,
- refined and processed foods,
- sugar and confectionery,
- fat meat,
- salt.
Products containing oxalic acid are strictly prohibited:
- chocolate,
- cocoa and cocoa products,
- spinach,
- rhubarb.
Features of diet for different types of jade
Depending on the type of jade, the doctor adjusts the patient’s diet:
- A nutrition plan for glomerulonephritis usually involves limiting the number of tea drinks and consumption of other drinks to make it easier for the kidneys - instead, liquids from fruits and soups are recommended. The diet limits phosphorus intake. Milk, yogurt, peas, nuts and beans contain it and should be avoided.
- The diet for interstitial nephritis contains many B vitamins and calcium, while being low in calories. Fluid intake may also be limited.
- The diet during pyelonephritis, on the contrary, includes drinking plenty of fluids. It helps to naturally flush out pathogenic microorganisms. Patients are advised to drink a lot of water; cranberry juice is very useful, which is a natural antiseptic for the urinary tract. Food should not contain too much salt, oil and spices.
The basic concept of nutrition for any type of nephritis is to avoid foods that accumulate large amounts of toxins or other substances excreted by the kidneys. The prescribing of a diet for a specific patient is carried out exclusively by a nephrologist.
How to treat kidney inflammation
A nephrologist or urologist prescribes drug therapy, bed rest and a diet with strict salt restriction. This measure will force the body to intensively secrete water and lead to a decrease in swelling and hypertension.
In case of acute pyelonephritis, it is advisable to go to the hospital. If the disease occurs in a purulent form, being under the supervision of doctors is mandatory.
Treatment with medications
Nephritis is treated with penicillin antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Carbenicillin, Ticarcillin) and fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Norfloxacin). Medicine to reduce edema - Furosemide and similar diuretics. Cardiac activity is supported by antihypertensive drugs (Atenolol, Metoprolol).
If necessary, drug therapy for nephritis is supplemented with antihistamines (Kestin, Loratadine).
For normal functioning of the urinary system, vitamins A, C, E, which have antioxidant properties, are necessary. Vitamin P (rutin) stimulates urine production.
Blood purification
A diseased nephron may not cope with its functions of cleaning the body. In this case, treatment of kidney nephritis involves hemodialysis. This is a procedure for cleansing the blood of nitrogenous substances using an artificial kidney medical device. A process that replaces the natural function of the kidneys removes toxic substances, fluid, urea, and creatinine from the body.
To connect to the device, a preliminary operation is performed on the forearm, forming a vessel. During the hemodialysis procedure, a needle with a tube is inserted into the vessel, the blood enters the “artificial kidney” machine, where it is purified. After which the blood is delivered back to the patient’s vessels.
Hemodialysis is carried out 3 times a week, the duration of the procedure is 4 hours. The patient is on artificial purification until transplantation of a donor kidney or for life.
For chronic renal failure, peritoneal dialysis is also used. The abdominal cavity is periodically filled with a special saline solution through a drainage tube inserted through a puncture in the abdominal wall. A person is injected with about 2 liters of dialysate. The solution is in the abdomen, equalizing the concentration of harmful substances, then an excretory catheter is used to drain it.
Diet
A necessary condition for therapy is treatment table No. 7, developed by M.I. Pevzner, and his variants. A salt-free, gentle diet involves limiting proteins, especially meat and fish. Instead, they eat eggs and dairy products. Carbohydrates and fats are included in the menu in the same way as in a normal diet.
The diet is designed to reduce swelling and stimulate the removal of metabolic products from the body. Meals are fractional, 5-6 times a day, the amount of free liquid is limited to a liter per day.
Surgical techniques
Surgery is indicated for purulent pyelonephritis. Doctors decapsulate the kidney, remove ulcers and carbuncles. If it is impossible to excise the affected areas, the kidney is removed (an operation called nephrectomy).
In incurable stages of chronic renal failure, a donor kidney transplant is performed. Of all the means of renal replacement therapy - hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and kidney transplantation - transplantation is the most effective. Whenever possible, such operations are performed on children, since the development of a child on hemodialysis causes difficulties.
Folk remedies
In the acute stage, using folk remedies is pointless and even dangerous. When nephritis is in remission, herbal kidney teas are brewed. They eat lingonberries, bearberry (1 tbsp per glass of boiling water), and a decoction of young birch leaves.
The decoction is prepared in this way: 200 g of leaves and a tablespoon of birch buds are poured with a liter of boiled water. Heat over low heat for 20 minutes, cool, filter. Drink a tablespoon 3-4 times a day.
Lingonberry has a diuretic (diuretic) and antiseptic effect. To treat jade, take a decoction of lingonberries (100 g of leaves per 2.5 liters of boiling water), lingonberry juice (a quarter glass of berry juice in 3/4 glass of water). Pharmacies sell ready-made tea or herbal tea Nephrotin Healthy Kidneys. Lingonberries are used with caution for urolithiasis.
Folk remedies are used on the principle of “do no harm” after mandatory consultation with the attending physician.
Prevention and lifestyle for nephritis
Certain lifestyle habits can help protect your kidneys. People with nephritis should do the following:
- Follow a low-salt diet, especially if you have renal hypertension.
- Eat foods low in potassium, phosphorus, and protein if decreased kidney function is detected.
- Drink enough fluids for pyelonephritis and lupus nephritis, or adhere to the drinking regimen prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Engage in moderate physical activity regularly.
- Monitor blood pressure readings.
- Limit cholesterol intake.
- Avoid frequent use of medications that may affect the kidneys, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, etc.
Following these recommendations will contribute to successful recovery from the disease and prevent possible relapses or exacerbations of nephritis in the future.
Treatment of kidney inflammation (nephritis) with folk remedies
Important!
Before using folk remedies for treating jade, be sure to consult your doctor! Collection for nephritis - 1. Mix crushed flax seeds, birch leaves, stinging nettle and strawberries in equal proportions. Next, 1 tbsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture and place it in a water bath for 15 minutes, covering with a lid. Afterwards, cool the product, strain and drink 2 times a day, a glass at a time, 15 minutes before meals.
Collection for jade - 2. Mix the following crushed ingredients in the following proportion - 30 g of tall ash root, 10 g of oregano herb, 10 g of lingonberry leaves and 5 g of common hop cones. Pour this mixture into 1 liter. Place the water on the fire, boiling the product for about 20 minutes. Cool the product, strain and take 100 ml 3 times a day.
Collection for jade - 3. Mix the following crushed ingredients in the following proportion - 30 g of coltsfoot leaves, 25 g of yarrow flowers, 25 g of St. John's wort herb and 20 g of nettle leaves. 1 tbsp. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over a spoonful of the mixture, cover with a lid and set aside for a couple of hours to infuse. Next, you need to strain the product and drink half a glass 2 times a day for 25 days.
Parsley. Chop 2 thick parsley roots and pour 500 ml of water and 500 ml of milk into them. Stir, boil and boil the product a little, then cool it. You need to take the decoction 100 ml per day for 30 days, after which you take a month break and the course can be repeated.
Pumpkin. Remove the top of the pumpkin and remove the inner fibers and seeds. Pour a mixture of 250 g of sunflower oil and 250 g of sugar into the pumpkin and cover it with the cut off top. Place the pumpkins in the oven and bake it. Next, remove the crust from the baked pumpkin and grind it with the internal contents until smooth. You need to eat 1 tbsp of cooked porridge. spoon 3 times a day.
Complications and prognosis
The long-term outlook for a patient with nephritis depends on the type of disease and the extent of kidney damage. If the acute stage of glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis is treated in time, the disease can be temporary and reversible. The chronic course can also slow down with timely and adequate therapy. The main complications accompanying nephritis:
- accumulation of waste in the blood (azotemia),
- high blood pressure, edema, congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema due to excess fluid in the body,
- loss of electrolytes, such as sodium chloride and potassium, affecting nerve and muscle function (dangerous from the point of view of disruption of normal heart function),
- a decrease in the secretion of acids leads to their accumulation in the blood (metabolic acidosis), which causes neurological and muscle disorders,
- the danger of infection spreading throughout the body through the blood (septicemia) and death.
A more serious prognosis is for persons with hereditary nephritis or nephritis of an autoimmune nature, where preventive measures are powerless. The complex of therapeutic measures is designed to “slow down” nephrosclerotic processes for as long as possible. However, the fatal outcome of this disease ranges from 10 to 30%. And with hereditary nephritis with simultaneous hearing damage, mortality at a young age reaches 40% of patients (usually males).
Pregnancy in women with hereditary nephritis should be under the strict supervision of a nephrologist and a geneticist to exclude serious renal pathology in the child, especially a boy. It is known that pregnant women suffering from chronic kidney inflammation are characterized by an exacerbation of the manifestations of the disease while expecting a child: an increase in proteinuria, azotemia, and an increase in arterial hypertension.
The most serious complication of nephritis is kidney failure. People with this diagnosis require either dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis is usually the first choice for treatment, but it will not work indefinitely. Most dialysis patients eventually require a kidney transplant. Unfortunately, it can take years to receive a donor organ.
Treatment
Treatment of nephritis is carried out only in a hospital setting with strict adherence to bed rest. The doctor must prescribe a diet for nephritis. During the first two days, the patient should drink only 400 ml of water and eat 100 grams of sugar. The dose cannot be exceeded! This is the first stage of the diet for nephritis. Next, a diet with limited consumption of table salt is prescribed. It is allowed to eat no more than five grams of salt and drink up to 1500 ml of liquid. Animal proteins should also be limited in the diet. Fatty broths, spicy and salty foods are completely excluded. All this is replaced by low-fat varieties of fish, which are recommended to be consumed only in steamed form. The patient is also advised to eat fruits, vegetables and dairy products.
If you have nephritis, it is recommended to eat fruits and vegetables
Conservative therapy involves prescribing the following groups of synthetic medications:
- antibacterial;
- cardiac;
- antihypertensive;
- diuretic;
- antiallergic;
- immunosuppressants;
- calcium;
- routine;
- ascorbic acid.
In case of complex nephritis, treatment should only be comprehensive. Cytostatics and glucocorticosteroids are also added to the above medications. In emergency cases, hemosorption and plasmapheresis are indicated. Surgical treatment is also used, which will be aimed at removing the source of infection from the body.
If severe renal failure has developed, then the only correct method of treatment is kidney transplantation.
Complications
Kidney inflammation is a serious pathology that requires timely and adequate treatment. If the symptoms of the disease are ignored, the problem progresses with the development of undesirable consequences.
Complications of nephritis:
- Acute or chronic renal failure.
- Sepsis.
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys.
- Hypertension.
- Blood clotting disorder with the formation of blood clots and the development of stroke or myocardial infarction.
To minimize the risk of developing corresponding nephritis complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time for qualified help.