Paracetamol suspension for children instructions for use
How long does it take for paracetamol suspension for children to start working? What are the indications and contraindications for use? In order to answer these questions, you must carefully study the instructions for use of the product.
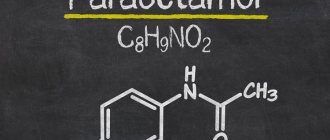
Paracetamol is a non-steroidal analgesic that has a powerful antipyretic and analgesic effect on the body. However, it should be used only on the recommendation of doctors, especially for the treatment of young children, since the drug has a number of contraindications and side effects. We will consider the composition, release forms and negative effects on the body in the following paragraphs.
Tips for taking medications that contain paracetamol
- There are various forms of release of this active ingredient. It can be in candles, syrups or in the form of a suspension. They are best suited for children under one year old.
- To reduce the harmful effects on the liver, the medicine should be given after meals.
- A dosage of 150 mg per kilogram of weight is dangerous for a child’s body.
- An overdose can be recognized by the following symptoms: the skin becomes pale, nausea and vomiting appear. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Sometimes, when the temperature is high and falls heavily, children are prescribed two drugs at the same time: Nurofen and Paracetamol. These drugs are given at intervals. Nurofen acts quickly and the effect is longer lasting.
You can combine Nurofen with paracetamol at the same time. In this case, half the dose is taken from each drug.
Release form and composition
Paracetamol has several forms of release:
- Suppositories;
- Pills;
- Syrup;
- Capsules;
- Effervescent solution;
- Syrup.
The suspension contains 2.4 grams of the active ingredient. As additional ingredients, it contains liquid sorbitol, strawberry flavor, purified water, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, xanthan gum, sucrose, glycerol.
Note! In addition to ready-made syrup, you can purchase special granules in pharmacies for preparing paracetamol suspension. Pharmstandard granules are the same paracetamol suspension for children, but not in a diluted form, but in a dry form. According to the instructions for use, they have similar therapeutic properties and are diluted in boiled water.
We are treated correctly
Paracetamol is not a panacea for all diseases. Yes, it helps relieve pain and relieve fever. But there is no need to force medication on your baby if there is a small mark on the thermometer or if there is a slight malaise. It is necessary to observe the measure, maintain intervals. You should always consult a doctor first, as thoughtless self-medication will only aggravate the situation and harm the baby’s health. You must read the instructions carefully. Inaccessibility to children is an important storage condition.
Previous post How to teach a child to eat with a spoon on his own - when to teach children to eat, recommendations
Next entry Sore throat in a child - causes and symptoms, treatment of sore throat in children
pharmachologic effect
The therapeutic properties of the drug lie in its effect on thermoregulation centers and pain centers, resulting in an increase in the threshold of sensitivity to pain. The drug has high absorption and reaches its maximum concentration in plasma after two hours.
The main advantage of the drug is the fact that it does not accumulate in the blood and is completely eliminated from the body four hours after administration. Excretion is carried out through the kidneys. But at the same time, the substance tends to accumulate in small quantities in breast milk, which precludes taking paracetamol during lactation.
Overdose
In case of overdose, there is a risk of developing intoxication, especially in patients receiving concomitant inducers of microsomal liver enzymes, in persons with malnutrition, patients with liver diseases and children. As a result, cholestatic hepatitis, liver failure, cytolytic hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, sometimes with death, may occur.
Symptoms of acute poisoning: pale skin, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, metabolic acidosis, impaired glucose metabolism (sweating, dizziness, loss of consciousness). After 1-3 days, signs of liver damage appear (pain in the liver area, decreased prothrombin levels, increased bilirubin concentrations and liver enzyme activity), which reach a maximum on days 3-4. In the case of a single dose of paracetamol in a dose of 10,000 mg/kg for an adult, and a dose of 125 mg/kg for children, cytolysis of hepatitis occurs with the development of encephalopathy, metabolic acidosis, complete and irreversible liver necrosis, liver failure - serious complications that can lead to coma and fatal outcome.
In case of severe overdose, progressive encephalopathy, liver failure, coma, and death occur. Acute renal failure with tubular necrosis without severe liver damage may also develop. Its characteristic symptoms are pain in the lumbar region, proteinuria, hematuria, as well as pancreatitis and arrhythmia.
In case of long-term use of the drug in doses exceeding the recommended ones, the development of hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects is possible: nonspecific bacteriuria, renal colic, interstitial nephritis and papillary necrosis.
In case of overdose, you should stop taking paracetamol, if possible, do a gastric lavage, take an enterosorbent (activated carbon or polyphepane) and immediately consult a doctor. Treatment is predominantly symptomatic. As soon as possible after an overdose, it is necessary to determine the content of paracetamol in the blood plasma. In case of poisoning, SH-group donors, acetylcysteine and methionine (precursors for glutathione synthesis) must be administered within the first 10 hours. The need for additional therapeutic measures (including further administration of methionine and acetylcysteine) is determined by the doctor depending on the level of paracetamol in the blood and the time that has passed since its administration. Liver tests are performed at the start of treatment and every 24 hours thereafter. Liver enzymes return to normal within 1-2 weeks in most cases. Severe overdose may require a liver transplant.
If a child accidentally takes the drug on his own, he should immediately seek medical help, even if he feels well. 24 hours after taking paracetamol, in case of serious liver disorders, treatment is carried out jointly with specialists from a specialized hepatology department or a toxicology center.
Indications for use
Children's syrup or suspension of paracetamol according to the instructions for use is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- Pain syndrome of various types, including headaches and toothaches.
- Painful sensations during teething.
- Migraine.
- High fever along with infectious and viral diseases.
- Neuralgia.
- Hyperthermia after vaccination.
What kind of medicine is this
Paracetamol is a non-narcotic pain reliever. The anti-inflammatory effect is so little expressed that it is not taken into account when prescribing. For problems with blood pressure, the drug is also absolutely safe.
The drug is not an antiviral or antibiotic; its effect is purely symptomatic.
Paracetamol should be taken with caution in case of kidney and liver diseases, as well as diabetes mellitus, when it comes to suspension or syrup. This drug is also contraindicated in case of fructose intolerance. Allergic skin reactions in the form of urticaria, itching, and redness are possible.
The action of Paracetamol begins on average forty minutes after administration . It is more rational to take it an hour or two after a meal, since the medicine taken immediately after a meal will be absorbed much longer, which will delay the onset of the effect.
Taking Paracetamol on an empty stomach is also contraindicated to avoid reactions from the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications
If you follow the method of using children's paracetamol in suspension according to the instructions, the drug rarely causes side effects and is well tolerated by the body. But in some cases, using the product is contraindicated. Such contraindications include the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity to components;
- Kidney or liver failure;
- In complex treatment along with other medications that contain a similar active substance;
- Lack of glucose in the blood;
- Pathologies of the organs of the hematopoietic system;
- Children under three months of age.
Note! In addition to a number of contraindications presented, this drug should be used with caution in patients who suffer from viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, Gilbert's syndrome, anorexia and diabetes mellitus.
Drug interactions
Caution should be exercised when concomitant use of drugs that induce microsomal liver enzymes is necessary, such as ethanol, barbiturates, phenylbutazone, anticoagulants, rifampicin, tricyclic antidepressants, zidovudine, isoniazid, anticonvulsants, amoxicillin + clavulanic acid.
Preparations of St. John's wort, butadione and flumecinol increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, as a result of which in case of overdose (taking 5000 mg or more), the risk of developing severe liver damage increases.
Paracetamol increases the elimination time of chloramphenicol by 5 times, which increases the likelihood of poisoning. Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Paracetamol, taken in a daily dose of 4000 mg for 4 or more days, when administered simultaneously, can enhance the effect of indirect anticoagulants, so the International Normalized Ratio should be monitored during and after taking this combination. If paracetamol is taken irregularly, it does not have a significant effect on the effect of anticoagulants.
With long-term simultaneous use of other NSAIDs, the risk of developing renal papillary necrosis, “analgesic” nephropathy and end-stage renal failure increases.
Alcohol consumed during treatment with paracetamol contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis.
Simultaneous long-term use of paracetamol in high doses in combination with salicylates increases the risk of developing bladder or kidney cancer.
Possible drug effects of other drugs on paracetamol:
- probenecid reduces its clearance by almost 2 times due to inhibition of the process of its conjugation with glucuronic acid;
- domperidone and metoclopramide increase the rate of its absorption;
- cholestyramine reduces the rate of its absorption;
- Long-term use of barbiturates reduces its effectiveness;
- diflunisal increases its plasma concentration by 2 times, as a result of which the risk of developing hepatotoxicity increases;
- phenytoin reduces its effect and increases the risk of hepatotoxicity;
- myelotoxic drugs enhance the manifestations of its hematotoxicity.
Inhibitors of microsomal oxidation (including cimetidine), when used simultaneously, reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Directions for use and doses
According to the instructions for use, 5 ml of suspension contains 120 mg of the active substance - paracetamol. The product should be used orally, undiluted, after meals and with plenty of water. Shake the medicine well before use. The frequency of taking paracetamol suspension for children and adults should not exceed four times, and it is necessary to maintain an interval of four hours between doses. It is during this time that the substance is completely excreted by the kidneys.
The dosage for infants is determined by the doctor depending on weight and age. A single dosage should not exceed 15 milligrams. To dose the drug according to the instructions for use, use a special measuring spoon or syringe, which comes with the bottle.
In order to use the measuring syringe correctly, you must perform the following steps:
- Shake the medicine well.
- Unscrew the cover.
- Insert the syringe tightly into the opening of the bottle in the neck and turn the bottle vertically.
- Take the required amount of suspension that corresponds to the given age category of the child.
- Return the bottle to its original position and carefully remove the syringe from the neck.
- Give the child the medicine internally by gently pressing the plunger of the measuring syringe.
- Wash the syringe with running water and dry at room temperature until the next use.
Depending on the age category of the child, the medicine is prescribed in the following dosages:
- For a single dose for children 3-6 months after vaccination – 2 milliliters;
- From three months to one year – 5 milliliters;
- From one year to six years – 10 milliliters;
- From six to ten years - 15 milliliters.
The duration of treatment for fever should not exceed three days. For the treatment of pain syndromes, the drug can be used for five days.
At what age can children take paracetamol tablets?
Paracetamol for children can be given in 200 mg tablets from the age of three years. However, for a child it is better to choose children's forms in the form of syrup, suspension or suppositories.
For some children, even after three years, it is problematic to swallow even a crushed tablet. Since the crumbs of the medicine stick to the oral mucosa, they can cause a gag reflex. And of course the pill tastes terrible. But sometimes it happens that mom only has pills on hand, and there is no way to run to the pharmacy.
Before giving paracetamol tablets to a young child, you need to crush them and dilute them in water.
Paracetamol for children dosage in tablets from 3 to 12 years
IMPORTANT! Children at the same age can weigh differently! Therefore, it is better to calculate the dose by weight. To do this, multiply the child’s weight in kilograms by 10 and get the number of milligrams of medicine that can be given in one dose.
EXAMPLE : If a child weighs 20 kg, then a single dosage (20*10=200) is 200 mg.
The daily amount of paracetamol should not be more than 60 mg of the drug per 1 kg of the child’s weight. If a child weighs 15 kilograms, then the maximum you can give per day (60*15=900 mg) is 4 tablets. The maximum number of doses per day should not be more than four.
Take the drug an hour or two after meals. Paracetamol begins to act 30-60 minutes after administration.
IMPORTANT! If after taking paracetamol for more than three days, the rise in temperature does not stop, call your doctor again!
Other children's antipyretics READ
conclusions
Despite the relative safety of the drug, it is necessary to remember the possible serious consequences and under no circumstances self-medicate, especially when it comes to the health of the child. However, in emergency cases, parents need to know what to do to provide emergency assistance to their baby before the doctor arrives.
A rise in temperature is just a symptom. By acting only on it, it is impossible to stop the course of the disease. Therefore, taking Paracetamol will help relieve symptoms of fever or pain, but only the attending physician should identify the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
How to choose a thermometer for a child, read here, because, in addition to mercury, there are more convenient forms for newborns, in the form of a pacifier, or for capricious ones - non-contact thermometers.
We recommend reading the article about what first measures should be taken if a child gets his feet wet.
Dosage and rules of administration
Parents are primarily interested in how many Paracetamol tablets to give to a child aged 7 years. Tablets may contain 0.2, 0.325 and 0.5 g of active ingredient. When calculating the dose of medicine for a baby, his age and weight are taken into account. If the baby’s weight is within its age norm, then the dosage of Paracetamol for children 7 years old (up to 30 kg) is no more than 1.5 g per day . This dosage should be divided into 4 doses, with at least 4 hours between them.
Description and properties of the drug
The appearance of the drug depends on the form of release. As for the tablets, they are white. The syrup is presented in liquid form, making it convenient for newborns to drink. The suppositories are white with a creamy tint; they are inserted into the anus; it is recommended at a very high temperature.
In any form, paracetamol is primarily an antipyretic drug that relieves muscle pain and headaches.