Medicines for the treatment of bronchial asthma are often produced in the form of aerosols. This type of drug is most convenient to use. The active ingredients quickly get where they are needed and produce the desired effect. Due to this, it is possible to relieve an asthmatic attack and achieve improvement.
Many patients use the asthma inhaler Salbutamol. This drug contains an active substance with the same name. Its main task is to restore the patency of the airways, which helps relieve the attack. This is a potent remedy, so it can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. You also need to know the rules for its use.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Salbutamol
Salbutamol is a selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Stimulates mainly β2-adrenergic receptors localized in the bronchi, myometrium, and blood vessels. When administered by inhalation, it acts mainly on β2-adrenergic receptors of the bronchi, with little effect on β2-adrenergic receptors of other localizations. Has a pronounced bronchodilator effect. By causing dilation of the bronchi, it relieves and prevents bronchospasm. Has virtually no effect on β1-adrenergic receptors of the heart. Prevents the release of allergy and inflammatory mediators (histamine, SRSA) from mast cells. Improves mucociliary clearance. The effect of the drug develops quickly and lasts 3–4 hours. After inhalation, approximately 10–20% of the active substance reaches the small bronchi, the rest settles in the upper respiratory tract. Plasma protein binding is 10%. Salbutamol is metabolized in the liver. It is excreted mainly in the urine unchanged and as an inactive metabolite. Most of the dose of salbutamol administered by inhalation or taken orally is eliminated within 72 hours.
Drug interactions
When using Salbutamol in combination with certain drugs/substances, the following effects may develop:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants: increased effect of salbutamol, increased likelihood of a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- non-selective β-adrenergic receptor blockers (propranolol): antagonism of action (the combination is contraindicated);
- glucocorticosteroids, diuretics: increased hypokalemic effect of salbutamol;
- drugs that stimulate the action of the central nervous system: enhancing their effect;
- theophylline and other xanthines: increased risk of tachyarrhythmias;
- levodopa, drugs for inhalation anesthesia: increased risk of developing severe ventricular arrhythmias;
- m-anticholinergics (including inhaled): increased risk of increased intraocular pressure.
Possible combined use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Indications for use of the drug Salbutamol
BA (prevention and relief of attacks), chronic obstructive bronchitis, emphysema and other diseases that occur with bronchospasm. As a tocolytic agent, it is indicated for the threat of premature birth, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, a decrease in the fetal pulse depending on uterine contractions during periods of cervical dilatation and expulsion, for prophylactic purposes - during operations on the pregnant uterus (application of a circular suture for insufficiency of the internal uterine pharynx) .
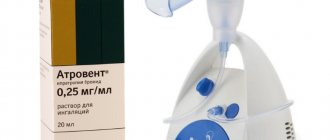
Inhalation of Salbutamol through a nebulizer
Before the inhalation procedure, it is necessary to check the device for serviceability. This is done as follows:
- the cap is removed from the device, then the outlet tube is checked for dust and dirt;
- the can is installed in a vertical position and shakes well;
- the medicine is placed in a nebulizer.
Then the inhalation procedure begins:
- the patient takes a deep breath, throws his head up and firmly clamps the outlet tube with his lips;
- Inhaling slowly and deeply, you need to press the valve of the canister, thus releasing a dose of medicine;
- slowly remove the tube from your mouth, hold your breath for 10 seconds and exhale through your nose.
If you need to take more than 1 dose of Salbutamol during one inhalation procedure, you should repeat all the steps described above, but only after a minute pause. The can is then closed with a cap.
When using an inhaler with Salbutamol, to achieve maximum effectiveness, it is important to follow these recommendations:
The air should be inhaled slowly
- do not rush when releasing the medicine;
- inhale air slowly;
- Before the procedure, it is advisable to practice in front of a mirror.
The duration of inhalation does not exceed 5 minutes. After the procedure, it is necessary to rinse the device thoroughly, carefully removing any remaining solution.
It is important to remember that the initial dosage of Salbutamol should not exceed 2 mg. In severe cases, inhalation of Salbutamol can be carried out every 6 hours. In especially severe cases, the use of Salbutamol solution is possible every 60 minutes. The effect is observed 10 minutes after the procedure.
Use of the drug Salbutamol
Inhalation - adults and children over 4 years of age are prescribed 0.1 mg of salbutamol for inhalation to eliminate bronchial obstruction. If the attack does not stop within 5–10 minutes after the first inhalation, inhalation can be repeated. For preventive purposes, 0.1 mg of salbutamol is also recommended to be administered by inhalation 10–15 minutes before possible contact with the suspected allergen. With long-term use of salbutamol, use 1-2 inhalations (0.1 mg) 3-4 times a day with an interval of at least 3 hours. Long-term use of salbutamol for COPD or asthma is carried out only against the background of basic therapy. Do not use more than 10 doses (1 mg of salbutamol) per day. Orally, adults are usually prescribed 0.002 g 3-4 times a day. As a tocolytic agent to eliminate the threat of premature birth, as well as after operations on the pregnant uterus, it is administered intravenously in a dose of 5 mg in 400–500 ml of isotonic solution or 5% glucose solution at a rate of 15–20 drops (starting from 5 drops) per minute. The infusion rate is adjusted taking into account the intensity of uterine contractions and tolerance (heart rate and other hemodynamic indicators are monitored). Duration of administration: 6–12 hours.
Release form and composition
Dosage forms of Salbutamol:
- tablets (in blisters of 15 pieces, 2 blisters in a cardboard box; 30 pieces in bottles, 1 bottle in a cardboard box; in packages of 100, 500 or 1000 pieces);
- metered aerosol for inhalation: a suspension of almost white or white color, which is under pressure, when exiting the cylinder, it is sprayed in the form of an aerosol stream (in aluminum cylinders with a metering valve and an inhaler nozzle with a protective cap, 1 cylinder in a cardboard box).
Active ingredient in 1 tablet: salbutamol sulfate – 2 or 4 mg.
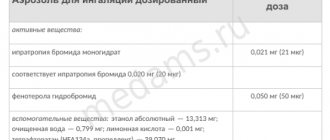
Aerosol composition (1 dose/1 12 ml bottle):
- active substance: salbutamol – 0.1/24 mg (in terms of 100% substance; salbutamol sulfate – 0.1208/29 mg);
- auxiliary components: oleyl alcohol – 0.0625/15 mg; propellant R 134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, HFA 134a) – 56.91/13659 mg; ethanol (rectified ethyl alcohol) – 2.02/485 mg.
The drug does not contain chlorofluorocarbon propellants.
Special instructions for the use of the drug Salbutamol
Use with extreme caution in case of hypersensitivity to sympathomimetics, severe heart disease (chronic ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, rhythm disturbances), hyperthyroidism, unstable diabetes mellitus, pheochromocytoma. During pregnancy, it can be used only for health reasons. Since salbutamol passes into breast milk, its use during breastfeeding is possible only if the expected therapeutic effect for the mother outweighs the potential risk for the child. The use of salbutamol in high doses may worsen the reaction when driving a car or operating machinery. This effect is enhanced by simultaneous use of alcohol and tranquilizers.
Side effects and contraindications
There are no side effects when using Salbutamol in the form of inhalations. They may appear when the daily dose is exceeded or if the patient is overly sensitive. In this case, you may experience:
- decreased blood pressure;
- trembling of fingers and hands;
- dizziness;
- increased irritability;
- convulsions;
- increased heart rate;
- headache;
- angioedema;
- hives;
- redness of the facial skin;
- chest pain;
- anxiety;
- insomnia;
- rhinitis;
- attacks of nausea.
Children experience arrhythmia, excessive excitability, hyperactivity, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
Contraindications
The likelihood of side effects with this drug is minimal if you follow the instructions. Very often, negative reactions to Salbutamol appear due to contraindications that have not been identified. These include:
- heart disease;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- myocarditis;
- IHD;
- glaucoma;
- diabetes mellitus of decompensated type;
- epileptic seizures;
- liver failure;
- aortic stenosis;
- pyloroduodenal narrowing;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- renal failure;
- intolerance to active substances.
There are also conditions for which the drug is prescribed with caution. This:
- pheochromocytoma;
- hypertension;
- hyperthyroidism;
- heart failure.
Salbutamol should not be used together with non-selective beta-blockers, as complications may occur in this case. The drug in the form of inhalations is not prescribed to children under 2 years of age, as well as to pregnant women.
Analogs
The following drugs have a similar effect to Salbutamol:
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Berotek | from 380 rub. | |
| Foradil | from 598 rub. | |
| Onbrez Breezhaler | from 1596 rub. | |
| Clenbuterol | specify |
Analogues in structure:
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Ventolin | from 148 rub. | |
| Saltos | specify |
Medicines with similar composition and principle of action:
Salbutamol or Ventolin - which is better?
Salbutamol and Ventolin are beta-agonists or bronchodilators, so it is difficult to say which is better. Both of them appeared at the end of the twentieth century and have already proven their effectiveness. Some data indicate that people with low sensitivity to one drug remain sensitive to another, so the choice may be more likely to be guided by substitution.
Also, the manufacturer of the first forms of Salbutamol has developed a convenient form of use in the form of a nebulizer, which may serve as a basis for choosing Ventolin.
We recommend reading the article about the drug Pulmicort for inhalation. From it you will learn about the main characteristics of the inhalation drug Pulmicort, how to breathe Pulmicort through a nebulizer, as well as the side effects of the drug and its analogues. And here is more information about the use of the drug Budesonide in the treatment of bronchial asthma.
Salbutamol is an effective drug that is used primarily to treat respiratory diseases and associated bronchospasms. The drug is available only with a doctor's prescription, as it requires strict adherence to doses and consideration of contraindications for use. It is safe to use as directed. There are a number of analogue drugs with identical and similar effects.
Useful video
Watch this video for complete instructions for the drug Salbutamol:
Similar articles
- Inhalations for bronchitis: what can you breathe, how often...
Why are inhalations carried out for bronchitis, which ones can be done - through a nebulizer, inhaling steam. What you can breathe in - oils, saline, soda. What will help with acute, chronic, allergic, obstructive, asmatic bronchitis. Read more - Pulmicort for inhalation: dosage, features...
How to use Pulmicort for inhalation correctly, what doses and course duration for adults and children. How to dilute with saline, breathe correctly with a nebulizer. What is included in the composition, analogues of the drug. Indications and possible harm to the child. Read more
- Asthma inhaler: which one to choose for asthmatics...
How to choose the right asthma inhaler depending on your age. Which is suitable for bronchial or cardiac asthma, for athletes and children. What medicine should I fill the nebulizer with? How to use an inhaler correctly. Read more
- Lazolvan for inhalation: dosage, benefits and harms...
When and to whom is Lazolvan prescribed for inhalation. The benefits and harms of the drug for adults and children. What is better - drinking syrup or inhaling. Dosage of the drug, the possibility of diluting it with saline, water, proportions. How to breathe Lazolvan correctly through a nebulizer. Read more
- Types of inhalers: when to choose a steam...
Main types of inhalers and their main characteristics. What is better to buy - an inhaler or a nebulizer, which one to get for your child. What is different about the Soviet inhaler, how to understand the finely dispersed, steam inhalers. What is a MESH inhaler? Read more
- Is it possible to do inhalations at the temperature and at what...
What do doctors think about whether inhalations can be done at a temperature and what temperature it is - 37, 37.5, 38, why not. What drugs can be inhaled for adults and children - Pulmicort, saline solution, Lazolvan. How you can do inhalations - a nebulizer, an ultrasonic inhaler, MESH. Read more