Arrhythmia is a heart rhythm disorder with an increase, decrease, or periodic change in heart rate (HR) under the influence of external or internal factors. This term combines pathologies of generation and conduction of electrical impulses that are different in their symptoms, mechanism of manifestation and prognosis of development.
Diagnosis and treatment of the abnormality is carried out by a cardiologist, as well as a more specialized specialist - an arrhythmologist. Depending on the etiology of the disease, consultations with a therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, or vertebrologist are required.
Possible causes, risk factors
If we consider all existing cardiac pathologies, the share accounted for by various types of heart rhythm disturbances is impressive. Approximately 10% of people over 60 years of age show signs of arrhythmia, and the prevalence of such diseases among men is one and a half times higher than among women.
Children and adolescents are less susceptible to diseases associated with changes in heart rate: the proportion of sick children is 0.6%.
Disruption of the processes of the myocardial conduction system occurs due to improper formation of electrical signals or failures in the process of their conduction to different areas. As a result, the current jumps to the next node in the chain, so the rhythm gets lost.
Reasons for violations
The described disorder occurs due to the presence of cardiac pathologies or negative manifestations of an internal or external nature.
Pathology is caused by the following heart diseases:
- Cardiomyopathy,
- Heart attacks,
- Ischemic disease
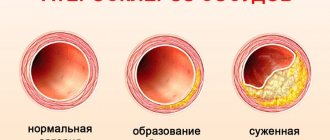
- Atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels,
- Heart defects (especially in children),
- Dystrophy and other myocardial anomalies.
Also, heart rate disturbances can be caused by such phenomena as:
- Diseases of internal organs,
- Vegetovascular dystonia,
- Obesity,
- Hormonal imbalance
- Pathologies of the nervous, endocrine system,
- Poisoning, drug overdose, intoxication,
- Severe stress, emotional distress,
- Anemia,
- electric shock,
- Anesthesia,
- Surgical operations.
At-risk groups
The main factors that can cause various types of pathological changes in the rhythm of contractions are:
- Excessive drinking,
- Smoking,
- Regular infectious diseases
- Mental, physical stress,
- Excessive consumption of energy drinks, caffeine,
- Incorrect medication intake
- Genetic factors (heredity),
- Aged people.
In rare cases, spontaneous arrhythmia is observed, characteristic of people with a quick temper. Why is this variety dangerous? In cases of serious anxiety, patients complain of an irregular heartbeat immediately after the excitement passes.
Heart blocks
This is the name for disruptions in the rhythm of contractions that occur due to problems associated with the passage of nerve impulses through the muscle conduction system. Treatment always depends on the severity of the blockade. Here are the brief principles:
- The second degree of type 2 involves constant stimulation with an external pacemaker. At an early stage, this disease can be stopped, but only if the cause does not lie in heredity. Often this disease develops as a result of drug or medication abuse.
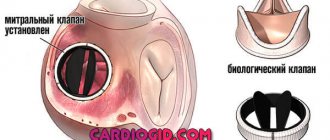
- If the blockage is caused by another heart pathology, the person may have a pacemaker installed.
- The third degree of the disease cannot be treated. Therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. The goal of treatment is to prevent cardiac arrest. So a pacemaker is installed in all cases.
Incomplete second- and first-degree blockades are asymptomatic and therefore require only observation and routine examinations. Although first they need to be identified, but they are detected only during an ECG.
The greatest risk to human life is posed by high-degree blockades, as well as rapidly progressing diseases. Because in such cases, impaired blood flow and heart failure are observed.
Surgery to install a pacemaker is always performed urgently. The procedure is performed using Atropine, Adrenaline, Theophylline and Dopamine. Rehabilitation involves the mandatory use of m-anticholinergic blockers, beta-agonists and sympathomimetics.
Types of arrhythmia
To classify, diseases should be divided into several groups according to the location of the malfunction.
- Malfunction of the sinus node.
- The sinus type is characterized by an abnormal rate of contraction, is common in people under 30 years of age, and often occurs during heavy physical exertion.
- Sinus tachycardia is an increased heart rate.
- Sinus bradycardia is a slow heartbeat.
- Atrial asystole is a total suppression of the functioning of the sinus node.
- Failures in myocardial conduction function or inflammatory processes within this area.
- Blockades in different departments (slowing or stopping the transmission of impulses).
- Excitation of the ventricles too early.
- Simultaneous failures of the processes of conduction, automaticity, excitability.
- Rapid flutter of the ventricles or atria.
- Extrasystole is characterized by the presence of premature contractions.
- Atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation - irregular frequency of contractions.
In addition to the listed diseases, there are other forms caused by the combination of several pathological factors.
A separate group should include functional rhythm disorders, which include:
- Disorders of neurogenic origin. The functioning of the heart is directly influenced by the nervous system, which controls the functioning of all internal organs. The nervous system is a branched network of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that influence the heart muscle in different directions. Increased tone of the vagus (parasympathetic) nerve slows down the rhythm of contractions, and the sympathetic nervous system, with increased tone, increases the heart rate. The reasons for the activation of sympathetic tone are stress, experiencing strong emotions, mental and physical overload, frequent smoking, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, large amounts of caffeine per day, spicy, fatty foods. In addition, sympathetic tone increases in the presence of thyroid diseases, as well as intoxication and blood diseases. There are vagodependent arrhythmias that occur mainly at night, when the activity of the parasympathetic system increases. The causes of increased tone can be various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diselectrolytes cause altered blood composition or the content of chemical elements in the heart muscle (potassium, magnesium levels).
- Iatrogenic types occur due to improper treatment.
- Mechanical ones are provoked by injuries to the sternum, falls from great heights, and electric shock.
- Idiopathic arrhythmias is a term for abnormal heartbeats for which no cause has been identified.
Pediatric arrhythmia
A separate topic is heartbeat disorders in children. They can be congenital or acquired.
The first type occurs while the baby is in the womb, so the task of doctors leading the pregnancy is to regularly listen to the fetal heartbeat. Why does it occur? The main reason is genetic predisposition.
Young children are sensitive to any negative events that cause them strong emotional stress. Frequent scandals between parents and other events that affect the baby’s psyche can cause the development of cardiac diseases.
Diet
It is also necessary to briefly talk about the specifics of nutrition for cardiac arrhythmia. The diet should be different from the usual one - the patient must actively consume foods with a high content of calcium, potassium, magnesium, as well as other microelements necessary for the functioning of the heart.
Also, by adjusting your diet, you can extinguish the receptors of the vagus nerve. After all, it is he who blocks or inhibits the function of the sinus node, thereby provoking malfunctions of the cardiac system.
In addition, healthy eating is a way to combat excess weight and improve metabolic processes. These factors are also the main provocateurs of cardiac failure.
How to cure cardiac arrhythmia at home? Full recovery is a purely individual matter, but what every person suffering from this disease definitely needs to do is include the following products in their menu:
- Fruits rich in microelements and vitamins. These are pears, plums, bananas, raspberries, apples, oranges and currants.
- Vegetables: cabbage, tomatoes, pumpkin, cucumbers, potatoes, beans, beets, red peppers.
- Boiled meat (turkey, chicken and rabbit) and lean fish (steamed, preferably).
- Honey.
- Dairy products - yogurt and low-fat cottage cheese.
- Rosemary, as it strengthens blood vessels.
- Broccoli, because it contains many microelements and vitamins (fiber, iron, phosphorus, among others).
- Avocado, because it contains copper and iron in huge quantities, as well as enzymes that stop the development of arrhythmia.
- Grapefruit, because it is considered the most valuable source of glycosides and plant fiber. Eating it regularly helps strengthen the heart muscle and normalize the metabolic process.
- Parsley, because it is an excellent diuretic, indispensable for arrhythmia.
Prohibited foods also need to be listed, since we are talking about how to cure heart arrhythmia. It is always recommended to give up smoked meats, offal, fatty meat, pickled and salted products, fatty fermented milk, semi-finished products, canned food, eggs (only steamed and soft-boiled omelettes are allowed) and spices.
Symptoms
Since this is a complex of diseases with different characteristics, their symptoms also differ from each other. Let's look at the symptoms of the most common manifestations:
- With sinus tachycardia, an increase in heart rate of 90 beats/min and above is observed. The patient reports shortness of breath, increased fatigue, palpitations, and a feeling of weakness throughout the body.
- In the case of paroxysmal tachycardia, the correct rhythm is traced, but at the same time it is more rapid - from 140 beats per minute. A patient with arrhythmia complains of profuse sweating, weakness, and frequent urination. With a prolonged attack, chest pain appears, even to the point of fainting.
- Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a contraction frequency of 55 beats per minute or lower. Symptoms include low blood pressure, a feeling of weakness, slight dizziness, and “aching” pain in the heart area.
- Symptoms of the sinus type are slow contractions when inhaling and rapid contractions when exhaling. This disease is common among teenagers and women during pregnancy.
- Extrasystole is difficult to diagnose, since the patient usually does not feel any changes in the body. A rare patient may notice a slight increase in the impulse to the heart muscle, which immediately freezes.
- With atrial fibrillation, the ventricles of the heart contract at a rate of up to 150 beats/min, which is a sign of severe heart defects, causing severe pain in the chest, insufficient pulse compared to the frequency of contractions, as well as an irregular heart tone.
- Signs of fluttering of different parts of the heart or their blockade may include such phenomena as cardiac arrest, fainting, thready pulse, convulsions, interruptions in breathing, dilated pupils.
As you can see, the specific symptoms are completely dependent on the species. The list of classification of symptoms is determined by the type of disease, but sometimes arrhythmia is practically asymptomatic, so prevention plays a key role in the fight against the disease.
Let's look at the most common symptoms inherent in different types in more detail.
Increased SS rhythm
A heart rate exceeding 90 beats/min is considered pathologically high. This is a recognized clinical sign of a large group of tachycardias. Often, a rapid heartbeat is accompanied by a feeling of weakness, heavy sweating, and slight shortness of breath. The highest heart rate is considered to be 180 beats in 60 seconds - this is a serious danger to the patient’s life.
Increased heart rate is usually caused by a cold, anemia, high blood pressure, exercise, excessive caffeine consumption, and frequent smoking.
If this indicator is detected, you should undergo electrocardiography and other examination methods. If a stable, frequent rhythm above 100 beats is observed, the doctor determines tachycardia and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Slow SS rhythm
This symptom is not a clinical sign of cardiac pathology, since it is quite often observed in completely healthy people, especially in old age. Bradycardia is dangerous along with such phenomena as dizziness, loss of consciousness, dark spots before the eyes. If the listed ailments are absent, treatment is not required.
Chest pain
Sometimes the pain occurs due to muscle spasms caused by overeating or intense exercise. However, pain in the heart area, which is accompanied by an increase in heart rate and does not stop for a sufficiently long period of time, can be a consequence of a violation of the normal function of the heart muscle. Then you need to call an ambulance and ensure complete rest for the patient.
Loss of consciousness
Practical diagnosis of the cause of fainting is a difficult task. This symptom is characteristic not only of arrhythmia, but also of other pathologies: strong emotional shocks, taking medications, problems with the cardiovascular system. An attack of tachycardia or bradycardia often leads to loss of consciousness, since these types of arrhythmic heartbeat provoke a decrease in cardiac output and an excessive decrease in blood pressure.
Fainting is a short-term period of loss of consciousness, which manifests itself as a person falling to the floor. The main cause of fainting is an interruption in blood supply to the brain. Before fainting, people experience increased sweating, a feeling of nausea, and palpitations. You should be concerned if this symptom recurs frequently - you need to see a doctor to get an ECG.
Dizziness
Usually this sign of arrhythmia is accompanied by a feeling of muscle weakness, nausea, and sweating. Dizziness can also be caused by cervical osteochondrosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia, so for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to undergo a special examination.
Briefly about the pathology
Before we talk about how to cure cardiac arrhythmia, we need to briefly discuss the specifics of this disorder. In general, this term refers to heart disorders that vary in manifestations and mechanisms of occurrence and relate to its rhythm.
Arrhythmias can cause severe disruption of the activity of this muscle and other organs. Often this disorder turns out to be a complication or consequence of serious pathologies.
Symptoms of arrhythmias can be summarized as follows:
- A distinct feeling of heartbeat.
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Interruptions and freezing of the heart.
- Chest pain and pressure.
- Fainting.
- Dyspnea.
If arrhythmia is not treated, the disease will begin to progress. And this is fraught with attacks of angina pectoris, thromboembolism, pulmonary edema, acute heart failure or even death.
What causes cardiac arrhythmia? In general, this pathology can be either a consequence of cardiovascular pathology or an independent phenomenon. That is, the reason lies either in damage to the heart muscle or in other changes in the body: problems with the central nervous system, diseases of the thyroid gland or gastrointestinal tract, electrolyte imbalance, chest trauma, etc.
Diagnostics
As it became clear from the previous part of the article, the clinical manifestations of the disease are quite diverse and numerous, so making a diagnosis requires several studies at once.
If you identify the above-described signs, you should contact a specialist in such diseases - a cardiologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, prescribe an examination of the heart and blood vessels based on the patient’s complaints to determine the cause, and make prognoses for the near future.
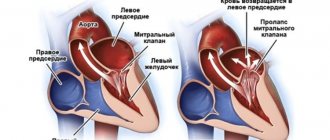
The main methods for diagnosing arrhythmias are listening to the heartbeat, electrocardiography, and echocardiography.
- Electrocardiography allows, through the use of electrodes installed on the surface of the chest, to obtain data on heart rhythm, the presence of ischemia, and residual effects from past diseases. Interpretation of the resulting ECG serves to identify atrial fibrillation.
- Echocardiography uses the properties of ultrasound to assess the condition of the parts of the heart and their functioning. The doctor will be able to measure the size of the sections, determine the thickness of the myocardium, and identify various pathologies.
For irregular manifestations of symptoms, Holter monitoring is used, which consists of round-the-clock monitoring of the heartbeat through sensors, performed on a stationary basis. The purpose of monitoring is to identify daily attacks of atrial fibrillation, assess the correctness of sinus rhythm restoration, and determine the average heart rate.
In situations where the signs of the disease cannot be identified using the listed methods, the doctor may prescribe provoking procedures:
- Tilt test. It is carried out on a rotary table in the laboratory, subject to comfortable conditions and strict safety precautions (resuscitation methods have been prepared).
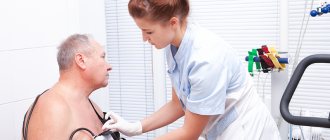
- A treadmill test is a special test with physical activity (an exercise bike or treadmill), during which an ECG is performed, the pulse, blood pressure, and general well-being of the patient are monitored. Used in the absence of regular attacks in order to correct the course of treatment.
- Stimulation through the esophagus.
- Invasive examination (electrophysiology) using thin catheters.
The doctor may also prescribe a general and biochemical blood test, each of which performs separate functions. General analysis reveals inflammatory processes, and biochemistry detects hyperlipidemia - elevated levels of cholesterol, electrolytes or liver enzymes, which is important when prescribing drugs.
Forecast
Is it possible to cure cardiac arrhythmia forever? In fact, the prognosis for disorders of this type is extremely ambiguous. Some arrhythmias do not pose a threat to life and health if they are not associated with organic heart pathology. Others, on the contrary, can lead to ischemic stroke, severe heart failure and other consequences.
Be that as it may, it is impossible to completely cure the disease. But achieving stable remission is real! The main thing is to follow all medical recommendations. The doctor will definitely tell the patient in detail how to deal with cardiac arrhythmia individually, based on the results of the diagnosis he has undergone.
First aid for an attack
What should you do if you or a loved one has a seizure?
If an attack occurs for the first time, it is necessary to call an ambulance, since it is almost impossible to independently determine the type of illness and choose a method of assistance.
- While waiting for an ambulance, you need to lie down and ask relatives to ventilate the room, but if you have shortness of breath, it is recommended to maintain a semi-sitting position. Often, changing the position from sitting to lying down and vice versa allows you to relieve the manifestations of arrhythmia, along with this, breathing exercises and inducing vomiting can help.
- Doctors advise taking 40 drops of Corvalol, one tablespoon of valerian or motherwort.
- To suppress a panic attack, you need to enlist the support of loved ones.
- Some patients benefit from manual therapy. You need to close your eyes and gently press on your eyelids with your fingers every three seconds.
If the pulse drops, you need to tilt the patient's head back to open the airways, then loosen the collar of the clothes. In case of fainting, it is necessary to perform a chest massage and perform artificial respiration on the patient.
Loads
Discussing how cardiac arrhythmia manifests itself and what is generally necessary to treat this disease, we must say a few words about the lifestyle that every person faced with this pathology should adhere to.
It is necessary to give up fast running, walking, physical overexertion, heavy lifting, and also eliminate from your life all factors that provoke anxiety, anxiety and stress. Any of the listed loads are dangerous for cardiac arrhythmia.
It is recommended to take walks in the fresh air more often, relax by the sea and in the forest, and also perform short sets of exercises when you feel well for the purpose of general strengthening.
Source: fb.ru
Treatment at home
Some types of arrhythmia, such as chronic ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation, pose a threat to the patient’s life, so they require constant therapy and treatment with folk remedies. Unfortunately, existing methods of drug treatment can only relieve the patient from attacks of the disease, and complete relief often requires surgical intervention.
Medicines
Antiarrhythmic drugs for the described disease are dispensed from pharmacies with a prescription from a cardiologist. Depending on the tablet, the heart muscle has different effects: some prolong the rhythm of contractions, others speed it up.
The most common medications are trimecaine, disoperamide, quinidine, lidocaine, etacizine, metoprolol, atenolol, amiodarone, verapamil.
- For sinus tachycardia, beta-blockers are prescribed along with sedatives and vitamins.
- The diagnosis of “sinus bradycardia” will require the use of vasodilating drugs (for example, Actovegin, aminophylline and others).
- For extrasystole, atropine-type medications, herbal infusions are prescribed, and potassium supplements are often prescribed. If attacks occur regularly, the patient is admitted to a hospital and treated with a course of lidocaine and other procedures.
- In case of atrial fibrillation, digoxin, electric pulse treatment, as well as anticoagulants along with potassium supplements are prescribed to improve the patient’s condition. Often the only treatment option is surgery.
- Ventricular flutter requires an injection of lidocaine or potassium chloride. In case of cardiac arrest, urgent defibrillation or surgery is performed.
Anticoagulants have a number of contraindications, so many patients are advised to agree to surgery or the installation of a pacemaker.
Folk remedies
Arrhythmia is one of the phenomena in which doctors recommend resorting to traditional recipes, since they can complement and enhance the effect of taking medications. How to treat arrhythmia using traditional recipes?
The main components of most herbal infusions and infusions are plants that have a sedative effect on the body: valerian, motherwort, hawthorn.
If there are heart rhythm disturbances, it is necessary to pay attention to the underlying disease that disrupts the normal functioning of the heart: cardiosclerosis, myocarditis, neurosis, etc.
Traditional medicine contains dozens of recipes to alleviate symptoms and restore normal heartbeat. Which ones are most effective? We present a list of the most popular options, the use of which is not only not dangerous, but, on the contrary, is very useful for heart patients. At least, the positive reviews from patients on the forums speak for themselves.
- Pour boiling water (half a liter) over dried calendula flowers (a couple of teaspoons) and let it brew for about two hours. Take half a glass of solution four times a day.
- A collection of yarrow, hop cones, valerian root, lemon balm in a ratio of 2:2:3:3. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of this mixture, leave for 1 hour, then strain. Drink 50 ml four times a day.
- Pour 2 teaspoons of dried cornflower flowers with a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 60 minutes. Drink 60-70 ml 4 times a day.
- Take equal parts of strawberry leaves, sweet clover herb, rose hips, hawthorn fruits, calendula flowers, chicory root, asparagus roots, peppermint, mix. An infusion is prepared from one tablespoon of the collection and 300 ml of boiling water overnight. You need to take 100 ml every 4 hours.
- The procedure for preparing the previous infusion is suitable for a mixture of equal parts of fennel fruits, rose hips, honey leaves, watch leaves, strawberries, foxgloves, wild rosemary.
- Another infusion using a similar technology is prepared from a mixture with the following ingredients: meadow clover, yarrow, apple peel, watch leaves, fennel fruits, strawberries, valerian (equal parts).
- Pour 30 g of dried belozer grass into 500 ml of vodka, leave for two weeks, shaking regularly, then strain the resulting liquid, take 30 drops four times a day.
- Infusion of European sage and vodka in a ratio of 1:5 (stand for 6 days), take 10 drops 3 times a day.
- Pour 120g of pine tops with 500 ml of vodka and leave in daylight for 10 days. Take 20 drops 3 times a day, before meals.
- For high blood pressure, you should take a remedy of 1 tablespoon of any honey with 100 ml of beet juice 3 times a day.
- If you have a racing heart, you can eat figs.
- If you have arrhythmia of atherosclerotic origin, it is useful to make a salad from a mixture of fresh onions and apple pulp.
Aromatherapy can also help you fight attacks at home. Mix equal amounts of clove, lemon balm, pine, lavender, nutmeg, sage, thyme, anise, eucalyptus oils, pour the resulting mixture into the aroma lamp, inhale after the next attack.
Infusions of valerian, hawthorn, mint, lemon balm can be added to baths, or teas can be brewed with these herbs.
Tachycardia
Now we can talk about how to cure cardiac arrhythmia. Tachycardia is a type of pathology in which the rhythm exceeds 90 beats per minute.
Treatment involves taking sedatives, the most effective of which are Relanium, Phenobarbital and Diazepam. Doctors often prescribe herbal medications: Novo-Passit, Persen, valerian and motherwort extracts, hawthorn tincture.
It is mandatory to take beta-blockers. They regulate the effects of norepinephrine and adrenaline on the body. Here are the recommended products:
- Bisoprolol (“Bisomor”, “Coronal”, “Concor”).
- Metoprolol (Vasocardin, Logimax, Betaloc).
- Atenolol (“Tenolol” and “Prinorm”).
- Nebivolol (“Binelol” and “Nebilet”).
- Timolol (“Ocumed” and “Arutimol”).
- Propranolol (“Anaprilin”, “Propamin” and “Noloten”).
- Nadolol (“Korgard”).
- Oxprenolol (Trazicor and Koretal).
When talking about how to cure cardiac arrhythmia, it is necessary to make a reservation that for tachycardia, medications based on bisoprolol and propranolol are the most effective.
Preventive measures
Since various types of arrhythmia are life-threatening and can increase the risk of blood clots, prevention of such diseases is indicated for all patients, even with irregular symptoms.
The main goal of preventive measures is to prevent sudden death from an attack. According to statistics, approximately 40% of deaths occurred in people who had never experienced a seizure before. Therefore, even feeling normal, the absence of obvious symptoms is not a guarantee that you are an absolutely healthy person.
Nutrition
The key to good health for people with heart palpitations is proper nutrition. When planning your daily diet, it is recommended to choose foods high in potassium and magnesium, which have a positive effect on the heart muscle. When selecting products, you need to take into account that some magnesium-rich foods (seeds, nuts, cereals) contain calcium and phosphorus, which significantly reduce the positive effect of magnesium.
The daily need for magnesium and potassium increases with severe physical activity and stress, as well as with active intellectual work and digestive disorders.
Prevention is a mandatory component in the presence of diseases such as diabetes, gastritis, ulcers, problems with the pancreas, and diseases of the endocrine system.
Potassium-rich foods:
- Vegetables (carrots, potatoes, cabbage);
- Cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal, millet);
- Dried fruits;
- Nuts.
Magnesium-rich foods:
- Sea kale;
- Cocoa;
- Bran;
- Dried apricots;
- Beans;
- Shrimps;
- Nuts;
- Buckwheat honey;
- Sesame;
- Peas.
You should reduce your consumption of fatty foods and concentrate on vegetables, fruits, and grains. You should not overeat, especially in the afternoon, because an overfilled stomach can cause irritation of the parasympathetic nerve, which threatens the normal functioning of the sinus node.
Do not underestimate the beneficial effects of vitamins on the body suffering from arrhythmia. Since one of the common causes of heart rhythm disturbances is general weakness of the body, vitamins will come in handy. It is recommended to eat more fresh berries and fruits, and also take multivitamin complexes that saturate the body with useful microelements.
Extrasystole
This type of arrhythmia is manifested by extraordinary heart contractions. In this case, therapy involves a gradual transition from weak drugs to strong ones. Treatment begins with taking sedatives, but if they do not help, the patient is prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs.
What to take for cardiac arrhythmia is decided by the doctor, but here are the medications that are usually prescribed:
- Sedatives that prevent excessive stimulation of extrasystole foci. These drugs affect brain signals.
- Magnesium and potassium containing drugs that strengthen the heart muscle. The most effective are “Panangin” and “Asparkam”. If the patient is taking diuretics that wash out electrolytes, then intravenous administration of these medications is prescribed.
- If extrasystole occurs against the background of bradycardia, then drugs are prescribed that contain belladonna (“Atropine” in particular).
- Antiarrhythmic drugs. Bretilium, Moracizine, Amiodarone and Propafenone work best. Prescribed to people with rhythm disturbances in the ventricles of the heart and atria. There are a number of serious contraindications and possible side effects.
- In case of extrasystole as a result of tachycardia, the use of glycosides - medicines from digitalis - is indicated. They are administered in small quantities.
It is worth listing some more drugs that help cope with extrasystole, since we are talking about the symptoms, causes and treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. Metoprolol, Cardanol, Betacardin, Sinopril, Pyramil, Enalapril, Amprilan, Moracizine, Bretilium, Nifedipine, Cinnarizine, Verapamil have proven themselves well. , "Propafenone" and "Amiodarone".
Complications
There are several consequences:
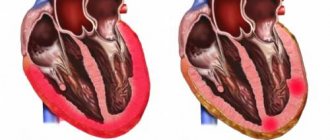
- Heart failure.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Heart attack. Acute necrosis as a result of insufficient blood circulation in the myocardium.
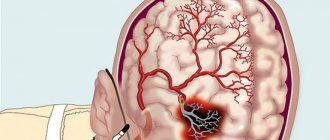
- Stroke. The death of cerebral structures, nervous tissues of the brain as a result of the same ischemia.
- Vascular dementia. Dementia, decreased efficiency of thinking, loss of memory, cognitive and mental abilities in general.
It appears when there is little nutrition to the brain. If it is possible to completely eliminate the cause, it disappears without any special consequences. The symptoms resemble Alzheimer's disease and require differential diagnosis with it.
In all cases, the result of emergency conditions (except for dementia) is death, or at least severe disability.