Congenital and acquired anomalies in the development of cardiac structures are considered to be common causes of early onset of disability among patients of all ages. Also a likely outcome is the death of the patient in the short term (3-5 years).
Recovery is unlikely, but the reasons for this do not lie in the potential incurability of the pathological processes. Everything is much simpler.
On the one hand, patients do not monitor their own health closely enough; this is the result of low medical culture and poor education.
On the other hand, most countries do not have an early screening program for heart problems. This is unusual, given that cardiac pathologies are practically in first place in the number of deaths.
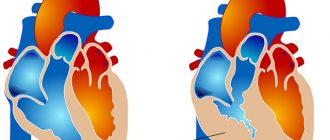
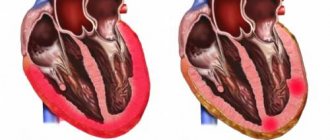
Mitral regurgitation is a condition in which the valve is unable to close completely. Hence regurgitation or reverse flow of blood from the ventricles into the atria.
The working volumes of liquid connective tissue fall, not reaching adequate values. The weakness of the release causes insufficient functional activity of the structures.
Hemodynamics are disrupted, tissues do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, hypoxia results in degenerative and dystrophic changes. This is a generalized process that disrupts all body systems.
Description of the disease
MVR (mitral valve insufficiency) is the most common cardiac anomaly. Of all patients, 70% suffer from an isolated form of cerebrovascular accident . Typically, rheumatic endocarditis is the main underlying cause of the disease. Often a year after the first attack, the heart condition leads to chronic failure, which is quite difficult to cure.
The highest risk group includes people with valvulitis . This disease damages the valve leaflets, as a result of which they undergo processes of wrinkling, destruction, and gradually become shorter than their original length. If valvulitis is at an advanced stage, calcification develops.
Additionally, as a result of these diseases, the length of the chords is reduced, and dystrophic and sclerotic processes occur in the papillary muscles.
Septic endocarditis leads to the destruction of many cardiac structures, so NMC has the most severe manifestations. The valve flaps do not fit together tightly enough. When they are not completely closed, too much blood comes out , which provokes its reboot and the formation of stagnant processes and an increase in pressure. All signs lead to increasing insufficiency of uric acid.
Treatment
The therapeutic effect is combined, using surgical techniques and conservative methods. Depending on the stage. One way or another prevails. The main characteristic of supervision is expediency.
Medication
Mitral regurgitation of the 1st degree is eliminated with medications, while the specific choice of drugs falls on the shoulders of the doctor.
Approximate diagram:
- Use of antihypertensive drugs. From ACP inhibitors to calcium antagonists and beta blockers. It is a classic treatment for hypertension and symptomatic increased arterial pressure.
- Antiplatelet agents. To normalize the rheological properties of blood. Fluidity is one of the main qualities of liquid connective tissue. Aspirin Cardio is prescribed.
- Statins. Against the background of cholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in this regard.
Other pathological processes, non-cardiac, but causing the failure itself, are eliminated accordingly.
For systemic lupus erythematosus, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are prescribed; for recovery from liver failure, hepatoprotectors, etc.
Operational
Surgical methods are shown somewhat less frequently; this is a last resort. In fact, even stage 2 mitral valve insufficiency is not yet a reason for intervention.
Vital indicators are considered the basis for radical supervision, depending on the degree of their decline. Long-term follow-up and the use of medications as part of supportive care are possible.
When conservative recovery is not possible, cardiac surgery is no longer necessary.
Appointed:
- prosthetics (replacement) of the mitral valve with a biological or mechanical one;
- excision of adhesions for stenosis;
- stenting of coronary arteries, other methods.
Particularly severe cases require organ transplantation. This is akin to a death sentence, since the likelihood of finding a donor is extremely low even in developed countries, especially in backward countries.
Lifestyle changes are not effective. Unless you can give up smoking and alcohol. Folk remedies are strictly contraindicated. MK insufficiency is eliminated only by classical methods.
Causes and risk factors
NMC affects people with one or more of the following pathologies:
- Congenital predisposition.
- Connective tissue dysplasia syndrome.
- Mitral valve prolapse , characterized by regurgitation of degrees 2 and 3.
- Destruction and breakage of the chords, rupture of the valves of the mitral valve due to injuries in the chest area.
- Rupture of the valves and chords with the development of infectious endocarditis.
- Destruction of the apparatus that unites the valves in endocarditis resulting from connective tissue diseases.
- Infarction of part of the mitral valve with subsequent scar formation in the subvalvular region.
- Changes in the shape of the valves and tissues under the valves in rheumatism .
- Enlarged mitral annulus in dilated cardiomyopathy .
- Insufficiency of valve function in the development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- MK insufficiency due to surgery.
Mitral regurgitation is often accompanied by another defect - mitral valve stenosis.
Types, forms, stages
With NMC, the total stroke volume of the blood of the left ventricle is assessed . Depending on its quantity, the disease is divided into 4 degrees of severity (the percentage indicates the part of the blood that is redistributed incorrectly):
- I (the softest) - up to 20%.
- II (moderate) - 20-40%.
- III (medium form) - 40-60%.
- IV (the heaviest) - over 60%.
According to the forms of its course, the disease can be divided into acute and chronic:
When determining the characteristics of movement of the mitral leaflets, 3 types of pathology classification :
- 1 - standard level of mobility of the leaflets (in this case, painful manifestations consist of dilatation of the fibrous ring, perforation of the leaflets).
- 2 - destruction of the valves (the chords take the greatest damage, as they are stretched or ruptured, and a violation of the integrity of the papillary muscles also occurs.
- 3 - decreased mobility of the valves (forced connection of commissures, reduction in the length of the chords, as well as their fusion).
Classification
Clinical typification of a pathogenic phenomenon is carried out for various reasons. Thus, depending on the origin, an ischemic form is distinguished, which is associated with hemodynamic disturbances. This is a classic variety.
The second is non-ischemic, that is, not associated with deviations in the provision of oxygen to tissues. It occurs less frequently, and only in the early stages.
Another way to classify the condition is based on the severity of the clinical picture.
- The acute type occurs as a result of rupture of the chordae tendineae of the valve and is determined by severe symptoms, as well as a high probability of complications and even death.
- Chronic and formed as a result of a long course of the main process, without treatment and goes through 3 stages. Recovery requires a lot of effort, more often it is prompt, which in itself can lead to fatal consequences (a relatively rare occurrence).
The main clinical classification is characterized by the severity of the pathological process:
- I. Full compensation phase. The organ is still able to realize its functions, the volume of returning blood is no more than 15-20% of the total amount (hemodynamically insignificant). This is a classic option, corresponding to the very beginning of the disease. At this moment, the patient does not yet feel the problem or the manifestations are so scarce that they do not provoke any suspicion. This is the best time for therapy.
- II. Partial compensation. The body can no longer cope. The amount of blood refluxing into the atrium is more than 30% of the total volume. Recovery is possible through surgical methods, dynamic monitoring is no longer carried out, the problem needs to be eliminated. The atria and ventricles are overloaded, the former are stretched, the latter are hypertrophied to compensate for the stretch. It is possible to stop the work of a muscle organ.
- III. Decompensation. Complete disruption of the activity of cardiac structures. Regurgitation is equivalent to grade 3 and is more than 50%; this leads to a pronounced clinical picture with shortness of breath, asphyxia, pulmonary edema, and acute arrhythmia. The prospects for a cure are vague; it is impossible to say exactly how likely a return to normal life is. Even with complex exposure, there is a high risk of permanent defect and disability.
Slightly less often, 5 clinical stages are distinguished, which is not of great importance. These are all the same variants of the 3rd phase of pathology, however, more differentiated in terms of prognosis and symptoms. Accordingly, they also talk about the dystrophic and terminal stages. Classification is required to develop treatment pathways.
Danger and complications
With the gradual progression of NMC, the following disorders appear:
- The development of thromboembolism due to constant stagnation of a large part of the blood.
- Valve thrombosis.
- Stroke. Previously occurring valve thrombosis is of great importance in the risk factors for stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Symptoms of chronic heart failure.
- Mitral regurgitation (partial failure of the mitral valve to perform functions).
Mitral valve insufficiency is a type of valvular heart disease. Pathogenesis is caused by incomplete closure of the mitral orifice, which is preceded by disturbances in the structure of the leaflets and tissues located under the valves. The pathology is characterized by regurgitation of blood into the left atrium from the left ventricle.
What examination is needed?
At the slightest complaint from the circulatory system, the patient should undergo a standard minimum of examinations. In the first place are a cardiogram and ultrasound examination (cardioscopy). These techniques are absolutely available in any multidisciplinary medical institution and make an invaluable contribution to the diagnosis of the defect. Thus, on the ECG one can see signs of hypertrophy of the left atrium (P-mitral - widened and bifurcated P wave) and hypertrophy of the remaining parts of the heart as the disease progresses.
mitral regurgitation on echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart)
Using a cardiac ultrasound, an experienced specialist will not only identify the degree of mitral regurgitation, but also assess the degree of enlargement of the heart chambers and the overall contractility of the myocardium.
In addition, a chest X-ray, long-term monitoring of blood pressure and ECG, and, if necessary, an MRI of the heart are prescribed.
Symptoms and signs
The severity and severity of MCT depends on the degree of its development in the body:
- Stage 1 of the disease has no specific symptoms.
- Stage 2 does not allow patients to carry out physical activity in an accelerated manner, since shortness of breath, tachycardia, pain in the chest, loss of heart rhythm, and discomfort immediately appear. Auscultation with mitral insufficiency determines increased tone intensity and the presence of background noise.
- Stage 3 is characterized by left ventricular failure and hemodynamic pathologies. Patients suffer from constant shortness of breath, orthopnea, increased heart rate, chest discomfort, and their skin is paler than in a healthy state.
Find out more about mitral regurgitation and hemodynamics with it from the video:
Types and features of mitral prostheses
Cardiac surgeons use three types of prostheses:
- Mechanical ones, which were initially made in the shape of a ball, and a little later - in the form of hinges. Blood clots often form on them, and installation may be complicated by embolism. The patient has to constantly take antiplatelet drugs. The most modern are products that are processed with a biologically intact titanium alloy.
- Biological. They are created from pericardium or other natural tissues. They do not have the ability to form blood clots.
- Allografts are taken from a corpse and cryopreserved before being implanted into a suitable donor.
Case study: advanced mitral regurgitation
I would like to give an example of a clinical case in which the lack of timely treatment led to such a diagnosis - mitral regurgitation of the 3rd degree. A patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of severe shortness of breath at rest, worsening with physical activity, cough with sputum, which sometimes contains streaks of blood, weakness, and swelling.
He considers himself unhealthy for many years, often suffered from sore throats, and had joint problems. The deterioration occurred after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection. When listening to the lungs, fine bubbling rales are detected, a weakening of the apical impulse, a click of the opening of the mitral valve, and systolic murmur are observed. The liver is enlarged, the lower edge is determined 5 cm below the hypochondrium. EchoCG shows thickening of the valve leaflets, calcification, dilatation of the left atrium, grade III mitral valve regurgitation.
The patient is scheduled for prosthetic surgery, after which he can be saved. Get treatment on time!
When to see a doctor and which one
If you identify symptoms characteristic of MCT, you must immediately contact a cardiologist to stop the disease in the early stages. In this case, you can avoid the need to consult with other doctors.
Sometimes there is suspicion of a rheumatoid etiology of the disease. Then you should visit a rheumatologist for diagnosis and proper treatment. If there is a need for surgical intervention, treatment and subsequent elimination of the problem is carried out by a cardiac surgeon .
Symptoms of mitral regurgitation may be similar to those of other acquired heart defects. We wrote more about how they manifest themselves here.
Diagnostics
Common methods for detecting NMC:
- Physical. The speed and uniformity of the pulse, features of changes in blood pressure, and the severity of systolic murmurs in the lungs are assessed.
During the examination, doctors pay attention to the patient’s breathing pattern. During the disease, shortness of breath does not stop even when the patient moves to a horizontal position, and manifests itself when distractions, physical and mental stimuli are excluded. On examination, a pasty appearance of the feet and legs and decreased urine output are noted. - Electrocardiography. Determines the intensity of the bioelectric potentials of the heart during its functioning. If the pathology reaches the terminal stage, severe arrhythmia is noted.
- Phonocardiography. Allows you to visualize the noise of the heart, as well as changes in its tones. Auscultation shows:
- Apexcardiography. Allows you to see vibrations of the upper chest that occur at low frequencies.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound diagnostics, revealing all the features of the work and movements of the heart. Requires care and skills from the specialist performing it.
- X-ray. The image shows a picture of areas of damage to the heart muscles, valves and connective tissue. You can not only identify diseased areas, but also identify absolutely healthy areas. This method is used only from stage 2 of pathology development.
Learn more about symptoms and diagnosis from the video:
It is necessary to distinguish NMC from other heart pathologies:
- Myocarditis in severe form.
- Congenital and acquired heart defects of related etiology.
- Cardiomyopathies.
- MK prolapse.
How dangerous is pulmonary artery stenosis and how to cure this problem? You will find all the details in the available review. You can read about the symptoms of aortic valve insufficiency and the differences between this heart defect and the one described in this article in another material.
Also read the information about how Behcet's disease appears and how dangerous it is, with methods for treating this complex vascular pathology.
How to live with mitral regurgitation
At the initial stage, when there are no circulatory problems, the patient can simply lead a normal healthy lifestyle. Strong psycho-emotional shocks and heavy physical labor in unfavorable conditions are contraindicated for him. When the first signs of abnormality develop, we recommend:
- transition to easier work;
- for young people – learning a new profession;
- mental activity is not limited;
- service in the army is determined by a commission; most often the conscript is sent to the communications and radio engineering departments.
In case of edema, enlarged liver, ascites, severe shortness of breath and arrhythmia, a person must undergo a commission where he may be assigned a disability with the possibility of partial work or complete exemption from it. In this case, the conscript is considered unfit for service.
Therapy methods
If symptoms of cervical urinary tract are severe, surgical intervention is indicated for the patient. The operation is performed urgently for the following reasons:
- In the second and later stages, despite the fact that the volume of blood ejected is 40% of its total amount.
- In the absence of effect from antibacterial therapy and worsening of infectious endocarditis.
- Increased deformation, sclerosis of the valves and tissues located in the subvalvular space.
- In the presence of signs of progressive left ventricular dysfunction together with general heart failure occurring at 3-4 degrees.
- Heart failure in the early stages can also be a reason for surgery, however, to form an indication, thromboembolism of large vessels located in the systemic circulation must be detected.
The following operations are practiced:
- Valve-sparing reconstructive surgeries are necessary to correct cerebrovascular accidents in childhood.
- Commissuroplasty and decalcification of the leaflets are indicated for severe MV insufficiency.
- Chordoplasty is intended to normalize the mobility of the valves.
- Translocation of cords is indicated when they fall off.
- Fixation of parts of the papillary muscle is carried out using Teflon gaskets. This is necessary when separating the head of the muscle from the remaining components.
- Prosthetics of the chords is necessary when they are completely destroyed.
- Valvuloplasty avoids leaflet rigidity.
- Anuloplasty is intended to relieve the patient of regurgitation.
- Valve replacement is carried out when it is severely deformed or when fibrosclerosis develops irreparably and interferes with normal functioning. Mechanical and biological prostheses are used.
Learn about minimally invasive operations for this disease from the video:
How does vice manifest itself?
Symptoms of MN may linger for a long time. In some patients, symptoms are not observed for several months or even years, when the muscle’s abilities fully compensate for the growing problems in the functioning of the organ.
Then the initial signs of MN may appear - shortness of breath attacks and a feeling of lack of air, frequent fatigue and decreased tolerance to previously habitual household stress.
As it progresses, phenomena of congestive insufficiency develop - episodes of cardiac (not to be confused with bronchial!) asthma and pulmonary edema, severe edema of the lower extremities, abdominal enlargement and pain when palpated in the right hypochondrium. In the later stages, difficulty breathing accompanies the patient at rest constantly, swelling takes on a very pronounced character, the abdomen increases to enormous sizes, and effusion accumulates in the pleural cavity, squeezing the lungs. Without proper treatment, these changes quickly lead to death. Often such patients experience a permanent form of atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles and other disorders.
What to expect and preventative measures
With the development of cerebrovascular accident, the prognosis determines the severity of the disease, that is, the level of regurgitation, the occurrence of complications and irreversible changes in cardiac structures. Survival over 10 years after diagnosis is higher than for similar severe pathologies .
If valve insufficiency manifests itself in moderate or moderate form, women are able to bear and give birth to children . When the disease becomes chronic, all patients should undergo an annual ultrasound and visit a cardiologist. If worsening occurs, you should visit the hospital more often.
If the condition worsens, surgical intervention is undertaken, so patients should always be prepared for this measure of cure for the disease.
Prevention of NMC consists of preventing or promptly treating the diseases that cause this pathology . All diseases or manifestations of mitral valve insufficiency due to an abnormal or reduced valve must be quickly diagnosed and promptly treated.
NMC is a dangerous pathology that leads to severe destructive processes in the heart tissue, and therefore requires proper treatment. return to normal life and cure the disorder some time after starting treatment