Roza Ismailovna Yagudina , Ph.D. Sc., prof., head. Department of Organization of Drug Supply and Pharmacoeconomics and Head. laboratory of pharmacoeconomic research of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov.
Evgenia Evgenievna Arinina , Ph.D., leading researcher at the laboratory of pharmacoeconomic studies of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death worldwide. WHO estimates that 17.3 million people died from CVDs in 2008, accounting for 30% of all deaths worldwide. Of this number, 7.3 million died from coronary heart disease. According to WHO forecasts, by 2030, approximately 23.3 million people will die from CVDs annually.
The group of cardiovascular diseases includes several nosological units:
- coronary heart disease - a disease of the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle;
- disease of the blood vessels in the brain that supply it with blood;
- disease of the peripheral arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs;
- rheumatic carditis - damage to the heart muscle and heart valves as a result of a rheumatic attack caused by streptococcal bacteria;
- congenital heart disease - deformations of the structure of the heart existing from birth;
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism - the formation of blood clots in the leg veins that can dislodge and move towards the heart and lungs.
One of the most common pathologies in the structure of CVD is coronary heart disease (CHD), to which we will devote a number of articles. IHD, as defined by WHO, is acute or chronic cardiac dysfunction resulting from an absolute or relative decrease in the supply of arterial blood to the myocardium.
In more than 90% of cases, the anatomical basis for the development of coronary artery disease is damage to the coronary arteries of the heart, leading to a decrease in coronary blood flow and an imbalance between the need of the heart muscle for oxygen and nutrients and the blood supply capabilities of the heart. Often this effect is caused by dyslipidemias, leading to the development of atherosclerosis, therefore, in the first article devoted to the problem of pharmacotherapy of IHD, we will dwell in detail on dyslipidemias (hyperlipidemias).
Currently, the following forms of IHD are distinguished:
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Angina pectoris
- Silent cardiac ischemia
- Syndrome X (microvascular angina)
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiosclerosis (atherosclerosis)
- Heart failure
- Heart rhythm disturbances
Development mechanism
The basis of the pathological process is metabolic disorders. Without going into details, the deviation progresses gradually and consists in the impossibility of normal fat deposition.
They are stored in unnaturally large quantities, penetrate the bloodstream, cling to arteries, clog them, and form atherosclerotic plaques.
To process such amounts of lipids, the liver and pancreas function especially intensely, which leads to the rapid development of inflammatory and degenerative processes in these organs.
Hyperlipidemia begins spontaneously; the disorder often manifests itself during puberty, when hormonal changes begin.
This is a particularly unfavorable moment; throughout maturation, you need to undergo regular preventive examinations under the supervision of an endocrinologist, at a minimum.
Men during puberty are less likely to develop metabolic disorders than women. When approaching the age group of 30+, the situation is diametrically opposite; it smooths out with the advent of menopause.
A huge role in the development of hyperlipidemia is assigned to the hereditary factor. According to specialized studies, patients in whom at least one parent has metabolic problems, the likelihood of developing hyperlipidemia is about 30%. Two - more than 60%.
At the same time, it is also necessary to take into account ancestors in the ascending line who lived even earlier: grandfathers, grandmothers. But such a deep assessment is not always possible.
Deviations exist for years undetected and do not progress in all cases.
But if there is movement, dynamics, it will not stop as long as the provoking factor exists. When heredity and genetics act as such, one cannot count on spontaneous recovery, much less regression of deviations. Diagnosis and treatment are necessary.
Attention:
The only way to detect a disorder in a timely manner is to regularly conduct laboratory tests with an expanded picture of lipid compounds.
Prevention
Hereditary hyperlipidemia cannot be prevented. The basic principle of preventing other disorders of fat metabolism is to exclude all possible causes of the development of pathology:
- smoking;
- excess weight;
- lack of mobility;
- poor nutrition;
- timely treatment of diseases occurring with the development of hyperlipidemia.
At the ages of 9-11, and then 17-21 years old, children should take their first tests for total cholesterol or lipid profile. After 20 years, they must be repeated every 4-6 years. If there is a tendency towards hyperlipidemia, more frequent screening is recommended.
Classification
The division of the pathological process is carried out on a key basis - the type of lipid that provokes the disorder (Fredrickson classification of hyperlipidemia).
It also indirectly takes into account the complication that develops as the disease moves forward.
Type 1
It is extremely rare. Among all other varieties, it is the least likely to be detected.
Accompanied by an increase in the concentration of special transport substances that transport fats (chylomicrons). There is a clear connection between certain biochemical processes and the development of such a phenomenon.
The main complication encountered by patients with type 1 hyperlipidemia is pancreatitis. Inflammatory lesion of the pancreas.
There are also varieties of the pathological process that are absolutely determined by genetics. They develop as a result of mutations.
However, the share of hereditary forms accounts for less than a percent of the total number of cases. Approximately 0.5%. This is the so-called type IIa hyperlipidemia. Accompanied by an increase in the concentration of LDL (low density lipoprotein).
Another name for the substance is bad cholesterol; according to established opinion, it is considered the most atherogenic. Causes deposition on the walls of blood vessels and the development of plaques and insufficient blood circulation.
The vast majority of situations are associated with a nutritional factor—poor nutrition.
Mainly causes the development of atherosclerosis throughout the body, affecting large vessels: lower limbs, heart (aorta), brain
Type IIb
It is found a little less frequently. If in the first case there is a deviation in the production of one factor that regulates the concentration of fatty substances (apo B or coenzyme A), in this case the production of two compounds is changed at once, plus the amount of triglycerides increases.
In the system they can be classified as VLDL. Very low density lipoproteins. Hyperlipidemia type 2a occurs in 7% of the population, which is quite high and mainly causes coronary insufficiency and increases the risk of heart attack.
Signs of a pre-infarction condition are described here.
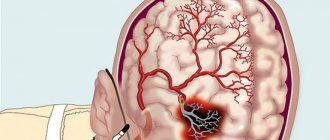
However, other disorders are also possible, such as coronary artery disease, problems with brain nutrition (ischemia), which leads to stroke.
Type III
It is extremely rare, much less than a tenth of a percent. In terms of the planet's population, that's about one and a half million people.
The pathology is of purely hereditary origin and is caused by a violation of the synthesis of a special substance called apo E.
This protein plays a key role in metabolic processes involving cholesterol, which is why disorders are always severe. Like atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, angina pectoris, coronary heart disease.
This form is characterized by spontaneous long-term development and relatively early manifestation several years after the onset of the disease.
The trigger, the factor that will cause the disorder and initiate changes, may be hormonal imbalance, obesity, puberty, pregnancy. And many more points.
Assessing them is the task of epidemiology as a science; knowing the features and mechanisms, it is possible to develop ways of prevention. There is no clear answer yet on how to prevent the disease.
IV type
Occurs in 1% of cases. Accompanied by increased production of triglycerides and very low density lipoproteins.
A slight increase in cholesterol levels is typical for hypertriglyceridemia, but not always. A rapid increase in the concentration of fatty substances is detected later, as the deviation progresses.
This pathology increases the risk of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and causes further weight gain.
V type
Another hereditary form of the disorder. It resembles the very first named species, with the difference that the concentration of not only chylomicrons, but also very low-density lipoproteins increases.
Most often, the disorder provokes severe forms of inflammation of the pancreas - pancreatitis.
The exact mechanism of manifestation of the disorder is unclear. It is assumed that the impetus for development is an unbalanced diet.
Attention:
With all these diseases, cholesterol itself may be normal or very slightly elevated.
Although it is one of the key substances in the development of the negative consequences of hyperlipidemia, the basis, the fundamental mechanism of the disease is made up of special proteins and substances named above, which are involved in the transport of cholesterol.
There is another way to classify hyperlipidemia. Based on its origin, there are two large groups of violations:
- Disease of specified genesis. The reason is obvious, or at least it is possible to assess the nature of the deviation and make an accurate diagnosis as a result of the diagnosis. Most of the problems relate specifically to this type. Although a complete examination may require more than one month of dynamic laboratory observation.
- Hyperlipidemia, unspecified. It is impossible to identify the exact factor in the development of the pathological process. However, this is often where diagnosis begins. It can take quite a long time before a diagnosis is made. It is not always possible to determine the origin of the metabolic disorder.
Both classifications are actively used by doctors. The first plays a key role in prescribing a special therapeutic course.
Complications
blockage of a vessel by a lipid plaque, thrombus formation
Acute complications develop quickly and end in death. The blood vessel narrows, the thrombus breaks off and blocks the lumen of the vessel. Acute complications include myocardial infarction and stroke.
Chronic complications develop gradually and are treatable. A thrombus in the lumen of the affected vessel causes chronic ischemia of this area. The chronic consequences of hyperlipidemia include: aortic valve stenosis, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, hypertension, renal failure, atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels of the legs, intermittent claudication syndrome, trophic ulcers.
Treatment of dyslipidemia is a long and complex process that requires discipline, patience and strength from the patient. Timely and complete therapy, as well as the elimination of risk factors, significantly prolong and improve the lives of patients.
Symptoms
An increase in the concentration of fats in the blood does not manifest itself as such until the disease caused by the disorder begins.
There can be many options here: from angina or arrhythmia, to diabetes, pancreatitis and, most often, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, brain, cardiac structures (coronary arteries).
It is impossible to single out a single set of characteristics, because there are too many forms and consequences of the course of exchange deviation. Strictly speaking, these are not symptoms of hyperlipidemia, we are talking about the clinic of the complications that it provoked.
The development of a pathological process sometimes takes more than a year or even more than a dozen. Depends on the body’s safety margin, resistance and ability to self-regulate.
Men are more susceptible to the disease than women, because in the latter the role of a fat breaker and a regulator of metabolic processes is played by estrogen, which has a negligible concentration in the body of the stronger sex.
How is hyperlipidemia treated?
The treatment complex for hyperlipidemia consists of 4 main components: diet therapy, statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs), cleansing procedures and increased physical activity.
We also recommend studying this topic:
Anisocytosis - change in blood cell size
Diet therapy
Nutrition for hyperlipidemia should contain a minimum of fat - no more than 30%. It is recommended to replace animal fats with vegetable oils, not refined ones containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (sunflower, olive, flaxseed, sesame). It is recommended to take them raw, that is, without heat treatment. You should also reduce the amount of carbohydrates - sweet foods, flour and confectionery products.
Food should contain a large amount of coarse fiber - at least 40-50 g per day, it is found in raw vegetables and fruits, cereals, legumes, herbs, and they also contain many vitamins and microelements. Artichokes, pineapple, citrus fruits, and celery are recommended as fat-burning foods. Alcohol, which contains large amounts of carbohydrates, is contraindicated.
Statins
This is a whole group of drugs that block the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, necessary for the synthesis of cholesterol. Practice has shown that regular use of statins reduces the number of heart attacks and strokes by 30-45%. The most popular are simvastatin, lovastatin, rosuvastatin, fluvastatin and others.
Cleansing the body
This refers to cleansing of accumulated toxins and excess nutrients. It is recommended to periodically take sorbents, which are also available in a large selection. These are activated carbon, sorbex, enterosgel, polysorb, atoxol and others. Chitosan, a preparation made from crustacean shell powder, has proven itself to be excellent in adsorbing and removing fat molecules from the intestines.
In severe cases of hyperlipidemia, extracorporeal blood purification is performed in a hospital setting. The patient’s venous system is connected to a device with many membrane filters, passes through them and returns back, already cleared of “bad” lipids.
Important: The use of sorbents should be agreed with your doctor. Excessive passion for them can lead to the removal from the body, in addition to fat and toxins, of useful and necessary substances.
Increasing physical activity
Exercise therapy for hyperlipidemia is a prerequisite for improving blood circulation, removing lipids and reducing their sedimentation in blood vessels and organs. Also, any sports, games, hiking, cycling, visiting the pool, just hygienic exercises in the morning - everyone can choose for themselves according to their taste and capabilities. The main thing is to eliminate physical inactivity.
Causes
The list of such is huge. It is worth mentioning just a few:
- Diabetes.
- Hypertension or a symptomatic increase in blood pressure to consistently high levels.
- Obesity. Change in body weight, unadjusted.
Paradoxically, the triad of these abnormalities can be the cause of hyperlipidemia and a consequence of its course, as a complication. Ties need to be “untangled” together with the doctor.
- Kidney pathologies. Failure in any phase. Especially in decompensation.
- Hereditary factor. Plays a certain role in all five forms of the disease. The key fundamental culprit comes in two cases. As part of the diagnosis, a family history assessment is required.
- Pathologies of the liver, pancreas. Inflammatory, degenerative in nature.
- Pregnancy, especially difficult, late, multiple pregnancy.
- Puberty with hormonal instability.
- Hypothyroidism. Decrease in the concentration of specific substances of the thyroid gland: T3, T4, TSH (formally it refers to compounds synthesized by the pituitary gland).
- Uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives. They kill the normal background of specific substances of the female reproductive system. They are not recommended for use even on the advice of a doctor and with his consent; the consequences are unpredictable. These are not only problems with lipid levels, but also infertility and a drop in libido. Disorders of the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol. Especially drugs. This is extremely dangerous. Bad habits slow down metabolic processes. Even after refusal, the body will need time to adjust to an adequate, physiological way.
- Disorders of the pituitary gland.
A huge role is played by poor nutrition with excess fast food, salt, fatty, fried foods.
Content:
- What are lipids, lipoproteins and hyperlipidemia?
- Lipids
- Lipoproteins
- Diet therapy
- Statins
- Cleansing the body
- Increasing physical activity
← Leukopenia - causes of decreased leukocyte concentration
Anisocytosis - change in blood cell size →
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of at least an endocrinologist. If necessary, other specialists are also involved.
The identification measures are always approximately the same:
- Oral questioning of the patient. Are there any complaints, if so, when did they arise and so on in the chain. To get a complete clinical picture. But, as was said, in the initial stage and even with a long course in most cases, there are no manifestations.
- Anamnesis collection. Habits, nutritional patterns, professional activity, family medical history.
- Blood test for lipid profile substances. Aimed at a detailed description of the concentration of various structures: low-density lipoproteins, high-density lipoproteins, cholesterol, and the atherogenic index is determined. It is recommended to conduct this study regularly, for patients with current hyperlipidemia - once every six months. As part of preventive screening - at 12 months or a little less often.
- These are the main methods for diagnosing the disorder itself. Regarding identifying complications of this problem:
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, neck, assessment of the coronary arteries, including the ECHO method.
- Angiography if necessary.
- MRI or CT as needed.
It is likely that other studies will be prescribed.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the form of the pathological process. Based on the type of hyperlipidemia, a specific regimen is prescribed.
Type 1
Requires diet, this is the main method of recovery. There are no strict rules. It is enough to diversify your diet, include more fresh and thermally processed vegetables and fruits, the share of plant components in the menu is at least 50%. It is better to bring it to 60%.
Protein is required, a vegetarian diet is possible, but if desired. For meat you need to consume chicken breast and turkey. In reasonable quantities it is possible to use veal without fat in cooking.
Fried, smoked foods, pickles and marinades are excluded with great care. There are fewer sweets, except homemade jam without sugar.
Salt is limited. No more than 5-7 grams per day, therefore we are not talking about any canned food or semi-finished products.
The duration of such a diet is from 3 to 12 months. You may need to return to it regularly or switch to a new diet.
Type 2a
It is treated with statins. They remove excess lipids from the body. Options include Atorvastatin, Atoris and similar ones. Nicotinic acid-based products are also prescribed.
Type 2b
It involves the use of the same drugs plus the inclusion of another group - fibrates. Eliminating excess synthesis of conditionally harmful substances. Gemfibrozil is prescribed as the main name.
Type 3
The use of statins and nicotinic acid is possible, but clinical practice suggests minimal effectiveness in this case.
The use of fibrates is indicated. The already named drug. The duration of treatment is significant, about several months until a lasting result is achieved.
Type 4
Nicotinic acid must be used.
In the last, 5th form of the pathological process, in addition to it, Gemfibrozil is also used. Or its analogues from the group of fibrates.
Attention:
All of the treatment plans mentioned are very approximate. There are a huge number of drugs and trade names. An effective combination can only be prescribed by a specialist.
There is no point in surgical treatment of hyperlipidemia. We are talking about a fundamental disorder.
Clinics offer innovative, untested methods, such as gravitational blood purification, but the effectiveness of this method is unclear. There are still more questions than answers.
Surgery is required if complications develop. Like critical narrowing of the vessels of the lower extremities, blockage of the arteries of the heart, plaque calcification, when the formation of cholesterol becomes hard as a stone.
Hyperlipidemia should be treated under the supervision of an endocrinologist. It makes sense for other forms of the process, in addition to the first, to stick to a diet, give up smoking, alcohol, and especially drugs.
If the disorder has become secondary, that is, due to other diagnoses, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause and only then deal with the consequences.
What is gravity blood surgery?
Gravity blood surgery is a new direction in medicine, which includes more than 30 high-tech methods, with the help of which pathological substances are removed from the body, the properties of blood cells and their number are changed, and medications are delivered directly to the site of the disease.
As a result of this blood purification, a clear effect of treating hyperlipidemia occurs even in cases where other methods do not help.
Make an appointment now.